
How Models Work Risk adjustment uses statistical models that measure incremental predictive costs of a beneficiary’s demographic and disease characteristics and age, sex, and certain statuses such as Medicaid Medicaid in the United States is a federal and state program that helps with medical costs for some people with limited income and resources. Medicaid also offers benefits not normally covered by Medicare, including nursing home care and personal care services. The Health Insurance As…Medicaid
What does risk adjustment really mean?
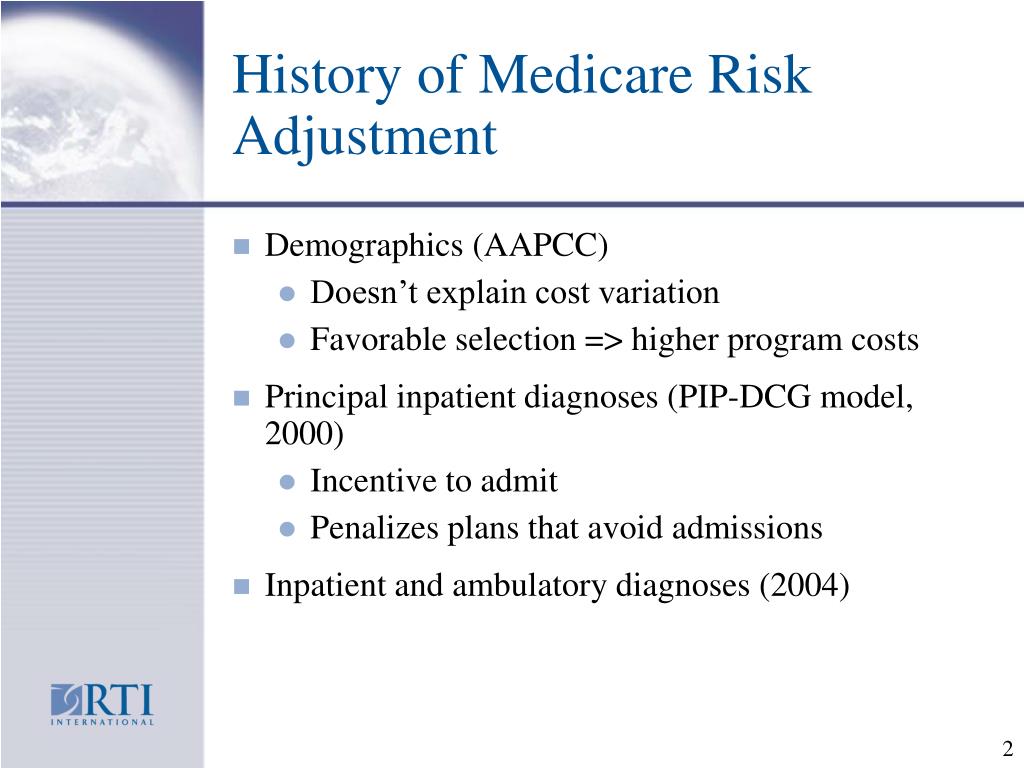
- HHS-HCC is the newest model, implemented in 2014.
- They work on a risk pool model, meaning its budget-neutral by transferring funds from low-risk plans to high-risk enrollee plans.
- Again, only the most severe or highest-cost diagnoses are counted.
- Age and sex are the demographics that most affect risk scores.
What does risk adjustment stand for?
What Is Risk Adjustment? Risk adjustment is a methodology that equates the health status of a person to a number, called a risk score, to predict healthcare costs. The “risk” to a health plan insuring members with expected high healthcare use is “adjusted” by also insuring members with anticipated lower healthcare costs.
What is going on with risk adjustment payments?
- “Ensure the accuracy and integrity of risk adjustment data submitted to CMS. ...
- Implement procedures to ensure that diagnoses are from acceptable data source. ...
- Submit the required data elements from acceptable data sources according to the coding guidelines.
Why is risk adjustment so important?
- Hospital inpatient facilities
- Hospital outpatient facilities
- Physicians
How is risk adjustment done?
Risk adjustment starts with gathering statistics—including patient demographics, diagnoses and professional encounter data. The data is used to assign each member in the plan a risk score. Risk scores are based on members' active chronic medical conditions and the additional Medicare-approved services they require.
How does HCC coding work?
HCC coding relies on ICD-10-CM coding to assign risk scores to patients. Each HCC is mapped to an ICD-10-CM code. Along with demographic factors such as age and gender, insurance companies use HCC coding to assign patients a risk adjustment factor (RAF) score.
What is Medicare risk Adjustment Factor?
A risk adjustment factor system is used to adjust plan payments to ensure fair payment for providing healthcare services and benefits for a population of patients, sometimes know as population health management.
How is Medicare risk score calculated?
The purpose of the Medicare risk scores is to estimate a relative cost factor. (i.e., it is a payment risk score). CMS calculates individual beneficiary-level risk scores by adding the relative factors associated with each beneficiary's demographic and disease factors.
What is HCC risk adjustment?
The Hierarchical Condition Category (HCC) risk adjustment model is used by CMS to estimate predicted costs for Medicare Advantage beneficiaries, and the results directly impact the reimbursement healthcare organizations receive.
How is HCC risk score calculated?
There are relative factors associated with each HCC and interaction. Sum of Factors Demographic + Disease = raw risk score The relative factors for all of the demographic variables, HCCs, and interactions are added together. The result is the raw risk score.
How do RAF scores work?
Medicare Advantage and exchange plans are paid based on patients' RAF scores. A score of 1.00 is average, with the decimal places representing percentages above or below average. For example, if a plan's average patient RAF score is 1.10, it will receive 10 percent more from Medicare.
WHO calculates RAF score?
CMSThe county rate is determined by CMS and published yearly through their website on an enormous spreadsheet called a “rate book”. You can download the rate book and look up your county if you like. The county rate usually runs from $800-$1200, with urban areas carrying the higher amounts.
What is CMS risk score?
The CMS-HCC risk score for a beneficiary is the sum of the score or weight attributed to each of the demographic factors and HCCs within the model. The CMS-HCC model is normalized to 1.0. Beneficiaries would be considered relatively healthy, and therefore less costly, with a risk score less than 1.0.
What are risk adjustment scores?
Risk adjustment is a methodology that equates the health status of a person to a number, called a risk score, to predict healthcare costs. The “risk” to a health plan insuring members with expected high healthcare use is “adjusted” by also insuring members with anticipated lower healthcare costs.
What is risk adjustment coding?
Risk adjustment coding requires health plan management, provider group management, physicians, non-physician providers, and highly skilled coding professionals to work together to capture the health status of their patient membership. Each player is critical for success under the risk adjustment programs.
What is the purpose of the risk adjustment values?
The goal of risk adjustment is to enable more accurate comparisons across TINs that treat beneficiaries of varying clinical complexity, by removing differences in health and other risk factors that impact measured outcomes but are not under the TIN's control.
What is Medicare Part C?
It includes both hospital insurance (Part A) and medical insurance (Part B). Medicare Part C, aka Medicare Advantage, is an alternative to Original Medicare.
Does Medicare pay per capita?
The federal government pays Medicare Advantage plans a "per capita" rate for each Medicare beneficiary. This rate is based on a risk assessment score. In order to boost those scores and to maximize the dollars they get from the federal government, insurers may offer you a free home visit with one of their medical providers.
What is risk adjustment?
Risk adjustment is an essential mechanism used in health insurance programs to account for the overall health and expected medical costs of each individual enrolled in a health plan. Accurate documentation of diagnoses by clinicians is a critical component of the risk adjustment process.
What is the coding intensity adjustment for Medicare Advantage?
Since 2010, Congress has required CMS to apply a coding intensity adjustment to Medicare Advantage payments that is an across the board cut to Medicare Advantage risk scores. The purpose of the adjustment is to account for differences in coding patterns between Medicare Advantage and FFS Medicare — differences that are a function of the differences between the structural payment and care models in the Medicare Advantage and FFS Medicare programs. Per statute, the coding intensity adjustment has increased from a 3.41% reduction in 2010 to a 5.91% reduction for payment year 2018. The coding intensity adjustment must remain no less than a 5.91% reduction to risk scores for all subsequent years. CMS has the authority to determine the amount above the statutory minimum. To date, CMS has applied the minimum coding intensity adjustment required by law.
What is Medicare Advantage?
These plans are approved and regulated by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and the program undergoes an annual review process that makes policy changes and sets payment rates for the next year .
What is the difference between FFS and Medicare Advantage?
Accurately identifying illness is key to the comprehensive approach to care in Medicare Advantage. FFS Medicare reimburses providers separately for each episode of care. In contrast, Medicare Advantage is structured to encourage early identification of illness, coordinated care, and improved beneficiary health outcomes.
What is the purpose of risk adjustment?
The official definition of risk adjustment, according to HealthCare.gov, is “a statistical process that takes into account the underlying health status and health spending of the enrollees in an insurance plan when looking at their health care outcomes or health care costs.”
What are risk adjustment factor scores (RAF)?
Risk Adjustment Factors — known as RAFs — are the average risk scores for specific HCCs. They’re used in combination with demographics to determine an individual’s final risk score.
What are the three risk adjustment models?
Depending on the situation, there are three different ways to adjust for risk. Each model has a different purpose and goal in mind.
Risk Adjustment and Healthcare
Risk adjustment allows for proper cost adjustments as well as setting a standard of premiums for high-risk enrollees. This is because people who are sick or have chronic conditions will be more expensive to treat than someone with few or no health issues.
What Is Risk Adjustment In Healthcare?
In healthcare, risk adjustment is used to predict healthcare costs by understanding the patient’s health status—health insurance plans calculate the “risk” of insuring someone with an anticipated high level of healthcare, which is then “adjusted” by that insurance company covering members with lower healthcare costs.
Why Is Risk Adjustment Important To Your Practice?
Risk adjustment plays a vital role in your medical practice’s bottom line because of its relation to health insurance companies, coverage, and patient plans.
Who Benefits From Risk Adjustment?
Risk adjustment has a multitude of benefits for you and your patients, including:
How To Calculate Risk Adjustment
As mentioned above, individual medical practices aren’t in control of calculating a patient’s risk factor; instead, government agencies, such as the Center for Medicaid and Medicare Services (CMS), determine which factors are used in conjunction with which diagnoses.
Trust Your Medical Billing and Collections to the Experts at NCG!
Navigating important regulations regarding a core component of delivering quality care can take a lot of time and energy; let us handle the medical billing and coding for you! We also know that choosing the right medical billing company when outsourcing your billing processes is incredibly important for building and sustaining a successful healthcare practice.
What are the most critical challenges we face in caring for patients?
Age, gender, diseases all matter. Social factors , however, are some of the most critical and costly challenges we face in caring for patients and they are totally absent. Social determinants of health (SDOH) impact how hard it is and how much it will likely cost to manage a patient’s disease.
Can you win the game of care management?
You can win the “game” by doing a so-so job at care management so long as you diagnose well. Many companies use special providers who only exist to capture all the codes they can find.
