
How is Medicare funded?
How is Medicare funded? The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is the federal agency that runs the Medicare Program. CMS is a branch of the
How much will Medicare spending increase between 2018 and 2028?
Between 2018 and 2028, net Medicare spending is also projected to grow as a share of the federal budget—from 14.1 percent to 17.9 percent—and the nation’s economy—from 2.9 percent to 4.2 percent of gross domestic product (GDP).
What does the FY 2018 budget mean for Medicare?
The FY 2018 Budget reflects the President’s commitment to preserve Medicare and does not include direct Medicare cuts. The Budget repeals the Independent Payment Advisory Board, commits to improving the Medicare appeals process, and supports efforts to limit defensive medicine as a part of a larger medical liability reform effort.
How much does the government spend on Medicare each year?
In Fiscal Year (FY) 2018, the Office of the Actuary has estimated that gross current law spending on Medicare benefits will total $704.6 billion. Medicare will provide health insurance to 60 million individuals who are age 65 or older, disabled, or have end-stage renal disease.
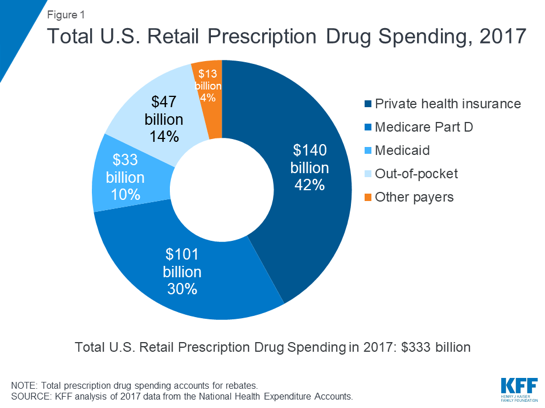
What is the funding source of Medicare?
Funding for Medicare comes primarily from general revenues, payroll tax revenues, and premiums paid by beneficiaries (Figure 1). Other sources include taxes on Social Security benefits, payments from states, and interest.
Is Medicare funded by taxpayers?
Medicare is federally administered and covers older or disabled Americans, while Medicaid operates at the state level and covers low-income families and some single adults. Funding for Medicare is done through payroll taxes and premiums paid by recipients. Medicaid is funded by the federal government and each state.
How did the government fund Medicare?
Hospital Insurance (HI) Trust Fund Income taxes paid on Social Security benefits. Interest earned on the trust fund investments. Medicare Part A premiums from people who aren't eligible for premium-free Part A.
Is Medicare federally funded or state funded?
Medicare is a federal program. It is basically the same everywhere in the United States and is run by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, an agency of the federal government.
What happens when Medicare runs out of money?
It will have money to pay for health care. Instead, it is projected to become insolvent. Insolvency means that Medicare may not have the funds to pay 100% of its expenses. Insolvency can sometimes lead to bankruptcy, but in the case of Medicare, Congress is likely to intervene and acquire the necessary funding.
Is Medicare underfunded?
Politicians promised you benefits, but never funded them.
How much is Medicare in debt?
Medicare accounts for a significant portion of federal spending. In fiscal year 2020, the Medicare program cost $776 billion — about 12 percent of total federal government spending. Medicare was the second largest program in the federal budget last year, after Social Security.
Does Medicare run a deficit?
Last year, the Medicare Part A fund ran a deficit of $5.8 billion, and that excess of spending over revenue is expected to continue until it finally runs dry.
How much of our taxes go to healthcare?
How much does the federal government spend on health care? The federal government spent nearly $1.2 trillion in fiscal year 2019. In addition, income tax expenditures for health care totaled $234 billion. The federal government spent nearly $1.2 trillion on health care in fiscal year 2019 (table 1).
Who controls Medicare premiums?
The State of California participates in a buy-in agreement with the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), whereby Medi-Cal automatically pays Medicare Part B premiums for all Medi-Cal beneficiaries who have Medicare Part B entitlement as reported by Social Security Administration (SSA).
Is Medicare state or federal?
federalMedicare is the federal health insurance program for: People who are 65 or older. Certain younger people with disabilities. People with End-Stage Renal Disease (permanent kidney failure requiring dialysis or a transplant, sometimes called ESRD)
How many people did Medicare cover in 2017?
programs offered by each state. In 2017, Medicare covered over 58 million people. Total expenditures in 2017 were $705.9 billion. This money comes from the Medicare Trust Funds.
What is Medicare Part B?
Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) Part B covers certain doctors' services, outpatient care, medical supplies, and preventive services. and. Medicare Drug Coverage (Part D) Optional benefits for prescription drugs available to all people with Medicare for an additional charge.
What is the CMS?
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services ( CMS) is the federal agency that runs the Medicare Program. CMS is a branch of the. Department Of Health And Human Services (Hhs) The federal agency that oversees CMS, which administers programs for protecting the health of all Americans, including Medicare, the Marketplace, Medicaid, ...
What is SNF in nursing?
Skilled nursing care and rehabilitation services provided on a daily basis, in a skilled nursing facility (SNF). Examples of SNF care include physical therapy or intravenous injections that can only be given by a registered nurse or doctor. , home health care.
What is covered by Part A?
Part A covers inpatient hospital stays, care in a skilled nursing facility, hospice care, and some home health care. The health care items or services covered under a health insurance plan. Covered benefits and excluded services are defined in the health insurance plan's coverage documents.
Does Medicare cover home health?
Medicare only covers home health care on a limited basis as ordered by your doctor. , and. hospice. A special way of caring for people who are terminally ill. Hospice care involves a team-oriented approach that addresses the medical, physical, social, emotional, and spiritual needs of the patient.
How many people are on Medicare Advantage in 2018?
In 2018, Medicare Advantage enrollment will total approximately 20.8 million, or approximately 38 percent of all Medicare beneficiaries. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) data confirm that 99 percent of Medicare beneficiaries will have access to at least one Medicare Advantage plan in 2018.
What is the FY 2018 budget?
The FY 2018 Budget reflects the President’s commitment to preserve Medicare and does not include direct Medicare cuts. The Budget repeals the Independent Payment Advisory Board, commits to improving the Medicare appeals process, and supports efforts to limit defensive medicine as a part of a larger medical liability reform effort.
What percentage of Medicare beneficiaries are covered by Part B?
Part B coverage is voluntary, and about 91 percent of all Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in Part B. Approximately 25 percent of Part B costs are financed by beneficiary premiums, with the remaining 75 percent covered by general revenues.
How much is Medicare Part D deductible?
Medicare Part D offers a standard prescription drug benefit with a 2017 deductible of $400 and an average estimated monthly premium of $35.
What is the Medicare Part D coverage gap?
The Medicare Part D coverage gap, or “donut hole, ” is being closed through a combination of manufacturer discounts and gradually increasing Federal subsidies. Beneficiaries fall into the coverage gap once their total drug spending exceeds an initial coverage limit ($3,700 in 2017), until they reach the threshold for qualified out-of-pocket spending ($4,950 in 2017), at which point they are generally responsible for five percent of their drug costs. Previously beneficiaries were responsible for 100 percent of their drug costs in the coverage gap. In 2018, non-low income subsidy beneficiaries who reach the coverage gap will pay 35 percent of the cost of covered Part D brand drugs and biologics and 44 percent of the costs for all generic drugs in the coverage gap. Cost-sharing in the coverage gap will continue to decrease each year until beneficiaries are required to pay only 25 percent of the costs of covered Part D drugs in 2020 and beyond.
How much is Medicare Part C?
Part C ($203.0 billion gross spending in 2018) Medicare Part C, the Medicare Advantage Program, pays plans a capitated monthly payment to provide all Part A and B services, and Part D services if offered by the plan.
What is the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services?
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services ensure s availability of effective, up-to-date health care coverage and promotes quality care for beneficiaries.
How much did Medicare increase in 2018?
As a share of total Medicare benefit spending, payments to Medicare Advantage plans for Part A and Part B benefits increased by nearly 50 percent between 2008 and 2018, from 21 percent ($99 billion) to 32 percent ($232 billion) of total spending, as enrollment in Medicare Advantage plans increased over these years.
How much does Medicare cost?
In 2018, Medicare spending (net of income from premiums and other offsetting receipts) totaled $605 billion, accounting for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1).
Why is Medicare spending so slow?
Slower growth in Medicare spending in recent years can be attributed in part to policy changes adopted as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Budget Control Act of 2011 (BCA). The ACA included reductions in Medicare payments to plans and providers, increased revenues, and introduced delivery system reforms that aimed to improve efficiency and quality of patient care and reduce costs, including accountable care organizations (ACOs), medical homes, bundled payments, and value-based purchasing initiatives. The BCA lowered Medicare spending through sequestration that reduced payments to providers and plans by 2 percent beginning in 2013.
What is the average annual growth rate for Medicare?
Average annual growth in total Medicare spending is projected to be higher between 2018 and 2028 than between 2010 and 2018 (7.9 percent versus 4.4 percent) (Figure 4).
What has changed in Medicare spending in the past 10 years?
Another notable change in Medicare spending in the past 10 years is the increase in payments to Medicare Advantage plans , which are private health plans that cover all Part A and Part B benefits, and typically also Part D benefits.
What is excess health care cost?
Over the next 30 years, CBO projects that “excess” health care cost growth—defined as the extent to which the growth of health care costs per beneficiary, adjusted for demographic changes, exceeds the per person growth of potential GDP (the maximum sustainable output of the economy)—will account for half of the increase in spending on the nation’s major health care programs (Medicare, Medicaid, and subsidies for ACA Marketplace coverage), and the aging of the population will account for the other half.
What percentage of Medicare is spending?
Key Facts. Medicare spending was 15 percent of total federal spending in 2018, and is projected to rise to 18 percent by 2029. Based on the latest projections in the 2019 Medicare Trustees report, the Medicare Hospital Insurance (Part A) trust fund is projected to be depleted in 2026, the same as the 2018 projection.
How much will Social Security increase in 2018?
After several years of no or very small increases, Social Security benefits will increase by 2.0 percent in 2018 due to the Cost of Living adjustment.
What is Medicare Part A?
Medicare Part A Premiums/Deductibles. Medicare Part A covers inpatient hospital, skilled nursing facility, and some home health care services. About 99 percent of Medicare beneficiaries do not have a Part A premium since they have at least 40 quarters of Medicare-covered employment. The Medicare Part A annual inpatient hospital deductible ...
What is the deductible for Medicare Part B?
The annual deductible for all Medicare Part B beneficiaries will be $183 in 2018, the same annual deductible in 2017. Premiums and deductibles for Medicare Advantage and Medicare Prescription Drug plans are already finalized and are unaffected by this announcement. Since 2007, beneficiaries with higher incomes have paid higher Medicare Part B ...
What is the Medicare Part B premium?
Medicare Part B Premiums/Deductibles. Medicare Part B covers physician services, outpatient hospital services, certain home health services, durable medical equipment, and other items. The standard monthly premium for Medicare Part B enrollees will be $134 for 2018, the same amount as in 2017.
How much is the Part B premium in 2018?
The 30 percent of all Part B enrollees who are not subject to the “hold harmless” provision will pay the full premium of $134 per month in 2018. Part B enrollees who were held harmless in 2016 ...
How much is Medicare Part A deductible?
The Medicare Part A annual inpatient hospital deductible that beneficiaries pay when admitted to the hospital will be $1,340 per benefit period in 2018, an increase of $24 from $1,316 in 2017. The Part A deductible covers beneficiaries’ share of costs for the first 60 days of Medicare-covered inpatient hospital care in a benefit period.
When did Medicare Part A and B premiums come out?
2018 Medicare Parts A & B Premiums and Deductibles. On November 17, 2017 , the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) released the 2018 premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance amounts for the Medicare Part A and Part B programs.
When will Medicare Part B and Part D premiums increase?
To offset some of the changes brought on by the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018, Medicare Part B and Part D premiums will increase in 2019 for high-income beneficiaries.
When will the Medicare donut hole close?
The Medicare Part D “ donut hole ” will close completely for brand-name drugs in 2019, one year earlier than originally scheduled. The donut hole, which represents a temporary coverage gap of prescription medications, will also get smaller for generic drugs in 2019 before disappearing in 2020.
What is a two year extension for Medicare?
A two-year funding extension was granted to community-based organizations to conduct outreach and enrollment for low-income Medicare beneficiaries. These organizations include State Health Insurance Assistance Programs (SHIPs), Area Agencies on Aging, Aging and Disability Resource Centers and the National Center for Benefits and Outreach Enrollment.
How long is home health coverage?
The number of days required for coverage of home health care services was reduced from 60 days to 30, and associated therapy thresholds have been eliminated. In addition, the Medicare Independence at Home Demonstration was extended by two years.
What is the bipartisan budget act?
While structured mainly around government spending and the federal budget, the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 included several items that directly affect Medicare.
Is speech therapy covered by Medicare?
The Medicare Part B payment limit on outpatient physical, occupational and speech therapy is now permanently lifted. Speech generating devices are now categorized as durable medical equipment, which makes them more commonly covered by Medicare for qualified beneficiaries.
How many people are on medicaid in 2018?
In Fiscal Year (FY) 2016, more than one in five individuals were enrolled in Medicaid for at least one month during the year, and in FY 2018, over 76 million people on average will receive health care coverage through Medicaid under current law.
What is the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services?
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services ensure s availability of effective, up-to-date health care coverage and promotes quality care for beneficiaries.
What is CMS Administrator Verma's letter to the governors?
On March 14, 2017, Secretary Price and CMS Administrator Verma sent a letter to all 50 State governors committing to “…usher in a new era for the federal and state Medicaid partnership” and to “… empower all States to advance the next wave of innovative solutions to Medicaid’s challenges.” The Administration also supports legislation to build on the tools provided within existing authorities to further expand State flexibility in how they spend their Medicaid dollars. The letter notes several key areas of focus for the Administration:
What is Medicaid 1/?
1/ Includes outlays from the Vaccines for Children Program, administered by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2/ Totals may not add due to rounding. Medicaid is the primary source of medical assistance for millions of low-income and disabled Americans, providing health coverage to many of those who would otherwise be unable ...
How much is Medicaid spending in 2027?
Without reforms, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Office of the Actuary estimates total Federal and State Medicaid spending will be nearly $1.1 trillion by FY 2027, comprising 3.5 percent of the Nation’s gross domestic ...
What does HHS do with DPC?
Working with States and primary care physicians, HHS will support the development of DPC practices, identify barriers to their entry into Medicaid, and outline flexibilities under existing authorities to facilitate these innovative approaches to strengthening the relationships between patients and physicians.
How does medicaid work?
Although the Federal Government establishes general guidelines for the program, States design, implement, and administer their own Medicaid programs. The Federal Government matches State expenditures on medical assistance based on the Federal Medical Assistance Percentage, which can be no lower than 50 percent. ...
How much did Medicare spend?
Medicare spending increased 6.4% to $750.2 billion, which is 21% of the total national health expenditure. The rise in Medicaid spending was 3% to $597.4 billion, which equates to 16% of total national health expenditure.
What percentage of Medicare is paid to MA?
Based on a federal annual report, KFF performed an analysis to reveal the proportion of expenditure for Original Medicare, Medicare Advantage (MA) and Part D (drug coverage) from 2008 to 2018. A graphic depiction on the KFF website illustrates the change in spending of Medicare options. Part D benefit payments, which include stand-alone and MA drug plans, grew from 11% to 13% of total expenditure. Payments to MA plans for parts A and B went from 21% to 32%. During the same time period, the percentage of traditional Medicare payments decreased from 68% to 55%.
What is the agency that administers Medicare?
To grasp the magnitude of the government expenditure for Medicare benefits, following are 2018 statistics from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), which is the agency that administers Medicare:
What is the largest share of health spending?
The biggest share of total health spending was sponsored by the federal government (28.3%) and households (28.4%) while state and local governments accounted for 16.5%. For 2018 to 2027, the average yearly spending growth in Medicare (7.4%) is projected to exceed that of Medicaid and private health insurance.
Is Medicare a concern?
With the aging population, there is concern about Medicare costs. Then again, the cost of healthcare for the uninsured is a prime topic for discussion as well.
Does Medicare pay payroll taxes?
Additionally, Medicare recipients have seen their share of payroll taxes for Medicare deducted from their paychecks throughout their working years.
How much did Medicare spend in 2017?
Total Medicare expenditures were $710 billion in 2017. The Board projects that expenditures will increase in future years at a faster pace than either aggregate workers’ earnings or the economy overall and that, as a percentage of GDP, they will increase from 3.7 percent in 2017 to 6.2 percent by 2092 (based on the Trustees’ intermediate set of assumptions). If the relatively low price increases for physicians and other health services under Medicare are not sustained and do not take full effect in the long range as in the illustrative alternative projection, then Medicare spending would instead represent roughly 8.9 percent of GDP in 2092. Growth under any of these scenarios, if realized, would substantially increase the strain on the nation’s workers, the economy, Medicare beneficiaries, and the Federal budget. The Trustees project that HI tax income and other dedicated revenues will fall short of HI expenditures in all future years. The HI trust fund does not meet either the Trustees’ test of short-range financial adequacy or their test of long-range close actuarial balance. The Part B and Part D accounts in the SMI trust fund are expected to be adequately financed because premium income and general revenue income are reset each year to cover expected costs. Such financing, however, would have to increase faster than the economy to cover expected expenditure growth. The financial projections in this report indicate a need for substantial steps to address Medicare’s remaining financial challenges.
What is Medicare Part A?
HI, otherwise known as Medicare Part A, helps pay for hospital, home health services following hospital stays, skilled nursing facility, and hospice care for the aged and disabled. SMI consists of Medicare Part B and Part D. Part B helps pay for physician, outpatient hospital, home health, and other services for the aged and disabled who have voluntarily enrolled. Part D provides subsidized access to drug insurance coverage on a voluntary basis for all beneficiaries and premium and cost-sharing subsidies for low-income enrollees. Medicare also has a Part C, which serves as an alternative to traditional Part A and Part B coverage. Under this option, beneficiaries can choose to enroll in and receive care from private Medicare Advantage and certain other health insurance plans. Medicare Advantage and Program of All-Inclusive Care for the Elderly (PACE) plans receive prospective, capitated payments for such beneficiaries from the HI and SMI Part B trust fund accounts; the other plans are paid from the accounts on the basis of their costs. The Social Security Act established the Medicare Board of Trustees to oversee the financial operations of the HI and SMI trust funds.
What will affect Medicare future expenditures?
Future Medicare expenditures will depend on a number of factors, including the size and composition of the population eligible for benefits, changes in the volume and intensity of services, and increases in the price per service. Future HI trust fund income will depend on the size of the covered work force and the level of workers’ earnings, and future SMI trust fund income will depend on projected program costs. These factors will depend in turn upon future birth rates, death rates, labor force participation rates, wage increases, and many other economic and demographic factors affecting Medicare. To illustrate the uncertainty and sensitivity inherent in estimates of future Medicare trust fund operations, the Board has prepared current-law projections under a low-cost and a high-cost set of economic and demographic assumptions as well as under an intermediate set. In addition, the Trustees asked the CMS Office of the Actuary to develop the illustrative alternative projections to demonstrate the potential effect on the Medicare financial status if certain current-law features are not fully implemented in the future. Table II.C1 summarizes the key assumptions used in this report. Many of the demographic and economic variables that determine Medicare costs and income are common to the Old-Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance (OASDI) program, and the OASDI annual report explains these variables in detail. These variables include changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and wages, real interest rates, fertility rates, mortality rates, and net immigration levels. (Realindicates that the effects of inflation have been removed.) The assumptions vary, in most cases, from year to year during the first 5 to 25 years before reaching the ultimate values7assumed for the remainder of the 75-year projection period.
What is the cost of Medicare in 2042?
MACRA45and ACA cost-reduction measures prove problematic and new legislation scales them back. As figure I.1 shows, Medicare’s costs under current law rise steadily from their current level of 3.7 percent of GDP in 2017 to 5.9 percent in 2042. Costs then continue to grow, but at a slower rate, until reaching 6.2 percent in 2092. Under the illustrative alternative, in which adherence to the MACRA and ACA cost-reducing measures erodes, projected costs would continue rising steadily throughout the projection period, reaching 6.2 percent of GDP in 2042 and 8.9 percent in 2092. As the preceding discussion explains, and as the substantial differences between current-law and illustrative alternative projections demonstrate, Medicare’s actual future costs are highly uncertain for reasons apart from the inherent challenges in projecting health care cost growth over time. The Board recommends that readers interpret the current-law estimates in the report as the outcomes that would be experienced under the Trustees’ economic and demographic assumptions if the productivity adjustments in the ACA and the physician price updates in MACRA can be and are sustained in the long range. Readers are encouraged to review section V.C for further information on this important subject. The key financial outcomes under the illustrative alternative scenario are shown with the current-law projections throughout this report.
How many people did Medicare cover in 2017?
In 2017, Medicare covered 58.4 million people: 49.5 million aged 65 and older, and 8.9 million disabled. Over 34 percent of these beneficiaries have chosen to enroll in Part C private health plans that contract with Medicare to provide Part A and Part B health services. Total expenditures in 2017 were $710.2 billion, and total income was $705.1 billion, which consisted of $694.3 billion in non-interest income and $9.8 billion in interest earnings. Assets held in special issue U.S. Treasury securities decreased by $5.0 billion to $289.6 billion.
What would happen if the Medicare trust fund was depleted?
Under current law, payments would be reduced to levels that could be covered by incoming tax and premium revenues when the HI trust fund was depleted. If the projections reflected such payment reductions, then any imbalances between payments and revenues would be automatically eliminated, and the report would not fulfill one of its critical functions, which is to inform policy makers and the public about the size of any trust fund deficits that would need to be resolved to avert program insolvency. To date, lawmakers have never allowed the assets of the Medicare HI trust fund to become depleted. Projections of Medicare costs are highly uncertain, especially when looking out more than several decades. One reason for uncertainty is that scientific advances will make possible new interventions, procedures, and therapies. Some conditions that are untreatable today will be handled routinely in the future. Spurred by economic incentives, the institutions through which care is delivered will evolve, possibly becoming more efficient. While most health care technological advances to date have tended to increase expenditures, the health care landscape is shifting. No one knows whether future developments will, on balance, increase or decrease costs. While the physician payment updates and new incentives put in place by the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA) avoid the significant short-range physician payment issues that would have resulted from the sustainable growth rate (SGR) system approach, they nevertheless raise important long-range concerns. In particular, additional payments of $500 million per year for one group of physicians and 5-percent annual bonuses for another group are scheduled to expire in 2025, resulting in a significant one- time payment reduction for most physicians. In addition, the law specifies the physician payment update amounts for all years in the future, and these amounts do not vary based on underlying economic conditions, nor are they expected to keep pace with the average rate of physician cost increases. The specified rate updates could be an issue in years when levels of inflation are high and would be problematic when the cumulative gap between the price updates and physician costs becomes large. The gap will continue to widen throughout the projection, and the Trustees previously estimated that physician payment rates under current law will be lower than they would have been under the SGR formula by 2048. Absent a change in the delivery system or level of update by subsequent legislation, access to Medicare- participating physicians may become a significant issue in the long term under current law.
What would happen to Medicare payments under the ACA?
5Under the ACA, Medicare’s annual payment rate updates for most categories of provider services would be reduced below the increase in providers’ input prices by the growth in economy-wide productivity (1.1 percent over the long range).

Summary
Health
Cost
Causes
- Slower growth in Medicare spending in recent years can be attributed in part to policy changes adopted as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Budget Control Act of 2011 (BCA). The ACA included reductions in Medicare payments to plans and providers, increased revenues, and introduced delivery system reforms that aimed to improve efficiency and quality of patient care …
Effects
- In addition, although Medicare enrollment has been growing around 3 percent annually with the aging of the baby boom generation, the influx of younger, healthier beneficiaries has contributed to lower per capita spending and a slower rate of growth in overall program spending. In general, Part A trust fund solvency is also affected by the level of growth in the economy, which affects …
Impact
- Prior to 2010, per enrollee spending growth rates were comparable for Medicare and private health insurance. With the recent slowdown in the growth of Medicare spending and the recent expansion of private health insurance through the ACA, however, the difference in growth rates between Medicare and private health insurance spending per enrollee has widened.
Future
- While Medicare spending is expected to continue to grow more slowly in the future compared to long-term historical trends, Medicares actuaries project that future spending growth will increase at a faster rate than in recent years, in part due to growing enrollment in Medicare related to the aging of the population, increased use of services and intensity of care, and rising health care pri…
Funding
- Medicare is funded primarily from general revenues (41 percent), payroll taxes (37 percent), and beneficiary premiums (14 percent) (Figure 7). Part B and Part D do not have financing challenges similar to Part A, because both are funded by beneficiary premiums and general revenues that are set annually to match expected outlays. Expected future inc...
Assessment
- Medicares financial condition can be assessed in different ways, including comparing various measures of Medicare spendingoverall or per capitato other spending measures, such as Medicare spending as a share of the federal budget or as a share of GDP, as discussed above, and estimating the solvency of the Medicare Hospital Insurance (Part A) trust fund.
Purpose
- The solvency of the Medicare Hospital Insurance trust fund, out of which Part A benefits are paid, is one way of measuring Medicares financial status, though because it only focuses on the status of Part A, it does not present a complete picture of total program spending. The solvency of Medicare in this context is measured by the level of assets in the Part A trust fund. In years whe…
Benefits
- A number of changes to Medicare have been proposed that could help to address the health care spending challenges posed by the aging of the population, including: restructuring Medicare benefits and cost sharing; further increasing Medicare premiums for beneficiaries with relatively high incomes; raising the Medicare eligibility age; and shifting Medicare from a defined benefit s…