How much would 'Medicare for all' cost taxpayers?
- Americans spend 160% more on drugs vs. the Netherlands, and about 36% more than the next-highest-spending countries (Japan and Canada). ...
- The US has a big obesity problem, ranking first in the world. 28.7% of Americans are obese versus 11.8% of people in the Netherlands. ...
- Hospital costs in the US are the highest in the world at $10,300 per stay. ...
Does Medicare have monthly premiums?
Most people don't pay a monthly premium for Part A (sometimes called " premium-free Part A "). If you buy Part A, you'll pay up to $471 each month in 2021 ($499 in 2022). If you paid Medicare taxes for less than 30 quarters, the standard Part A premium is $471 ($499 in 2022).
What is the average cost of Medicare per month?
With Medicare Advantage plans, Medicare pays a fixed amount toward your care each month to the private companies providing Medicare Part C plans. While the average cost for Medicare Part C is $25 per month, it’s possible to get a Medicare Advantage plan with a $0 monthly premium.
What percentage of the budget is Medicare?
Medicare spending was 15 percent of total federal spending in 2018, and is projected to rise to 18 percent by 2029. Based on the latest projections in the 2019 Medicare Trustees report, the...
How much did Medicare spend?
What is the agency that administers Medicare?
What is the largest share of health spending?
Does Medicare pay payroll taxes?

How much money did the government spend on Medicare in 2021?
$696 billionWhat is the spending on Medicare? In FY 2021 the federal government spent $696 billion on Medicare.
How much did us spend on Medicare in 2020?
$829.5 billionMedicare spending totaled $829.5 billion in 2020, representing 20% of total health care spending. Medicare spending increased in 2020 by 3.5%, compared to 6.9% growth in 2019. Fee-for-service expenditures declined 5.3% in 2020 down from growth of 2.1% in 2019.
Does the government pay for Medicare?
Medicare is federally administered and covers older or disabled Americans, while Medicaid operates at the state level and covers low-income families and some single adults. Funding for Medicare is done through payroll taxes and premiums paid by recipients. Medicaid is funded by the federal government and each state.
How much did the government spend on Medicare in 2019?
$630 billionLooking ahead, CBO projects Medicare spending will double over the next 10 years, measured both in total and net of income from premiums and other offsetting receipts. CBO projects net Medicare spending to increase from $630 billion in 2019 to $1.3 trillion in 2029 (Figure 6).
What percent of the federal budget is Medicare?
12 percentMedicare accounts for a significant portion of federal spending. In fiscal year 2020, the Medicare program cost $776 billion — about 12 percent of total federal government spending. Medicare was the second largest program in the federal budget last year, after Social Security.
Does Medicare run a deficit?
Last year, the Medicare Part A fund ran a deficit of $5.8 billion, and that excess of spending over revenue is expected to continue until it finally runs dry.
Is Medicare funded by income tax?
Medicare is funded by the Social Security Administration. Which means it's funded by taxpayers: We all pay 1.45% of our earnings into FICA - Federal Insurance Contributions Act, if you're into deciphering acronyms - which go toward Medicare.
Where does Medicare get its money?
Funding for Medicare, which totaled $888 billion in 2021, comes primarily from general revenues, payroll tax revenues, and premiums paid by beneficiaries (Figure 1). Other sources include taxes on Social Security benefits, payments from states, and interest.
Is Medicare underfunded?
Politicians promised you benefits, but never funded them.
HOW MUCH OF US taxes go to healthcare?
Tax-funded health expenditures totaled $1.877 trillion in 2013 and are projected to increase to $3.642 trillion in 2024. Government's share of overall health spending was 64.3% of national health expenditures in 2013 and will rise to 67.1% in 2024.
Who paid for Medicare?
Medicare is funded by the Social Security Administration. Which means it's funded by taxpayers: We all pay 1.45% of our earnings into FICA - Federal Insurance Contributions Act - which go toward Medicare.
What percentage of healthcare is paid by the government?
Government Now Pays For Nearly 50 Percent Of Health Care Spending, An Increase Driven By Baby Boomers Shifting Into Medicare. A new CMS report projects that U.S. health care spending will surpass $5.9 trillion in 2027, growing to represent more than 19 percent of the economy.
How is Medicare Part D funded?
Part D is financed by general revenues (71 percent), beneficiary premiums (17 percent), and state payments for beneficiaries dually eligible for Medicare and Medicaid (12 percent). Higher-income enrollees pay a larger share of the cost of Part D coverage, as they do for Part B.
How fast will Medicare spending grow?
On a per capita basis, Medicare spending is also projected to grow at a faster rate between 2018 and 2028 (5.1 percent) than between 2010 and 2018 (1.7 percent), and slightly faster than the average annual growth in per capita private health insurance spending over the next 10 years (4.6 percent).
How much does Medicare cost?
In 2018, Medicare spending (net of income from premiums and other offsetting receipts) totaled $605 billion, accounting for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1).
Why is Medicare spending so high?
Over the longer term (that is, beyond the next 10 years), both CBO and OACT expect Medicare spending to rise more rapidly than GDP due to a number of factors, including the aging of the population and faster growth in health care costs than growth in the economy on a per capita basis.
What has changed in Medicare spending in the past 10 years?
Another notable change in Medicare spending in the past 10 years is the increase in payments to Medicare Advantage plans , which are private health plans that cover all Part A and Part B benefits, and typically also Part D benefits.
How is Medicare's solvency measured?
The solvency of Medicare in this context is measured by the level of assets in the Part A trust fund. In years when annual income to the trust fund exceeds benefits spending, the asset level increases, and when annual spending exceeds income, the asset level decreases.
How much will Medicare per capita increase in 2028?
Medicare per capita spending is projected to grow at an average annual rate of 5.1 percent over the next 10 years (2018 to 2028), due to growing Medicare enrollment, increased use of services and intensity of care, and rising health care prices.
Would Medicare For All Save Billions Or Cost Billions
How much would a Medicare for all plan, like the kind endorsed by the Democratic presidential candidates Bernie Sanders and Elizabeth Warren, change health spending in the United States?
What Does Medicare Part C Cover
A Medicare Part C plan will cover the same medical services as Original Medicare. That means plans will cover doctors, hospital care and many other types of health services. Coverage includes:
Income Related Adjustment Amounts
The cost of your premium can be affected by your income level. The higher your income, the more youll be asked to pay in premiums. The income used to determine your premium payment is based on the income you reported on your IRS tax return from two years prior. See the table below.5
The Medicare Part D Donut Hole Coverage Gap
After 2020, Medicare Part D plans have a shrunken coverage gap, or donut hole, which represents a temporary limit on what the plan will cover for prescription drugs.
Nhe By Age Group And Gender Selected Years 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010 2012 And 201
Per person personal health care spending for the 65 and older population was $19,098 in 2014, over 5 times higher than spending per child and almost 3 times the spending per working-age person .
Reimbursement For Part A Services
For institutional care, such as hospital and nursing home care, Medicare uses prospective payment systems. In a prospective payment system, the health care institution receives a set amount of money for each episode of care provided to a patient, regardless of the actual amount of care.
Comparison With Private Insurance
Medicare differs from private insurance available to working Americans in that it is a social insurance program. Social insurance programs provide statutorily guaranteed benefits to the entire population . These benefits are financed in significant part through universal taxes.
How does Medicare work?
Although we often use the name "Medicare" as a blanket term, there are actually several distinct Medicare programs. While there are some similarities, such as all falling under the umbrella of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), there are a number of important differences, including funding.
What does Original Medicare include?
Original Medicare refers to Medicare Part A, hospital insurance, and Medicare Part B, health insurance. These are the parts of Medicare that are administered and paid for directly by the federal government. The other two parts of Medicare, C and D, receive input, funding, and regulation by the U.S.
Medicare Part C
Medicare Part C is more commonly known as Medicare Advantage. These plans are provided by private insurance companies working within guidelines established by United States government.
Medicare Supplement Plans
Medicare Supplement policies, more commonly known as Medigap, are private insurance plans that help pay your out-of-pocket fees under Original Medicare. These plans are only offered by private insurance companies, although they are regulated by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
The Medicare Tax
The government's main funding source for Medicare is the Medicare Tax. This is a payroll tax that workers and employers split. It comes to a total of 2.9% of an individual's wages.
The Social Security Administration
The Social Security Administration (SSA) processes and holds the funds collected by the Medicare Tax. As the name implies, SSA also processes payments related Social Security and the Social Security Tax.
Where is the Medicare Tax money stored?
The money that funds Medicare is stored in two trust funds. These monies are held by the United States Treasury and can only be used for Medicare. We look at each fund individually below.
What percentage of Medicare is home health?
Medicare is a major player in our nation's health system and is the bedrock of care for millions of Americans. The program pays for about one-fifth of all healthcare spending in the United States, including 32 percent of all prescription drug costs and 39 percent of home health spending in the United States — which includes in-home care by skilled nurses to support recovery and self-sufficiency in the wake of illness or injury. 4
How much of Medicare was financed by payroll taxes in 1970?
In 1970, payroll taxes financed 65 percent of Medicare spending.
How is Medicare self-financed?
One of the biggest misconceptions about Medicare is that it is self-financed by current beneficiaries through premiums and by future beneficiaries through payroll taxes. In fact, payroll taxes and premiums together only cover about half of the program’s cost.
What are the benefits of Medicare?
Medicare is a federal program that provides health insurance to people who are age 65 and older, blind, or disabled. Medicare consists of four "parts": 1 Part A pays for hospital care; 2 Part B provides medical insurance for doctor’s fees and other medical services; 3 Part C is Medicare Advantage, which allows beneficiaries to enroll in private health plans to receive Part A and Part B Medicare benefits; 4 Part D covers prescription drugs.
How is Medicare funded?
Medicare is financed by two trust funds: the Hospital Insurance (HI) trust fund and the Supplementary Medical Insurance (SMI) trust fund. The HI trust fund finances Medicare Part A and collects its income primarily through a payroll tax on U.S. workers and employers. The SMI trust fund, which supports both Part B and Part D, ...
What percentage of GDP will Medicare be in 2049?
In fact, Medicare spending is projected to rise from 3.0 percent of GDP in 2019 to 6.1 percent of GDP by 2049. That increase in spending is largely due to the retirement of the baby boomers (those born between 1944 and 1964), longer life expectancies, and healthcare costs that are growing faster than the economy.
How much did Medicare cost in 2019?
In 2019, it cost $644 billion — representing 14 percent of total federal spending. 1. Medicare has a large impact on the overall healthcare market: it finances about one-fifth of all health spending and about 40 percent of all home health spending. In 2019, Medicare provided benefits to 19 percent of the population. 2.
How much did Medicare spend in 2019?
If we look at each program individually, Medicare spending grew 6.7% to $799.4 billion in 2019, which is 21% of total NHE, while Medicaid spending grew 2.9% to $613.5 billion in 2019, which is 16% of total NHE. 3 . The CMS projects that healthcare spending is estimated to grow by 5.4% each year between 2019 and 2028.
What is CMS and Medicaid?
CMS works alongside the Department of Labor (DOL) and the U.S. Treasury to enact insurance reform. The Social Security Administration (SSA) determines eligibility and coverage levels. Medicaid, on the other hand, is administered at the state level.
How is Medicare supplemental insurance fund funded?
Medicare's supplementary medical insurance trust fund is funded by Congress, premiums from people enrolled in Medicare, and other avenues, such as investment income from the trust fund. These funds pay for Medicare Part B benefits, Part D benefits, and program administration expenses.
How is Medicare funded?
How Medicare Is Funded. Medicare is funded by two trust funds that can only be used for Medicare. The hospital insurance trust fund is funded by payroll taxes paid by employees, employers, and the self-employed. These funds are used to pay for Medicare Part A benefits. 11 .
What is Medicare contribution tax?
It is known as the unearned income Medicare contribution tax. Taxpayers in this category owe an additional 3.8% Medicare tax on all taxable interest, dividends, capital gains, annuities, royalties, and rental properties that are paid outside of individual retirement accounts or employer-sponsored retirement plans .
What is the Medicare tax rate for 2013?
On Jan. 1, 2013, the ACA also imposed an additional Medicare tax of 0.9% on all income above a certain level for high-income taxpayers. Single filers have to pay this additional amount on all earned income they receive above $200,000 and married taxpayers filing jointly owe it on earned income in excess of $250,000.
What is Medicare 2021?
Updated Jun 29, 2021. Medicare, and its means-tested sibling Medicaid, are the only forms of health coverage available to millions of Americans today. They represent some of the most successful social insurance programs ever, serving tens of millions of people including the elderly, younger beneficiaries with disabilities, ...
Medicare Advantage Plan (Part C)
Monthly premiums vary based on which plan you join. The amount can change each year.
Medicare Supplement Insurance (Medigap)
Monthly premiums vary based on which policy you buy, where you live, and other factors. The amount can change each year.
How much did the NHE increase in 2019?
NHE grew 4.6% to $3.8 trillion in 2019, or $11,582 per person, and accounted for 17.7% of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Medicare spending grew 6.7% to $799.4 billion in 2019, or 21 percent of total NHE. Medicaid spending grew 2.9% to $613.5 billion in 2019, or 16 percent of total NHE.
What was the per person spending for 2014?
In 2014, per person spending for male children (0-18) was 9 percent more than females. However, for the working age and elderly groups, per person spending for females was 26 and 7 percent more than for males. For further detail see health expenditures by age in downloads below.
How much did hospital expenditures grow in 2019?
Hospital expenditures grew 6.2% to $1,192.0 billion in 2019, faster than the 4.2% growth in 2018. Physician and clinical services expenditures grew 4.6% to $772.1 billion in 2019, a faster growth than the 4.0% in 2018. Prescription drug spending increased 5.7% to $369.7 billion in 2019, faster than the 3.8% growth in 2018.
How much did prescription drug spending increase in 2019?
Prescription drug spending increased 5.7% to $369.7 billion in 2019, faster than the 3.8% growth in 2018. The largest shares of total health spending were sponsored by the federal government (29.0 percent) and the households (28.4 percent). The private business share of health spending accounted for 19.1 percent of total health care spending, ...
How much did Utah spend on health care in 2014?
In 2014, per capita personal health care spending ranged from $5,982 in Utah to $11,064 in Alaska. Per capita spending in Alaska was 38 percent higher than the national average ($8,045) while spending in Utah was about 26 percent lower; they have been the lowest and highest, respectively, since 2012.
How much did Medicaid spend in 2019?
Medicaid spending grew 2.9% to $613.5 billion in 2019, or 16 percent of total NHE. Private health insurance spending grew 3.7% to $1,195.1 billion in 2019, or 31 percent of total NHE. Out of pocket spending grew 4.6% to $406.5 billion in 2019, or 11 percent of total NHE.
Which region has the lowest health care spending per capita?
In contrast, the Rocky Mountain and Southwest regions had the lowest levels of total personal health care spending per capita ($6,814 and $6,978, respectively) with average spending roughly 15 percent lower than the national average.
What is managed care expenditure?
Managed care expenditures cover the same services that are delivered via fee-for-service. Data do not permit allocation of managed care expenditures to the different service categories.
Who funds Medicaid and CHIP?
The federal government and states jointly fund and administer Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP). The following data present a snapshot of recent annual expenditure statistics, such as expenditures by service category and state.
How much did Medicare spend?
Medicare spending increased 6.4% to $750.2 billion, which is 21% of the total national health expenditure. The rise in Medicaid spending was 3% to $597.4 billion, which equates to 16% of total national health expenditure.
What is the agency that administers Medicare?
To grasp the magnitude of the government expenditure for Medicare benefits, following are 2018 statistics from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), which is the agency that administers Medicare:
What is the largest share of health spending?
The biggest share of total health spending was sponsored by the federal government (28.3%) and households (28.4%) while state and local governments accounted for 16.5%. For 2018 to 2027, the average yearly spending growth in Medicare (7.4%) is projected to exceed that of Medicaid and private health insurance.
Does Medicare pay payroll taxes?
Additionally, Medicare recipients have seen their share of payroll taxes for Medicare deducted from their paychecks throughout their working years.
Summary
- Medicare, the federal health insurance program for nearly 60 million people ages 65 and over and younger people with permanent disabilities, helps to pay for hospital and physician visits, prescription drugs, and other acute and post-acute care services. This issue brief includes the most recent historical and projected Medicare spending data published in the 2018 annual repor…
Health
- In 2017, Medicare spending accounted for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1). Medicare plays a major role in the health care system, accounting for 20 percent of total national health spending in 2016, 29 percent of spending on retail sales of prescription drugs, 25 percent of spending on hospital care, and 23 percent of spending on physician services.
Cost
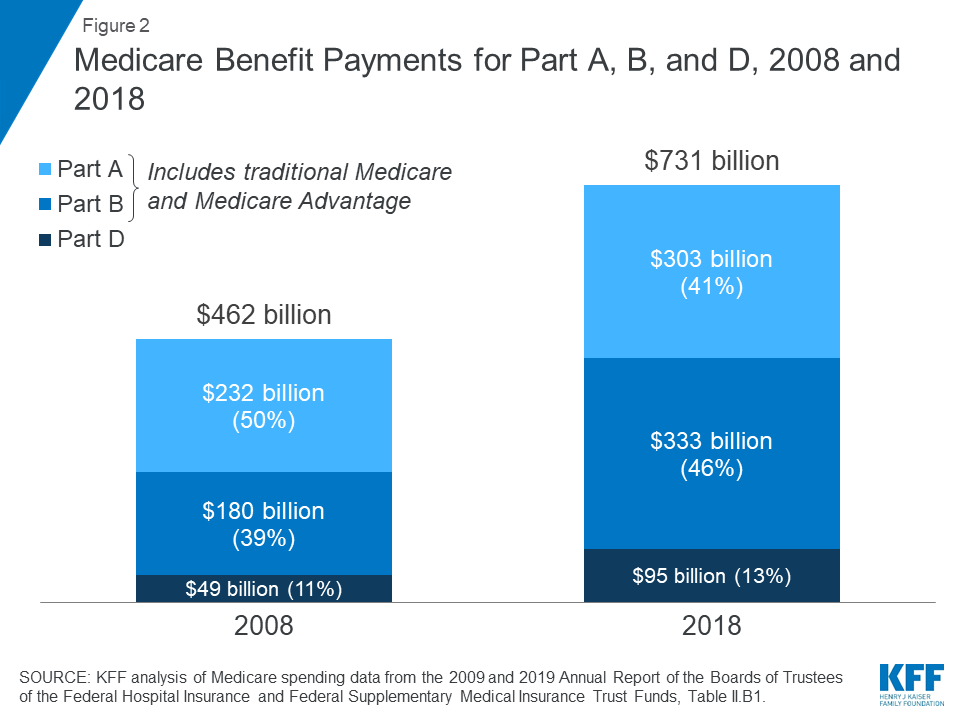
- In 2017, Medicare benefit payments totaled $702 billion, up from $425 billion in 2007 (Figure 2). While benefit payments for each part of Medicare (A, B, and D) increased in dollar terms over these years, the share of total benefit payments represented by each part changed. Spending on Part A benefits (mainly hospital inpatient services) decreased ...
Causes
- Slower growth in Medicare spending in recent years can be attributed in part to policy changes adopted as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Budget Control Act of 2011 (BCA). The ACA included reductions in Medicare payments to plans and providers, increased revenues, and introduced delivery system reforms that aimed to improve efficiency and quality of patient care …
Effects
- In addition, although Medicare enrollment has been growing around 3 percent annually with the aging of the baby boom generation, the influx of younger, healthier beneficiaries has contributed to lower per capita spending and a slower rate of growth in overall program spending. In general, Part A trust fund solvency is also affected by the level of growth in the economy, which affects …
Impact
- Prior to 2010, per enrollee spending growth rates were comparable for Medicare and private health insurance. With the recent slowdown in the growth of Medicare spending and the recent expansion of private health insurance through the ACA, however, the difference in growth rates between Medicare and private health insurance spending per enrollee has widened.
Future
- While Medicare spending is expected to continue to grow more slowly in the future compared to long-term historical trends, Medicares actuaries project that future spending growth will increase at a faster rate than in recent years, in part due to growing enrollment in Medicare related to the aging of the population, increased use of services and intensity of care, and rising health care pri…
Funding
- Medicare is funded primarily from general revenues (41 percent), payroll taxes (37 percent), and beneficiary premiums (14 percent) (Figure 7). Part B and Part D do not have financing challenges similar to Part A, because both are funded by beneficiary premiums and general revenues that are set annually to match expected outlays. Expected future increases in spending under Part B and …
Assessment
- Medicares financial condition can be assessed in different ways, including comparing various measures of Medicare spendingoverall or per capitato other spending measures, such as Medicare spending as a share of the federal budget or as a share of GDP, as discussed above, and estimating the solvency of the Medicare Hospital Insurance (Part A) trust fund.
Purpose
- The solvency of the Medicare Hospital Insurance trust fund, out of which Part A benefits are paid, is one way of measuring Medicares financial status, though because it only focuses on the status of Part A, it does not present a complete picture of total program spending. The solvency of Medicare in this context is measured by the level of assets in the Part A trust fund. In years whe…
Benefits
- A number of changes to Medicare have been proposed that could help to address the health care spending challenges posed by the aging of the population, including: restructuring Medicare benefits and cost sharing; further increasing Medicare premiums for beneficiaries with relatively high incomes; raising the Medicare eligibility age; and shifting Medicare from a defined benefit s…