How did tax reform affect Medicare tax treatment?
While the recently passed Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) did repeal the individual health coverage mandate under the Affordable Care Act, it left in place the 0.9% Additional Medicare tax on high-income individuals. The takeaway here is that there were no changes to the tax treatment of Medicare benefits or rules due to tax reform.
How did the Affordable Care Act change the tax code?
The ACA also changed the tax code as a way to increase revenue for the Medicare program. Starting in 2013, the Medicare payroll tax increased by 0.9% (from 1.45 to 2.35%) for individuals earning more than $200,000 and for married couples with income above $250,000 who file jointly.
What does the tax cuts and Jobs Act mean for Medicare?
Editor’s Note: This article was originally published on April 09, 2018. While the recently passed Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) did repeal the individual health coverage mandate under the Affordable Care Act, it left in place the 0.9% Additional Medicare tax on high-income individuals.
How has the Affordable Care Act (ACA) reduced costs?
The ACA gradually reduced costs by restructuring payments to Medicare Advantage, based on the fact that the government was spending more money per enrollee for Medicare Advantage than for Original Medicare. But implementing the cuts has been a bit of an uphill battle.

What would happen to taxes if healthcare was free?
Funding universal health insurance through taxes would lead to a large tax cut for the vast majority of workers. It would abolish the huge poll tax they currently shoulder, and the data show that for most workers, it would lead to the biggest take-home pay raise in a generation.
What impact did Medicare and Medicaid have on society?
Medicare and Medicaid have greatly reduced the number of uninsured Americans and have become the standard bearers for quality and innovation in American health care. Fifty years later, no other program has changed the lives of Americans more than Medicare and Medicaid.
Is there a tax on Medicare benefits?
As long as you use them for a qualified medical expense, which includes premiums for Medicare Parts A, B, C, and D, you don't have to pay taxes on the money.
How does Medicare impact the US today?
Providing nearly universal health insurance to the elderly as well as many disabled, Medicare accounts for about 17 percent of U.S. health expenditures, one-eighth of the federal budget, and 2 percent of gross domestic production.
How does Medicare and Medicaid affect the economy?
In short, Medicaid adds billions of dollars in economic activity. The federal government boosts this activity by matching state Medicaid spending at least dollar for dollar, bringing new money into states.
What is the economic impact of Medicare?
In addition to financing crucial health care services for millions of Americans, Medicare benefits the broader economy. The funds disbursed by the program support the employment of millions of workers, and the salaries paid to those workers generate billions of dollars of tax revenue.
What is the Medicare tax rate for 2021?
1.45%FICA tax includes a 6.2% Social Security tax and 1.45% Medicare tax on earnings. In 2021, only the first $142,800 of earnings are subject to the Social Security tax ($147,000 in 2022). A 0.9% Medicare tax may apply to earnings over $200,000 for single filers/$250,000 for joint filers.
Can I opt out of paying Medicare tax?
To do that, you'll use IRS Form 4029, Application for Exemption From Social Security and Medicare Taxes and Waiver of Benefits.
Who is exempt from paying Medicare tax?
The Code grants an exemption from Social Security and Medicare taxes to nonimmigrant scholars, teachers, researchers, and trainees (including medical interns), physicians, au pairs, summer camp workers, and other non-students temporarily present in the United States in J-1, Q-1 or Q-2 status.
Why are Medicare costs rising?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) announced the premium and other Medicare cost increases on November 12, 2021. The steep hike is attributed to increasing health care costs and uncertainty over Medicare's outlay for an expensive new drug that was recently approved to treat Alzheimer's disease.
What would happen without Medicare?
Payroll taxes would fall 10 percent, wages would go up 11 percent and output per capita would jump 14.5 percent. Capital per capita would soar nearly 38 percent as consumers accumulated more assets, an almost ninefold increase compared to eliminating Medicare alone.
How much does the US spend on Medicare and Medicaid?
The federal government spent nearly $1.2 trillion on health care in fiscal year 2019 (table 1). Of that, Medicare claimed roughly $644 billion, Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Pro-gram (CHIP) about $427 billion, and veterans' medical care about $80 billion.
How will the new tax plan affect health care?
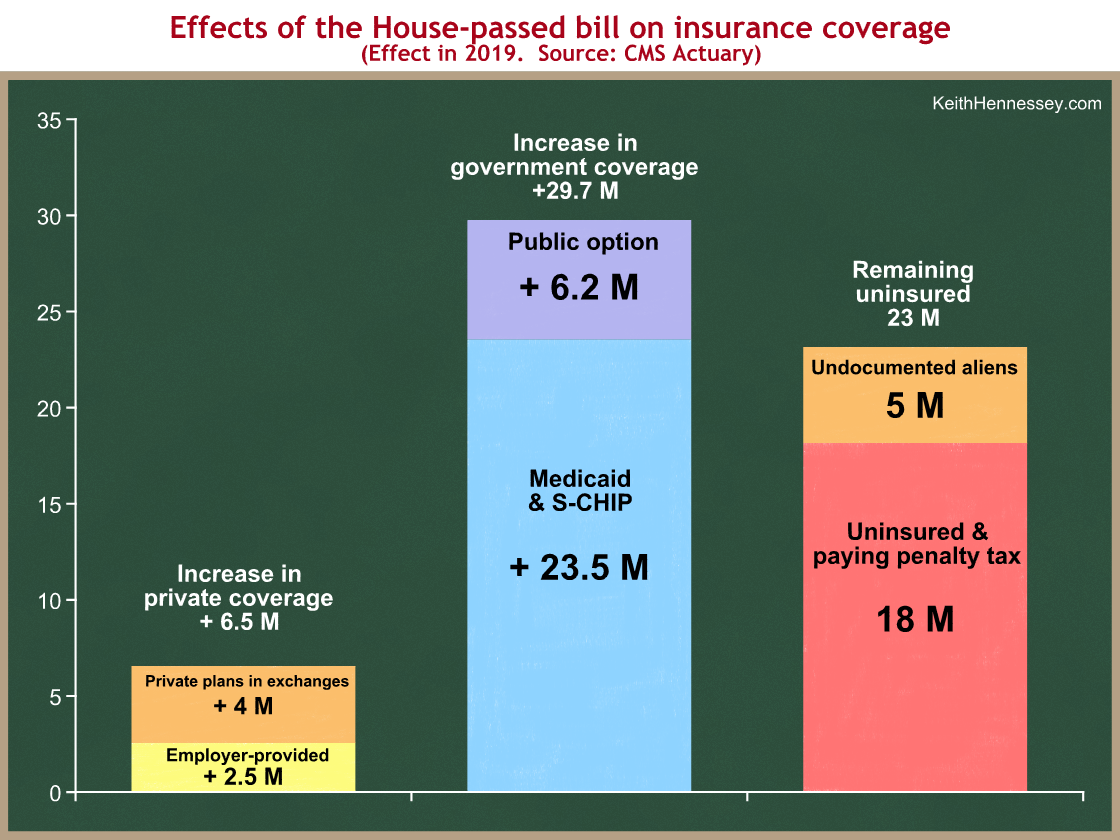
How the New U.S. Tax Plan Will Affect Health Care. It will mean less coverage, less revenue, and a less productive workforce. Summary. Earlier today, the U.S. House of Representatives passed a new tax bill which will eliminate the penalties against people who don’t have health insurance and significantly increase the federal deficit.
How much of the federal budget was spent on Medicare and Medicaid in 2016?
Because Medicare and Medicaid together accounted for about $1.25 trillion in federal spending in 2016, about 30% of the federal budget, they will be the major targets for deficit reduction. There is no guarantee that such efforts will succeed, but if they do, reforms could take a number of directions.
What age can you get Medicare?
For Medicare, this could include increasing the eligibility age from 65 to 67 or beyond (resulting in fewer covered elderly), caps on spending per beneficiary (possibly reducing covered benefits), or increases in cost-sharing that would lead to beneficiaries using fewer services.
How many Americans will lose health insurance?
But there are also practical questions for American businesses. The 13 million Americans who will lose health insurance and many millions of Medicaid eligible individuals who may lose coverage or benefits are current or potential workers whose health influences their productivity.
What does the tax bill mean for healthcare?
It will mean less health insurance for individuals; less coverage for elderly and poor Americans; less revenue for doctors, hospitals, and myriad health care businesses; and, quite possibly, a less-healthy, less-productive workforce. The tax bill will be the most important health care legislation enacted since the Affordable Care Act (ACA) in 2010.
Is a precipitous cut bad for Medicare?
Precipitous cuts, however, could be damaging. In any case, if the nation were to embark on a drive to make the delivery of health care more efficient, Medicare and Medicaid would not be the most promising places to start.
Will Medicaid reforms reduce the size of government?
For Medicaid, reforms would likely lead similarly to fewer people covered, reduced benefits, and/or higher cost-sharing. For conservatives who have long sought to reduce the generosity of entitlements in the United States, these changes would be a welcome way to reduce the size of government.
How much will CMS reduce payments?
Through current law, CMS is already set to reduce payments to all plans by a minimum of 5.9%. CBO proposed raising that to 8%, which it says would save an additional $47 billion over 10 years. Alternatively, CMS could change the formula for health risk scores by using two years' worth of diagnostic data instead of one.
How much would the deficit be reduced if the eligibility age was raised to 67?
As a result, if Congress raised the eligibility age by two months a year, ending at 67, it would only decrease the deficit by $15.4 billion. Even if it took the slightly speedier route of raising it by three months a year, it would only save $21.8 billion.
How much would the per enrollee cap reduce the deficit?
All else being equal, a per-enrollee cap would reduce the deficit more than an overall cap, CBO said. The per-enrollee cap would decrease the deficit by $703 billion between 2019-2028, while the overall cap would decrease it by $496 billion over the same period.
How much money will the government save by paying for brand name drugs?
At a rebate of 23.1% of a drug's average manufacturer price, CBO said the government could save $154 billion between 2019 and 2028.
Does Medicare have cost sharing?
While Medicare has cost-sharing rules built in , most enrollees have some form of supplemental insurance that eliminates their cost-sharing obligations. This diminishes the impact cost-sharing rules are supposed to have—namely reducing the amount of unnecessary care.
Does raising the age for Medicare save money?
Interestingly, the controversial option of raising the Medicare eligibility age doesn't actually produce much savings, according to CBO. That's because many of those in the 65-67 age bracket would be able to get coverage through Medicaid or the ACA marketplaces, both of which are on the federal government's dime anyway.
Will Medigap pay coinsurance?
Another option would be to leave the cost-sharing rules as they are but restrict Medigap policies from paying portions of enrollees' deductible and coinsurance. This could save the federal government $72 billion between 2019 and 2028, though the new rules would only come into effect in 2022.
How did the ACA reduce Medicare costs?
Cost savings through Medicare Advantage. The ACA gradually reduced costs by restructuring payments to Medicare Advantage, based on the fact that the government was spending more money per enrollee for Medicare Advantage than for Original Medicare. But implementing the cuts has been a bit of an uphill battle.
Why did Medicare enrollment drop?
When the ACA was enacted, there were expectations that Medicare Advantage enrollment would drop because the payment cuts would trigger benefit reductions and premium increases that would drive enrollees away from Medicare Advantage plans.
How much does Medicare Part B cost in 2020?
Medicare D premiums are also higher for enrollees with higher incomes .
What is Medicare D subsidy?
When Medicare D was created, it included a provision to provide a subsidy to employers who continued to offer prescription drug coverage to their retirees, as long as the drug covered was at least as good as Medicare D. The subsidy amounts to 28 percent of what the employer spends on retiree drug costs.
What percentage of Medicare donut holes are paid?
The issue was addressed immediately by the ACA, which began phasing in coverage adjustments to ensure that enrollees will pay only 25 percent of “donut hole” expenses by 2020, compared to 100 percent in 2010 and before.
How many Medicare Advantage enrollees are there in 2019?
However, those concerns have turned out to be unfounded. In 2019, there were 22 million Medicare Advantage enrollees, and enrollment in Advantage plans had been steadily growing since 2004.; Medicare Advantage now accounts for well over a third of all Medicare beneficiaries.
How many Medicare Advantage plans will be available in 2021?
For 2021, there are 21 Medicare Advantage and/or Part D plans with five stars. CMS noted that more than three-quarters of all Medicare beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans with integrated Part D prescription coverage would be in plans with at least four stars as of 2021.
When did Medicare start?
Originating in the Social Security Amendments Act of 1965 (H.R. 6675), Medicare began its life as a traditional FFS health plan with the aim of providing coverage to impoverished elderly Americans in the remaining few years of their life; average life expectancy at birth was 70.5 years. 7.
What is Medicare Advantage?
Medicare Advantage, an alternative that uses defined contribution payments to private companies that administer health care benefits, provides greater financial protections and benefits for consumers while providing the potential for budgetary control in a way that does not exist in traditional Medicare.
What is the Medicare program?
The Medicare program consists of two primary programs: traditional Medicare (a FFS model) and MA, which is based on market-driven health plan competition.
When did Medicare extend to disabled people?
In 1972 Medicare coverage was extended to people with significant disabilities. But Medicare’s success in providing access to health care for millions of people is in danger. Ironically, the threat comes from private insurance plans.
Why was Medicare created?
It was intended to provide basic coverage through one health insurance system, with a defined set of benefits. Reforms to Medicare should honor and maintain its core values to ensure its continued success for future generations.
What is the Medicare platform?
Medicare Platform: Principles to Improve Medicare for All Beneficiaries Now and In the Future. Improve Consumer Protections and Quality Coverage. Cap out-of-pocket costs in traditional Medicare [1] Require Medigap plans to be available to everyone in traditional Medicare, regardless of pre-existing conditions and age.
How to ensure Medicare is comprehensive?
Ensure traditional Medicare is comprehensive, simple to navigate, and affordable. Add oral health, audiology, and vision coverage for all beneficiaries in traditional Medicare. Increase low-income protections and reduce cost-sharing. Add coverage for long-term care.
Why was the nursing home billed for $13,000?
She went from a hospital to a nursing home and was being billed for $13,000 because the nursing home was out of her MA plan’s network. She had been told by both the hospital and nursing home staff that original Medicare would cover her nursing home stay, even though she had an MA plan. This is not true.
When did Newt Gingrich say Medicare would be privatized?
In 1995 Newt Gingrich predicted that privatization efforts would lead Medicare to wither on the vine. He said it was unwise to get rid of Medicare right away, but envisioned a time when it would no longer exist because beneficiaries would move to private insurance plans.
Is Medicare a success?
When Medicare was created in 1965 over 50% of everyone 65 or older had no health insurance. Private insurance failed to meet their needs. Medicare, on the other hand, is a success. It increased the number of insured older adults to 95%. In 1972 Medicare coverage was extended to people with significant disabilities. But Medicare’s success in providing access to health care for millions of people is in danger. Ironically, the threat comes from private insurance plans. Funded by windfall subsidies from taxpayer dollars, privatization is jeopardizing the cost-effective, dependable Medicare program.
Medicaid work requirements
Section 1115 of the Social Security Act empowers the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) to approve state demonstrations that promote the objectives of the Medicaid program.
Medicaid Fiscal Reform
The Medicaid Fiscal Accountability Regulation (MFAR) sought to improve program integrity in the Medicaid program and ensure payment mechanisms would not be gamed to increase federal expenditures. To further this goal, MFAR proposed a number of technical changes to the Medicaid program.
Conclusion
In the future, it should be possible to design work requirements that clear the legal hurdles the current effort ran into, particularly as the Supreme Court has yet to rule on waivers.