Full Answer
How much does Medicare cost per month?
· A new study finds that a full-scale single-payer health insurance program, also called “Medicare for All,” would cost about $32 trillion over 10 years.
How much do you pay for Medicare after deductible?
· Sanders has said publicly that economists estimate Medicare for All would cost somewhere between $30 trillion and $40 trillion over 10 years.
How much will health care spending increase under Medicare for all?
Part A costs: What you pay in 2022: Premium. $0 for most people (because they paid Medicare taxes long enough while working - generally at least 10 years). This is sometimes called “premium-free Part A.”
Would Medicare for all cost more than the current system?
· The Mercatus Center, a libertarian think-tank out of George Mason University, is releasing a study today that will show how much Vermont senator Bernie Sanders's "Medicare for all" idea would cost ...
How many cosponsors did the Medicare for All Act have?
The study looked at the impact of the Medicare for All Act introduced by Sanders on Sept. 13, 2017. The bill, which has 16 Democratic cosponsors, would expand Medicare into a universal health insurance program, phased in over four years. (The bill hasn’t gone anywhere in a Republican-controlled Senate.)
Why do M4A payments exceed current Medicare payment rates?
Anticipating these difficulties, some other studies have assumed that M4A payment rates must exceed current-law Medicare payment rates to avoid sending facilities into deficit on average or to avoid triggering unacceptable reductions in the provision and quality of healthcare services. These alternative payment rate assumptions substantially increase the total projected costs of M4A.
Who tweeted "Thank you Koch brothers for accidentally making the case for Medicare for All"?
Our fact-checking colleagues at the Washington Post first wrote about this when, on July 30, Sanders tweeted, “Thank you, Koch brothers, for accidentally making the case for Medicare for All!”
Will Medicare have negative margins in 2040?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Office of the Actuary has projected that even upholding current-law reimbursement rates for treat ing Medicare beneficiaries alone would cause nearly half of all hospitals to have negative total facility margins by 2040. The same study found that by 2019, over 80 percent ...
Is 40 percent reduction in reimbursement rate an unlikely outcome?
Or, as Blahous told us via email, achieving a 40 percent reduction in reimbursement rates is an “unlikely outcome” and “actual costs are likely to be substantially greater.”
How much would Medicare cost?
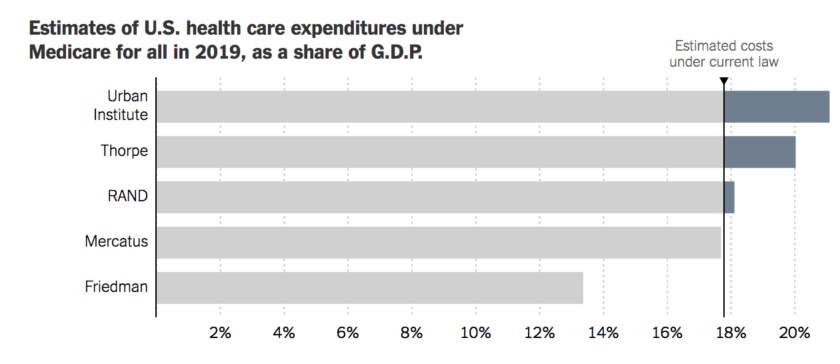
Sanders has said publicly that economists estimate Medicare for All would cost somewhere between $30 trillion and $40 trillion over 10 years. Research by the nonpartisan Urban Institute, a Washington, D.C., think tank, puts the figure in the $32 trillion to $34 trillion range.
Why is Biden's comparison of Medicare for All's price to total federal spending misses the mark?
But it turns out, based on the numbers and interviews with independent experts, Biden’s comparison of Medicare for All’s price to total federal spending misses the mark because the calculation is flawed.
What did Biden argue about Medicare for All?
Biden argued that Medicare for All “would cost more than the entire federal budget that we spend now.”
How much did Biden's budget cost?
Biden’s campaign directed us to the 2018 federal budget, which totaled $4.1 trillion. It compared that amount with the estimated cost of Sanders’ single-payer proposal: between $30 trillion and $40 trillion over a decade. The math, they said, shows Medicare for All would cost more than the national budget.
Who questioned the price tag of Medicare for All?
During the Feb. 7 Democratic presidential debate, former Vice President Joe Biden once again questioned the price tag of “Medicare for All,” the single-payer health care proposal championed by one of his key rivals, Sen. Bernie Sanders of Vermont. Biden argued that the plan was fiscally irresponsible and would require raising middle-class taxes.
How much money will the federal budget consume in 2030?
Goldwein looked at the numbers another way: Including interest, he found, the federal budget would consume about $55 trillion between now and 2030. Again, that’s more than what Medicare for All would cost during the same period.
How much do you pay for Medicare after you pay your deductible?
You’ll usually pay 20% of the cost for each Medicare-covered service or item after you’ve paid your deductible.
How much will Medicare premiums be in 2021?
If you don’t qualify for a premium-free Part A, you might be able to buy it. In 2021, the premium is either $259 or $471 each month, depending on how long you or your spouse worked and paid Medicare taxes.
How often do you pay premiums on a health insurance plan?
Monthly premiums vary based on which plan you join. The amount can change each year. You may also have to pay an extra amount each month based on your income.
How often do premiums change on a 401(k)?
Monthly premiums vary based on which plan you join. The amount can change each year.
Is there a late fee for Part B?
It’s not a one-time late fee — you’ll pay the penalty for as long as you have Part B.
Do you have to pay Part B premiums?
You must keep paying your Part B premium to keep your supplement insurance.
What is Medicare today?
Medicare Today. Medicare is a program that benefits Americans who are age 65 or older or who have disabilities. The current program has two parts: Part A for hospital care and Part B for doctors’ visits, outpatient care, and some forms of medical equipment.
Why would doctors receive less pay under the new Medicare system?
Doctors and Hospitals. They would most likely receive less pay under the new system because Medicare pays lower rates for all forms of care than private insurers do. On the plus side, they would no longer have to worry about unpaid bills from patients who don’t have insurance or insurers who refuse claims. They would also have to spend less time on paperwork, which would keep their administrative costs down. Still, the lower payment rates could force some hospitals to close if they can no longer meet their expenses.
How much of healthcare costs go to administration?
According to the JAMA study, 8% of all health care costs in the U.S. went toward administration — that is, planning, regulating, billing, and managing health care services and systems. By contrast, the 10 other countries in the study spent only 1% to 3% of total costs on administration.
What is the average life expectancy of a baby?
The average life expectancy for Americans is 78.8 years, while in other countries it ranged from 80.7 to 83.9 years. Infant Mortality. Out of 1,000 babies born in the U.S., 5.8 die in infancy, according to the JAMA study. The average for all 11 countries in the study was only 3.6 deaths per 1,000 live births.
Why do people put off medical care?
These uninsured and underinsured Americans are likely to put off necessary medical treatment because they can’t afford it. Often, they don’t seek medical care until they have a problem serious enough to land them in the emergency room, the most expensive possible place to receive care. Thus, having large numbers of uninsured and underinsured Americans drives up health care costs for the country as a whole.
How much did healthcare cost in 2016?
In 2016, the cost of care in the U.S. came to $9,982 per person. That’s about 25% more than Sweden, the country with the second-costliest care at $7,919 per person, and more than twice as much as Canada at $4,753. The average for all developed nations was only $4,033, about 40% of what Americans spent. The U.S. spent a total of 17.2% of its gross domestic product (GDP) on health care, while the average developed country spent only 8.9% of GDP.
Why are generalist doctors paid higher?
One reason health care prices are higher in the U.S. is that most Americans get their coverage from private insurers, and these companies pay much higher rates for the same health care services than public programs such as Medicare.
What happens if you increase your Medicare premium?
2 This means that, generally, if you increase your earnings over certain limits and the cost of living continues to increase, you'll keep seeing increases in Medicare Part B premiums.
What is the Medicare premium for 2017?
The monthly premium for Medicare Part B was $134 for tax years 2017 and 2018. This rate was for single or married individuals who filed separately with MAGIs of $85,000 or less and for married taxpayers who filed jointly with MAGIs of $170,000 or less. 4 The 2017 premium rate was an increase of 10% over the 2016 rate that was not based on the Social Security Administration's cost-of-living adjustments (COLA).
How much is Medicare Part B 2021?
Medicare Part B premiums for 2021 increased by $3.90 from the premium for 2020. The 2021 premium rate starts at $148.50 per month and increases based on your income to up to $504.90 for the 2021 tax year. Your premium depends on your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) from your tax return two years before the current year (in this case, 2019). 2.
When do you get Medicare if you don't have Social Security?
If you're not receiving Social Security, though, be sure to contact the Social Security Administration about three months prior to your 65th birthday in order to receive Medicare .
Is Medicare Part B indexed for inflation?
Updated July 07, 2021. Medicare Part B premiums are indexed for inflation — they're adjusted periodically to keep pace with the falling value of the dollar. What you pay this year may not be what you pay next year. 1 Premiums are also means-tested, which means they're somewhat dependent upon your income. The more income you have, the higher your ...
Does Medicare have a hold harmless?
Medicare has a "hold harmless" provision for seniors. This provision prevents Medicare from raising the premiums more than the cost of living increases. 4 While this keeps seniors from paying more than they should, you'll have to pay the increased premiums if your COLA is higher than the increase.
What is the Medicare for All Act?
Representative Jayapal’s Medicare for All Act would replace nearly all current insurance with a government-run single-payer plan and extend that plan to those who currently lack health coverage. The plan itself would be far more generous than either Medicare or most private coverage, as it would include no deductibles or copayments, would not restrict beneficiaries to networks of care, and would offer a broad suite of benefits including dental care, vision care, transportation for disabled and low-income patients, certain dietary and nutritional care, long-term care, and other long-term services and support. The proposal also establishes a global health budget, moves away from fee-for-service and toward lump-sum payments for many providers, includes a number of measures to hold down drug prices, and makes a variety of other changes to the health care system.
How much would the single payer plan cost?
While the campaign itself estimated that plan would cost the federal government about $14 trillion over a decade, most other estimates that we are aware of are at least twice that high.
How much will the Sanders Plan cost in 2026?
At the time, for example, the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget estimated roughly that the plan would cost $28 trillion through 2026 (we estimated the Sanders plan in particular would also raise $11 trillion of revenue, leading to $17 trillion of net costs). All other estimates come to similar conclusions.
How much will single payer healthcare cost in 2026?
For example, economist Kenneth Thorpe estimated that single-payer health care would cost the federal government $24.7 trillion through 2026, excluding the costs associated with long-term care benefits (likely about $3 trillion).
How much will the government cost in 2029?
The Center for Health and Economy (H&E) produced an estimate that the American Action Forum calculates would cost the federal government $36 trillion through 2029.
Is Medicare a single payer system?
Representative Pramila Jayapal (D-WA), a co-chair of the Medicare for All Caucus, released a bill today that would adopt a single-payer system, where the federal government replaces private health insurance companies as the sole provider of most health care financing.
How many people would have Medicare for all?
Medicare for all would give insurance to around 28 million Americans who don’t have it now. And evidence shows that people use more health services when they’re insured. That change alone would increase the bill for the program. Other changes to Medicare for all would also tend to increase health care spending.
What would happen if Medicare was for all?
Under a Medicare for all system, Medicare would pick up all the bills. Paying the same prices that Medicare pays now would mean an effective pay cut for medical providers who currently see a lot of patients with private insurance.
How did Charles Blahous calculate Medicare for all?
Charles Blahous calculated the cost of Medicare for all by making adjustments to current health care spending using assumptions he derived from the research literature. His measurements didn’t capture the behavior of individual Americans, but estimated broader changes as groups of people gained access to different insurance, and as medical providers earned a different mix of payments. His calculations were made based on Mr. Sanders’s 2017 Medicare for All Act, which indicated that states would continue to pay a share of long-term care costs. A 2018 paper with more of his findings is available here, and includes both sets of estimates for Medicare provider payments.
How did Gerald Friedman calculate the cost of Medicare for all?
Gerald Friedman calculated the cost of Medicare for all by making adjustments to current health care spending using assumptions he derived from the research literature. His measurements didn’t capture the behavior of individual Americans, but estimated broader changes as groups of people gained access to different insurance, and as medical providers earned a different mix of payments. A 2018 paper with his analysis of several different variations on Medicare for all is available here.
How does Urban Institute estimate health care?
The Urban Institute built its estimates using a microsimulation model, which estimates how individuals with different incomes and health care needs would respond to changes in health insurance. The model does not consider the effects of policy changes on military and veterans’ health care or the Indian Health Service, so its totals assumed those programs would not change. It also measures limits on the availability of doctors and hospitals using evidence from the Medicaid program. The team at Urban that prepared the calculations includes John Holahan, Lisa Clemans-Cope, Matthew Buettgens, Melissa Favreault, Linda J. Blumberg and Siyabonga Ndwandwe. Its detailed report on Mr. Sanders’s presidential campaign proposal from 2016 is available here.
Why would Medicare have more leverage with the drug industry?
A Medicare for all system would have more leverage with the drug industry because it could bargain for the whole country’s drug supply at once. But politics would still be a constraint. A system willing to pay for fewer drugs could probably get bigger discounts than one that wanted to preserve the current set of choices. That would mean, though, that some patients would be denied the medications they want.
Does Medicare for all cost more than the current system?
Even without including all the costs for long-term care, which some Medicare for all proposals include, this estimate still finds that Medicare for all would cost substantially more than the current system.
