An Emergency Department visit (code 99285) had a national average facility charge of $1,171, with Medicare allowing just $171 for the ER visit facility charge. A CBC lab test 85025 had an average charge of $34 (Medicare allowed $8); a blood test coded 88053 had an average charge of $55, with Medicare allowing $11.
How much does Medicare pay for emergency room visits?
If you go to the emergency room and receive care from a doctor but are not admitted as an inpatient, Medicare Part B will typically cover a portion of your medical costs. After your Part B deductible is met, you typically pay 20 percent of the Medicare-approved amount for most services, and Medicare pays the rest.
What is the Medicare emergency room copay?
What is the Copay for Medicare Emergency Room Coverage? A copay is the fixed amount that you pay for covered health services after your deductible is met. In most cases, a copay is required for doctor’s visits, hospital outpatient visits, doctor’s and hospital outpatients services, and prescription drugs.
How much does it cost to go to the ER without insurance?
In the United States, an emergency room visit without insurance can cost anywhere between $150 and $3000. Since the actual price you pay out of pocket will depend on how severe your condition is as well as what diagnostic tests and treatments you undergo, a visit to the emergency room can sometimes exceed these prices.
Do I have to pay copay for emergency department visits?
applies. If your doctor admits you to the same hospital for a related condition within 3 days of your emergency department visit, you don't pay the copayment because your visit is considered part of your inpatient stay. To find out how much your test, item, or service will cost, talk to your doctor or health care provider.

Does Medicare cover emergency treatment?
Yes, Medicare covers emergency room visits for injuries, sudden illnesses or an illness that gets worse quickly. Specifically, Medicare Part B will cover ER visits.
Will Medicare pay for 2 ER visits on the same day?
For instance, Medicare will “not pay two E/M office visits billed by a physician (or physician of the same specialty from the same group practice) for the same beneficiary on the same day,” according to the Medicare Claims Processing Manual, chapter 12, section 30.6.
Does Medicare pay 100 percent of hospital bills?
According to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), more than 60 million people are covered by Medicare. Although Medicare covers most medically necessary inpatient and outpatient health expenses, Medicare reimbursement sometimes does not pay 100% of your medical costs.
What is the Medicare deductible for an emergency room visit?
Outpatient Emergency Department Costs Under Medicare Part B Copays typically can't exceed the $1,556 Part A deductible for each service. The Part B deductible — $233 in 2022 — also applies. You may not owe this if you've already met your yearly deductible before arriving at the hospital.
Does Medicare Part A cover emergency room visits?
Does Medicare Part A Cover Emergency Room Visits? Medicare Part A is sometimes called “hospital insurance,” but it only covers the costs of an emergency room (ER) visit if you're admitted to the hospital to treat the illness or injury that brought you to the ER.
What will Medicare not pay for?
In general, Original Medicare does not cover: Long-term care (such as extended nursing home stays or custodial care) Hearing aids. Most vision care, notably eyeglasses and contacts. Most dental care, notably dentures.
What does Medicare cover in hospital?
Medicare generally covers 100% of your medical expenses if you are admitted as a public patient in a public hospital. As a public patient, you generally won't be able to choose your own doctor or choose the day that you are admitted to hospital.
How many days will Medicare pay for hospital stay?
90 daysMedicare covers a hospital stay of up to 90 days, though a person may still need to pay coinsurance during this time. While Medicare does help fund longer stays, it may take the extra time from an individual's reserve days. Medicare provides 60 lifetime reserve days.
What is the Copay for Medicare Emergency Room Coverage?
A copay is the fixed amount that you pay for covered health services after your deductible is met. In most cases, a copay is required for doctor’s visits, hospital outpatient visits, doctor’s and hospital outpatients services, and prescription drugs. Medicare copays differ from coinsurance in that they're usually a specific amount, rather than a percentage of the total cost of your care.
How does Medicare pay for outpatient services?
How You Pay For Outpatient Services. In order for your Medicare Part B coverage to kick in, you must pay the yearly Part B deductible. Once your deductible is met, Medicare pays its share and you pay yours in the form of a copay or coinsurance.
What is a Medigap plan?
Medigap is private health insurance that Medicare beneficiaries can buy to cover costs that Medicare doesn't, including some copays. All Medigap plans cover at least a percentage of your Medicare Part B coinsurance or ER copay costs.
What is Medicare Part B?
Medicare Part B pays for outpatient services like the ones listed above, under the Outpatient Prospective Payment System (OPPS). The OPPS pays hospitals a set amount of money (or payment rate) for the services they provide to Medicare beneficiaries.
How much is the deductible for Medicare Part B?
In most cases, if you receive care in a hospital emergency department and are covered by Medicare Part B, you'll also be responsible for: An annual Part B deductible of $203 (in 2021). A coinsurance payment of 20% of the Medicare-approved amount for most doctor’s services and medical equipment.
What are the services covered by Medicare?
Most ER services are considered hospital outpatient services, which are covered by Medicare Part B. They include, but are not limited to: 1 Emergency and observation services, including overnight stays in a hospital 2 Diagnostic and laboratory tests 3 X-rays and other radiology services 4 Some medically necessary surgical procedures 5 Medical supplies and equipment, like splints, crutches and casts 6 Preventive and screening services 7 Certain drugs that you wouldn't administer yourself
What are the services of a hospital?
Emergency and observation services, including overnight stays in a hospital. Diagnostic and laboratory tests. X-rays and other radiology services. Some medically necessary surgical procedures. Medical supplies and equipment, like splints, crutches and casts. Preventive and screening services.
How Much Does an ER Visit Cost if You Have Medicare?
Medicare Part A only covers an emergency room visit if you’re admitted to the hospital. Medicare Part B covers 100% of most ER costs for most injuries, or if you become suddenly ill. Unlike private insurance and insurance purchased on the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Marketplace, Medicare rarely covers ER visits that happen while you’re outside of the United States.
How Much Does an ER Visit Cost Without Insurance?
According to UnitedHealth, a trip to the emergency department can cost 12 times more than a typical doctor’s office visit. The average ER visit is $2,200, and doesn’t include procedures or medications.
What percentage of Medicare pays for Part B?
After your Part B deductible is met, you typically pay 20 percent of the Medicare-approved amount for most services, and Medicare pays the rest.
How much is Medicare Part A deductible for 2021?
In 2021, the Medicare Part A deductible is $1,484 per benefit period.
What does Medicare Part B cover?
What Medicare Part B covers. Medicare Part B is known as medical insurance and helps cover medically necessary services and preventive services, which can include: Medicare Part B may also cover services you receive when you visit the emergency room as an outpatient. Medicare Part B is optional, and if you enroll in Part B you must also enroll in ...
Do you pay for an emergency room visit?
Typically, you pay a Medicare emergency room copayment for the visit itself and a copayment for each hospital service.
Does Medicare cover inpatients?
If you go to the emergency room and are admitted as an inpatient, Medicare Part A helps cover some of the costs related to your hospital stay once your Part A deductible is met.
Does Medicare cover emergency room visits?
Learn more and find the Medicare plan that offers the coverage you need. Yes, emergency room visits are typically covered by Medicare. Most outpatient emergency room services are covered by Medicare Part B, and inpatient hospital stays are covered by Medicare Part A.
Does Medicare Advantage cover prescriptions?
Most Medicare Advantage plans also cover prescription drugs, and many plans may also offer additional benefits such as dental, vision and hearing coverage.
How much is a hospital visit covered by Medicare?
If Medicare Part A pays for the hospital visit, a person is responsible for a deductible of $1,260. A deductible is a spending total that a person must self-fund on a policy before coverage commences. Once a person spends this amount out of pocket on treatment, Medicare Part A pays 100% of the hospital costs for up to 60 days.
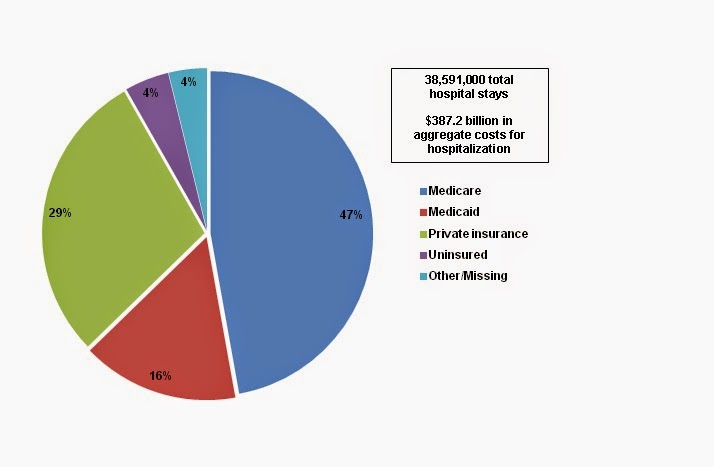
How many visits did Medicare beneficiaries make to the ER in 2012?
Medicare beneficiaries made between 4.2 and 5.3 million visits — depending on the definition — to an ER in 2012, according to an article in the journal Academic Emergency Medicine.
What is a scenario in Medicare Part B?
The following are some example scenarios: Scenario 1. Scenario: An ambulance brought you to the ER. What pays: Medicare Part B generally covers ambulance transportation to a hospital, skilled nursing facility, or critical access hospital.
How often do copayments and deductibles vary?
These copayments and deductibles may vary on a yearly basis.
What is Medicare Part A?
Medicare Part A provides hospital coverage. If a doctor admits an individual into the hospital for at least 2 midnights, Medicare Part A covers hospital services, such as accommodation costs and testing, while a person stays in the facility. If Medicare Part A pays for the hospital visit, a person is responsible for a deductible of $1,260.
What is Medicare Supplement?
Medicare supplement, or Medigap, policies may provide emergency health coverage if a person is traveling outside the United States.
Which Medicare Part covers ER visits?
Medicare Part B is the portion of Medicare that most often covers ER visits if the doctor does not request inpatient admission.
How much does an ER visit cost?
The price of your ER visit will depend on what types of treatments and medications you receive. For patients without health insurance , an emergency room visit can cost less than $2200. If the treatment you receive is extensive, an ER visit can exceed this price. For instance, in some cases, especially where critical care is required and/or a procedure or surgery is performed, the cost could reach $20,000 or more.
How much does an ER visit cost without insurance?
How Much an ER Visit Costs Without Insurance in 2021. In the United States, an emergency room visit costs $2200 on average, according to a research done by UnitedHealth, the largest insurance carrier in the U.S. Since the actual price you pay out of pocket will depend on how severe your condition is as well as what diagnostic tests ...
How much is triage fee at ER?
When you get registered as a patient at the ER, you get charged a triage fee, typically ranging from $200-$1000. Next, when you are assigned into a room, you will incur a facility charge that averages at $1,118, covering your time in the room and nurses' time. Contrary to common beliefs, the attending physician or professional fees are not included within the facility charge and often get billed separately, along with any medications or medical supplies during your visit.
How to access ER program after visit?
You will get a reduced charge for your ER visits. You can access these program after your visit by contacting the hospital patient advocacy department. Tips: It is important to determine if your condition is truly emergent or could be treated as a lower-cost facilities such as an urgent care center.
What do emergency rooms pay for?
Emergency rooms have to pay for utility bills such as electricity, water, food, and supplies, along with medical care. These costs then get passed to the patients.
What is the medical emergency for abdominal pain?
Abdominal pain: If you are experiencing extreme or severe abdominal pain, you may consider going to the emergency room. Uncontrolled bleeding: Uncontrolled bleeding is a medical emergency and necessitates an emergency room visit.
How many conditions are there in the ER in NY?
According to research done by NY state, there are 25 conditions that are most common for ER visits. Notice that a large percentage of visits are non-emergent, primary care treatable, or emergent but avoidable. In another research, the state found that more than half of the total 7 million ER visits in 2018 could be treated elsewhere.