As a result of using HCCs, Medicare Advantage plans are paid using a risk-adjusted payment model that reimburses Medicare Advantage plans based on the actual costs of care for each individual beneficiary rather than an average per-capita payment for everyone. Why are HCCs important?
Full Answer
What is an HCC and how does it work?
CMS uses HCCs to reimburse Medicare Advantage plans based on the health of their members. It pays accurately for the predicted cost expenditures of patients by adjusting those payments based on demographic information and patient health status.
What happens if a hospital omits HCCS from Medicare?
When a hospital inadvertently omits HCCs, it essentially deprives itself of payment because it fails to provide insurers with an accurate picture of the severity of conditions of patients across its patient population. Medicare Advantage (MA) plans receive a per-member-per-month (PMPM) payment from CMS to cover the cost of their enrollees.
Should Medicare Advantage plans have HCCS?
Without HCCs, Medicare Advantage plans would receive a fixed payment rate that doesn’t take each beneficiary’s unique risks into account. This would incentivize plans to avoid the sickest, most expensive patients.
What is the Centers for Medicare&Medicaid Services HCC model?
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) HCC model was initiated in 2004 but is becoming increasingly prevalent as the environment shifts to value-based payment models. Hierarchical condition category relies on ICD-10 coding to assign risk scores to patients. Each HCC is mapped to an ICD-10 code.

What is HCC reimbursement?
What are HCCs? CMS uses HCCs to reimburse Medicare Advantage plans based on the health of their members. It pays accurately for the predicted cost expenditures of patients by adjusting those payments based on demographic information and patient health status.
How is HCC calculated?
The CMS-HCC risk score for a beneficiary is the sum of the score or weight attributed to each of the demographic factors and HCCs within the model. The CMS-HCC model is normalized to 1.0. Beneficiaries would be considered relatively healthy, and therefore less costly, with a risk score less than 1.0.
How does Medicare Advantage risk adjustment work?
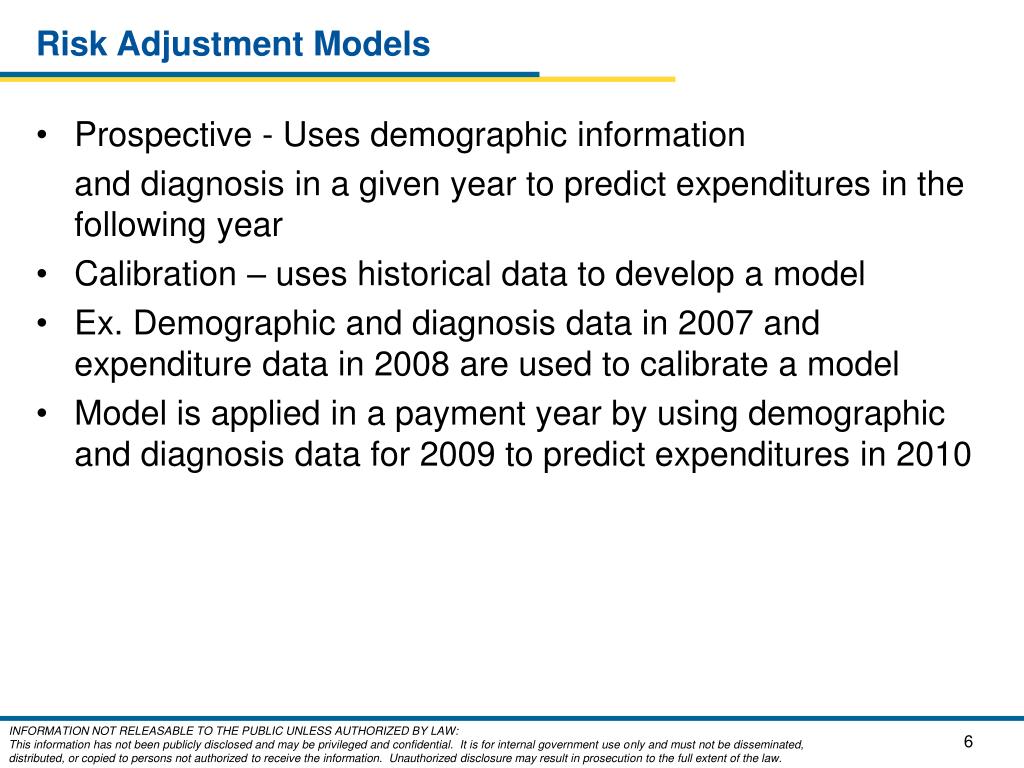
Risk adjustment is a statistical method that seeks to predict a person's likely use and costs of health care services. It's used in Medicare Advantage to adjust the capitated payments the federal government makes to cover expected medical costs of enrollees.
What does HCC mean in Medicare?
Hierarchical Condition CategoryRisk Adjustment and Hierarchical Condition Category (HCC) coding is a payment model mandated by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) in 1997.
What are HCC categories?
Created by CMS in 1997 and implemented in 2003, HCC or “Hierarchical Condition Category” is a risk adjustment model that calculates risk scores for aged and disabled Medicare beneficiaries. These scores represent the expected medical costs of a Medicare member in the coming year.
How is Medicare risk adjustment score calculated?
The purpose of the Medicare risk scores is to estimate a relative cost factor. (i.e., it is a payment risk score). CMS calculates individual beneficiary-level risk scores by adding the relative factors associated with each beneficiary's demographic and disease factors. The CMS Payment Risk Score is built up each year.
What is HCC risk adjustment?
Hierarchical condition category (HCC) coding is a risk-adjustment model originally designed to estimate future health care costs for patients.
Which Medicare Part uses the HCC risk adjustment payment model?
The CMS-HCC model adjusts Part C monthly payments to Medicare Advantage plans, PACE organizations, and certain demonstrations.
How does risk adjustment affect payments to managed care plans?
Risk adjustment allows CMS to pay plans for the risk of the beneficiaries they enroll, instead of an average amount for Medicare beneficiaries. By risk adjusting plan payments, CMS is able to make appropriate and accurate payments for enrollees with differences in expected costs.
What does HCC coding mean?
Hierarchical Condition Category codingHierarchical Condition Category coding — or HCC coding — was implemented by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) in 2004 to help estimate the healthcare costs of Medicare enrollees in the coming year.
Which part of Medicare is affected by CMS HCC?
The CMS- HCC model adjusts Part C monthly payments to Medicare Advantage plans and PACE organizations. Risk scores are relative and reflect the standard benefit: Each beneficiary's risk score is calculated to estimate that specific beneficiary's expected costs, relative to the average beneficiary.
Who assigns each HCC a number?
CMSNote that CMS assigns each HCC a number, such as CMS-HCC 17. A patient may see multiple providers throughout the year with each submitting a claim for services.
Why do hospitals use HCCs?
HCCs ultimately provide a snapshot into patient severity, giving insurers valuable information that they can use to assess outcomes, predict costs, and gauge overall hospital performance. It behooves executives to examine hospital data from the insurer’s point of view. For example, when claims data reveal relatively low RAF scores, it may be difficult to explain consistently high costs associated with patient care. (See sidebar)
Why are HCCs important?
HCCs are therefore essential for any health plan providing coverage or any health system providing care for a Medicare beneficiary.
What is PMPM in Medicare?
Medicare Advantage (MA) plans receive a per-member-per-month (PMPM) payment from CMS to cover the cost of their enrollees. In some cases, this payment is passed on to the providers if there is a shared-savings program between the provider and the MA plan. As part of the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015, CMS will begin to adjust fee-for-service payments using HCCs and other factors as a basis for the adjustment. If an ACO or health plan is involved, then the payment is set up to cover the cost of the enrollees, similar to a budget for care. Depending on the arrangement, most participants share in savings generated within the health plan or ACO. To accurately control costs, both types of programs need an accurate evaluation of the status of the health of their enrollees.
How to identify HCC gaps?
Another way to identify HCC gaps is to follow patient claims throughout the continuum of care. A hospital can aggregate two years’ worth of claims data from all care settings—inpatient, outpatient, and physician practice—to establish each patient’s HCC baseline and annual RAF score. The next step is to monitor claims going forward to determine what HCC diagnoses might be missing in a given year. These missing diagnoses can be used to drive physician workflow changes and process improvements. This type of large-scale analysis can be enlightening because it includes various touch points for clinical care and may identify other opportunities for HCC capture, such as a hospital’s outpatient or referring facilities.
How often can a physician see a patient with HCC?
Address clinical care gaps. Physicians can capture HCCs for patients effectively only if the physicians see the patients at least once every year. The key is for the physician practices to identify patients without scheduled visits and encourage them to make appointments so the physicians can evaluate and document all conditions, including the HCC diagnoses, for appropriate billing.
When did HCCs start?
HCCs in Brief. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) originally developed HCCs in 2004 to adjust capitated payments for its Medicare Advantage (Part C) plans based on risk. However, with the growth of population health payment models in the past decade, HCCs have become more popular.
How can hospitals help physicians?
Hospitals can help physicians by providing pertinent and reliable real-time documentation alerts. An alert might notify a physician that he or she should assess and document the specific type of diabetes, for example, thereby sparing the physician from the guesswork of trying to understand what documentation affects HCC reporting.
What is HCC in Medicare?
Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) oversees the HHS-HCC risk adjustment model 2020, which covers commercial payers of all ages and determines risk payments for the current year. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) uses the CMS-HCC model for the Medicare Advantage program and those who qualify for Medicare or patients 65 and older, calculating risk payments for the next year ( Wolters Kluwer, 2016).
How many HCC categories are there in CMS?
The CMS risk adjustment model includes 79 HCC categories for chronic illnesses, and here are the most common ( Formativ Health, 2018):
How does the CMS-HCC Risk Adjustment Model 2020 work?
Demographics include the person’s age, gender, and, for the CMS-HCC model, the place of residence (in a community or skilled nursing facility), and enrollment in Medicare and/or Medicaid.
What is RAF score in HCC?
Both HCC models use a risk adjustment factor (RAF) score to calculate expected future health costs for each patient. Instead of providing one base payment for every patient, the risk adjustment model allows for more accurate payments for expected costs based on health status and demographics of every enrollee.
What is the M.E.A.T. in HCC?
To help properly code patient diagnoses and assign RAF scores, healthcare organizations use the M.E.A.T. (monitoring, evaluation, assessment, and treatment ) criteria application.
Does HIM Consulting offer HCC?
YES HIM Consulting employs a qualified team of experienced coding and auditing specialists who can consult your organization on the HCC risk adjustment models, as well as provide assistance with HCC coding. If you’re interested in our consulting services, education, and training, or other valuable programs, contact YES today!
How does HCC improve patient scores?
Reporting a complete picture for the risk adjustment factor through HCC increases the accuracy of the patient score and ideally, reduces the need to request medical records or audit provider’s claims. When done correctly, HCC streamlines the process creating clean claims and allowing for fast reimbursements.
When did HCCs start?
Let’s be clear: This isn’t a new idea. Medicaid mandated this model in 1997 and began using it in 2004. Because of the proven success of HCCs in predicting resource use by Medicare Advantage enrollees, and because the general trend is to follow CMS’s lead, it’s a natural expectation that HCCs will become the model for commercial payers sooner rather than later.
What is meat in HCC?
MEAT is an acronym used in HCC to ensure that the most accurate and complete information is being documented: Monitor signs and symptoms, disease process. E valuate-test results, meds, patient response to treatment. A ssess/Address-ordering tests, patient education, review records, counseling patient and family members.
What does the ACA mean?
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) ensures that insurance companies are no longer offering less expensive insurance plans to healthy patients who rarely visit the doctor and ...
Why are patients assigned to more than one category?
Patients are often assigned to more than one category because the combination of demographic information and risk factors can cumulate to represent more than one kind of illness or potential for illness.
Can two patients have different payment rates?
Under this payment model, two patients in the same practice can have a different payment rate. This is based on a variety of factors that determine the amount of risk/work involved to maintain the health of a patient.
Is HCC coding good?
Since costs can vary widely among patients, risk adjustment can now be used to evaluate patients on an equal scale. It opens up a world of new opportunities for coders and providers and may make reimbursements more efficient. And that’s good news for your revenue cycle performance.
How does HCC model work?
HCC models organize the disease process and conditions into body systems and diagnostic groups. The diagnostic groups are then separated into condition categories.
What are the benefits of HCC risk scoring?
These include achieving higher reimbursement, helping to achieve financial benchmarks, assisting in the development of programs for population health management to improve outcomes and maintaining a practice’s financial viability.
When was the HCC model introduced?
CMS first introduced the HCC risk adjustment model in 2004 and has been refining it ever since, especially with the shift to value-based payment. Four new HCCs were introduced for 2019.
What is a progress note for HCC?
A well-documented progress note includes a review of systems (ROS), a history of present illness (HPI), a physician exam and a show of the medical decision process. If you’re interested in learning more about proper chart documentation for HCC risk coding, take a few minutes to view our recent webinar.
Why are value based payment programs important?
Why are they important for the healthcare industry? Because they’ve proven repeatedly that they can generate savings, improve patient health and even increase patient retention. An essential part of these programs, though, is how they’re managed. This is where risk adjustment or scoring comes in.
Does ACO accept MA plans?
If you work for a practice that accepts MA plans or is participating in an accountable care organization (ACO), give them a call to find out what you can do to be more successful in the program, and be sure to get a list of the participating patients. Each ACO and MA plan is different and offers bonuses based on certain criteria met, cost savings and/or quality measures reported. In 2018, CMS distributed $780 million in performance payments to ACOs.
How does HCC affect healthcare?
HCCs directly impact the amount of money received by healthcare organizations from the largest single payer in healthcare, CMS. Patients with high HCCs are expected to require intensive medical treatment, and clinicians that enroll these high-risk patients are reimbursed at higher rates than those with enrollees who have low HCCs. Organizations who do not document HCC codes properly or to the highest specificity will not receive these additional reimbursement amount for applicable patients.
What are HCCs?
HCCs, or Hierarchical Condition Categories, are sets of medical codes that are linked to specific clinical diagnoses. Since 2004, HCCs have been used by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) as part of a risk-adjustment model that identifies individuals with serious acute or chronic conditions. This allows Medicare to project the expected risk and future annual cost of care. Each HCC represents diagnoses with similar clinical complexity and expected annual care costs.
How and by whom are HCCs used?
HCCs are used to calculate payments to healthcare organizations for patients who are insured by Medicare Advantage (MA) plans, Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs), some Affordable Care Act (ACA) plans and many more. Clinicians add HCCs to a patient’s medical record along with supporting documentation as required by CMS.
How many HCC codes are there in 2020?
HCC codes represent costly chronic health conditions, as well as some severe acute conditions. As of 2020, there are 86 HCC codes, arranged into 19 categories. These 86 codes are comprised of 9,700 ICD-10-CM codes, each representing a singular medical condition. The top HCC categories include major depressive and bipolar disorders, asthma and pulmonary disease, diabetes, specified heart arrhythmias, congestive heart failure, breast and prostate cancer, and rheumatoid arthritis.
How much is the bonus for HCC code 19?
For example, diabetes with no complications, HCC code 19, pays a $894.40 premium bonus, while diabetes with ESRD, requires 2 HCC codes, 18 and 136, and has a bonus of $1273.60. The ability to document with greater precision can dramatically impact payment amounts.
What is a RAF score and what does it have to do with HCCs?
A Risk Adjustment Factor, known as a RAF score, is a measure of the estimated cost of an individual’s care based on their disease burden and demographic information. The RAF score is then used to calculate payments to healthcare organizations. Each HCC associated with a patient is assigned a relative factor that is averaged with any other HCC code factors and a demographic score. The resulting score is then multiplied by a predetermined dollar amount to set the per-member-per-month (PMPM) capitated reimbursement for the next period of coverage. The PMPM is the payment amount a provider receives for a patient enrolled in an MA plan regardless of services provided. Healthier patients will have a below average RAF while sicker patients will have a higher one, which impacts the calculated payment amount. Scores are calculated on an annual basis.
When was the HCC model implemented?
CMS first implemented the Hierarchical Condition Category (HCC) risk adjustment model in 2004 as the methodology to risk adjust Medicare capitation payments to private health insurance companies offering Medicare Advantage plans. Since then, the HCC model has been refined and its utilization expanded to include the risk adjustment of patients in a variety of value-based reimbursement plans, including ACOs, Direct Contracting (CMS), Comprehensive Primary Care Plus (CPC+), and many others.
What is fee for service in healthcare?
In the traditional fee-for-service payment model that healthcare organizations have been using for decades, providers are paid for the volume and types of services performed. For example, each MRI performed, or unit of anesthesia delivered would be billed at a predetermined rate. As a result, providers had incentive to order more tests, perform more procedures, and take on more patients to receive more payment.
Why is Medicare pushing for value based programs?
As a result, Medicare is pushing for more value-based programs to reduce overall costs and improve quality for Medicare beneficiaries. Employers are pushing insurance companies to reduce the cost of providing healthcare coverage to their employees.
Why is value based care so popular?
Value-based care (also referred to as accountable care or population health management) is growing in popularity in part because the value-based reimbursement model provides incentives for providers to offer the best care at the lowest cost. As the name suggests, patients are receiving more value for their money.
What is bundled payment?
Under bundled payments, a single, fixed payment covers all services associated with an episode of care. An episode of care could be a hip replacement or cardiac surgery, for example, and could include any inpatient, outpatient, and rehabilitation care costs. Insurance companies determine the fixed payment based on the historical performance of the hospital and providers.
What is value based care?
In more basic terms, value-based care models center on patient outcomes and how well healthcare providers can improve quality of care based on specific measures (e.g. reducing hospital readmissions and improving preventative care).
When will Medicare run out of money?
There are primarily three groups pushing for this shift for varying reasons: The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), the largest single payer for healthcare, is projected to run out of money by 2026 at its current funding levels.