Hospital-level fixed effects regression analysis finds that hospitals with higher Medicare and Medicaid payer mix collect somewhat higher average patient care revenues than hospitals with more privately insured and self-pay patients.
What would be the impact of Medicare for all on hospitals?
One positive impact of Medicare for All would be that hospitals are guaranteed payment under a single-payer system. This would be especially beneficial to hospitals in rural communities that often serve larger proportions of uninsured or impoverished patients.
Do hospitals with higher Medicare and Medicaid payer mix have higher revenues?
Hospital-level fixed effects regression analysis finds that hospitals with higher Medicare and Medicaid payer mix collect somewhat higher average patient care revenues than hospitals with more privately insured and self-pay patients.
What percentage of Medicare reimbursements does a hospital receive?
In addition, Medicare will only reimburse patients for 95 percent of the Medicare approved amount. This means that the patient may be required to pay up to 20 percent extra in addition to their standard deductible, copayments, coinsurance payments, and premium payments. While rare, some hospitals completely opt out of Medicare services.
How does Medicare assign costs to hospitals?
Each DRG is assigned a cost based on the average cost based on previous visits. This assigned cost provides a simple method for Medicare to reimburse hospitals as it is only a simple flat rate based on the services provided. How Much Does Medicare Cost the Government? (Opens in a new browser tab)

How does Medicare reimbursement affect hospitals?
Under this system, hospitals receive a fixed payment for each patient that is determined by the patient's diagnosis-related group (DRG) at the time of admission; thus, reimbursement is unaffected by the hospital's actual expenditures on the patient.
Do hospitals lose money on Medicare?
Those hospitals, which include some of the nation's marquee medical centers, will lose 1% of their Medicare payments over 12 months. The penalties, based on patients who stayed in the hospitals anytime between mid-2017 and 2019, before the pandemic, are not related to covid-19.
Is Medicare an important source of revenue for hospitals?
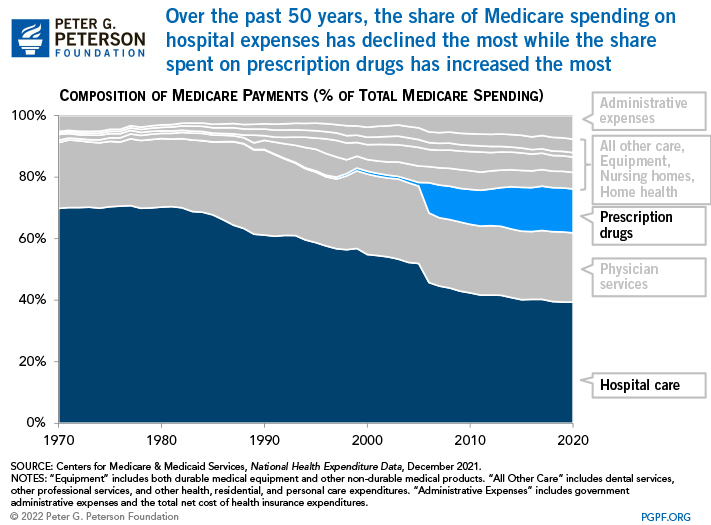
Medicare plays a major role in the health care system, accounting for 20 percent of total national health spending in 2017, 30 percent of spending on retail sales of prescription drugs, 25 percent of spending on hospital care, and 23 percent of spending on physician services.
What percent of hospital revenue is from Medicare?
The percentage of the total payor mix from private/self-pay increased from 66.5% in 2018 to 67.4% in 2020. The Medicare percentage decreased from 21.8% to 20.5%.
How do hospitals make a profit?
The American health care system for years has provided many hospitals with a clear playbook for turning a profit: Provide surgeries, scans and other well-reimbursed services to privately insured patients, whose plans pay higher prices than public programs like Medicare and Medicaid.
What part of the hospital makes the most money?
Ten Physician Specialties That Generate Most Revenue for...Cardiovascular surgery. Average revenue: $3.7 million. Average salary: $425,000.Cardiology (invasive) Average revenue: $3.48 million. ... Neurosurgery. Average revenue: $3.44 million. ... Orthopedic surgery. Average revenue: $3.29 million. ... Gastroenterology.
What are the two most important sources of hospital revenue?
Hospital operating revenue comes from two payment sources: public payers and private payers.
How does Medicare affect the economy?
In addition to financing crucial health care services for millions of Americans, Medicare benefits the broader economy. The funds disbursed by the program support the employment of millions of workers, and the salaries paid to those workers generate billions of dollars of tax revenue.
What is the largest expense for a hospital?
The greatest expense of hospitals in the United States is paying wages and benefits. Wages and benefits account for around 56 percent of all hospital expenses.
Is Medicare underfunded?
Politicians promised you benefits, but never funded them.
Why does Medicare cost so much?
Medicare Part B covers doctor visits, and other outpatient services, such as lab tests and diagnostic screenings. CMS officials gave three reasons for the historically high premium increase: Rising prices to deliver health care to Medicare enrollees and increased use of the health care system.
What percentage of hospitals are for profit?
For taxation purposes, there are two broad categories of private hospitals: for-profit and nonprofit. Of the private hospitals in California, about 30 percent are for-profit and about 70 percent are nonprofit. The for-profit hospitals pay corporate income taxes to the state.
How does Medicare for All affect hospitals?
One positive impact of Medicare for All would be that hospitals are guaranteed payment under a single-payer system. This would be especially beneficial to hospitals in rural communities that often serve larger ...
What would happen if Medicare for All became the new American healthcare system?
If Medicare for All becomes the new American healthcare system, many healthcare industry professionals could face major changes.
What is Medicare for All?
Most bills fall under the umbrella of Medicare for All and share the commonality of providing healthcare coverage for every single American.
How much more do private insurers pay than Medicare?
Private insurers pay around 100-200 percent more than Medicare pays for the same services and treatments, so eliminating this sector of the American healthcare industry would greatly affect hospital profits. This is a problem because hospitals often use excess funds to invest in healthcare innovations.
Why is it bad for doctors to have less money?
However, if physician salaries are affected at all by a shift to a single-payer system, it would be the result of shrinking long-term pay raises rather than direct salary reductions.
Can insurance companies budge on Canadian doctors?
If a doctor pushes hard enough for their patient, the insurance company may budge, but that kind of ruthless advocacy can take a mental toll and isn’t sustainable when doctors have hundreds of patients. Canadian doctors are less than one-third as likely to dispute with insurance companies compared to American doctors.
Will Medicare for All affect private insurance companies?
The impact of Medicare for All on private insurance companies would be the most drastic, aggressive change by far. Many of the proposed Medicare for All bills advocate for a complete elimination of private insurers.
How did Medicare help offset declining hospital revenues?
One of the impetuses for Medicare was to offset declining hospital revenues by “transforming the elderly into paying consumers of hospital services.” As expected, the demographics of the average patient changed; prior to 1965, more than two-thirds of hospital patients were under the age of 65, but by 2010, more than one-half of patients were aged 65 or older.
Why did Medicare drop in 2009?
According to a Kaiser Family foundation study, the number of firms offering retirement health benefits (including supplements to Medicare) dropped from a high of 66% in 1988 to 21% in 2009 as healthcare costs have increased . In addition, those companies offering benefits are much more restrictive regarding eligibility, often requiring a combination of age and long tenure with the company before benefits are available. In addition, retirees who have coverage may lose benefits in the event of a corporate restructuring or bankruptcy, as healthcare benefits do not enjoy a similar status to pension plans.
What is Medicare akin to?
Medicare is akin to a home insurance program wherein a large portion of the insureds need repairs during the year; as people age, their bodies and minds wear out, immune systems are compromised, and organs need replacements. Continuing the analogy, the Medicare population is a group of homeowners whose houses will burn down each year.
What is the average age for a person on Medicare?
According to research by the Kaiser Family Foundation, the typical Medicare enrollee is likely to be white (78% of the covered population), female (56% due to longevity), and between the ages of 75 and 84. A typical Medicare household, according to the last comprehensive study of Medicare recipients in 2006, had an income less than one-half of the average American household ($22,600 versus $48,201) and savings of $66,900, less than half of their expected costs of healthcare ($124,000 for a man; $152,000 for a woman).
What were the new treatments and technologies that Medicare provided?
The development and expansion of radical new treatments and technologies, such as the open heart surgery facility and the cardiac intensive care unit, were directly attributable to Medicare and the new ability of seniors to pay for treatment.
How many elderly people are without health insurance?
Today, as a result of the amendment of Social Security in 1965 to create Medicare, less than 1% of elderly Americans are without health insurance or access to medical treatment in their declining years.
How many hospital beds have fallen since 1965?
As a consequence, the number of hospital beds across the nation has fallen by 33% from 1965.
What percentage of hospital bills are covered by Medicare?
The Medicare program accounts for some 27 percent of all expenditures on hospital care in the United States, clearly establishing Medicare as the largest single consumer of hospital services ( Gibson, Waldo, and Levit, 1983 ). Given the dominant role played by Medicare, and the dramatic change in the way that Medicare pays for hospital services under PPS, it would not be unreasonable to expect that the entire hospital payment environment might be altered by the new system. Among those most likely to be directly affected by such a change are those who pay the bulk of the remaining portion of the Nation's hospital bill, the most prominent of these being the State Medicaid programs (on the public side) and the Blue Cross/Blue Shield plans (on the private side).
When did hospitals get reimbursed by Medicare?
Prior to the passage of Public Law 98-21, the Social Security Amendments of 1983, hospitals were reimbursed by Medicare on a retrospective cost basis. Under this system, hospitals were paid whatever they spent; there was little incentive to control costs, because higher costs brought about higher levels of reimbursement. Partly as a result of this system of incentives, hospital costs increased at a rate much higher than the overall rate of inflation.
What was the primary motivation of Congress in enacting prospective payment for Medicare inpatient hospital services?
The principal motivation of Congress in enacting prospective payment for Medicare inpatient hospital services was to constrain the depletion of the Medicare Trust Funds, therefore, a primary indicator of the success or failure of PPS would be its effect on the volume and rate of growth in Medicare program expenditures.
What is SNF reimbursement?
SNF's are currently reimbursed for routine costs per Medicare patient day, subject to an upper reimbursement limit, with hospital-based SNF's having higher limits than do freestanding SNF's. With hospitals seeking to reduce lengths of stay for Medicare patients under PPS, an increase is anticipated in the rate of transfer of Medicare cases to long-term care providers. Data on SNF admission notices show a slight acceleration in the projected rate of increase in SNF admissions during fiscal year 1984. Although the rate of increase in SNF admission notices processed by HCFA for the previous two fiscal years was 4.7 percent, the projected rate of increase for fiscal year 1984 was 5.7 percent.
How much did Medicare increase in the year 1984?
Inpatient hospital payments have risen from about $2.4 billion in fiscal year 1967 to more than $39 billion (estimated) in fiscal year 1984. The apparent effect of recent efforts to control the increase in Medicare hospital expenditures is shown in Table 10. From fiscal year 1974 (after temporary wage and price controls were removed) through fiscal year 1982 (the last year prior to the imposition of TEFRA restrictions), Medicare inpatient hospital benefit payments increased at an annual rate of 19.9 percent (10 percent in real terms), never falling below 14.3 percent in any given year. Under TEFRA (during fiscal year 1983), this rate of increase was only 10.2 percent (6.8 percent in real terms), lower than at any time in the previous 10 years. Furthermore, the estimated rate of increase under PPS (during fiscal year 1984) was lower still, at 8.2 percent (3.8 percent in real terms), among the smallest percent increases in the program's history.
What is the source of Medicare data?
SOURCES: Health Care Financing Administration, Bureau of Data Management and Strategy: Data from the Medicare Statistical System; Office of the Actuary: Data from the Division of Medicare Cost Estimates.
How many hospitals were under PPS in 1984?
By the end of September 1984, a total of 5,405 hospitals (81 percent of all Medicare-participating hospitals) were operating under PPS. This number represents virtually 100 percent of “PPS-eligible” hospitals (that is, short-stay acute care hospitals subject to the new payment system).
How does Medicare affect healthcare?
How Medicare Impacts U.S. Healthcare Costs. A recent study suggests that Medicare does much more than provide health insurance for 48 million Americans. It also plays a significant role in determining the pricing for most medical treatments and services provided in the U.S. For almost every procedure – from routine checkups to heart transplants – ...
Why is correcting Medicare pricing errors important?
Economists believe that correcting Medicare pricing errors will be crucial in stabilizing healthcare costs because, in the absence of a traditional consumer market for medical services and because setting pricing is a complex and time-consuming task, Medicare forms the foundation of pricing for private insurers.
How Are Medicare Rates Set?
Medicare compensates physicians based on the relative cost of providing services as calculated by the Resource-Based Relative Value Scale (RBRVS).
Is Medicare overspending?
Currently, the government is overspending by billions of dollars on Medicare payments. And because of the influence, Medicare has on the prices set by private insurers, these mistakes are being replicated by payers across the industry.
Does Medicare pay rates to private health insurance?
Pay rates are then opened to public and private health insurers for comment and analysis. After an agreed-upon fee is decided, Medicare applies this to all medical services.
Does Medicare pay fair prices?
For almost every procedure – from routine checkups to heart transplants – Medicare sets what it considers a “fair price” for services rendered. And because of its enormous size, Medicare’s rates seem to have a significant impact on what other insurers pay as well.
What is Medicare Part A?
What Medicare Benefits Cover Hospital Expenses? Medicare Part A is responsible for covering hospital expenses when a Medicare recipient is formally admitted. Part A may include coverage for inpatient surgeries, recovery from surgery, multi-day hospital stays due to illness or injury, or other inpatient procedures.
What is Medicare reimbursement based on?
Reimbursement is based on the DRGs and procedures that were assigned and performed during the patient’s hospital stay. Each DRG is assigned a cost based on the average cost based on previous visits. This assigned cost provides a simple method for Medicare to reimburse hospitals as it is only a simple flat rate based on the services provided.
What does it mean when a provider is not a participating provider?
If a provider is a non-participating provider, it means that they have not signed a contract with Medicare to accept the insurance company’s prices for all procedures, but they do for accept assignment for some. This is mainly due to the fact that Medicare reimbursement amounts are often lower than those received from private insurance companies. For these providers, the patient may be required to pay for the full cost of the visit up front and can then seek personal reimbursement from Medicare afterwards.
How much higher is Medicare approved?
The amount for each procedure or test that is not contracted with Medicare can be up to 15 percent higher than the Medicare approved amount. In addition, Medicare will only reimburse patients for 95 percent of the Medicare approved amount.
How much extra do you have to pay for Medicare?
This means that the patient may be required to pay up to 20 percent extra in addition to their standard deductible, copayments, coinsurance payments, and premium payments. While rare, some hospitals completely opt out of Medicare services.
Does Medicare cover permanent disability?
Medicare provides coverage for millions of Americans over the age of 65 or individuals under 65 who have certain permanent disabilities. Medicare recipients can receive care at a variety of facilities, and hospitals are commonly used for emergency care, inpatient procedures, and longer hospital stays. Medicare benefits often cover care ...
Is Medicare reimbursement lower than private insurance?
This is mainly due to the fact that Medicare reimbursement amounts are often lower than those received from private insurance companies . For these providers, the patient may be required to pay for the full cost of the visit up front and can then seek personal reimbursement from Medicare afterwards.
