Original Medicare costs (Part A and B) in Indiana are the same nationwide. The Medicare Part A premium can cost you $0, $274, or $499, depending on how long you or your spouse worked and paid Medicare taxes. For Part A hospital inpatient deductibles and coinsurance, you pay:
Full Answer
How many people in Indiana have Medicaid coverage?
And nearly 700,000 of those enrollees have Medicaid coverage as a result of the expanded eligibility guidelines implemented by the ACA and the state’s HIP 2.0 waiver. From 2013 to 2014, the uninsured rate in Indiana declined slightly from 14% to 11.9%, according to U.S. Census data.
Does Indiana Medicaid pay for nursing home care?
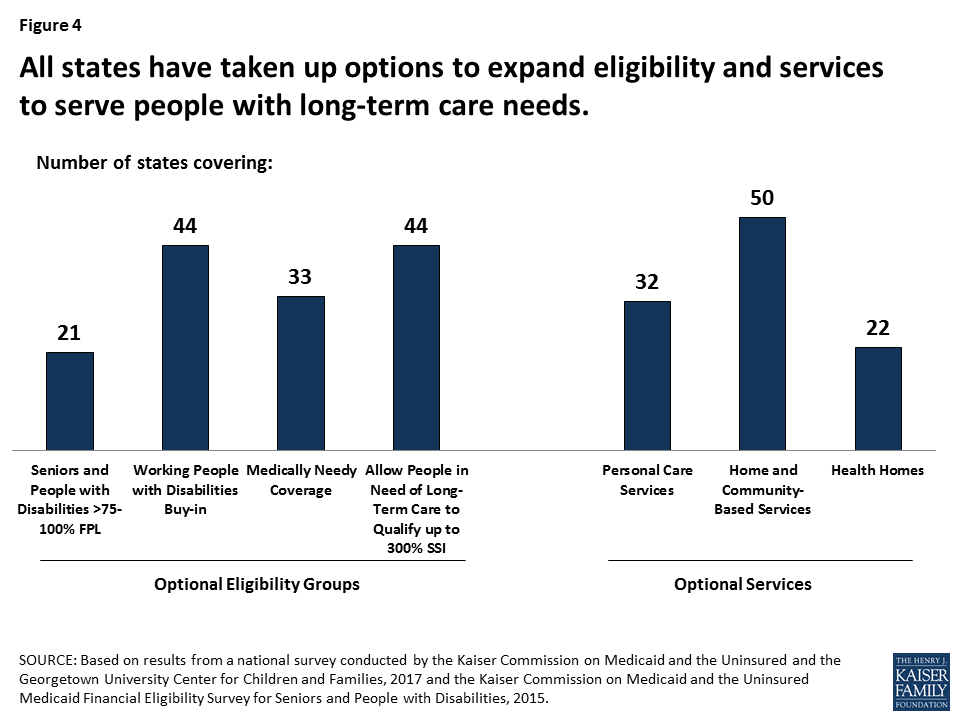
Phrased differently, if an Indiana resident is medically and financially eligible for nursing home care, then the Indiana Medicaid program is required by law to pay for it. Waiting lists cannot exist.
Will Indiana ever expand Medicaid?
Although Indiana expressed willingness to consider a modified version of Medicaid expansion, both Governor Pence and the head of the Indiana Family and Social Services Administration took the position that Medicaid must be reformed, not just expanded. But there was significant federal money available to states that expand Medicaid.
When did Medicaid start in Indiana?
Background on Indiana’s Medicaid program After Medicaid was founded in 1965, Indiana was one of the last states to implement a Medicaid program, waiting until Jan. 1, 1970. Legislation authorizing the state-federal partnership was enacted in July 1965.

How much money does the government take for Medicare?
Medicare accounts for a significant portion of federal spending. In fiscal year 2020, the Medicare program cost $776 billion — about 12 percent of total federal government spending.
How much does Indiana spend on Medicaid?
Spending details[hide]Medicaid spending detailsStateTotal spending (2016)Percent of state budget (2015)Indiana$10,446,713,81531.2%Illinois$19,298,315,09627.1%Michigan$16,881,112,46830.2%3 more rows
How is the Indiana Medicaid program funded?
Medicaid is jointly funded by the federal and state government. Medicaid programs vary from state to state though there are some services that are required by the federal government. Optional services can be offered by each state.
How much is Medicare in Indiana?
Medicare in Indiana by the NumbersPeople enrolled in Original MedicareAverage plan costAnnual state spending per beneficiary818,031Plan A: $0 to $499 per month* Plan B: $170.10 per month**$10,570Apr 6, 2022
Which state spends the most on Medicaid?
state of CaliforniaTotal Medicaid spending surpassed 662 billion U.S. dollars in 2020. The state of California had the highest expenditure throughout the year, followed by New York and Texas.
How much do the individual states contribute to Medicaid?
States together spent 17.1 cents of every state-generated dollar in fiscal year 2017 to provide Medicaid health care coverage to low-income Americans—nearly 5 cents more than in fiscal 2000 and the largest amount since that year.
Did Indiana expand Medicaid under Obamacare?
Indiana's expansion under the Affordable Care Act covers 570,000 low-income adults. In the 38 states that have expanded, Medicaid is available to everyone with incomes under 138% of the federal poverty level, or $17,774 for an individual.
How is Healthy Indiana Plan funded?
Under the plan, Indiana uses Medicaid funds to provide a benefit package modeled after a high-deductible health plan and health savings account to previously uninsured very poor and low-income adults.
Who pays for Medicaid?
The Medicaid program is jointly funded by the federal government and states. The federal government pays states for a specified percentage of program expenditures, called the Federal Medical Assistance Percentage (FMAP).
Does Indiana pay for Medicare Part B?
Original Medicare costs (Part A and B) in Indiana are the same nationwide. The Medicare Part A premium can cost you $0, $274, or $499, depending on how long you or your spouse worked and paid Medicare taxes. For Part A hospital inpatient deductibles and coinsurance, you pay: $1,556 deductible for each benefit period.
How much does Medicare Part B cost in Indiana?
Part B - Monthly Premium 2022Beneficiaries who file an individual tax return with income:Beneficiaries who file a joint tax return with income:Total monthly Part B premium amountabove $114,000 up to $142,000above $228,000 up to $284,000$340.20above $142,000 up to $170,000above $284,000 up to $340,000$442.304 more rows
How many people are on Medicare in Indiana?
1.2 million peopleOver 1.2 million people, roughly 18% of the population of Indiana, are Medicare beneficiaries. Fewer people were enrolled in Medicare Advantage in Indiana than in Original Medicare in 2020.
Has Indiana implemented Medicaid expansion?
In January 2015 —a year after many other states had expanded Medicaid — Indiana won approval from CMS for its amended Healthy Indiana Plan, known a...
Does Indiana have a Medicaid work requirement?
No, Indiana does not have a Medicaid work requirement. A work requirement was approved by the Trump administration but never implemented, and the a...
Who is eligible for Medicaid in Indiana?
Indiana’s Medicaid eligibility guidelines are average for children and pregnant women. Low-income adults can obtain Medicaid coverage under the Hea...
How does Medicaid provide financial help to Medicare beneficiaries in Indiana?
Many Medicare beneficiaries receive help through Medicaid with the cost of Medicare premiums, prescription drug expenses, and costs that aren’t cov...
How do I apply for Medicaid in Indiana?
If you believe you or a family member may qualify for Medicaid, you have several options for submitting an application: Apply online through the In...
When did Indiana start accepting Medicaid applications?
Indiana began accepting applications for Medicaid under HIP 2.0 in late January 2015, with coverage beginning as soon as Feb. 1, 2015.
How to apply for medicaid in Indiana?
If you believe you or a family member may qualify for Medicaid, you have several options for submitting an application: 1 Apply online through the Indiana Family and Social Services Administration or at HealthCare.gov. 2 Call 1-800-403-0864 to apply by phone. 3 Apply in person at a Division of Family Resources office. Find a nearby office.
What is the waiver amendment for Medicaid expansion?
The waiver amendment proposed a work requirement for Indiana’s Medicaid expansion population, as opposed to the voluntary job training and employment services program that Indiana already had in place.
What is the lawsuit against CMS in Indiana?
The lawsuit contends that CMS overstepped its bounds in approving the state’s work requirement, and that the approval constitutes “unauthorized attempts to re-write the Medicaid Act.”
What is the Medicaid eligibility for Indiana in 2021?
Indiana’s Medicaid eligibility standards as of 2021 are: 208% percent of the federal poverty level (FPL) for children up to 1 year old. 158% percent of FPL for children 1 to 18 years old; the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) covers children at higher income levels, up to 250% of FPL. 208% of FPL for pregnant women.
How long is the lockout period in Indiana?
In April 2016, Indiana asked CMS to make the lock-out (now set at six months, and effectively only three months since there’s an initial 90-day reinstatement period) officially part of HIP 2.0, but in August 2016, CMS denied the request.
When will Indiana's waiver end?
On February 1, 2018, CMS approved Indiana’s amended waiver through the end of 2020. The state’s updated waiver included several changes, but the community engagement provision (aka, work requirement) was the most significant.
What is Medicaid in Indiana?
Medicaid is a wide-ranging, jointly funded state and federal program that provides low-income individuals of all ages health care coverage. However, the focus here will be specifically on long-term care Medicaid eligibility for senior Indiana residents (65 years of age and over). With long-term care, services may be provided in a variety ...
How long does Medicaid last in Indiana?
It’s important to be aware that Indiana has a 5-year Medicaid Look-Back Period. This is a period in which Medicaid checks to see if any assets were sold, gifted, or transferred during the 60 months immediately preceding one’s Medicaid application date.
What is CSRA in Medicaid?
This, in Medicaid speak, is called the Community Spouse Resource Allowance (CSRA). As with the spousal income allowance, this asset allowance does not extend to non-applicant spouses whose spouses are regular Medicaid applicants. It’s important to be aware that Indiana has a 5-year Medicaid Look-Back Period.
How much can a spouse retain for nursing home?
For married couples with one spouse applying for nursing home Medicaid or a HCBS Medicaid waiver, in 2021, the community spouse (the non-applicant spouse) can retain half of the couples’ joint assets, up to a maximum of $130,380, as the chart indicates above.
How much is the shelter cost for a non-medical spouse in 2021?
As of January 2021 through December 2021, this figure is $3,260.00 / month. This spousal impoverishment rule is not relevant for non-applicant spouses of regular Medicaid applicants.
What income is counted for Medicaid?
Examples include employment wages, alimony payments, pension payments, Social Security Disability Income, Social Security Income, IRA withdrawals, and stock dividends.
Does Medicaid cover nursing home care in Indiana?
Nursing home care paid for by Indiana’s Medicaid program is an entitlement. Phrased differently, if an Indiana resident is medically and financially eligible for nursing home care, then the Indiana Medicaid program is required by law to pay for it. Waiting lists cannot exist. Indiana Medicaid also pays for care outside of nursing homes, in assisted living, adult foster care homes, or in the home of the beneficiary. These benefits are paid for through a program called a Medicaid waiver. Medicaid waivers are not entitlements and waiting lists can exist.
Background
Established in 1965, Medicaid is the primary source of health insurance coverage for low-income and disabled individuals and the largest source of financing for the healthcare services they need. In 2014, about 80 million individuals were enrolled in Medicaid, or 25.9 percent of the total United States population.
Eligibility
Eligibility for each state's Medicaid program is subject to minimum federal standards, both in the population groups states must cover and the maximum amount of income enrollees can make. States are required to cover the following population groups and income levels:
Benefits
In large part, the states "determine the type, amount, duration, and scope" of benefits offered to individuals enrolled in Medicaid, according to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. However, benefits are subject to federal minimum standards. The federal government has outlined 16 benefits that are required of all Medicaid programs:
State and federal spending
During fiscal year 2016, Medicaid spending nationwide amounted to nearly $553.5 billion. Spending per enrollee amounted to $7,067 in fiscal year 2013, the most recent year for which per-enrollee figures were available as of June 2017. Total Medicaid spending grew by 33 percent between fiscal years 2012 and 2016.
Children's Health Insurance Program
The Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) is a public healthcare program for low-income children who are ineligible for Medicaid. CHIP and Medicaid are related programs, and the former builds on Medicaid's coverage of children. States may run CHIP as an extension of Medicaid, as a separate program, or as a combination of both.
Historical data
To view detailed historical data on Medicaid enrollment in Indiana for 2010, click "Show more" below to expand the section.
Recent news
The link below is to the most recent stories in a Google news search for the terms Medicaid Indiana. These results are automatically generated from Google. Ballotpedia does not curate or endorse these articles.
What is Medicare?
Medicare is a federal health insurance program for people 65 and older, and for eligible people who are under 65 and disabled. Medicare is run by the Centers of Medicare and Medicaid Services, an agency of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. It is controlled by Congress.
Am I eligible for Medicare?
To receive Medicare, you must be eligible for Social Security benefits.
What does Medicare cover?
Medicare helps pay for certain health care services and durable medical equipment. To have full Medicare coverage, Medicare beneficiaries must have Part A (Hospital Insurance) and Part B (Medical Insurance).
Part B Coverage
Physician services received in the doctor's office, patient's home, hospital, skilled nursing facility, or anywhere else in the United States
How much does Medicare cost?
Original Medicare is divided into Part A (Hospital Insurance) and Part B (Medical Insurance).
Should I take Medicare Part B?
You should take Medicare Part A when you are eligible. However, some people may not want to apply for Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) when they become eligible.
What are my rights as a Medicare beneficiary?
As a Medicare beneficiary, you have certain guaranteed rights. These rights protect you when you get health care, they assure you access to needed health care services, and protect you against unethical practices.
Professional Fee Schedule
The Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) Professional Fee Schedule includes reimbursement information for providers that bill services using professional claims or dental claims reimbursed under the fee-for-service (FFS) delivery system.
Outpatient Fee Schedule
The IHCP publishes the rates for outpatient hospitals and ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) on the Outpatient Fee Schedule. This fee schedule reflects current IHCP coverage and reimbursement policy for procedure codes and revenue codes billed for IHCP outpatient services under the FFS delivery system.