
For Medicare, hospitals received payment of only 87 cents for every dollar spent by hospitals caring for Medicare patients in 2019. For Medicaid, hospitals received payment of only 90 cents for every dollar spent by hospitals caring for Medicaid patients in 2019.
How does Medicare reimburse hospitals?
- asthma
- atrial fibrillation
- cellulitis
- congestive heart failure
- chronic kidney disease
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- diabetes
- gout
- hypertension
- infections
How long will Medicare pay for a hospital stay?
Once the deductible is paid fully, Medicare will cover the remainder of hospital care costs for up to 60 days after being admitted. If you need to stay longer than 60 days within the same benefit period, you’ll be required to pay a daily coinsurance.
How much does Medicare pay for hospital stays?
In 2020, Part A carries a deductible of $1,408 for each benefit period. In addition to these deductible costs, there are also copayment costs associated with hospital stays that are longer than 61 days. For each day between day 61 and 90 of your stay, there is a $352 daily copayment. For lifetime reserve days, there is a $704 daily copayment.
Does Medicare cover hospital visits?
Under Medicare you can be treated as a public patient in a public hospital, at no charge. Medicare will also cover some or all the costs of seeing a GP or specialist outside of hospital, and some pharmaceuticals.
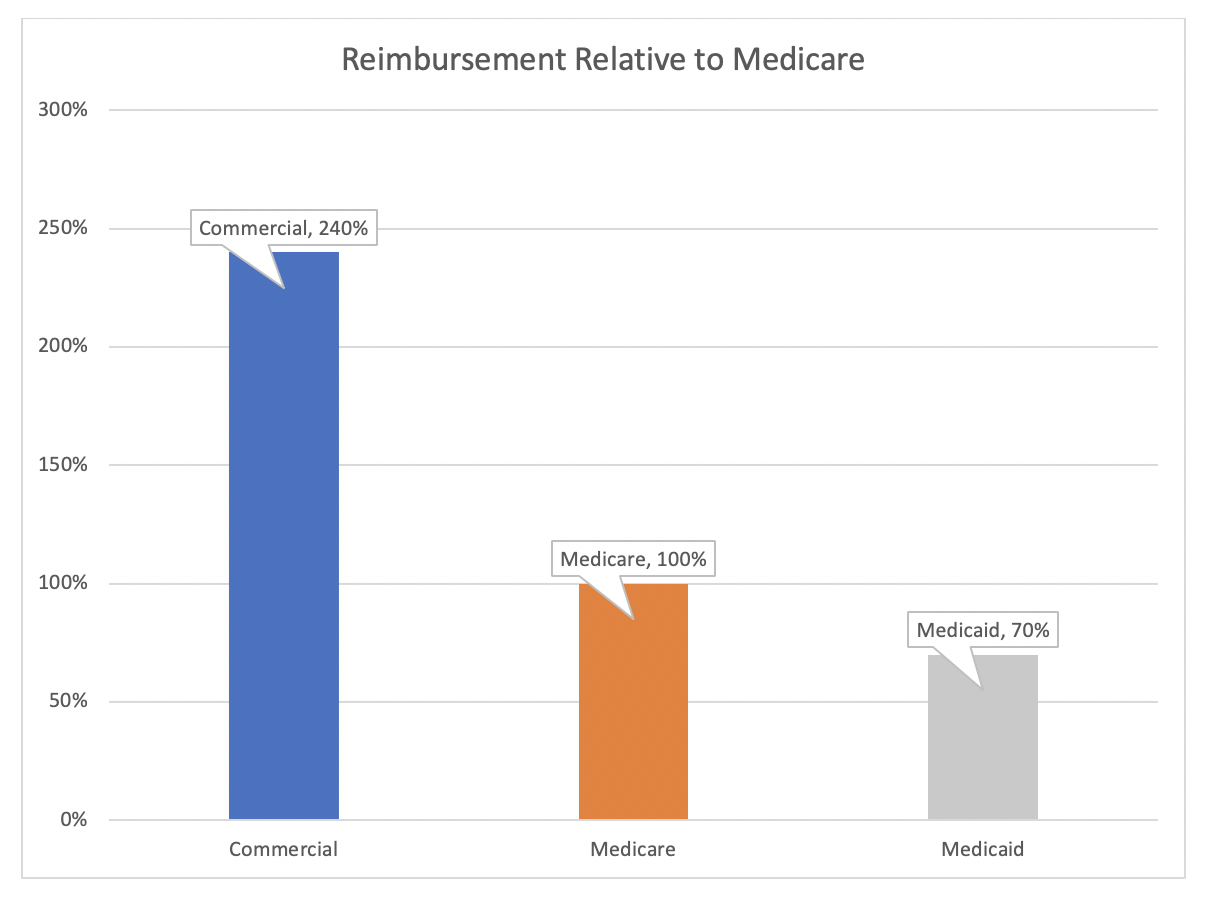
What percent of hospital revenue is from Medicare?
The percentage of the total payor mix from private/self-pay increased from 66.5% in 2018 to 67.4% in 2020. The Medicare percentage decreased from 21.8% to 20.5%.
What percentage of the average hospital budget is funded by Medicare?
Medicare plays a major role in the health care system, accounting for 20 percent of total national health spending in 2017, 30 percent of spending on retail sales of prescription drugs, 25 percent of spending on hospital care, and 23 percent of spending on physician services.
How are hospitals reimbursed by Medicare?
Hospitals are reimbursed for the care they provide Medicare patients by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) using a system of payment known as the inpatient prospective payment system (IPPS).
How are hospitals funded in the US?
Overall, 91 percent of total health and hospital spending ($291 billion) was funded by state and local governments in 2019. The remaining 9 percent ($30 billion) was funded by federal grants to state and local governments.
Do hospitals profit from Medicare?
While the average hospital profit margin on Medicare patients has been relatively steady at negative 10%, it is closer to negative 18% for the three-quarters of hospitals that lost money on their Medicare business.
How much profit does a hospital make?
The average profit margin for hospitals in the U.S. has been around 8% since 2012 even though more than 80% of hospitals admissions in the U.S. are to non-profit hospitals.
How do hospitals generate revenue?
The issue with traditional hospital revenue sources Revenue is earned from either 1) collecting out-of-pocket payments from patients; 2) filing a claim with private insurance companies and being paid via reimbursements; or 3) billing the government, in the case of Medicare and Medicaid.
Why do hospitals charge different prices?
Here's what the New York Times found. Relatively few hospitals have complied with a new law requiring them to publish the previously "secret" prices they negotiate with insurers—but of those that have, a new analysis from the New York Times suggests that prices vary widely based on a given patient's insurance plan.
Why do hospitals charge so much?
Why Is My Hospital Bill So Expensive? The cost of US healthcare is soaring. Elements that contribute to the high cost of medical bills include surprise medical bills, administrative costs, rising doctors' fees, the high cost of surgical procedures and diagnostic tests, and soaring drugs costs.
What is the single largest source of funding for hospitals?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services is the largest governmental source of health coverage funding. Medicare is financed through a combination of general federal taxes, a mandatory payroll tax that pays for Part A (hospital insurance), and individual premiums.
Are hospitals Federal or state funded?
The federal government also has the primary responsibility for keeping people out of hospital – through the primary care system, which includes general practice. South Australia is the latest state to pressure both major parties to commit to greater levels of federal funding for hospitals.
How much do hospitals spend on it?
Seven of the hospitals are in New York and four are in California. Their average total operating expense is nearly $4 trillion....Top 25 hospitals by IT operating budget.Definitive ID588Hospital nameStanford HospitalLocationStanford, CATotal operating expenses$4,734,759,01124 more columns
Why is it so hard to understand how much Medicaid pays hospitals?
Understanding how much Medicaid pays hospitals is difficult because there is no publicly available data source that provides reliable information to measure this nationally across all hospitals.
What is the Medicaid base rate?
In Medicaid, payment rates, sometimes called the “base rate,” are set by state Medicaid agencies for specific services used by patients. In addition, Medicaid also may make supplemental payments to hospitals (Figure 1). 6. Figure 1: Medicaid payment to hospitals consists of base payments as well as supplemental payments.
What payment policy changes could affect Medicaid hospital payments?
However, a number of upcoming policy changes, including reductions in DSH payments and limits on other supplemental payments , will restrict the use of supplemental payments. Federal officials believe that reform of Medicaid supplemental payments is needed to make payment more transparent, targeted, and consistent with delivery system reforms that reduce health care costs, and increase quality and access to care. However, these policy changes are causing concern among hospitals that have long been dependent on Medicaid revenue for their financial viability. 22,23,24 In addition, payment changes are occurring against the backdrop of coverage expansions under the ACA, which are affecting payer mix for some hospitals.
Why is Medicaid important?
Medicaid payments to hospitals and other providers play an important role in these providers’ finances, which can affect beneficiaries’ access to care. States have a great deal of discretion to set payment Medicaid rates for hospitals and other providers. Like other public payers, Medicaid payments have historically been (on average) below costs, ...
How does the ACA affect hospitals?
The ACA included a number of restrictions on Medicare payments for hospitals and expanded coverage has also resulted in markets shifts and new competition. Hospitals also may see shifts in patient acuity, Medicaid payment rate changes or other changes in Medicaid payment policy. In addition, hospitals are constantly implementing strategies to increase revenue (e.g. diversify payer mix) and reduce the costs of providing services. Many safety net hospitals are trying to diversify their payer mix by changing their “safety net image” in the community, competing more aggressively for privately insured patients, retaining the privately insured patients they already have, and expanding services beyond inner city service areas where they are typically located. 21 Thus, Medicaid expansion is just one of many factors that will influence hospitals’ financial viability in the future.
What is the ACA in healthcare?
First, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) is leading to changes in hospital payer mix, especially in states adopting the Medicaid expansion where studies have shown a decline in self-pay discharges ...
How much will the DSH be reduced?
27 These reductions will amount to $43 billion between 2018 and 2025; reductions start at $2 billion in FY 2018 and increase to $8 billion by FY 2025.
How much did Medicare spend in 2019?
If we look at each program individually, Medicare spending grew 6.7% to $799.4 billion in 2019, which is 21% of total NHE, while Medicaid spending grew 2.9% to $613.5 billion in 2019, which is 16% of total NHE. 3 . The CMS projects that healthcare spending is estimated to grow by 5.4% each year between 2019 and 2028.
What is CMS and Medicaid?
CMS works alongside the Department of Labor (DOL) and the U.S. Treasury to enact insurance reform. The Social Security Administration (SSA) determines eligibility and coverage levels. Medicaid, on the other hand, is administered at the state level.
How Does Medicaid Expansion Affect State Budgets?
That’s because the federal government pays the vast majority of the cost of expansion coverage , while expansion generates offsetting savings and , in many states, raises more revenue from the taxes that some states impose on health plans and providers. 19
What is Medicare contribution tax?
It is known as the unearned income Medicare contribution tax. Taxpayers in this category owe an additional 3.8% Medicare tax on all taxable interest, dividends, capital gains, annuities, royalties, and rental properties that are paid outside of individual retirement accounts or employer-sponsored retirement plans .
What is Medicare 2021?
Updated Jun 29, 2021. Medicare, and its means-tested sibling Medicaid, are the only forms of health coverage available to millions of Americans today. They represent some of the most successful social insurance programs ever, serving tens of millions of people including the elderly, younger beneficiaries with disabilities, ...
How much will healthcare cost in 2028?
The CMS projects that healthcare spending is estimated to grow by 5.4% each year between 2019 and 2028. This means healthcare will cost an estimated $6.2 trillion by 2028. Projections indicate that health spending will grow 1.1% faster than GDP each year from 2019 to 2028.
How much did the Affordable Care Act increase in 2019?
1 2 . According to the most recent data available from the CMS, national healthcare expenditure (NHE) grew 4.6% to $3.8 trillion in 2019.
What is Medicare and Medicaid?
Differentiating Medicare and Medicaid. Persons who are eligible for both Medicare and Medicaid are called “dual eligibles”, or sometimes, Medicare-Medicaid enrollees. Since it can be easy to confuse the two terms, Medicare and Medicaid, it is important to differentiate between them. While Medicare is a federal health insurance program ...
How much does Medicare Part B cost?
For Medicare Part B (medical insurance), enrollees pay a monthly premium of $148.50 in addition to an annual deductible of $203. In order to enroll in a Medicare Advantage (MA) plan, one must be enrolled in Medicare Parts A and B. The monthly premium varies by plan, but is approximately $33 / month.
What is the CMS?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, abbreviated as CMS, oversees both the Medicare and Medicaid programs. For the Medicaid program, CMS works with state agencies to administer the program in each state, and for the Medicare program, the Social Security Administration (SSA) is the agency through which persons apply.
What is the income limit for Medicaid in 2021?
In most cases, as of 2021, the individual income limit for institutional Medicaid (nursing home Medicaid) and Home and Community Based Services (HCBS) via a Medicaid Waiver is $2,382 / month. The asset limit is generally $2,000 for a single applicant.
How old do you have to be to apply for medicare?
Citizens or legal residents residing in the U.S. for a minimum of 5 years immediately preceding application for Medicare. Applicants must also be at least 65 years old.
Is Medicare the first payer?
For Medicare covered expenses, such as medical and hospitalization, Medicare is always the first payer (primary payer). If Medicare does not cover the full cost, Medicaid ...
Can you be disqualified from Medicaid if you have assets?
Please note that income and assets over the Medicaid limit (s) in one’s state is not cause for automatic disqualification. This is because there are Medicaid-compliant planning strategies intended to lower one’s countable income and / or assets in order to meet the limit (s). A word of caution: It is vital that assets not be given away a minimum of 5 years (2.5 years in California) prior to the date of one’s Medicaid application. (New York is in the process of implementing a 2.5 year look back for long-term home and community based services). This is because Medicaid has a look-back period in which past transfers are reviewed to ensure an applicant (and / or an applicant’s spouse) has not gifted assets or sold them under fair market value. If this rule has been violated, it is assumed the assets were transferred in order to meet Medicaid’s asset limit and a penalty period of Medicaid disqualification will be calculated.
How much extra do you have to pay for Medicare?
This means that the patient may be required to pay up to 20 percent extra in addition to their standard deductible, copayments, coinsurance payments, and premium payments. While rare, some hospitals completely opt out of Medicare services.
How much higher is Medicare approved?
The amount for each procedure or test that is not contracted with Medicare can be up to 15 percent higher than the Medicare approved amount. In addition, Medicare will only reimburse patients for 95 percent of the Medicare approved amount.
How many DRGs can be assigned to a patient?
Each DRG is based on a specific primary or secondary diagnosis, and these groups are assigned to a patient during their stay depending on the reason for their visit. Up to 25 procedures can impact the specific DRG that is assigned to a patient, and multiple DRGs can be assigned to a patient during a single stay.
What is Medicare reimbursement based on?
Reimbursement is based on the DRGs and procedures that were assigned and performed during the patient’s hospital stay. Each DRG is assigned a cost based on the average cost based on previous visits. This assigned cost provides a simple method for Medicare to reimburse hospitals as it is only a simple flat rate based on the services provided.
What is Medicare Part A?
What Medicare Benefits Cover Hospital Expenses? Medicare Part A is responsible for covering hospital expenses when a Medicare recipient is formally admitted. Part A may include coverage for inpatient surgeries, recovery from surgery, multi-day hospital stays due to illness or injury, or other inpatient procedures.
What does it mean when a provider is not a participating provider?
If a provider is a non-participating provider, it means that they have not signed a contract with Medicare to accept the insurance company’s prices for all procedures, but they do for accept assignment for some. This is mainly due to the fact that Medicare reimbursement amounts are often lower than those received from private insurance companies. For these providers, the patient may be required to pay for the full cost of the visit up front and can then seek personal reimbursement from Medicare afterwards.
Does Medicare cover permanent disability?
Medicare provides coverage for millions of Americans over the age of 65 or individuals under 65 who have certain permanent disabilities. Medicare recipients can receive care at a variety of facilities, and hospitals are commonly used for emergency care, inpatient procedures, and longer hospital stays. Medicare benefits often cover care ...
What is a hospital?
A hospital is an institution primarily engaged in providing, by or under the supervision of physicians, inpatient diagnostic ...
What is an accredited hospital?
Accredited Hospitals - A hospital accredited by a CMS-approved accreditation program may substitute accreditation under that program for survey by the State Survey Agency.
Is a psychiatric hospital a Medicare provider?
Psychiatric hospitals are subject to additional regulations beyond basic hospital conditions of participation. The State Survey Agency evaluates and certifies each participating hospital as a whole for compliance with the Medicare requirements and certifies it as a single provider institution.
Can a hospital have multiple campuses?
Under the Medicare provider-based rules it is possible for ‘one' hospital to have multiple inpatient campuses and outpatient locations. It is not permissible to certify only part of a participating hospital. Psychiatric hospitals that participate in Medicare as a Distinct Part Psychiatric hospital are not required to participate in their entirety.
Do psychiatrists have to participate in Medicare?
Psychiatric hospitals that participate in Medicare as a Distinct Part Psychiatric hospital are not required to participate in their entirety. However, the following are not considered parts of the hospital and are not to be included in the evaluation of the hospital's compliance:
Can a hospital's Medicare provider agreement be terminated?
Should an individual or entity (hospital) refuse to allow immediate access upon reasonable request to either a State Agency , CMS surveyor, a CMS-approved accreditation organization, or CMS contract surveyors, the hospital's Medicare provider agreement may be terminated.
Which pays first, Medicare or Medicaid?
Medicare pays first, and. Medicaid. A joint federal and state program that helps with medical costs for some people with limited income and resources. Medicaid programs vary from state to state, but most health care costs are covered if you qualify for both Medicare and Medicaid. pays second.
What is original Medicare?
Original Medicare. Original Medicare is a fee-for-service health plan that has two parts: Part A (Hospital Insurance) and Part B (Medical Insurance). After you pay a deductible, Medicare pays its share of the Medicare-approved amount, and you pay your share (coinsurance and deductibles). or a.
What is not covered by Medicare?
Offers benefits not normally covered by Medicare, like nursing home care and personal care services
Does Medicare have demonstration plans?
Medicare is working with some states and health plans to offer demonstration plans for certain people who have both Medicare and Medicaid and make it easier for them to get the services they need. They’re called Medicare-Medicaid Plans. These plans include drug coverage and are only in certain states.
Does Medicare cover health care?
If you have Medicare and full Medicaid coverage, most of your health care costs are likely covered.
Does Medicare Advantage cover hospice?
Medicare Advantage Plans provide all of your Part A and Part B benefits, excluding hospice. Medicare Advantage Plans include: Most Medicare Advantage Plans offer prescription drug coverage. . If you have Medicare and full Medicaid, you'll get your Part D prescription drugs through Medicare.
Can you get medicaid if you have too much income?
Even if you have too much income to qualify, some states let you "spend down" to become eligible for Medicaid. The "spend down" process lets you subtract your medical expenses from your income to become eligible for Medicaid. In this case, you're eligible for Medicaid because you're considered "medically needy."
How to find out how much a hospital gets paid?
In order to figure out how much a hospital gets paid for any particular hospitalization, you must first know what DRG was assigned for that hospitalization. In addition, you must know the hospital’s base payment rate, which is also described as the "payment rate per case." You can call the hospital’s billing, accounting, or case management department and ask what its Medicare base payment rate is.
How much did nonprofit hospitals make in 2017?
The largest nonprofit hospitals, however, earned $21 billion in investment income in 2017, 4 and are certainly not struggling financially. The challenge is how to ensure that some hospitals aren't operating in the red under the same payment systems that put other hospitals well into the profitable realm.
How many technologies are eligible for add on payments?
In 2020, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services approved 24 new technologies that are eligible for add-on payments, in addition to the amount determined based on the DRG. 6
Why are hospitals in rural areas losing money?
8 There are also indications that even well-established, heavily trafficked hospitals are losing money in some areas, but that's due in part to an overabundance of high-priced technology, replicated in multiple hospitals in the same geographic location, and hospital spending on facility and infrastructure expansions. 9
When do hospitals assign DRG?
When you've been admitted as an inpatient to a hospital, that hospital assigns a DRG when you're discharged, basing it on the care you needed during your hospital stay. The hospital gets paid a fixed amount for that DRG, regardless of how much money it actually spends treating you.
Does Medicare increase hospital base rate?
Each of these things tends to increase a hospital’s base payment rate. Each October, Medicare assigns every hospital a new base payment rate. In this way, Medicare can tweak how much it pays any given hospital, based not just on nationwide trends like inflation, but also on regional trends.
Does Medicare factor in blended rate?
Other things that Medicare factors into your hospital’s blended rate determination include whether or not it’s a teaching hospital with residents and interns, whether or not it’s in a rural area, and whether or not it cares for a disproportionate share of the poor and uninsured population. Each of these things tends to increase a hospital’s base payment rate.
What if Your Doctor Only Accepts Medicare and Not Medicaid?
Doctors are not required to accept Medicaid payment. Why? It requires more paperwork for them, and Medicaid reimbursements can be less than other forms of insurance. What can you do?
What is the maximum amount of money you can make on Medicare in 2021?
QI is another category in which Medicaid will only pay your Medicare Part B premium. In 2021, the maximum monthly income is $1,469 for an individual and $1,980 for a couple. For 2021, QI recipients, the maximum asset level allowed is $7,970 for an individual and $11,960 for couples.
How Do You Qualify for Medicaid?
You qualify for Medicaid based on your finances. Medicaid needs to see difficulties with one of two things:
What is QMB in medicaid?
Qualifying Medicaid Beneficiary (QMB) Only. This is for people who are not eligible to receive full Medicaid benefits. Medicaid will pay the recipient’s Medicare Part A premiums (if any). It will also pay their Medicare Part B premium for them.
What is the maximum income for Medicare Part B 2021?
If you’re an SLMB recipient, Medicaid will pay your Medicare Part B premium. In 2021, the maximum monthly income is $1,308 for an individual and $1,762 for a couple. For 2021, the maximum asset level is $7,970 for an individual and $11,960 for a couple.
What is dual eligible for medicaid?
If you have both Medicare and Medicaid coverage, then your status is called dual-eligible or Medicare dual eligible.
How much is Medicare Part B in 2021?
Everybody must pay a Medicare Part B premium of $148.50 monthly in 2021, regardless of income. Can’t afford it? If you qualify for Medicaid, it may pay the premium for you.
How much is healthcare spending?
Health care spending in the United States is high and growing faster than the economy. In 2018, health expenditures accounted for 17.7% of the national gross domestic product (GDP), and are projected to grow to a fifth of the national GDP by 2027. 1 Several recent health reform proposals aim to reduce future spending on health care while also expanding coverage to the nearly 28 million Americans who remain uninsured, and providing a more affordable source of coverage for people who struggle to pay their premiums. 2 Some have argued that these goals can be achieved by aligning provider payments more closely with Medicare rates, whether in a public program, like Medicare-for-All, a national or state-based public option, or through state rate-setting initiatives. 3,4,5,6,7,8 9,10,11
What percentage of healthcare expenditures are private insurance?
Private insurers currently play a dominant role in the U.S. In 2018, private insurance accounted for more than 40% of expenditures on both hospital care and physician services.
What is private insurance claims data?
As noted earlier, researchers are typically at a disadvantage without access to comprehensive private insurance payments from all insurers, or a sample that is representative of all private insurance claims to compare with publicly reported Medicare data. Studies that use data from larger insurers that have exceptionally strong market power relative to physicians in many markets, such as the Ginsburg 2010 study, may observe relatively low private payments. 68 A similar effect may be seen in the annual analyses conducted by MedPAC, which are based on claims data from only one large commercial PPO that operates nationwide. 69 In contrast, Song’s analysis makes use of data from the Truven MarketScan commercial claims database (now known as IBM MarketScan), which reflects over 300 private payers. 70 Compared to studies that use data only from a few large insurers, this dataset contains claims paid by several smaller insurers that do not have nationwide market penetration.
How many studies have addressed payment rates for hospitals?
Of these 19 studies, 14 addressed payments to hospitals, eight of which addressed payments for inpatient hospital services, five addressed payments for outpatient services, and seven reported relative payment rates for both types of hospital services combined, with some overlap across studies. Eight studies addressed payment rates for physician services. The full search methodology is described in the Methods section.
What is the difference between Medicare and private insurance?
The difference between private and Medicare rates was greater for outpatient than inpatient hospital services, which averaged 264% and 189% of Medicare rates overall, respectively. For physician services, private insurance paid 143% of Medicare rates, on average, ranging from 118% to 179% of Medicare rates across studies.
What is the literature review of Medicare?
This literature review summarizes findings from 19 studies that compare payment rates paid by private insurers and Medicare for hospital care and physician services, using data pertaining to the period from 2010 to the present. Studies that only addressed other types of providers such as home health services and long-term care facilities were excluded. The studies reviewed in this brief are limited to those that compare private insurance rates with rates under traditional fee-for-service Medicare; studies that addressed only payments by Medicare Advantage plans were excluded.
How are private insurance rates determined?
By contrast, private insurers’ payment rates are typically determined through negotiations with providers, and so vary depending on market conditions, such as the bargaining power of individual providers relative to insurers in a community.

Introduction
Background
- How Does Medicaid Pay Hospitals?
Hospital payment for a particular patient or service is usually different than the charge for that service (i.e., prices set by the hospital) or the cost to the hospital of providing the service (i.e., actual incurred expenses). In Medicaid, payment rates, sometimes called the “base rate,” are set … - How Much Does Medicaid Pay Hospitals?
Since payment rates are either negotiated (with health plans) or set by the federal government for Medicare or state governments for Medicaid fee-for-service, payments that hospitals receive for patient care do not necessarily reflect what hospitals charge for those services or the cost of pr…
How Has The Medicaid Expansion Affected Hospital Finances?
- Expanded health insurance coverage through the ACA (both Medicaid and private insurance) is having a major impact on hospital payer mix for many hospitals. A number of reports show increases in Medicaid discharges and declines in uninsured or self-pay discharges for hospitals located in states that implemented the Medicaid expansion. In contrast, hospitals located in stat…
What Payment Policy Changes Could Affect Medicaid Hospital Payments?
- Hospitals are facing several policy changes that may affect Medicaid payments. Over time, state budget pressures have resulted in an increasing reliance on supplemental payments (versus base payments) to finance Medicaid hospital services. However, a number of upcoming policy changes, including reductions in DSH payments and limits on other supplemental payments, wil…
Conclusion
- At this point, it is unclear how recent and upcoming policy changes in Medicaid will affect the financial viability of hospitals. Early analysis of the Medicare Care Report data show national declines in uncompensated care, especially in expansion states, although the data do not permit reliable estimates of trends in Medicaid payment amounts. However, hospital margins are influe…