How much did Medicare spending increase in the 1990s?
Nationally, per-capita spending by private health insurance grew an average of 4.0 percent per year from 1993 to 1997, while per-capita Medicare spending grew an average of 7.3 percent …
When did Medicare take effect?
But Medicare per capita spending has been growing at a much slower pace in recent years, averaging 1.5 percent between 2010 and 2017, as opposed to 7.3 percent between 2000 and …
Why did the cost of Medicare Part a go up?
Sep 08, 2021 · Total Medicare spending 1970-2020. In 1970, some 7.5 billion U.S. dollars were spent on the Medicare program in the United States. Fifty years later, this figure stood at 925.8 …
How did the Balanced Budget Act of 1997 affect Medicare Advantage?
Mar 22, 2013 · Taxpayers lose again. For example, between 1997 and 2001, Medicare physician fees increased by just 3.4 percent, but physician expenditures per beneficiary increased by 7.4 …
What was the principal effect of the Balanced Budget Act of 1997?
How fast has spending per person been increasing for Medicare?
How much did the government spend on Medicare?
Medicare spending grew 3.5% to $829.5 billion in 2020, or 20 percent of total NHE. Medicaid spending grew 9.2% to $671.2 billion in 2020, or 16 percent of total NHE. Private health insurance spending declined 1.2% to $1,151.4 billion in 2020, or 28 percent of total NHE.Dec 15, 2021
Which president expanded Medicare?
How much is Medicare increasing?
Why are Medicare costs rising?
How much did the government spend on Medicare in 2020?
In what area is the most Medicare dollars spent?
How much did the US spend on healthcare in 2021?
Which president started Medicare and Social Security?
How did Medicare Part D expand Medicare services?
What did the Medicare 1965 do?
When did Medicare start?
But it wasn’t until after 1966 – after legislation was signed by President Lyndon B Johnson in 1965 – that Americans started receiving Medicare health coverage when Medicare’s hospital and medical insurance benefits first took effect. Harry Truman and his wife, Bess, were the first two Medicare beneficiaries.
Who signed Medicare into law?
Medicare’s history: Key takeaways. President Harry S Truman called for the creation of a national health insurance fund in 1945. President Lyndon B. Johnson signed Medicare into law in 1965. As of 2021, 63.1 million Americans had coverage through Medicare. Medicare spending is expected to account for 18% of total federal spending by 2028.
How many people are covered by Medicare in 2019?
By early 2019, there were 60.6 million people receiving health coverage through Medicare. Medicare spending reached $705.9 billion in 2017, which was about 20 percent of total national health spending. Back to top.
Can I get Medicare if I have ALS?
Americans younger than age 65 with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) are allowed to enroll in Medicare without a waiting period if approved for Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) income. (Most SSDI recipients have a 24-month waiting period for Medicare from when their disability cash benefits start.)
What is the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act?
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010 includes a long list of reform provisions intended to contain Medicare costs while increasing revenue, improving and streamlining its delivery systems, and even increasing services to the program.
Is the Donut Hole closed?
The donut hole has closed, as a result of the ACA. It was fully eliminated as of 2020 (it closed one year early – in 2019 – for brand-name drugs, but generic drugs still cost more while enrollees were in the donut hole in 2019).
How much did Medicare cost in 1970?
In 1970, some 7.5 billion U.S. dollars were spent on the Medicare program in the United States. Almost fifty years later, this figure stood at some 796.2 billion U.S. dollars. This statistic depicts total Medicare spending from 1970 to 2019.
What percentage of the population is covered by Medicare?
In the U.S., the share of the population with any type of health insurance has increased to over 90 percent in the past decade. As of 2019, approximately 18 percent of the U.S. population was covered by Medicare in particular.
What is Medicare coverage?
Increasing Medicare coverage. Medicare is the federal health insurance program in the U.S. for the elderly and those with disabilities. In the U.S., the share of the population with any type of health insurance has increased to over 90 percent in the past decade.
How much will Alzheimer's cost in 2020?
In 2020, Alzheimer's disease was estimated to cost Medicare and Medicaid around 206 billion U.S. dollars in care costs; by 2050, this number is projected to climb to 777 billion dollars.
Is Medicare spending going up?
Over the longer term (that is, beyond the next 10 years), both CBO and OACT expect Medicare spending to rise more rapidly than GDP due to a number of factors, including the aging of the population and faster growth in health care costs than growth in the economy on a per capita basis. According to CBO’s most recent long-term projections, net Medicare spending will grow from 3.0 percent of GDP in 2019 to 6.0 percent in 2049.
How much did Medicare pay in 2018?
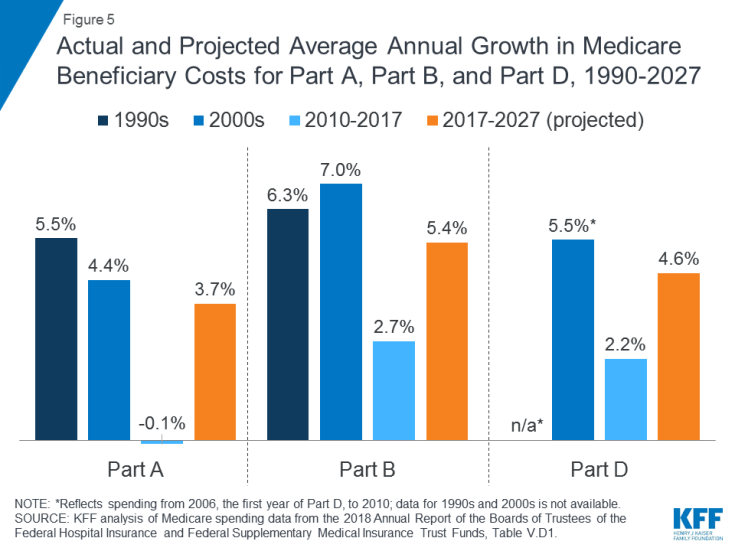
In 2018, Medicare benefit payments totaled $731 billion, up from $462 billion in 2008 (Figure 2) (these amounts do not net out premiums and other offsetting receipts). While benefit payments for each part of Medicare (A, B, and D) increased in dollar terms over these years, the share of total benefit payments represented by each part changed. Spending on Part A benefits (mainly hospital inpatient services) decreased from 50 percent to 41 percent, spending on Part B benefits (mainly physician services and hospital outpatient services) increased from 39 percent to 46 percent, and spending on Part D prescription drug benefits increased from 11 percent to 13 percent.
How many people are covered by Medicare?
Published: Aug 20, 2019. Medicare, the federal health insurance program for more than 60 million people ages 65 and over and younger people with long-term disabilities, helps to pay for hospital and physician visits, prescription drugs, and other acute and post-acute care services. This issue brief includes the most recent historical ...
Is Medicare spending comparable to private health insurance?
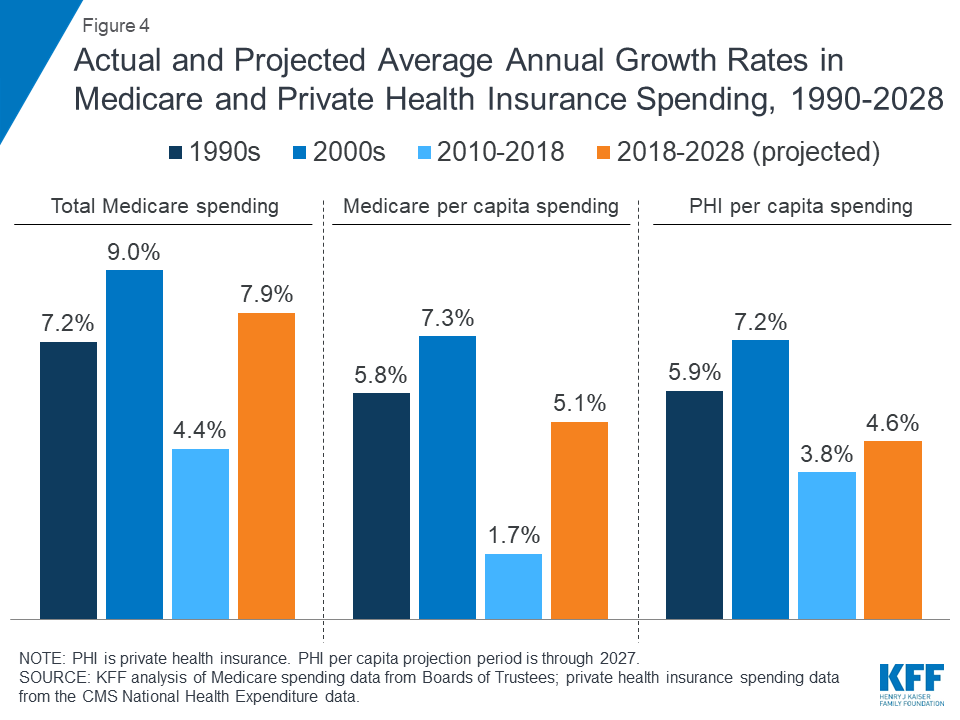
Prior to 2010, per enrollee spending growth rates were comparable for Medicare and private health insurance. With the recent slowdown in the growth of Medicare spending and the recent expansion of private health insurance through the ACA, however, the difference in growth rates between Medicare and private health insurance spending per enrollee has widened.
Does Medicare Advantage cover Part A?
Medicare Advantage plans, such as HMOs and PPOs, cover Part A, Part B, and (typically) Part D benefits. Beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans pay the Part B premium, and may pay an additional premium if required by their plan; about half of Medicare Advantage enrollees pay no additional premium.
When was Medicare enacted?
Since the enactment of Medicare in 1965, government actuaries have historically underestimated the true cost of Medicare. Outside of calculating on the basis of hard data, such as the age of those eligible or the size of enrollment, forecasting in Medicare (and health care in general) is inherently difficult.
What percentage of the economy is Medicare?
Medicare spending accounted for 3.67 percent of the entire economy, measured as gross domestic product (GDP), in 2011. It will be an estimated 5.8 percent of GDP in 2030, according to the Medicare Actuary’s full alternative scenario, which uses the most realistic assumptions.
Is Medicare forecasting difficult?
Since the enactment of Medicare in 1965, government actuaries have historically underestimated the true cost of Medicare. Outside of calculating on the basis of hard data, such as the age of those eligible or the size of enrollment, forecasting in Medicare (and health care in general) is inherently difficult. Projections can be wide off the mark because of the complex interplay of various mostly unpredictable factors, such as the impact of new medical technologies, the behavioral response of beneficiaries to benefit additions or payment changes, the level of participation or non-participation among Medicare doctors and hospitals, and the political willingness of Congress to take difficult steps to restrain Medicare spending. While predictability is difficult, there are a set of cost drivers that will inexorably raise Medicare costs and federal spending.
How many baby boomers are eligible for medicare?
There are roughly 77 million baby boomers—who will be eligible for Medicare at the rate of 10,000 per day over the next 19 years. [14] .
Is Medicare a long term program?
Medicare is a huge entitlement program, and its reform must, of necessity, be undertaken carefully. Congress and the Administration do not have time to waste, and should immediately undertake short-term reforms of the traditional Medicare program that can contain costs, while transitioning, as prudently but as quickly as possible, to a more effective program that will not only control costs over the long term, but will also provide high-quality health care to a rapidly rising Medicare population.
How much did Medicare cost in 2008?
By 2009, rising health care costs were consuming the federal budget. Medicare and Medicaid cost $671 billion in 2008. 25 Payroll taxes cover less than half of Medicare and none of Medicaid.
How much did health care cost in 1960?
It equals 17.7% of gross domestic product. 1 In comparison, health care cost $27.2 billion in 1960, just 5% of GDP. 2 That translates to an annual health care cost of $11,172 per person in 2018 versus just $147 per person in 1960. Health care costs have risen faster than the median annual income.
What are the causes of rising health care costs?
The second cause of rising health care costs is an epidemic of preventable diseases. The four leading causes of death are heart disease, cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder, and stroke. Chronic health conditions cause most of them. They can either be prevented or would cost less to treat if caught in time. Risk factors for heart disease and strokes are poor nutrition and obesity. Smoking is a risk factor for lung cancer (the most common type) and COPD. Obesity is also a risk factor for other common forms of cancer. 23
Who is Kimberly Amadeo?
Kimberly Amadeo is an expert on U.S. and world economies and investing, with over 20 years of experience in economic analysis and business strategy. She is the President of the economic website World Money Watch.
What was the HMO Act of 1973?
The HMO ACT of 1973 provided millions of dollars in start-up funding for HMOs. It also required employers to offer them when available. 10. From 1974 to 1982, health care prices rose by an average of 14.1% a year for three reasons. First, prices rebounded after the wage-price controls expired in 1974.
What is mandatory spending?
This is part of so-called mandatory spending also generally includes federal and veterans' pensions, welfare, and interest on the debt. It consumed 60% of the federal budget. 26 Congress knew something had to be done to rein in these costs. Federal health care costs are part of the mandatory budget.
What are the leading causes of death?
The four leading causes of death are heart disease, cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder, and stroke . Chronic health conditions cause most of them. They can either be prevented or would cost less to treat if caught in time. Risk factors for heart disease and strokes are poor nutrition and obesity.
When did Medicare Part B start?
The Social Security Administration has historical Medicare Part B and D premiums from 1966 through 2012 on its website. Medicare Part B premiums started at $3 per month in 1966. Medicare Part D premiums began in 2006 with an annual deductible of $250 per year. 7
How much is the 2021 Medicare premium?
The 2021 premium rate starts at $148.50 per month and increases based on your income to up to $504.90 for the 2021 tax year. Your premium depends on your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) from your tax return two years before the current year (in this case, 2019). 2.
How much is Medicare Part B 2021?
Medicare Part B premiums for 2021 increased by $3.90 from the premium for 2020. The 2021 premium rate starts at $148.50 per month and increases based on your income to up to $504.90 for the 2021 tax year. Your premium depends on your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) from your tax return two years before the current year (in this case, 2019). 2.
Who is Thomas Brock?
Thomas Brock is a well-rounded financial professional, with over 20 years of experience in investments, corporate finance, and accounting. Medicare Part B premiums are indexed for inflation — they're adjusted periodically to keep pace with the falling value of the dollar.
Who is Dana Anspach?
Linkedin. Follow Twitter. Dana Anspach is a Certified Financial Planner and an expert on investing and retirement planning. She is the founder and CEO of Sensible Money, a fee-only financial planning and investment firm.
When did Medicare extend to 65 year olds?
The Social Security Amendments of 1972 extend Medicare eligibility to people under age 65 with long-term disabilities and those with end-stage renal disease. They also establish the Professional Standards Review Organizations (PSROs) to review appropriateness of care.
Where was Medicare born?
Lyndon Johnson champions and signs the Social Security Amendments of 1965, creating Medicare and Medicaid, in Harry Truman's hometown of Independence, Missouri.
When was the Medicare Catastrophic Coverage Act repealed?
The major provisions of the law were repealed in 1989 .
What is Obama's Affordable Care Act?
Barack Obama signs the Affordable Care Act (ACA), which strengthens Medicare coverage of preventive care, reduces beneficiary liability for prescription drug costs, institutes reforms of many payment and delivery systems, and creates the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation.
What is the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act?
The Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1989 changes the way physicians are paid by Medicare to encourage more efficient care. The Act replaces the previous system, under which physicians were reimbursed based on their usual charges, with one based on an estimate of the resources required to provide the services.

Summary
- Medicare, the federal health insurance program for nearly 60 million people ages 65 and over and younger people with permanent disabilities, helps to pay for hospital and physician visits, prescription drugs, and other acute and post-acute care services. This issue brief includes the most recent historical and projected Medicare spending data published in the 2018 annual repor…
Health
- In 2017, Medicare spending accounted for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1). Medicare plays a major role in the health care system, accounting for 20 percent of total national health spending in 2016, 29 percent of spending on retail sales of prescription drugs, 25 percent of spending on hospital care, and 23 percent of spending on physician services.
Cost
- In 2017, Medicare benefit payments totaled $702 billion, up from $425 billion in 2007 (Figure 2). While benefit payments for each part of Medicare (A, B, and D) increased in dollar terms over these years, the share of total benefit payments represented by each part changed. Spending on Part A benefits (mainly hospital inpatient services) decreased ...
Causes
- Slower growth in Medicare spending in recent years can be attributed in part to policy changes adopted as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Budget Control Act of 2011 (BCA). The ACA included reductions in Medicare payments to plans and providers, increased revenues, and introduced delivery system reforms that aimed to improve efficiency and quality of patient care …
Effects
- In addition, although Medicare enrollment has been growing around 3 percent annually with the aging of the baby boom generation, the influx of younger, healthier beneficiaries has contributed to lower per capita spending and a slower rate of growth in overall program spending. In general, Part A trust fund solvency is also affected by the level of growth in the economy, which affects …
Impact
- Prior to 2010, per enrollee spending growth rates were comparable for Medicare and private health insurance. With the recent slowdown in the growth of Medicare spending and the recent expansion of private health insurance through the ACA, however, the difference in growth rates between Medicare and private health insurance spending per enrollee has widened.
Future
- While Medicare spending is expected to continue to grow more slowly in the future compared to long-term historical trends, Medicares actuaries project that future spending growth will increase at a faster rate than in recent years, in part due to growing enrollment in Medicare related to the aging of the population, increased use of services and intensity of care, and rising health care pri…
Funding
- Medicare is funded primarily from general revenues (41 percent), payroll taxes (37 percent), and beneficiary premiums (14 percent) (Figure 7). Part B and Part D do not have financing challenges similar to Part A, because both are funded by beneficiary premiums and general revenues that are set annually to match expected outlays. Expected future increases in spending under Part B and …
Assessment
- Medicares financial condition can be assessed in different ways, including comparing various measures of Medicare spendingoverall or per capitato other spending measures, such as Medicare spending as a share of the federal budget or as a share of GDP, as discussed above, and estimating the solvency of the Medicare Hospital Insurance (Part A) trust fund.
Purpose
- The solvency of the Medicare Hospital Insurance trust fund, out of which Part A benefits are paid, is one way of measuring Medicares financial status, though because it only focuses on the status of Part A, it does not present a complete picture of total program spending. The solvency of Medicare in this context is measured by the level of assets in the Part A trust fund. In years whe…
Benefits
- A number of changes to Medicare have been proposed that could help to address the health care spending challenges posed by the aging of the population, including: restructuring Medicare benefits and cost sharing; further increasing Medicare premiums for beneficiaries with relatively high incomes; raising the Medicare eligibility age; and shifting Medicare from a defined benefit s…