The Medicare reimbursement rates for traditional medical procedures and services are mostly established at 80 percent of the cost for services provided. Some medical providers are reimbursed at different rates.
Full Answer
How much do tax payers pay for Medicare?
The ACA study showed how much federal healthcare payments are below actual costs to the dollar. Medicare paid hospitals only 88 cents for every dollar spent by the hospital for a Medicare patient care in 2015. More troubling for providers is that Medicare underpayments may also be greater for hospitals in the near future.
Does Medicare have a premium payment?
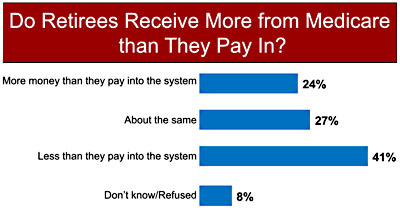
Mar 20, 2015 · out of $597 billion in total benefit spending in 2014, medicare paid $376 billion (63%) for benefits delivered by health care providers in traditional medicare. 2 these providers include hospitals...
What is the average cost of Medicare per month?
Because you have met your deductible for the year, you will split the Medicare-approved amount with Medicare in order to pay your doctor for the appointment. Typically, you will pay 20 percent of the Medicare-approved amount, and Medicare will pay the remaining 80 percent. Your 20 percent amount is called Medicare Part B coinsurance.
Is there a monthly premium for Medicare?
Apr 15, 2020 · The Medicare reimbursement rates for traditional medical procedures and services are mostly established at 80 percent of the cost for services provided. Some medical providers are reimbursed at different rates. Clinical nurse specialists are paid 85 percent for most of their billed services and clinical social workers are paid 75 percent for their billed services.
How Much Does Medicare pay a physician?
What percentage does Medicare pay to the providers?
How do doctors get paid by Medicare?
What amount does Medicare pay?
| If your yearly income in 2020 (for what you pay in 2022) was | You pay each month (in 2022) | |
|---|---|---|
| File individual tax return | File joint tax return | |
| $91,000 or less | $182,000 or less | $170.10 |
| above $91,000 up to $114,000 | above $182,000 up to $228,000 | $238.10 |
| above $114,000 up to $142,000 | above $228,000 up to $284,000 | $340.20 |
Can a provider charge more than Medicare allows?
What percentage of doctors do not accept Medicare?
What is a Medicare provider?
Does Medicare pay for functional medicine doctors?
Does Medicare pay hospitals?
How much is monthly Medicare premium?
How much does Medicare cost the government?
Who pays for Medicare Part A?
If you don't qualify for premium-free Part A, you can buy Part A. People who buy Part A will pay a premium of either $274 or $499 each month in 2022 depending on how long they or their spouse worked and paid Medicare taxes.
How much does Medicare pay for outpatient therapy?
After your deductible is met, you typically pay 20% of the Medicare-approved amount for most doctor services (including most doctor services while you're a hospital inpatient), outpatient therapy, and Durable Medical Equipment (DME) Part C premium. The Part C monthly Premium varies by plan.
How much will Medicare cost in 2021?
Most people don't pay a monthly premium for Part A (sometimes called " premium-free Part A "). If you buy Part A, you'll pay up to $471 each month in 2021. If you paid Medicare taxes for less than 30 quarters, the standard Part A premium is $471. If you paid Medicare taxes for 30-39 quarters, the standard Part A premium is $259.
How long does a SNF benefit last?
The benefit period ends when you haven't gotten any inpatient hospital care (or skilled care in a SNF) for 60 days in a row. If you go into a hospital or a SNF after one benefit period has ended, a new benefit period begins. You must pay the inpatient hospital deductible for each benefit period. There's no limit to the number of benefit periods.
How much is the Part B premium for 91?
Part B premium. The standard Part B premium amount is $148.50 (or higher depending on your income). Part B deductible and coinsurance.
What is Medicare Advantage Plan?
A Medicare Advantage Plan (Part C) (like an HMO or PPO) or another Medicare health plan that offers Medicare prescription drug coverage. Creditable prescription drug coverage. In general, you'll have to pay this penalty for as long as you have a Medicare drug plan.
How much is coinsurance for days 91 and beyond?
Days 91 and beyond: $742 coinsurance per each "lifetime reserve day" after day 90 for each benefit period (up to 60 days over your lifetime). Beyond Lifetime reserve days : All costs. Note. You pay for private-duty nursing, a television, or a phone in your room.
What is a copayment?
A copayment is usually a set amount, rather than a percentage. For example, you might pay $10 or $20 for a doctor's visit or prescription drug.
How does Medicare pay for hospital discharge?
Inpatient hospitals (acute care): Medicare pays hospitals per beneficiary discharge, using the Inpatient Prospective Payment System. The base rate for each discharge corresponds to one of over 700 different categories of diagnoses—called Diagnosis Related Groups (DRGs)—that are further adjusted for patient severity. DRGs that are likely to incur more intense levels of care and/or longer lengths of stay are assigned higher payments. Medicare’s payments to hospitals also account for a portion of hospitals’ capital and operating expenses. Some hospitals receive added payments, such as teaching hospitals and hospitals with higher shares of low-income beneficiaries. Recent Medicare policies also reduce payments to some hospitals, including hospitals that have relatively higher Medicare readmission rates following previous hospitalizations for certain conditions.
How does Medicare use prospective payment systems?
In general, these systems require that Medicare pre-determine a base payment rate for a given unit of service (e.g., a hospital stay, an episode of care, a particular service). Then, based on certain variables, such as the provider’s geographic location and the complexity of the patient receiving the service, Medicare adjusts its payment for each unit of service provided (see Appendix 4: Medicare Payments to Providers ). For most payment systems, Medicare updates payment rates annually to account for inflation adjustments. The main features of hospital, physician, outpatient, and skilled nursing facility payment systems (altogether accounting for almost three-quarters of spending in traditional Medicare) are described below:
What is the SGR for Medicare?
Under current law, Medicare’s physician fee-schedule payments are subject to a formula, called the Sustainable Growth Rate (SGR) system, enacted in 1987 as a tool to control spending. For more than a decade this formula has called for cuts in physician payments, reaching as high as 24 percent.
Does Medicare pay for nurse practitioners?
Physicians and other health professionals: Medicare reimburses physicians and other health professionals (e.g., nurse practitioners) based on a fee-schedule for over 7,000 services. Payment rates for these services are determined based on the relative, average costs of providing each to a Medicare patient, and then adjusted to account for other provider expenses, including malpractice insurance and office-based practice costs. This system, known as the Resource-Based Relative Value Update Scale (RBRVS), has been in place since 1992. Increases to Medicare’s payments include bonuses to those practicing in designated shortage areas. In general, health professionals who are not physicians but bill Medicare independently (e.g., nurse practitioners) receive a 15 percent reduction in payment.
Does Medicare have a fee for service?
Current payment systems in traditional Medicare have evolved over the last several decades, but have maintained a fee-for-service payment structure for most types of providers. In many cases, private insurers have modeled their payment systems on traditional Medicare, including those used for hospitals and physicians.
Does Medicare pay for outpatient services?
Hospital outpatient departments: Medicare pays hospitals for ambulatory services provided in outpatient departments, based on the classification of each service into more than 750 categories with similar expected costs. Final determination of Medicare payments for outpatient department services is complex and incorporates both individual service payments and payments “packaged” with other services, partial hospitalization payments, as well as numerous exceptions. Hospitals may receive additional payments for certain outpatient department services, such as specified drugs and devices; unusually costly (outlier) services; and adjustments for some rural hospitals and cancer hospitals.
How much does Medicare pay for a doctor appointment?
Typically, you will pay 20 percent of the Medicare-approved amount, and Medicare will pay the remaining 80 percent .
How much can a provider charge for not accepting Medicare?
By law, a provider who does not accept Medicare assignment can only charge you up to 15 percent over the Medicare-approved amount. Let’s consider an example: You’ve been feeling some pain in your shoulder, so you make an appointment with your primary care doctor.
What is Medicare Supplement Insurance?
Some Medicare Supplement Insurance plans (also called Medigap) provide coverage for the Medicare Part B excess charges that may result when a health care provider does not accept Medicare assignment.
What is Medicare Part B excess charge?
What are Medicare Part B excess charges? You are responsible for paying any remaining difference between the Medicare-approved amount and the amount that your provider charges. This difference in cost is called a Medicare Part B excess charge. By law, a provider who does not accept Medicare assignment can only charge you up to 15 percent over ...
What is Medicare approved amount?
The Medicare-approved amount is the total payment that Medicare has agreed to pay a health care provider for a service or item. Learn more your potential Medicare costs. The Medicare-approved amount is the amount of money that Medicare will pay a health care provider for a medical service or item.
What is 20 percent coinsurance?
Your 20 percent amount is called Medicare Part B coinsurance. Let’s say your doctor decides to refer you to a specialist to have your shoulder further examined. The specialist you visit agrees to treat Medicare patients but does not agree to accept the Medicare-approved amount as full payment. You still only pay 20 percent ...
Does Medicare cover a primary care appointment?
This appointment will be covered by Medicare Part B, and you have already satisfied your annual Part B deductible. Your primary care doctor accepts Medicare assignment, which means they have agreed to accept Medicare as full payment for their services. Because you have met your deductible for the year, you will split the Medicare-approved amount ...
How much does Medicare pay for medical services?
The Medicare reimbursement rates for traditional medical procedures and services are mostly established at 80 percent of the cost for services provided. Some medical providers are reimbursed at different rates. Clinical nurse specialists are paid 85 percent for most of their billed services and clinical social workers are paid 75 percent ...
What percentage of Medicare bill is not paid?
The majority of enrollee responsibility will be 20 percent , often referred to as coinsurance.
What is Medicare reimbursement rate?
The reimbursement rates are the monetary amounts that Medicare pays to health care providers, hospitals, laboratories, and medical equipment companies for performing certain services and providing medical supplies for individuals enrolled in Medicare insurance. To receive reimbursement payments at the current rates established by Medicare, health care professionals and service companies need to be participants in the Medicare program. While non-participating professionals and companies are able to submit claims and receive reimbursements for their services, their reimbursements will be slightly lower than the rates paid to participants.
What is the Medicare coinsurance?
Today, Medicare enrollees who use the services of participating health care professionals will be responsible for the portion of a billing claim not paid by Medicare. The majority of enrollee responsibility will be 20 percent, often referred to as coinsurance. With clinical nurse specialists that responsibility would be 15 percent and 25 percent for clinical social workers.
How many specialists are on the Medicare committee?
Medicare establishes the reimbursement rates based on recommendations from a select committee of 52 specialists. The committee is composed of 29 medical professionals and 23 others nominated by professional societies.
Why use established rates for health care reimbursements?
Using established rates for health care reimbursements enables the Medicare insurance program to plan and project for their annual budget. The intent is to inform health care providers what payments they will receive for their Medicare patients.
What is Medicare establishment rate schedule?
The establishment rate schedules are complex, multifunctional, and revised annually. The schedules for Medicare reimbursement rates are pre-determined base rates developed using a variety of factors that include the following.
How long does Medicare pay for hospital visits?
Remember those Part A costs you have to pay when you’ve been a hospital inpatient longer than 90 days? Medicare Supplement insurance plans typically pay up to 365 days of hospital costs when your Part A benefits are used up. (Under Medicare Supplement Plan N, you might have to pay a copayment up to $20 for some office visits, and up to $50 for emergency room visits if they don’t result in hospital admission.) Learn more about Medicare Supplement insurance plans.
What does Medicare cover?
Medicare coverage: what costs does Original Medicare cover? Here’s a look at the health-care costs that Original Medicare (Part A and Part B) may cover. If you’re an inpatient in the hospital: Part A (hospital insurance) typically covers health-care costs such as your care and medical services. You’ll usually need to pay a deductible ($1,484 per ...
What type of insurance is used for Medicare Part A and B?
This type of insurance works alongside your Original Medicare coverage. Medicare Supplement insurance plans typically help pay for your Medicare Part A and Part B out-of-pocket costs, such as deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments.
How much is a deductible for 2021?
You’ll usually need to pay a deductible ($1,484 per benefit period* in 2021). You pay coinsurance or copayment amounts in some cases, especially if you’re an inpatient for more than 60 days in one benefit period. Your copayment for days 61-90 is $371 for each benefit period in 2021.
What are the benefits of Medicare Advantage?
Most Medicare Advantage plans include prescription drug coverage, and many plans offer extra benefits. Routine vision and dental services and acupuncture are examples of some of the benefits a Medicare Advantage plan might offer.
How much is coinsurance for Medicare?
For example, if the Medicare-approved amount for a doctor visit is $85, your coinsurance would be around $17, if you’ve already paid your Part B deductible.
What does Part B cover?
Part B typically covers certain disease and cancer screenings for diseases. Part B may also help pay for certain medical equipment and supplies.
What is Medicare Part A?
Medicare Part A, the first part of original Medicare, is hospital insurance. It typically covers inpatient surgeries, bloodwork and diagnostics, and hospital stays. If admitted into a hospital, Medicare Part A will help pay for:
How much does Medicare Part A cost in 2020?
In 2020, the Medicare Part A deductible is $1,408 per benefit period.
How long does Medicare Part A deductible last?
Unlike some deductibles, the Medicare Part A deductible applies to each benefit period. This means it applies to the length of time you’ve been admitted into the hospital through 60 consecutive days after you’ve been out of the hospital.
How many days can you use Medicare in one hospital visit?
Medicare provides an additional 60 days of coverage beyond the 90 days of covered inpatient care within a benefit period. These 60 days are known as lifetime reserve days. Lifetime reserve days can be used only once, but they don’t have to be used all in one hospital visit.
What is the Medicare deductible for 2020?
Even with insurance, you’ll still have to pay a portion of the hospital bill, along with premiums, deductibles, and other costs that are adjusted every year. In 2020, the Medicare Part A deductible is $1,408 per benefit period.
How long do you have to work to qualify for Medicare Part A?
To be eligible, you’ll need to have worked for 40 quarters, or 10 years, and paid Medicare taxes during that time.
How long do you have to pay coinsurance?
If you need to stay longer than 60 days within the same benefit period, you’ll be required to pay a daily coinsurance. The coinsurance applies to an additional 30-day period — or days 61 through 90 if counted consecutively.
What is the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule?
The Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS) uses a resource-based relative value system (RBRVS) that assigns a relative value to current procedural terminology (CPT) codes that are developed and copyrighted by the American Medical Association (AMA) with input from representatives of health care professional associations and societies, including ASHA. The relative weighting factor (relative value unit or RVU) is derived from a resource-based relative value scale. The components of the RBRVS for each procedure are the (a) professional component (i.e., work as expressed in the amount of time, technical skill, physical effort, stress, and judgment for the procedure required of physicians and certain other practitioners); (b) technical component (i.e., the practice expense expressed in overhead costs such as assistant's time, equipment, supplies); and (c) professional liability component.
How to get Medicare fee schedule?
You may request a fee schedule adjusted for your geographic area from the Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC) that processes your claims. You can also access the rates for geographic areas by going to the CMS Physician Fee Schedule Look-Up website. In general, urban states and areas have payment rates that are 5% to 10% above the national average. Likewise, rural states are lower than the national average.
Why is Medicare fee higher than non-facility rate?
In general, if services are rendered in one's own office, the Medicare fee is higher (i.e., the non-facility rate) because the pratitioner is paying for overhead and equipment costs. Audiologists receive lower rates when services are rendered in a facility because the facility incurs ...
Why do audiologists get lower rates?
Audiologists receive lower rates when services are rendered in a facility because the facility incurs overhead/equipment costs. Skilled nursing facilities are the most common applicable setting where facility rates for audiology services would apply because hospital outpatient departments are not paid under the MPFS.
What is RVU in Medicare?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) determines the final relative value unit (RVU) for each code, which is then multiplied by the annual conversion factor (a dollar amount) to yield the national average fee. Rates are adjusted according to geographic indices based on provider locality. Payers other than Medicare that adopt these relative values may apply a higher or lower conversion factor.
What are the two categories of Medicare?
There are two categories of participation within Medicare. Participating provider (who must accept assignment) and non-participating provider (who does not accept assignment). You may agree to be a participating provider (who does not accept assignment). Both categories require that providers enroll in the Medicare program.
Do you have to bill Medicare for a physician fee?
You may agree to be a participating provider with Medicare. Once enrolled, you are required to bill on an assignment basis and accept the Medicare allowable fee as payment in full. Medicare will accept 80% of the allowable amount of the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS) and the patient will pay a 20 % co-insurance at the time services are rendered or ask you to bill their Medicare supplemental policy. Both participating and non-participating providers are required to file the claim to Medicare.
