Medicare is funded primarily through trust funds, monthly beneficiary premiums, Congress-approved funds, and trust fund interest. Medicare parts A, B, and D all utilize trust fund money to help pay for services. Additional Medicare Advantage coverage is funded with the help of monthly premiums.
What are the different types of Medicare Part A?
1 Medicare Part A. Medicare Part A is hospital insurance. ... 2 Medicare Part B. Medicare Part B is medical insurance that covers everyday care needs like doctor’s appointments, urgent care visits, counseling, medical equipment, and preventive care. 3 Medicare Part C. Medicare Part C is also called Medicare Advantage. ... 4 Medicare Part D. ...
What is the source of funding for Medicare?
Medicare is funded through two trust funds held by the U.S. Treasury. Funding sources include premiums, payroll and self-employment taxes, trust fund interest, and money authorized by the government.
How is the Medicare trust fund Fund funded?
How is it funded? 1 Funds authorized by Congress 2 Premiums from people enrolled in Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) and Medicare drug coverage (Part D) 3 Other sources, like interest earned on the trust fund investments
How much of the federal budget is spent on Medicare?
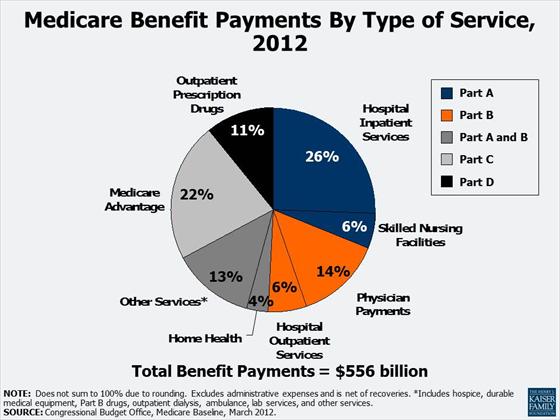
In 2018, Medicare spending (net of income from premiums and other offsetting receipts) totaled $605 billion, accounting for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1). In 2018, Medicare benefit payments totaled $731 billion, up from $462 billion in 2008 (Figure 2) (these amounts do not net out premiums and other offsetting receipts).
How are the different parts of Medicare funded?
Medicare is funded primarily from general revenues (43 percent), payroll taxes (36 percent), and beneficiary premiums (15 percent) (Figure 7). Part A is financed primarily through a 2.9 percent tax on earnings paid by employers and employees (1.45 percent each) (accounting for 88 percent of Part A revenue).
How is Medicare primarily funded?
A: Medicare is funded with a combination of payroll taxes, general revenues allocated by Congress, and premiums that people pay while they're enrolled in Medicare. Medicare Part A is funded primarily by payroll taxes (FICA), which end up in the Hospital Insurance Trust Fund.
How is Medicare funded in Australia?
The Australian government pays for Medicare through the Medicare levy. Working Australians pay the Medicare levy as part of their income tax. High income earners who don't have an appropriate level of private hospital insurance also pay a Medicare levy surcharge.
How is Medicare funded in America?
Medicare is funded primarily through trust funds, monthly beneficiary premiums, Congress-approved funds, and trust fund interest. Medicare parts A, B, and D all utilize trust fund money to help pay for services. Additional Medicare Advantage coverage is funded with the help of monthly premiums.
What are the four parts of Medicare?
There are four parts of Medicare: Part A, Part B, Part C, and Part D.Part A provides inpatient/hospital coverage.Part B provides outpatient/medical coverage.Part C offers an alternate way to receive your Medicare benefits (see below for more information).Part D provides prescription drug coverage.
What are the different Medicare trust funds?
The Medicare trust fund comprises two separate funds. The hospital insurance trust fund is financed mainly through payroll taxes on earnings and income taxes on Social Security benefits. The Supplemental Medical Insurance trust fund is financed by general tax revenue and premiums paid by enrollees.
Is Medicare federally funded?
As a federal program, Medicare relies on the federal government for nearly all of its funding. Medicaid is a joint state and federal program that provides health care coverage to beneficiaries with very low incomes.
Who pays the Medicare levy and how much do they pay?
Medicare levy The levy is about 2% of your taxable income. You pay the levy on top of the tax you pay on your taxable income. Your Medicare levy may reduce if your taxable income is below a certain amount. In some cases, you may not have to pay this levy at all.
How are hospitals funded in Australia?
Public hospitals are funded by the state and territory and Australian governments, but are largely owned and managed by the state and territory governments.
How is Medicare funded quizlet?
How is Medicare funded? Partially funded by federal government through tax dollars. -The rest is funded by premiums, deductibles and coninsurance payments.
How is Medicaid and Medicare funded?
Funding for Medicare is done through payroll taxes and premiums paid by recipients. Medicaid is funded by the federal government and each state. Both programs received additional funding as part of the fiscal relief package in response to the 2020 economic crisis.
Who administers funds for Medicare?
The federal agency that oversees CMS, which administers programs for protecting the health of all Americans, including Medicare, the Marketplace, Medicaid, and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP).
Is Medicare funded by Social Security?
Medicare is funded by the Social Security Administration. Which means it's funded by taxpayers: We all pay 1.45% of our earnings into FICA - Federal Insurance Contributions Act, if you're into deciphering acronyms - which go toward Medicare.
Is Medicare funded by taxes?
Funding for Medicare is done through payroll taxes and premiums paid by recipients. Medicaid is funded by the federal government and each state. Both programs received additional funding as part of the fiscal relief package in response to the 2020 economic crisis.
Is Medicare federally funded?
The federal agency that oversees CMS, which administers programs for protecting the health of all Americans, including Medicare, the Marketplace, Medicaid, and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP).
Is Medicare funded by private insurance companies?
Medicare is funded through a mix of general revenue and the Medicare levy. The Medicare levy is currently set at 1.5% of taxable income with an additional surcharge of 1% for high-income earners without private health insurance cover.
The Four Types of Medicare
While this process may seem overwhelming at first, the most important first question to ask is: What are the four types of Medicare? Here is a quick breakdown of Medicare the various coverage options available:
What Does Medicare Part A Cover?
Original Medicare coverage is regulated according to federal and state laws. As such, when you enroll in Medicare, you automatically receive Medicare Part A. There typically is not a monthly premium for this coverage, but you likely will have a deductible.
What Does Medicare Part B Cover?
The second component of Original Medicare is Medicare Part B. Just like with Part A, recipients automatically receive Medicare Part B coverage as soon as they enroll in Medicare. Recipients will, however, pay Part B premiums monthly.
What Does Medicare Part C Cover?
Medicare Part C, or Medicare Advantage, offers the same coverage as Original Medicare, but bundles the covered benefits with additional services. Medicare Advantage plans are available through private health insurance companies, which means that specific coverage varies.
What Does Medicare Part D Cover?
Medicare Part D is a prescription drug plan that is available to anyone with Medicare. These plans are offered through private insurance companies. Beneficiaries can enroll in a standalone Part D plan with Original Medicare, or obtain drug coverage through Medicare Advantage plans.
How Do You Choose a Medicare Plan?
As with any healthcare decision, your final choice ultimately will be determined by finding the best option to suit your individual needs. When comparing Medicare options, it is important to consider a range of factors, including premiums, out-of-pocket costs, provider availability, referrals and extra benefits.
1. Medicare Part A: Hospital insurance
Medicare Part A is one half of Original Medicare, the health insurance managed by the federal government, and is hospital insurance. Part A covers the following services:
2. Medicare Part B: Medical insurance
Medicare Part B is medical insurance, and is the other half of Original Medicare. It pays for medically necessary services that you need to diagnose or treat your condition that meet the accepted standards of care. It also covers preventative care, such as most vaccines and early-detection screenings.
3. Medicare Part C: Medicare Advantage plans
Many people opt for Medicare Part C, also known as a Medicare Advantage plan, rather than Original Medicare.
4. Medicare Part D: Prescription drug plans
Many people are surprised to find that Original Medicare — Parts A and B — don’t include coverage for prescription medications. If you want insurance for your medications, you can enroll in a Medicare Part D plan. This is an optional benefit that provides prescription drug coverage.
What are the parts of Medicare?
Each part covers different healthcare services you might need. Currently, the four parts of Medicare are: Medicare Part A. Medicare Part A is hospital insurance. It covers you during short-term inpatient stays in hospitals and for services like hospice.
How many people are on medicare in 2018?
Medicare is a widely used program. In 2018, nearly 60,000 Americans were enrolled in Medicare. This number is projected to continue growing each year. Despite its popularity, Medicare can be a source of confusion for many people. Each part of Medicare covers different services and has different costs.
What is the maximum amount you can pay for Medicare in 2021?
In 2021, the out-of-pocket maximum for plans is $7,550. Note.
What does Medicare Part A cover?
Medicare Part A covers the care you receive when you’re admitted to a facility like a hospital or hospice center. Part A will pick up all the costs while you’re there, including costs normally covered by parts B or D.
What is Medicare for seniors?
Medicare is a health insurance program for people ages 65 and older, as well as those with certain health conditions and disabilities. Medicare is a federal program that’s funded by taxpayer contributions to the Social Security Administration.
How old do you have to be to get Medicare?
You can enroll in Medicare when you meet one of these conditions: you’re turning 65 years old. you’ve been receiving Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) for 24 months at any age. you have a diagnosis of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) at any age.
When does Medicare enrollment start?
It begins 3 months before your birth month, includes the month of your birthday, and extends 3 months after your birthday. During this time, you can enroll for all parts of Medicare without a penalty. General enrollment period (January 1–March 31).
How does Medicare get money?
Medicare gets money from two trust funds : the hospital insurance (HI) trust fund and the supplementary medical insurance (SMI) trust fund. The trust funds get money from payroll taxes, as allowed by the Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) enacted in 1935.
How much is Medicare spending in 2019?
According to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, Medicare expenditures in 2019 totaled $796.2 billion. This article looks at the ways in which Medicare is funded. It also discusses changes in Medicare costs.
How much is the Medicare deductible for 2020?
A person enrolled in Part A will also pay an inpatient deductible before Medicare covers services. Most recently, the deductible increased from $1,408 in 2020 to $1,484 in 2021. The deductible covers the first 60 days of an inpatient hospital stay.
What is the best Medicare plan?
We may use a few terms in this piece that can be helpful to understand when selecting the best insurance plan: 1 Deductible: This is an annual amount that a person must spend out of pocket within a certain time period before an insurer starts to fund their treatments. 2 Coinsurance: This is a percentage of a treatment cost that a person will need to self-fund. For Medicare Part B, this comes to 20%. 3 Copayment: This is a fixed dollar amount that an insured person pays when receiving certain treatments. For Medicare, this usually applies to prescription drugs.
What is SMI trust fund?
The SMI trust fund covers the services offered by Medicare Part B, a portion of Part D, and some of the Medicare program’s administrative costs. Medicare Part B includes outpatient services, such as doctor’s visits, lab tests, certain cancer screenings and preventative care, and ambulance transport.
What is Medicare for adults?
Medicare is the federal healthcare program for adults aged over 65, adults with disabilities, and people with end stage renal disease. The program provides coverage for inpatient and outpatient services, and prescription drugs. Medicare gets money from two trust funds: the hospital insurance (HI) trust fund and the supplementary medical insurance ...
How many parts does SMI have?
The SMI trust fund has two parts, namely Part B and Part D, funded by the premiums paid for each part. In addition, it receives funds authorized by Congress, and the interest from trust fund investments.
What is Medicare funded by?
Medicare is funded by federal tax revenue, payroll tax revenue (the Medicare tax), and premiums paid by Medicare beneficiaries. The trust fund that pays for Medicare Part A is projected to run out of money in 2026 unless more tax revenue is raised.
How many parts does Medicare have?
There are four parts of Medicare, each of which covers different types of health care expenses. The source of funding for each part of Medicare is different. Technically, Medicare funding comes from the Medicare Trust Funds. Those are two separate funds — the Hospital Insurance (HI) Trust Fund and the Supplementary Medical Insurance (SMI) ...
How does Medicare Part B get paid?
Medicare Part B (outpatient insurance) is paid through the SMI Trust Fund. The fund gets money from the premiums paid by Medicare Part B and Part D beneficiaries, federal and state tax revenue, and interest on its investments.
What is the surtax for Medicare 2021?
If you have a high income, you may have to pay a surtax (an extra tax) called the Additional Medicare Tax. The surtax is 0.9% of your income and when you start paying it depends on your income and filing status. The table below has the thresholds for the Additional Medicare Tax in 2021. Filing status.
What is the Medicare trust fund?
The fund primarily comprises revenue from the Medicare tax. It is also maintained through taxes on Social Security benefits, premiums paid by Medicare Part A beneficiaries who are not yet eligible for other federal retirement benefits, and interest on the trust fund’ s investments.
How much will Medicare pay in 2021?
All workers pay at least 1.45% of their incomes in Medicare taxes. In 2021, Medicare Part B recipients pay monthly premiums of between $148.50 to $504.90. Most people qualify for premium-free Part A, but those who don’t will have premiums worth up to $471.
How many people will be covered by Medicare in 2020?
The future of Medicare funding. As of July 2020, Medicare covers about 62.4 million people, but the number of beneficiaries is outpacing the number of people who pay into the program. This has created a funding gap.
How Is Medicare Funded?
Medicare is a Federal program that is managed by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). The funds for the program come from a few different sources, with the primary source being FICA payroll taxes. These taxes are in addition to the 6.2% Social Security tax or OASDI tax that you will see withheld from your paycheck.
Is Medicare Funded By State Or Federal?
Many people wonder whether Medicare is a state or federal program. Medicare is really funded by you, the taxpayer. It is a Federal program that is administered by the Federal government. There is little to no state involvement with the Medicare program. Medicare provides health care coverage for retirees and disabled persons who can qualify.
How Does Medicare Work For Those Who Are Self-Employed?
Medicare insurance plans work exactly the same for those who are self-employed. If you have enough work credits to qualify for Medicare, then you will be automatically enrolled in Part A coverage at age 65. There is one major difference that self-employed individuals need to be aware of.
Conclusion
Medicare funding is extremely important to provide coverage to those individuals who rely on this insurance system, so it is helpful that you have a good understanding of where this funding comes from. Medicare is a Federally administered program that is funded primarily through taxpayer dollars.
Frequently Asked Questions
The government provides very few subsidies for Medicare. The program is almost entirely funded through federal income taxes, employer payroll taxes, and premium payments. However, with its current funding, the program may begin to run out of money in the next 5-10 years. The current funding model may be forced to change to keep the program running.
Does Medicare pay for health care?
Under Original Medicare, the government pays directly for the health care services you receive . You can see any doctor and hospital that takes Medicare (and most do) anywhere in the country. In Original Medicare: You go directly to the doctor or hospital when you need care.
Does Medicare Advantage have network restrictions?
On the other hand, Medicare Advantage Plans typically have network restrictions, meaning that you will likely be more limited in your choice of doctors and hospitals.
Does Medicare Advantage Plan cover Part A?
Each Medicare Advantage Plan must provide all Part A and Part B services covered by Original Medicare, but they can do so with different rules, costs, and restrictions that can affect how and when you receive care. It is important to understand your Medicare coverage choices and to pick your coverage carefully.
Do you have to pay coinsurance for Medicare?
You typically pay a coinsurance for each service you receive. There are limits on the amounts that doctors and hospitals can charge for your care. If you want prescription drug coverage with Original Medicare, in most cases you will need to actively choose and join a stand-alone Medicare private drug plan (PDP).
What percentage of Medicare is spending?
Key Facts. Medicare spending was 15 percent of total federal spending in 2018, and is projected to rise to 18 percent by 2029. Based on the latest projections in the 2019 Medicare Trustees report, the Medicare Hospital Insurance (Part A) trust fund is projected to be depleted in 2026, the same as the 2018 projection.
How much does Medicare cost?
In 2018, Medicare spending (net of income from premiums and other offsetting receipts) totaled $605 billion, accounting for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1).
How is Medicare Part D funded?
Part D is financed by general revenues (71 percent), beneficiary premiums (17 percent), and state payments for beneficiaries dually eligible for Medicare and Medicaid (12 percent). Higher-income enrollees pay a larger share of the cost of Part D coverage, as they do for Part B.
How fast will Medicare spending grow?
On a per capita basis, Medicare spending is also projected to grow at a faster rate between 2018 and 2028 (5.1 percent) than between 2010 and 2018 (1.7 percent), and slightly faster than the average annual growth in per capita private health insurance spending over the next 10 years (4.6 percent).
Why is Medicare spending so high?
Over the longer term (that is, beyond the next 10 years), both CBO and OACT expect Medicare spending to rise more rapidly than GDP due to a number of factors, including the aging of the population and faster growth in health care costs than growth in the economy on a per capita basis.
What has changed in Medicare spending in the past 10 years?
Another notable change in Medicare spending in the past 10 years is the increase in payments to Medicare Advantage plans , which are private health plans that cover all Part A and Part B benefits, and typically also Part D benefits.
How is Medicare's solvency measured?
The solvency of Medicare in this context is measured by the level of assets in the Part A trust fund. In years when annual income to the trust fund exceeds benefits spending, the asset level increases, and when annual spending exceeds income, the asset level decreases.