The ACA included provisions to improve Medicare benefits by providing free coverage for some preventive benefits, such as screenings for breast and colorectal cancer, cardiovascular disease
Heart diseases
Conditions of the heart including structural and functional abnormalities.
How does ACA affect Medicare?
Oct 02, 2014 · Among other benefits, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) helps individuals on Medicare to save money with preventative care and brand-name drugs. Starting in January 2014, Medicare began covering many preventative services. with no out-of-pocket expense. This coverage includes an annual wellness visit and screening tests as recommended, such as those for …
How did ACA affect Medicare?
There’s good news for those who believe in an “ounce of prevention.” Since 2011, Medicare beneficiaries have had access to free preventive care, with a free “Welcome to Medicare” visit, free annual wellness visits, personalized prevention plans, and some screenings, including mammograms – all thanks to the ACA. New funding for Medicare. The ACA also changed the …
How will ACA repeal affect Medicare?
Dec 10, 2019 · The Affordable Care Act has made Medicare prescription drug coverage (Part D) more affordable during the coverage gap by gradually closing the prescription drug donut hole over time. In 2016, people with Medicare paid 45% for brand-name drugs and 58% for generic drugs while in the coverage gap. These percentages have shrunk over the last few years.
What are the pros and cons of ACA?
Mar 20, 2017 · the aca uses two primary approaches to increase access to health insurance: it expands access to medicaid, based solely on income, for those with incomes up to 138% of the federal poverty level (fpl), and creates eligibility for those with incomes from 139% to 400% fpl to apply for subsidies [in the form of advance payment tax credits (aptcs)] to …
Did the Affordable Care Act expand Medicare?
How will repealing Obamacare affect Medicare?
How did the ACA impact Medicaid?
Who is the largest payer for healthcare in the US?
What is a new benefit that the ACA added for Medicare beneficiaries?
How is Medicare different from Obamacare?
How did the ACA improve access to healthcare?
Did the ACA Medicaid expansion save lives?
How did the ACA reduce Medicare costs?
Cost savings through Medicare Advantage. The ACA gradually reduced costs by restructuring payments to Medicare Advantage, based on the fact that the government was spending more money per enrollee for Medicare Advantage than for Original Medicare. But implementing the cuts has been a bit of an uphill battle.
Why did Medicare enrollment drop?
When the ACA was enacted, there were expectations that Medicare Advantage enrollment would drop because the payment cuts would trigger benefit reductions and premium increases that would drive enrollees away from Medicare Advantage plans.
What is Medicare D subsidy?
When Medicare D was created, it included a provision to provide a subsidy to employers who continued to offer prescription drug coverage to their retirees, as long as the drug covered was at least as good as Medicare D. The subsidy amounts to 28 percent of what the employer spends on retiree drug costs.
How much will Medicare Part B cost in 2021?
In 2021, most Medicare Part B enrollees pay $148.50/month in premiums. But beneficiaries with higher incomes pay additional amounts – up to $504.90 for those with the highest incomes (individuals with income above $500,000, and couples above $750,000). Medicare D premiums are also higher for enrollees with higher incomes.
What percentage of Medicare donut holes are paid?
The issue was addressed immediately by the ACA, which began phasing in coverage adjustments to ensure that enrollees will pay only 25 percent of “donut hole” expenses by 2020, compared to 100 percent in 2010 and before.
How many people will be on Medicare in 2021?
However, those concerns have turned out to be unfounded. In 2021, there were 26 million Medicare Advantage enrollees, and enrollment in Advantage plans had been steadily growing since 2004.; Medicare Advantage now accounts for 42% of all Medicare beneficiaries. That’s up from 24% in 2010, which is the year the ACA was enacted (overall Medicare enrollment has been growing sharply as the Baby Boomer population ages into Medicare, but Medicare Advantage enrollment is growing at an even faster pace).
What is the medical loss ratio for Medicare Advantage?
This is the same medical loss ratio that was imposed on the private large group health insurance market starting in 2011, and most Medicare Advantage plans were already conforming to this requirement; in 2011, the average medical loss ratio for Medicare Advantage plans was 86.3%. The medical loss ratio rules remain in effect, but starting in 2019, the federal government has reduced the reporting burden for Medicare Advantage insurers.
How did the Affordable Care Act affect Medicare?
The Affordable Care Act also affected Medicare by adding coverage for a "Wellness Visit" and a “Welcome to Medicare” preventative visit. It also eliminated cost-sharing for almost all of the preventive services covered by Medicare.
What is the Affordable Care Act?
The Affordable Care Act provides ways for hospitals, doctors and other health care providers to coordinate their care for Medicare beneficiaries. As a result, health care quality is improved and unnecessary spending is reduced.
What are the initiatives under the Affordable Care Act?
Under these initiatives, your doctor may get additional resources that will help ensure that your treatment is consistent. The Affordable Care Act provides ways for hospitals, doctors and other health care providers to coordinate their care for Medicare beneficiaries. As a result, health care quality is improved and unnecessary spending is reduced.
How much does Medicare pay for generic drugs?
In 2016, people with Medicare paid 45% for brand-name drugs and 58% for generic drugs while in the coverage gap. These percentages have shrunk over the last few years. Starting in 2020, however, you’ll pay only 25% for covered brand-name and generic drugs during the coverage gap.
How long does Medicare cover preventive visits?
This is a one-time visit. During the visit, your health care provider will review your health, as well as provide education and counseling about preventive services and other care.
How long does it take to sign up for Medicare?
You will get an initial enrollment period to sign up for Medicare. In most cases, the initial enrollment period begins three months before your 65th birthday and ends three months afterward. For most people, it’s beneficial to sign up for Medicare during this time. This is because those who sign up for Medicare after the initial enrollment period ends, face some negative consequences. For example, you might be required to pay a Part B (medical insurance) late enrollment penalty for as long as you have Medicare. Also, you are only permitted to enroll in Medicare Part B (and Part A in some cases) during the Medicare general enrollment period that runs from January 1 to March 31 each year. However, coverage will not begin until July of that year. This could create a gap in your insurance coverage.
When will Medicare be extended?
Under the Affordable Care Act, the Medicare Trust fund will be extended to at least the year 2029. This is a 12-year extension that is primarily the result of a reduction in waste, fraud, and abuse, as well as Medicare costs.
How does the ACA affect health care?
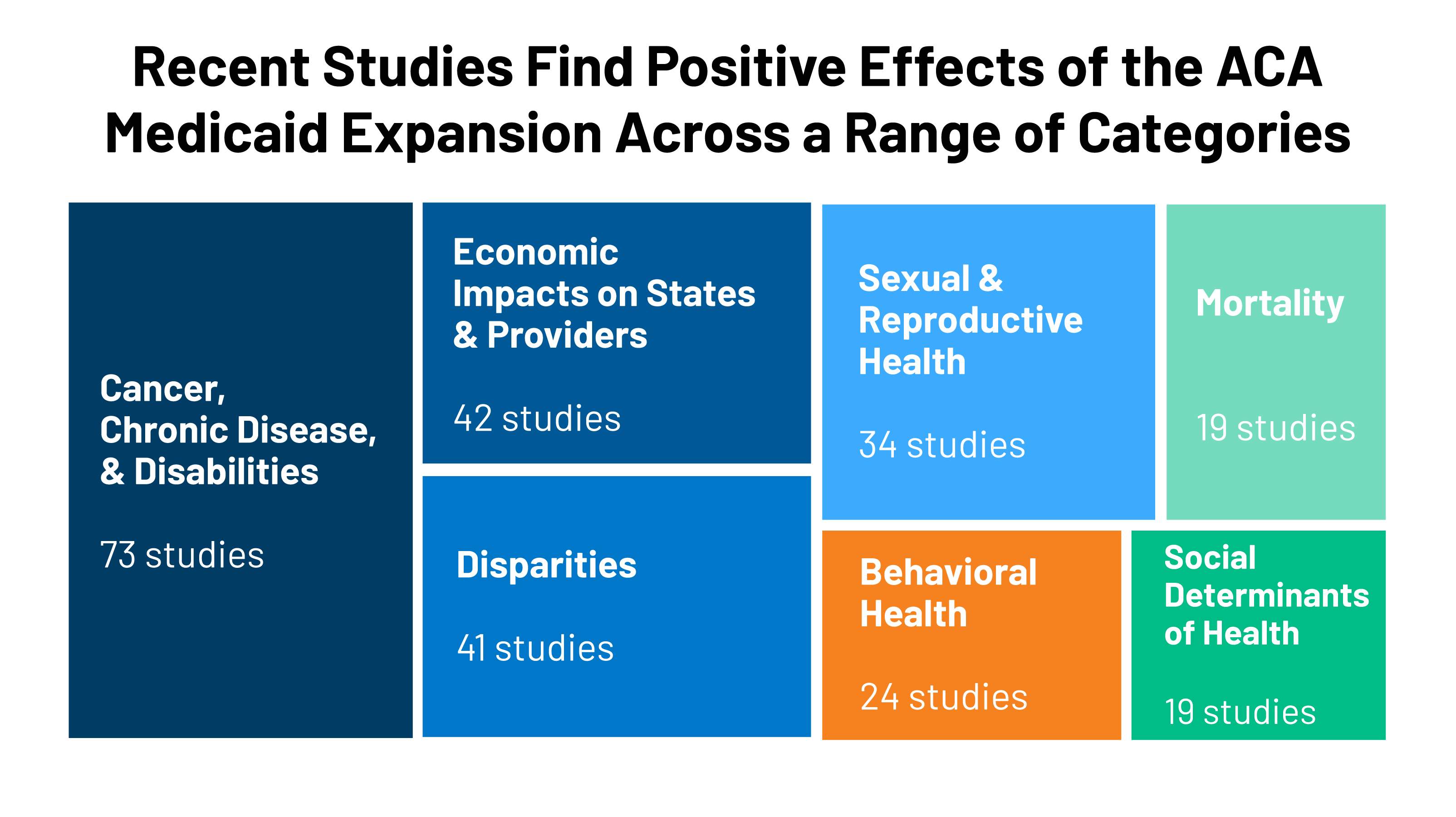
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) expands access to health insurance in the United States , and, to date, an estimated 20 million previously uninsured individuals have gained coverage. Understanding the law’s impact on coverage, access, utilization, and health outcomes, especially among low-income populations, is critical to informing ongoing debates about its effectiveness and implementation. Early findings indicate that there have been significant reductions in the rate of uninsurance among the poor and among those who live in Medicaid expansion states. In addition, the law has been associated with increased health care access, affordability, and use of preventive and outpatient services among low-income populations, though impacts on inpatient utilization and health outcomes have been less conclusive. Although these early findings are generally consistent with past coverage expansions, continued monitoring of these domains is essential to understand the long-term impact of the law for underserved populations.
How does the reliance on the ACA affect health insurance?
Despite the availability of subsidies and cost-sharing reductions, the reliance of the ACA on health insurance exchanges may both increase access to health insurance and simultaneously pose unintended barriers to access, particularly for low-income populations. These barriers can arise in two ways. The most publicized method is through the creation of narrow networks, where insurers offer plans and policies with fewer doctors and hospitals in an effort to keep premiums as competitive as possible. Whether narrow networks create actual, rather than perceived, barriers to care has not been well established yet through research. Nevertheless, the existence of narrow networks has created the perception that exchange-based QHPs are limiting access to a greater extent than did pre-ACA policies, despite the absence of adequate baseline data from pre-ACA years.
What is the coverage gap?
Approximately 9% of the remaining uninsured (almost 3 million Americans) fall into what is known as the “coverage gap.” This group represents poor, uninsured adults who reside in the 19 non–Medicaid expansion states whose income is above the state’s threshold for Medicaid eligibility but less than the 100% threshold for Marketplace subsidy eligibility. Also included are childless adults who were not previously eligible for Medicaid. Almost 90% of all adults in the coverage gap live in the South, half in either Texas or Florida, which aligns with this region’s high uninsurance rates, limited Medicaid eligibility, and low uptake of Medicaid expansion (37). Consistent with demographic characteristics and policies excluding nondisabled adults in states that did not expand Medicaid, African Americans and childless adults also account for a disproportionate share of individuals in the coverage gap (37). If all current nonexpansion states opted to expand Medicaid, 5.2 million currently uninsured adults would gain coverage: 2.9 million who are in the coverage gap, 0.5 million who are already eligible for Medicaid though alternate pathways, and an additional 1.8 million who are presently eligible for Marketplace subsidies with incomes from 100% FPL to 138% FPL yet did not enroll (37). Because a substantial portion of the remaining uninsured are either eligible for coverage or fall in the coverage gap, the law’s potential impact on the poor has not yet been fully realized.
How effective is Medicaid expansion?
The expansion of Medicaid has been particularly effective in states that took advantage of the opportunity for early Medicaid expansion allowed under the ACA. Between 2010 and 2014, six states (California, Colorado, Connecticut, Minnesota, New Jersey, Washington) and the District of Columbia extended Medicaid eligibility for low-income adults through the early Medicaid expansion option or the Section 1115 waiver process (18). In California, the LIHP significantly increased coverage by 7.3 percentage points for poor adults (up to 138% FPL) within the first two years (38). Similarly, one year after early expansion, Medicaid coverage increased significantly in Connecticut (4.9 percentage points) and modestly in Washington, DC (3.7 percentage points) among low-income childless adults—a key subpopulation targeted by Medicaid expansion (86). Trends in coverage gains in these early expansions echoed those of the Massachusetts health reform, which was associated with an estimated 18.4-percentage-point increase in coverage among low-income adults and even larger gains among low-income childless adults (54). Though these expansions were implemented prior to the ACA, their positive findings inform potential coverage gains for the poor under the ACA.
What are the effects of pre-ACA coverage?
Pre-ACA insurance expansions have largely demonstrated improved access to care for low-income populations. For example, the Massachusetts health reform was associated with significant reductions in forgone or delayed care and improvements in access to a personal doctor and usual source of care among adults overall (46, 54, 56, 58, 72, 88) and, in particular, for subgroups targeted by the ACA, such as low-income and childless adults (54, 56, 58). With regard to affordability, the Medicaid expansion in Oregon diminished financial hardship from medical costs, markedly reducing catastrophic OOP expenditures (5, 35, 98). In addition, other states that expanded public insurance prior to the ACA demonstrated improvements in access and affordability among low-income adults (62, 82) and children (33, 44) across comparable measures. More recently, the California LIHP waiver project found large reductions in the likelihood of any family OOP health care spending but did not detect significant differences in access to care, which may be explained by a well-established safety net in the state prior to program implementation (38). One ongoing concern about expanding coverage is that increased demand for services by newly insured individuals may limit access to care, but evidence from prior expansions does not appear to sufficiently support this hypothesis (67).
What is the goal of increased coverage eligibility and affordability?
An important goal of increased coverage eligibility and affordability is to increase access to adequate health care services for the poor. As a result, the ACA’s impact on access to high-quality health care has been evaluated across multiple dimensions, including access to a doctor, having a usual source of care, timeliness of care, affordability, and access to medications and preventive, primary, and specialty care.
Does the ACA expand Medicaid?
In summary, early evidence following ACA implementation has demonstrated significant progress toward its goal of expanding coverage for millions of low-income individuals who would have otherwise remained uninsured. Not all individuals equally experience the potential benefits of the law, however, and disparities have developed on the basis of state decisions regarding whether to expand Medicaid.
How does the Medicare law affect hospitals?
It also penalizes hospitals with too many readmissions of Medicare patients who have heart attacks , heart failure or pneumonia within 30 days of a hospital stay.
How much will Medicare be reduced?
The nonpartisan Congressional Budget Office estimated that Medicare spending would be reduced by $716 billion over 10 years, mainly because the law puts the brakes on annual increases in Medicare reimbursement for Medicare Advantage, hospital costs, home health services, hospices and skilled nursing services.
How many states have Medicare cut doctors?
The American Medical Association says that in at least 11 states, Medicare Advantage plans have cut thousands of physicians. Critics worry that more doctors may stop taking Medicare patients or that patients will face lengthy waits for appointments or other changes.
How much less will Medicare get in 2022?
Other cuts include $66 billion less for home health, $39 billion less for skilled nursing services and $17 billion less for hospice care — all by 2022. Medicare costs will still grow, just more slowly than they would without the ACA. But some experts predict that beneficiaries will feel ...
What is Medicare Advantage?
About three in 10 Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in Medicare Advantage options, which are premium insurance plans that often include dental, vision and drug insurance. These plans have been subsidized by the federal government for years. The ACA is simply aiming to equalize costs, according to its proponents.
Did Medicare change before the law?
Insurers changed Medicare Advantage plans before the law, and they're still changing them, he says. "Overall, seniors are not paying that much more, and more people are still enrolling in Medicare Advantage plans," says Gruber, who advised the Obama administration on the ACA.
Is the ACA good for Medicare?
But Henry J. Aaron of the Brookings Institution, a liberal think tank, insists that "the ACA is unalloyed good news" for Medicare beneficiaries because it improves the financial health of Medicare Part A, the hospital insurance program.
Why were people over 64 excluded from the ACA?
Individuals older than 64 years were excluded because the ACA was not intended to affect their health care coverage. Our sample starts in 2011 because this is the first year in which the BRFSS included cell phones in its sampling frame. A 2011-2016 sample period gives us 3 years of pretreatment data and 3 years of posttreatment data.
Why is BRFSS important?
The BRFSS is a commonly used data source in the ACA literature because it includes a number of questions related to health care access and self-assessed health. In addition, it is large enough to precisely estimate the effects of state policy interventions, with over 300 000 observations per year.
What is the BRFSS?
We use data from the BRFSS, an annual telephone survey organized by state health departments and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The survey collects information on various aspects of health care access and health for all 50 states and the District of Columbia. Having a large sample size is important for our study because the ACA affected health insurance coverage for only a fraction of the population, limiting plausible effect sizes. The BRFSS is the largest continuous health survey in the United States, collecting information on more than 300 000 adults per year.
How long did the Affordable Care Act last?
While the Affordable Care Act (ACA) increased insurance coverage and access to care after 1 (2014) or 2 (2014-2015) postreform years, the existing causally interpretable evidence suggests that effects on self-assessed health outcomes were not as clear after 2 years.
How many variables are used in the outcome of a health care study?
We utilize 9 outcome variables. The first 3 relate to access to care: indicators for any health insurance coverage, having a primary care doctor, and having any care needed but foregone because of cost in the past 12 months. The remaining outcomes relate to self-assessed health status. These include dummy variables for whether overall health is good or better (ie good, very good, or excellent), very good or excellent, and excellent, as well as days of the last 30 not in good mental health, not in good physical health, and with health-related functional limitations. Subjective self-assessed health variables such as these have been shown to be correlated with objective measures of health, including mortality.31-33
What effect did the third year of the health insurance policy have on the health insurance coverage?
We find that gains in health insurance coverage and access to care from the policy continued to increase, while an improvement in the probability of reporting excellent health emerged in the third year, with the effect being largely driven by the non-Medicaid expansions components of the policy .
Does the ACA affect mental health?
With respect to self-assessed health, we find that the ACA increased the probability of reporting excellent health and reduced days in poor mental health. In contrast, a recent article with only 2 posttreatment years found no evidence of gains in these outcomes despite also using BRFSS data and the same identification strategy.18The emergence of an impact on the probability of having excellent self-assessed health appears particularly gradual, as the effect of the full ACA was small and insignificant in 2014, 1.9 percentage points in 2015, and 2.7 percentage points in 2016. Improvements in self-assessed health at lower points of the distribution also emerge in 2016. Most of these gains appear to come from the non-Medicaid-expansion components of the law.
What would happen if Medicare spending increased?
The increase in Medicare spending would likely lead to higher Medicare premiums, deductibles, and cost sharing for beneficiaries, and accelerate the insolvency of the Medicare Part A trust fund. Policymakers will confront decisions about the Medicare provisions in the ACA in their efforts to repeal and replace the law.
What are the benefits of the ACA?
Medicare Benefit Improvements. The ACA included provisions to improve Medicare benefits by providing free coverage for some preventive benefits , such as screenings for breast and colorectal cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, and closing the coverage gap (or “doughnut hole”) in the Part D drug benefit by 2020.
How much will Medicare increase over 10 years?
Increase Part A and Part B spending. CBO has estimated that roughly $350 billion 3 of the total $802 billion in higher Medicare spending over 10 years could result from repealing ACA provisions that changed provider payment rates in traditional Medicare.
What is CMS in Medicare?
Through a new Center for Medicare & Medicaid Innovation (CMMI, or Innovation Center) within the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), the ACA directed CMS to test and implement new approaches for Medicare to pay doctors, hospitals, and other providers to bring about changes in how providers organize and deliver care. The ACA authorized the Secretary of Health and Human Services to expand CMMI models into Medicare if evaluation results showed that they either reduced spending without harming the quality of care or improved the quality of care without increasing spending. CMMI received an initial appropriation of $10 billion in 2010 for payment and delivery system reform model development and evaluation, and the ACA called for additional appropriations of $10 billion in each decade beginning in 2020.
How much will Medicare save in 2026?
Increase Medicare spending over time, in the absence of the Board’s cost-reducing actions. CBO projects Medicare savings of $8 billion as a result of the IPAB process between 2019 and 2026. 12
What would be expected from repealing the ACA?
Repealing the ACA’s Medicare benefit improvements would be expected to: Reduce Medicare Part B spending for preventive services and reduce Part D spending on costs in the coverage gap. Increase beneficiary cost sharing for Part B preventive benefits.
What is the ACA payment?
Payments to Health Care Providers. The ACA reduced updates in Medicare payment levels to hospitals, skilled nursing facilities, hospice and home health providers, and other health care providers. The ACA also reduced Medicare Disproportionate Share Hospital (DSH) payments that help to compensate hospitals for providing care to low-income ...
What happens if you don't enroll in Medicare at 65?
Even worse, if you fail to enroll in Medicare at age 65 because you choose to keep your Obamacare plan instead, you will later owe a Part B late enrollment penalty that will stay with you for as long as you remain enrolled in Medicare. It’s a 10% penalty per year for every year that you could have been enrolled in Medicare (at 65).
How long do you have to wait to cancel ACA?
Don’t be tempted to gamble with your health by cancelling your ACA plan early. If you have more than a 63-day window between when your ACA plan ends and your Medicare begins, then when you enroll in a Medigap plan, they can impose a waiting period for pre-existing conditions.
How much is the penalty for Medicare if you wait two years?
It’s a 10% penalty per year for every year that you could have been enrolled in Medicare (at 65). So if you waited two years, your would pay a 20% higher monthly premium for Part B for the rest of your life. This can be disappointing news if you’ve been getting your ACA plan very inexpensively due to a subsidy.
What happens if you miss your window to switch to Medicare?
If you miss your window to switch to Medicare, the federal government will catch up to you soon enough. When it finds that you should have moved to Medicare at age 65, it will assess you a fine to make you pay back any subsidy dollars that you have received toward your ACA coverage since you turn 65.
What is Medicare Supplement Plan G?
Coverage from Medicare and a Medicare Supplement Plan G would give you comprehensive benefits where you will pay nothing but the Part B deductible for Medicare-approved services and your monthly premiums.
Can you lose your Social Security if you are already on ACA?
Second, if you are already taking Social Security and you dis-enroll from Part A, you could forfeit your Social Security benefits. Finally, the ACA plans are quite expensive compared to Medicare when you can no longer take advantage of the subsidy that has been reducing the price. In many cases, paying for Medicare Part A can still provide you ...
Does ACA cover Medicare?
Your ACA coverage was never meant to replace Medicare. If you do not sign up for Medicare during your Initial Enrollment Period, you will be subject to substantial penalties when you later enroll in Medicare.
What is Medicare Advantage?
Medicare Advantage, also called Part C, is another way to get your Original Medicare (Part A and Part B) benefits through a private insurance company approved by Medicare. Medicare Advantage plans got their name in 2003 with the passage of the Medicare Modernization Act (MMA).
How many people will be enrolled in Medicare Advantage in 2020?
Since 2014, Medicare Advantage enrollments have increased, while premiums have decreased. In 2020, about 39% of Medicare beneficiaries (24.4 million) were enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans, according to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). This is a marked increase since 2009, pre-Obamacare, when Medicare Advantage enrollment was about 23% of Medicare beneficiaries (10.5 million) according to the Kaiser Family Foundation.
How long do you have to enroll in Medicare Advantage?
You can enroll in Medicare Advantage during your 7-month Medicare Initial Enrollment Period. This enrollment period: 1 Begins three months before you turn 65 2 Includes the month of your 65th birthday 3 Lasts for three months after your turn 65.
How much is the average health insurance premium in 2020?
The average premium overall (all ages) for a health insurance plan under the Affordable Care Act was $484 in 2020, eHealth reported. The average Medicare Advantage premium in an eHealth survey was $5 per month.
How to contact Medicare by phone?
You can enter your zip code on this page to get started. Call Medicare at 1-800-MEDICARE (1-800-633-4227) . TTY users should call 1-877-486-2048. Medicare representatives are available 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
When does Medicare disability end?
Includes the 25th month of getting disability benefits. Ends three months after your 25th month of getting disability benefits. Learn about the other time periods when you may be able to sign up for a Medicare Advantage plan.
Is Medicare Advantage still affordable?
Medicare Advantage plans may still be affordable despite Obamacare cuts. According to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), the estimated average premium for a Medicare Advantage plan is $21 a month in 2021. In fact, Medicare Advantage premiums have been going down year by year, CMS reports.
When does Medicare coverage take effect?
If you complete the enrollment process during the three months prior to your 65th birthday, your Medicare coverage takes effect the first of the month you turn 65 ( unless your birthday is the first of the month ). Your premium subsidy eligibility continues through the last day of the month prior to the month you turn 65.
What happens if you don't sign up for Medicare?
And if you keep your individual market exchange plan and don’t sign up for Medicare when you first become eligible, you’ll have to pay higher Medicare Part B premiums for the rest of your life, once you do enroll in Medicare, due to the late enrollment penalty.
How long does it take to get Medicare if you are not receiving Social Security?
If you’re not yet receiving Social Security or Railroad Retirement benefits, you’ll have a seven-month window during which you can enroll in Medicare, which you’ll do through the Social Security Administration. Your Medicare card will be sent to you after you enroll. Your enrollment window starts three months before the month you turn 65, ...
When does Medicare subsidy end?
The short story is that if you enroll in Medicare during the first four months of your initial enrollment window, your transition to Medicare will be seamless, with subsidy eligibility continuing through the last day of the month prior to the month that your Medicare coverage begins. If you enroll in Medicare during the final three months of your initial enrollment period, your premium subsidy will likely end before your Part B coverage begins, although your Part A coverage should be backdated to the month you turned 65. And if you don’t enroll in Medicare at all during your initial enrollment window, your premium subsidies will end a few months after you turn 65. Here are the details:
When will Medicare be enrolled in Social Security?
Here are the details: If you’re already receiving retirement benefits from Social Security or the Railroad Retirement Board, you’ll automatically be enrolled in Medicare with an effective date of the first of the month that you turn 65. As is the case for people who enroll prior to the month they turn 65, premium subsidy eligibility ends on ...
When will Medicare be sent to you?
Your Medicare card will be sent to you after you enroll. Your enrollment window starts three months before the month you turn 65, includes the month you turn 65, and then continues for another three months. (Note that you’ll need to enroll during the months prior to your birth month in order to have coverage that takes effect the month you turn 65.
When will Medicare be sent out to my 65 year old?
If you’re already receiving Social Security or Railroad Retirement benefits, the government will automatically enroll you in Medicare Part A the month you turn 65, with your Medicare card arriving in the mail about three months before you turn 65. If you’re not yet receiving Social Security or Railroad Retirement benefits, ...