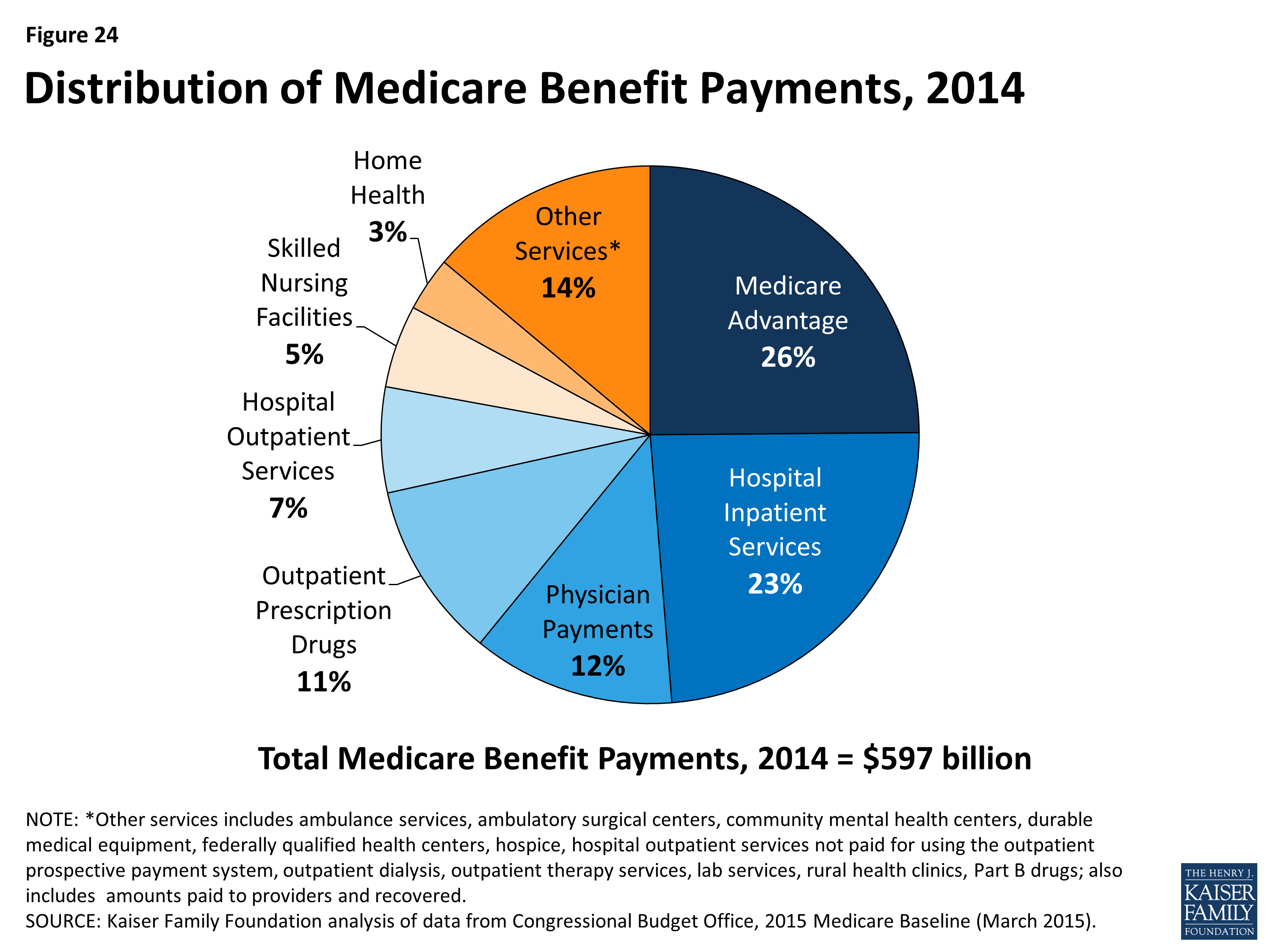
How long do you have to use Medicare Part A?
Medicare Part A and hospital care. You must use Medicare Part A hospital inpatient services for more than 90 days in a benefit period in order for a Medicare lifetime reserve day to be used.
What is the Medicare 3-day rule?
She was a victim of the Medicare 3-day rule. The 3-day rule is Medicare’s requirement that a patient has to be admitted to the hospital for at least 3 days in order for Medicare to cover the cost of a SNF after the hospitalization. If the patient is admitted for less than 3 days, then the patient pays the cost of the SNF and Medicare pays nothing.
What are Medicare lifetime reserve days and how do they work?
They also will cover hospital health care costs up to an additional 365 days after your Medicare benefits are used up. To use a lifetime reserve day, first you must be eligible for inpatient hospital care that is covered by Medicare Part A.
How long does Medicare pay for inpatient hospitalization?
During each benefit period, Medicare covers up to 90 days of inpatient hospitalization. After 90 days, Medicare gives you 60 additional days of inpatient hospital care to use during your lifetime.
What counts as a 30-day readmission?
The HRRP 30-day risk standardized unplanned readmission measures include: Unplanned readmissions that happen within 30 days of discharge from the index (i.e., initial) admission. Patients who are readmitted to the same hospital, or another applicable acute care hospital for any reason.
How does Medicare count days in hospital?
Patients meet the 3-day rule by staying 3 consecutive days in 1 or more hospital(s). Hospitals count admission day but not discharge day. Time spent in the ER or outpatient observation before admission doesn't count toward the 3-day rule. Inpatient days are counted using the midnight-to-midnight method.
What is considered a benefit period for Medicare?
A benefit period begins the day you're admitted as an inpatient in a hospital or SNF. The benefit period ends when you haven't gotten any inpatient hospital care (or skilled care in a SNF) for 60 days in a row. If you go into a hospital or a SNF after one benefit period has ended, a new benefit period begins.
What is the 3-day rule for Medicare?
Pursuant to Section 1861(i) of the Act, beneficiaries must have a prior inpatient hospital stay of no fewer than three consecutive days to be eligible for Medicare coverage of inpatient SNF care. This requirement is referred to as the SNF 3-Day Rule.
Do Medicare days reset every year?
Does Medicare Run on a Calendar Year? Yes, Medicare's deductible resets every calendar year on January 1st. There's a possibility your Part A and/or Part B deductible will increase each year. The government determines if Medicare deductibles will either rise or stay the same annually.
What is the 60 day Medicare rule?
A benefit period begins the day you are admitted to a hospital as an inpatient, or to a SNF, and ends the day you have been out of the hospital or SNF for 60 days in a row. After you meet your deductible, Original Medicare pays in full for days 1 to 60 that you are in a hospital.
What is the Part A benefit period?
What Is A Benefit Period? In Medicare Part A, which is hospital insurance, a benefit period begins the day you go into a hospital or skilled nursing facility and ends when you have been out for 60 days in a row.
What does calendar year mean for benefits?
A year of benefits coverage under an individual health insurance plan. The benefit year for plans bought inside or outside the Marketplace begins January 1 of each year and ends December 31 of the same year. Your coverage ends December 31 even if your coverage started after January 1.
What does per benefit period mean?
A benefit period is the length of time during which an insurance policyholder or their dependents may file and receive payment for a covered event. The length of an insurance policy's benefit period will affect the price of the premium because the longer the benefit period, the greater is the insurer's risk.
What is the CMS 72 hour rule?
The 72 hour rule is part of the Medicare Prospective Payment System (PPS). The rule states that any outpatient diagnostic or other medical services performed within 72 hours prior to being admitted to the hospital must be bundled into one bill.
What is the Medicare two midnight rule?
The Two-Midnight rule, adopted in October 2013 by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, states that more highly reimbursed inpatient payment is appropriate if care is expected to last at least two midnights; otherwise, observation stays should be used.
Which is the total number of Medicare lifetime reserve days?
In Original Medicare, these are additional days that Medicare will pay for when you're in a hospital for more than 90 days. You have a total of 60 reserve days that can be used during your lifetime. For each lifetime reserve day, Medicare pays all covered costs except for a daily coinsurance.
What is Medicare benefit period?
Medicare benefit periods mostly pertain to Part A , which is the part of original Medicare that covers hospital and skilled nursing facility care. Medicare defines benefit periods to help you identify your portion of the costs. This amount is based on the length of your stay.
How long does Medicare Advantage last?
Takeaway. Medicare benefit periods usually involve Part A (hospital care). A period begins with an inpatient stay and ends after you’ve been out of the facility for at least 60 days.
How much coinsurance do you pay for inpatient care?
Days 1 through 60. For the first 60 days that you’re an inpatient, you’ll pay $0 coinsurance during this benefit period. Days 61 through 90. During this period, you’ll pay a $371 daily coinsurance cost for your care. Day 91 and up. After 90 days, you’ll start to use your lifetime reserve days.
How long does Medicare benefit last after discharge?
Then, when you haven’t been in the hospital or a skilled nursing facility for at least 60 days after being discharged, the benefit period ends. Keep reading to learn more about Medicare benefit periods and how they affect the amount you’ll pay for inpatient care. Share on Pinterest.
What facilities does Medicare Part A cover?
Some of the facilities that Medicare Part A benefits apply to include: hospital. acute care or inpatient rehabilitation facility. skilled nursing facility. hospice. If you have Medicare Advantage (Part C) instead of original Medicare, your benefit periods may differ from those in Medicare Part A.
Why is it important to check deductibles each year?
It’s important to check each year to see if the deductible and copayments have changed, so you can know what to expect. According to a 2019 retrospective study. Trusted Source. , benefit periods are meant to reduce excessive or unnecessarily long stays in a hospital or healthcare facility.
How much is Medicare deductible for 2021?
Here’s what you’ll pay in 2021: Initial deductible. Your deductible during each benefit period is $1,484. After you pay this amount, Medicare starts covering the costs. Days 1 through 60.
How many days of Medicare Part A coverage are there?
The takeaway. If you receive inpatient care in a hospital or long-term care facility for longer than 90 days, Medicare Part A gives you 60 extra days of coverage called lifetime reserve days. This set number of lifetime reserve days can be used only once over the course of your lifetime.
How much will Medicare pay for lifetime reserve days in 2021?
For each of these “lifetime reserve days” you use in 2021, you’ll pay a daily coinsurance of $742. When you’re sick or injured and your doctor admits you to a hospital or long-term care facility, it’s important to understand what your costs and coverage will look like. If you have original Medicare, Part A will cover your hospital stay, ...
How much is the Medicare deductible per benefit period?
This is in addition to your Medicare Part A deductible of $1,484 per benefit period. If you think you may need more coverage, you can purchase a Medigap policy, which can provide additional lifetime reserve days or pay for your Part A deductible.
How much is the coinsurance for Medicare 2021?
When you use lifetime reserve days, you pay a coinsurance fee of $742 per day in 2021. This is in addition to your Medicare Part A deductible of $1,484 per benefit period.
How many days can you use Medicare for a lifetime reserve?
If you again need to stay in the hospital longer than 90 days, you’ll have only 40 lifetime reserve days left to use, assuming you decided to use 20 during your first stay. The hospital will notify you as you get close to using up your 90 days of coverage under Medicare Part A. At that point, you can let the hospital know if you want to save ...
How long is a lifetime reserve day?
What are lifetime reserve days? If you’re admitted to a hospital or long-term care facility for inpatient care, Medicare Part A covers up to 90 days of treatment during each benefit period. If you need to remain in the hospital after those 90 days are up, you have an additional 60 days of coverage, known as lifetime reserve days.
How to contact Medicare for lifetime reserve days?
For additional help understanding your Medicare lifetime reserve days or other benefits, try these resources: You can contact Medicare directly at 800-MEDICARE (800-633-4227). Get help from trained, impartial counselors through your local State Health Insurance Assistance Program (SHIP).
How long is a lifetime reserve day for Medicare?
Medicare lifetime reserve days are used if you have an inpatient hospital stay that lasts beyond the 90 days per benefit period covered under Medicare Part A. Medicare recipients have 60 Medicare lifetime reserve days available to them, and they come with a $682 daily co-insurance cost.
How much does Medicare pay for lifetime reserve days?
Medicare lifetime reserve days require a $682 daily co-insurance payment in 2019. All 10 standardized Medicare Supplement insurance plans will pay for this co-insurance cost. They also will cover hospital health care costs up to an additional 365 days after your Medicare benefits are used up.
How much is Medicare deductible for inpatient hospital stays?
The Medicare program will charge you deductibles and co-insurance for Part A inpatient hospital stays and health care costs, including a $682 co-insurance payment per lifetime reserve day in 2019. The table below outlines the 2019 costs associated with inpatient hospital stays.
How to use a lifetime reserve day?
To use a lifetime reserve day, first you must be eligible for inpatient hospital care that is covered by Medicare Part A. To qualify for inpatient hospital care, your hospital doctor must make an official order stating that “you need 2 or more midnights of medically necessary inpatient hospital care to treat your illness or injury and ...
What is Medicare Part A?
Medicare Part A inpatient hospital insurance covers “hospital services, including semi-private rooms, meals, general nursing, drugs as part of your inpatient treatment, and other hospital services and supplies ,” according to Medicare.gov. Medicare lifetime reserve days require a $682 daily co-insurance payment in 2019.
How long do you have to be in a hospital to qualify for Medicare?
You must use Medicare Part A hospital inpatient services for more than 90 days in a benefit period in order for a Medicare lifetime reserve day to be used.
Does Medicare Supplement pay for reserve day?
A Medicare Supplement insurance policy can pay for your Part A daily lifetime reserve day co-insurance. All Medigap plans offer full coverage for the Part A inpatient hospital care co-insurance. If you receive qualifying Part A hospital inpatient care and need to use a lifetime reserve day, your Medigap policy will pay for ...
What is HAO in Medicare?
The Healthy Adult Opportunity (HAO) emphasizes the concept of value-based care while granting states with extensive flexibility to administer and design their programs within a defined budget. This state opportunity will enhance the Medicaid program’s integrity through its focus on accountability for results and quality improvement, making the Medicaid program stronger for states and beneficiaries.
Is HAO available for Medicaid?
Beneficiary Protections. HAO is available to all states, with a focus on a limited population – adults under age 65 who are not eligible for Medicaid on the basis of disability or their need for long term care services and supports, and who are not eligible under a state plan.
How long is an inpatient in Medicare?
Medicare considers a patient to be in inpatient status if that patient is anticipated to need to be in the hospital for 2 midnights and in observation status if the patient is anticipated to be in the hospital for less than 2 midnights. Observation status was originally intended to be used to observe the patient to determine whether ...
How many days prior to SNF for Medicare?
However, for SNF coverage decisions, Medicare will not count the 3 days prior to the inpatient order toward the 3 inpatient days that Medicare requires in order for Medicare to pay for SNF charges. Medicare’s coverage rules are byzantine and indecipherable for the average patient.
How long does it take for Medicare to pay for SNF?
The 3-day rule is Medicare’s requirement that a patient has to be admitted to the hospital for at least 3 days in order for Medicare to cover the cost of a SNF after the hospitalization. If the patient is admitted for less than 3 days, then the patient pays the cost of the SNF and Medicare pays nothing. So, if this patient was in the hospital ...
How long does it take for a surgeon to change an order to inpatient?
The surgeon writes an order for the patient to be in observation status at the time of the surgery. After 2 days , the surgeon changes the order to inpatient status. The patient spends 4 nights in the hospital but still need more rehabilitation so the patient is discharged to a SNF.
How long do you have to stay in the hospital after a heart surgery?
The patient has difficult-to-control diabetes, heart failure, sleep apnea, and kidney failure so the surgeon anticipates that the patient will need to stay in the hospital for more than 2 midnights after the surgery to care for the medical conditions.
How long was a woman in the hospital after knee replacement?
She was in the hospital for 4 days after her surgery but was very slow to recover and was determined to be unsafe for discharge home without additional rehabilitation so she was discharged to a SNF (subacute nursing facility). She spent a week getting rehab at the SNF and then returned home only to find that she had a bill for the entire stay the nursing facility; Medicare covered none of it. She paid her bills but in doing so, wiped out most of her savings.
Is observation covered by Medicare?
However, if a patient is in observation status, then the hospital stay is not covered by Medicare part A but instead is covered by Medicare part B which requires the patient to pay a 20% co-pay for all of the charges plus pay for any medications administered during the hospitalization.
What calculations are being used?
Once the data has been gathered, the analysis begins......but what formula is the one to use? The three most often applied calculations include the Average, the Geometric Mean and finally, the Median.
Average
The most common statistic, which is applicable to many industries, is the average length of stay (ALOS). This average is simply the arithmetic mean of the data. Let d represent the patient days and N represent the total number of patients. Mathematically ALOS becomes,
Geometric Mean
The second statistic, and more accurate, is the Geometric Mean. It is a more precise representation of the central value of an ensemble of points since it is not as sensitive to outliers. Given N patients the geometric mean is the Nth root of the product of the individual patient days.
Median
Lastly, the Median statistic is a third alternative. The median is the middle number in a sequence of numbers. Otherwise defined as the 2nd quartile or 50th percentile and best describes the central value of a distribution. Harmony Healthcare International compiled the length of stay days for 9552 Skilled Nursing Facility Medicare Patients.
What formula is the most accurate?
Patient length of stay (LOS) is a metric used in the Prospective Payment System for Medicare reimbursement in Skilled Nursing Facilities (SNF). There is a trend to benchmark the LOS with a single number for prediction and comparison purposes.
Conclusion
To maintain a viable Medicare program in the skilled nursing facility setting, leadership must analyze the admission and discharge process for the Medicare Part A beneficiary, as well as all payor sources who are admitted for post acute care.
