- Hospital payment = DRG relative weight x hospital base rate.
- There are several formulas that allow payment transfers and calculations according to several groups.
- Formular for calculating MS-DRG.
- Hospital payment = DRG relative weight x hospital base rate.
How to calculate DRG reimbursement?
The formula used to calculate payment for a specific case multiplies an individual hospital's payment rate per case by the weight of the DRG to which the case is assigned. Each DRG weight represents the average resources required to care for cases in that particular DRG, relative to the average resources used to treat cases in all DRGs.
How to calculate a DRG?
Calculating DRG payments involves a formula that accounts for the adjustments discussed in the previous section. The DRG weight is multiplied by a “standardized amount,” a figure representing the average price per case for all Medicare cases during the year. Find out all about it here.
How are DRG rates calculated?
- Previous DRG Simulations. Note: The SFY 2019-20 Provider Specific Results have been updated with data reflecting the impact of changes to projected hospital inpatient reimbursement, by hospital and in the ...
- DRG Transitional Payments
- DRG Payment Options. ...
- Reimbursement Plans. ...
- Meeting Archive
How is DRG reimbursement calculated?
- Hospital payment = DRG relative weight x hospital base rate.
- There are several formulas that allow payment transfers and calculations according to several groups.
- Formular for calculating MS-DRG.
- Hospital payment = DRG relative weight x hospital base rate.
How are DRG rates calculated?
Calculating DRG payments involves a formula that accounts for the adjustments discussed in the previous section. The DRG weight is multiplied by a “standardized amount,” a figure representing the average price per case for all Medicare cases during the year.
What is Medicare DRG reimbursement?
Diagnosis-Related Group Reimbursement. Diagnosis-related group reimbursement (DRG) is a reimbursement system for inpatient charges from facilities. This system assigns payment levels to each DRG based on the average cost of treating all TRICARE beneficiaries in a given DRG.
How is APR DRG reimbursement calculated?
Just as with MS-DRGs, an APR-DRG payment is calculated by using an assigned numerical weight that is multiplied by a fixed dollar amount specific to each provider. Each base APR-DRG, however, considers severity of illness and risk of mortality instead of being based on a single complication or comorbidity.
What is a DRG base rate?
Under the IPPS, each case is categorized into a diagnosis-related group (DRG). Each DRG has a payment weight assigned to it, based on the average resources used to treat Medicare patients in that DRG. The base payment rate is divided into a labor-related and nonlabor share.
What is an example of DRG?
The top 10 DRGs overall are: normal newborn, vaginal delivery, heart failure, psychoses, cesarean section, neonate with significant problems, angina pectoris, specific cerebrovascular disorders, pneumonia, and hip/knee replacement. They comprise nearly 30 percent of all hospital discharges.
Which are used to calculate reimbursement for hospital based Medicare?
Uses ambulatory payment classifications (APCs) to calculate reimbursement; was implemented for billing of hospital-based Medicare outpatient claims.
What is the difference between DRG and APR DRG?
AP-DRGs are similar to DRGs, but also include a more detailed DRG breakdown for non-Medicare patients, particularly newborns and children. The APR-DRG structure is similar to the AP-DRG, but also measures severity of illness and risk of mortality in addition to resource utilization.
How do you calculate relative weight of MS-DRG?
A: CMS will establish the relative weight for an MS-DRG by calculating the ratio of the single weighted average standardized median MA organization payer-specific negotiated charge for that MS-DRG across hospitals to the single national weighted average standardized median MA organization payer-specific negotiated ...
How are DRG outliers calculated?
To qualify as a DRG high outlier claim, the estimated costs must be greater than the DRG allowed amount plus $40,000. The estimated costs equal the total submitted charges minus any noncovered and nonallowed charges multiplied by the hospital's ratio of costs-to-charges (RCC).
MS-DRG Definitions Manual and Software
We are providing a test version of the ICD-10 MS-DRG GROUPER Software, Version 39, so that the public can better analyze and understand the impact of the proposals included in the FY 2022 IPPS/LTCH PPS proposed rule. This test software reflects the proposed GROUPER logic for FY 2022.
HCPCS-MS-DRG Definitions Manual and Software
The 21 st Century Cures Act requires that by January 1, 2018, the Secretary develop an informational “HCPCS version” of at least 10 surgical MS-DRGs.
What is the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule?
The Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS) uses a resource-based relative value system (RBRVS) that assigns a relative value to current procedural terminology (CPT) codes that are developed and copyrighted by the American Medical Association (AMA) with input from representatives of health care professional associations and societies, including ASHA. The relative weighting factor (relative value unit or RVU) is derived from a resource-based relative value scale. The components of the RBRVS for each procedure are the (a) professional component (i.e., work as expressed in the amount of time, technical skill, physical effort, stress, and judgment for the procedure required of physicians and certain other practitioners); (b) technical component (i.e., the practice expense expressed in overhead costs such as assistant's time, equipment, supplies); and (c) professional liability component.
What are the two categories of Medicare?
There are two categories of participation within Medicare. Participating provider (who must accept assignment) and non-participating provider (who does not accept assignment). You may agree to be a participating provider (who does not accept assignment). Both categories require that providers enroll in the Medicare program.
Why is Medicare fee higher than non-facility rate?
In general, if services are rendered in one's own office, the Medicare fee is higher (i.e., the non-facility rate) because the pratitioner is paying for overhead and equipment costs. Audiologists receive lower rates when services are rendered in a facility because the facility incurs ...
Why do audiologists get lower rates?
Audiologists receive lower rates when services are rendered in a facility because the facility incurs overhead/equipment costs. Skilled nursing facilities are the most common applicable setting where facility rates for audiology services would apply because hospital outpatient departments are not paid under the MPFS.
Does Medicare pay 20% co-payment?
All Part B services require the patient to pay a 20% co-payment. The MPFS does not deduct the co-payment amount. Therefore, the actual payment by Medicare is 20% less than shown in the fee schedule. You must make "reasonable" efforts to collect the 20% co-payment from the beneficiary.
How to calculate DRG?
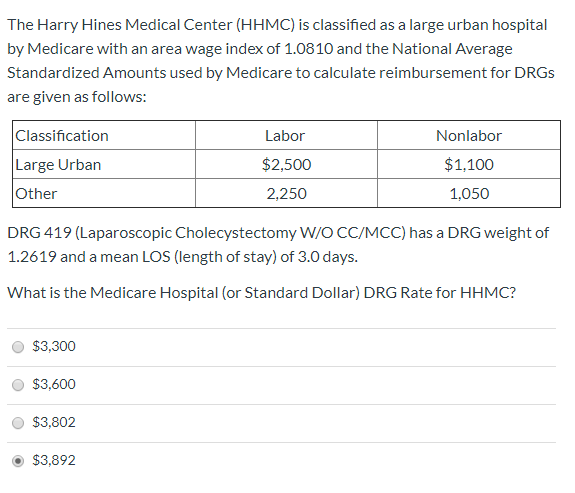
Calculating DRG payments involves a formula that accounts for the adjustments discussed in the previous section. The DRG weight is multiplied by a “standardized amount,” a figure representing the average price per case for all Medicare cases during the year. The standardized amount is the sum of: (1) a labor component which represents labor cost variations among different areas of the country and (2) a non-labor component which represents a geographic calculation based on whether the hospital is located in a large urban, or other area. The labor component is then adjusted by a wage index.42 If applicable, cost outlier, disproportionate share, and indirect medical education payments are added to the payment.
How does CMS update DRG weights?
The process by which the DRG weights are updated is referred to as recalibration. Through recalibration, CMS updates the DRG system to account for changes in medical practices, technology, and the range of cases within the DRGs (commonly referred to as “case complexity”). Recalibration ensures that the weights accurately reflect the value of resources used for each patient classification. The Social Security Act requires CMS to recalibrate the DRG weights in a manner that maintains “budget neutrality” of the total program. Budget neutrality requires that the estimated payments for the hospital benefit are not greater or less than 25 percent of the payment amounts that would have been payable for the same services in Fiscal Year 1984.51
How does CMS respond to MedPAC?
CMS responds to MedPAC’s recommendations in the same manner that it responds to the general public’s comments — through the public comment process in the Federal Register. CMS systematically responds to each MedPAC recommendation. Some of the recommendations are implemented, others are not. Some of MedPAC’s recommendations would require legislative changes which are beyond CMS’ control. In response to MedPAC’s June 2000 recommendation that the Secretary should adopt the All Patients Refined Diagnosis Related Groups, CMS agreed that this change would reduce discrepancies between payments and costs, but declined to adopt such a change because it would not be able to predict with accuracy how such a change may affect coding behavior. Furthermore, CMS believes that such a change would require specific legislative authority.62
What is the process of updating DRG codes?
The process by which the DRG codes are updated is called reclassification. It involves not only an assessment of the appropriateness of the DRG assignment within MDCs, but it also entails reclassifying the codes to account for new medical technologies and treatment patterns.
Why does CMS reclassify DRGs?
CMS reclassifies the DRGs and recalibrates the DRG weights to decide what changes are necessary to compensate adequately for costs under PPS. The recalibration and reclassification processes are integrally related. The reclassification update occurs first, followed by recalibration of the weights.
What are the factors that determine DRG payments?
In addition to the four factors discussed above, there are other factors considered in calculating DRG payments depending on whether the hospital is considered a sole community hospital, a Medicare dependent rural hospital, or a regional referral hospital. In each instance, there are special payment rules. A hospital may be designated as a sole community hospital if, among other things, it is (1) located more than 35 miles from another hospital, (2) the sole source of inpatient hospital services in a geographic area, or (3) designated by the Secretary as a “critical access hospital.”39 A Medicare dependent rural hospital is one that depends on Medicare for at least 60 percent of its patient days or discharges. A regional referral hospital is one that serves as a referral center for other hospitals in its area.40 These hospitals are reimbursed according to the payment rate for large urban areas.
What is a DRG in PPS?
A key part of PPS is the categorization of medical and surgical services into diagnosis-related groups (DRGs). The DRGs “bundle” services (labor and non-labor resources) that are needed to treat a patient with a particular disease. The DRG payment rates cover most routine operating costs attributable to patient care, including routine nursing services, room and board, and diagnostic and ancillary services.19 The CMS creates a rate of payment based on the “average” cost to deliver care (bundled services) to a patient with a particular disease. The DRG rates do not expressly include direct medical education costs, outpatient services, or services covered by Medicare Part B.20 For fiscal year 2002, there are 499 DRGs with a prospective price based on the average resources used in treating patients under the specific DRG.21
Transition of Inpatient Hospital Review Workload
Please see links below in the Downloads Section to some helpful informational materials on the subject of Inpatient Prospective Payment System Hospital and Long Term Care Hospital Review and Measurement.
Hospital Center
For a one-stop resource web page focused on the informational needs and interests of Medicare Fee-for-Service (FFS) hospitals, go to the Hospital Center (see under "Related Links Inside CMS" below).
