The Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 1 institutes three key changes to Medicare Part D’s “donut hole” (Coverage Gap) for applicable beneficiaries, 2 effective January 1, 2019: 1. Closes the coverage gap one year early for applicable drugs, 3 reducing standard beneficiary cost sharing in that phase from 30% to 25%
Full Answer
How much will Medicare spending increase between 2018 and 2028?
Between 2018 and 2028, net Medicare spending is also projected to grow as a share of the federal budget—from 14.1 percent to 17.9 percent—and the nation’s economy—from 2.9 percent to 4.2 percent of gross domestic product (GDP).
What does the FY 2018 budget mean for Medicare?
The FY 2018 Budget reflects the President’s commitment to preserve Medicare and does not include direct Medicare cuts. The Budget repeals the Independent Payment Advisory Board, commits to improving the Medicare appeals process, and supports efforts to limit defensive medicine as a part of a larger medical liability reform effort.
Will Medicare be cuts in 2018?
Medicare Spared From Budget Cuts in 2018. But this program and others essential to seniors still face threat of cuts. AARP supports responsible solutions to reduce health care spending without shifting costs onto Medicare beneficiaries or reducing their access to care.
How does the budget affect the Medicare appeals process?
The Budget repeals the Independent Payment Advisory Board, commits to improving the Medicare appeals process, and supports efforts to limit defensive medicine as a part of a larger medical liability reform effort. The Budget includes the following proposals to reform the Medicare appeals process.
What will Medicare cost in 2018?
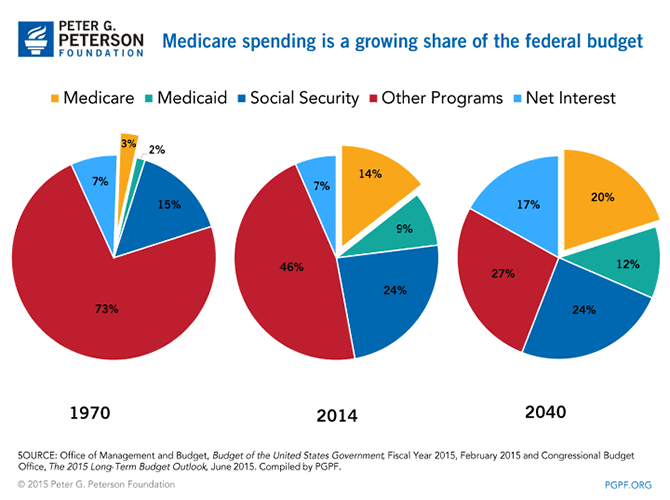
In 2018, Medicare spending (net of income from premiums and other offsetting receipts) totaled $605 billion, accounting for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1).
Did Medicare premiums go down?
Seniors could see a cut in their monthly Medicare Part B premiums for 2022 after a controversial new drug's price was slashed. In November, Medicare set the monthly Part B premium at $170.10 for this year, a more than 14% increase from 2021.
Did Medicare premiums go up?
The basic monthly premium will jump 15.5 percent, or $21.60, from $148.50 to $170.10 a month. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) announced the premium and other Medicare cost increases on November 12, 2021.
What are the big changes to Medicare?
The biggest change Medicare's nearly 64 million beneficiaries will see in the new year is higher premiums and deductibles for the medical care they'll receive under the federal government's health care insurance program for individuals age 65 and older and people with disabilities.
Are they going to reduce Medicare premiums in 2022?
About half of the larger-than-expected 2022 premium increase, set last fall, was attributed to the potential cost of covering the Alzheimer's drug Aduhelm.
Is Medicare Part B being reduced?
Medicare's Part B $170.10 basic monthly premium will not be reduced this year, but instead any savings from lower spending will be passed on to beneficiaries in 2023.
Why has Medicare become more expensive in recent years?
Americans spend a huge amount on healthcare every year, and the cost keeps rising. In part, this increase is due to government policy and the inception of national programs like Medicare and Medicaid. There are also short-term factors, such as the 2020 financial crisis, that push up the cost of health insurance.
What will the Medicare Part B premium be in 2022?
$170.10In November 2021, CMS announced that the Part B standard monthly premium increased from $148.50 in 2021 to $170.10 in 2022. This increase was driven in part by the statutory requirement to prepare for potential expenses, such as spending trends driven by COVID-19 and uncertain pricing and utilization of Aduhelm™.
Are Medicare Part B premiums going up in 2021?
In November 2021, CMS announced the monthly Medicare Part B premium would rise from $148.50 in 2021 to $170.10 in 2022, a 14.5% ($21.60) increase.
What are the changes to Medicare in 2021?
The Medicare Part B premium is $148.50 per month in 2021, an increase of $3.90 since 2020. The Part B deductible also increased by $5 to $203 in 2021. Medicare Advantage premiums are expected to drop by 11% this year, while beneficiaries now have access to more plan choices than in previous years.
How are Medicare benefits changing for 2022?
Key takeaways. The standard Part B premium is $170.10 for 2022 (largest increase in program history, but Social Security COLA also historically large). The Part B deductible is $233 in 2022 (up from $203 in 2021). Part A premiums, deductible, and coinsurance are also higher for 2022.
What changes are coming to Medicare in 2022?
Changes to Medicare in 2022 include a historic rise in premiums, as well as expanded access to mental health services through telehealth and more affordable options for insulin through prescription drug plans. The average cost of Medicare Advantage plans dropped while access to plans grew.
What percentage of Medicare beneficiaries are covered by Part B?
Part B coverage is voluntary, and about 91 percent of all Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in Part B. Approximately 25 percent of Part B costs are financed by beneficiary premiums, with the remaining 75 percent covered by general revenues.
How much is Medicare Part D deductible?
Medicare Part D offers a standard prescription drug benefit with a 2017 deductible of $400 and an average estimated monthly premium of $35.
How many people are on Medicare Advantage in 2018?
In 2018, Medicare Advantage enrollment will total approximately 20.8 million, or approximately 38 percent of all Medicare beneficiaries. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) data confirm that 99 percent of Medicare beneficiaries will have access to at least one Medicare Advantage plan in 2018.
What is the mission of Quality Improvement Organization?
The mission of the Quality Improvement Organization Program is to improve the effectiveness, efficiency, economy, and quality of services delivered to Medicare beneficiaries. The Organizations are experts in the field working to drive local change, which can translate into national quality improvement.
How much is Medicare Part C?
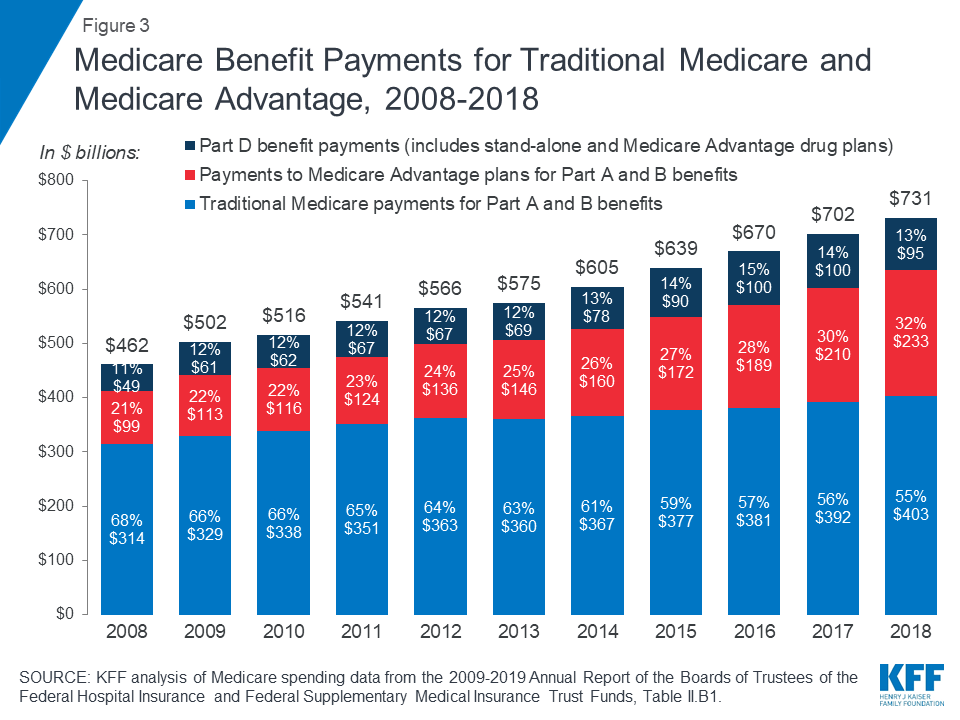
Part C ($203.0 billion gross spending in 2018) Medicare Part C, the Medicare Advantage Program, pays plans a capitated monthly payment to provide all Part A and B services, and Part D services if offered by the plan.
What is the FY 2018 budget?
The FY 2018 Budget reflects the President’s commitment to preserve Medicare and does not include direct Medicare cuts. The Budget repeals the Independent Payment Advisory Board, commits to improving the Medicare appeals process, and supports efforts to limit defensive medicine as a part of a larger medical liability reform effort.
What is Medicare Part A?
Medicare Part A pays for inpatient hospital, skilled nursing facility, home health related to a hospital stay, and hospice care. Part A financing comes primarily from a 2.9 percent payroll tax paid by both employees and employers.
What changes will be detrimental to Medicare?
To offset the costs of some of the above provisions, Congress chose certain changes that will be detrimental to the Medicare program and the health and financial security of older Americans and their families. These include: Increase Medicare Premiums for Higher-Income Beneficiaries— Beginning in 2019, the Part.
When was the Medicare budget passed?
February 22, 2018 By Karen Fletcher. In early February, Congress passed the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 which includes several changes to the Medicare program and to other health programs affecting older adults, people with disabilities and families with low incomes.
When will Medicare reduce home health payment?
The home health payment episode will be reduced from 60 days to 30 days and therapy thresholds will be eliminated. Beginning in 2019, Medicare will be allowed to base eligibility determinations for home. health services on a review of the patient’s medical record including a home health agency’s record beginning in 2019.
When did the Medicare Part D coverage gap end?
The law permanently repeals the payment cap on outpatient physical, occupational, and speech therapies effective January 1, 2018, and makes changes to the medical necessity review process for these services. The law closes the Medicare Part D “donut hole” or coverage gap faster.
When will Medicare start paying for speech generating devices?
The law changes how Medicare will pay for home health services beginning in 2020.
When will the Medicare donut hole close?
The law closes the Medicare Part D “donut hole” or coverage gap faster. Instead of in 2020, the donut hole will now close in 2019 at which time beneficiaries will be required to contribute 25% to the cost of prescription drugs. This provision does not affect coverage for beneficiaries who receive the Part D low-income subsidy known as “Extra Help,” ...
What is the CMS?
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services ensures availability of effective, up-to-date health care coverage and promotes quality care for beneficiaries. The Fiscal Year (FY) 2018 Budget estimate for the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is $1 trillion in mandatory and discretionary outlays, a net increase ...
How does CMS work?
CMS is dedicated to moving toward a health care system that will drive down costs, give Americans more choices, and put patients and doctors in control of their health care. To achieve this, CMS will empower patients and doctors to make decisions about their health care while reducing burdensome regulations and building a patient-centered system of care that increases competition, quality, and access. CMS will usher in a new era of state flexibility and local leadership. Because the States are in the best position to assess the unique needs of their populations and drive reforms, this shift will result in better health care outcomes.
Does CMS include Medicare cuts?
Medicare. The Budget does not include any direct Medicare cuts.
How long is the Children's Health Insurance Program?
Extends the Children’s Health Insurance Program. The bill also includes a four-year extension of the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), from 2024 through 2027. This is on top of a six-year extension that Congress approved last month as part of a broader continuing resolution to fund the federal government. CHIP provides affordable health coverage for over 9 million children and gives working families—many of which include people with Medicare—much-needed health and economic security.
What is the BBA of 2018?
The BBA of 2018 includes all provisions of the bipartisan Creating High-Quality Results and Outcomes Necessary to Improve Chronic (CHRONIC) Care Act (S. 870) . Introduced by leaders of the Senate Committee on Finance—Chairman Orrin Hatch (R–UT) and Ranking Member Ron Wyden (D–OR)—the CHRONIC Care Act unanimously passed the Senate in 2017. A key focus of the Act is on improving and expanding services and coverage in Medicare Advantage (MA) for beneficiaries with complex medical conditions.
What is the budget deal for FY19?
The budget deal raises the limits on defense and non-defense appropriations in Fiscal Years 2018 (FY18) and 2019 (FY19) that were set by the 2011 Budget Control Act and subsequently reduced further by the sequestration process. The agreement follows three bipartisan deals of recent years raising those caps, each of which reflected the reality that post-sequestration appropriations caps were simply too low to meet national needs. This agreement provides the largest increase in the series, raising the non-defense cap by $63 billion in FY18 and $68 billion in FY19. While this relief is welcome, it’s notable that even with this boost, overall funding for non-defense appropriations—which support key aging and health priorities outside of Medicare—will remain below 2010 levels after adjusting for inflation.
When will the government raise its borrowing caps?
The legislation—the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 (P.L. 115-123, BBA of 2018)—also suspends the government’s cap on borrowing through March 2019, and contains a number of health care provisions important to people with Medicare and their families.
Is Medicare Rights Center included in the Medicare package?
Several of the Medicare Rights Center’s priorities were not included in the package. We will continue to support these changes and advocate in particular for the inclusion of the BENES Act in the March 23 spending bill:
Is Medicare Rights Center engaged with lawmakers?
Accordingly, the Medicare Rights Center will stay engaged with lawmakers and the administration to ensure these policies are implemented in a way that prioritizes older adults and people with disabilities.
How much money does the Australian government invest in sport?
To better support the health and wellbeing of Australians, the Government will also invest $230 million to implement a range of sport and physical activity initiatives that will see more Australians, more active, more often. In particular, the Government will invest $28.9 million in participation grants targeted at less active Australians.
How much money is needed to make a digital baby book?
And to help parents keep track of their children’s health from birth, the Government will also introduce a national digital baby book with $5.0 million of funding, replacing state and territory hard copy baby books, and giving children their passport to a lifelong health record.
How much is the Pregnancy Health Program?
Health professionals will give parents-to-be simple and effective guidance on staying healthy during pregnancy with a $3.0 million program. The Government will also extend the childhood immunisation education campaign, targeting areas with low vaccination rates.
How much is the Indigenous Health Budget?
Better targeting support to improve Indigenous health. The Budget provides funding for Indigenous Health of $3.9 billion from 2018-19 to 2021-22 and $10 billion over a decade. In particular, the Government will deliver $33.4 million for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander health workforce, and provide funding to prevent and treat complex ...
How much money will the government give to clinical trials?
Recognising that clinical trials offer the hope of better diagnosis, treatment and ultimately, the Government will also inject $248 million to support clinical trial activity through the highly successful rare cancer, rare diseases and unmet need clinical trials and registries program.
How much is the Australian genomics plan?
According to Hunt, the centrepiece of the Plan is a $500 million Australian Genomics Health Futures Mission which will help more than 200,000 Australians live longer and receive better treatment tailored to their medical needs.
How much is the Mental Health Fund in Australia?
Supporting better mental health for all Australians. Mental health funding will receive an additional $338.1 million, with a focus on suicide prevention, research and older Australians and advancing the Fifth National Mental Health and Suicide Prevention Plan.
How much will Medicare per capita increase in 2028?
Medicare per capita spending is projected to grow at an average annual rate of 5.1 percent over the next 10 years (2018 to 2028), due to growing Medicare enrollment, increased use of services and intensity of care, and rising health care prices.
What has changed in Medicare spending in the past 10 years?
Another notable change in Medicare spending in the past 10 years is the increase in payments to Medicare Advantage plans , which are private health plans that cover all Part A and Part B benefits, and typically also Part D benefits.
How is Medicare Part D funded?
Part D is financed by general revenues (71 percent), beneficiary premiums (17 percent), and state payments for beneficiaries dually eligible for Medicare and Medicaid (12 percent). Higher-income enrollees pay a larger share of the cost of Part D coverage, as they do for Part B.
How fast will Medicare spending grow?
On a per capita basis, Medicare spending is also projected to grow at a faster rate between 2018 and 2028 (5.1 percent) than between 2010 and 2018 (1.7 percent), and slightly faster than the average annual growth in per capita private health insurance spending over the next 10 years (4.6 percent).
How much does Medicare cost?
In 2018, Medicare spending (net of income from premiums and other offsetting receipts) totaled $605 billion, accounting for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1).
Why is Medicare spending so high?
Over the longer term (that is, beyond the next 10 years), both CBO and OACT expect Medicare spending to rise more rapidly than GDP due to a number of factors, including the aging of the population and faster growth in health care costs than growth in the economy on a per capita basis.
How is Medicare's solvency measured?
The solvency of Medicare in this context is measured by the level of assets in the Part A trust fund. In years when annual income to the trust fund exceeds benefits spending, the asset level increases, and when annual spending exceeds income, the asset level decreases.
