What is the Qualified Medicare beneficiary program (QMB)?
The Qualified Medicare Beneficiary (QMB) program provides Medicare coverage of Part A and Part B premiums and cost sharing to low-income Medicare beneficiaries. In 2017, 7.7 million people (more than one out of eight people with Medicare) were in the QMB program.
What is the quality payment program (QPP)?
What’s the Quality Payment Program? The Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA) ended the Sustainable Growth Rate (PDF) (SGR) formula, which would have significantly cut payment rates for participating Medicare clinicians. MACRA requires us to implement an incentive program, the Quality Payment Program.
What are the benefits of The QMB program?
The Benefits of the QMB Program. The QMB Program provides Medicare participants with a number of benefits that make it easier to cover their financial obligations that Medicare doesn’t cover. The QMB Program helps to cover: Medicare Part A monthly premiums. Medicare Part B monthly premiums and the annual deductible.
Do I need Medigap If I’m on QMB?
Medigap coverage isn’t necessary for anyone on the QMB program. This program helps you avoid the need for a Medigap plan by assisting in coverage for copays, premiums, and deductibles. Those that don’t qualify for the QMB program may find that a Medigap plan helps make their health care costs much more predictable.

What is Medicare MIPS?
The Merit-Based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) is the program that will determine Medicare payment adjustments. Using a composite performance score, eligible clinicians (ECs) may receive a payment bonus, a payment penalty or no payment adjustment.
What are the criteria to be considered an advanced alternative payment model APM )?
In order for a clinician to receive a bonus payment through an APM, the APM must be considered an Advanced APM (AAPM) by meeting the following eligibility requirements: Use of quality measures comparable to measures under MIPS; Use of a certified electronic health record (EHR) technology; and.
What is a qualifying APM participant?
Qualifying APM Participant (QP) Advanced APMs allow eligible clinicians to become QPs. To become a QP, clinicians must receive at least 50 percent of Medicare Part B payments or see at least 35 percent of Medicare patients through an Advanced APM Entity during the QP performance period (January 1 - August 31).
What is CMS QPP?
The Quality Payment Program improves Medicare by helping you focus on care quality and the one thing that matters most — making patients healthier. MACRA ended the Sustainable Growth Rate formula, which threatened clinicians participating in Medicare with potential payment cliffs for 13 years.
What is the difference between MIPS and APM?
MIPS stands for Merit-Based Incentive Payment System, while APM stands for Alternative Payment Model. Health care providers need to begin the verification process this year, and the first payments under these systems will be made in 2019. Both MIPS and APMs are processes that use value-based payment models.
What is an example of an advanced alternative payment model?
A common example of an APM is a Medicare Shared Savings Plan (MSSP) also known as an Accountable Care Organization (ACO).
What is APM in CMS?
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services' Innovation Center develops and evaluates alternative payment models (APMs), which test new healthcare payment and service delivery approaches and reward model participants for effectively delivering value-based care.
What is a medical APM?
An Alternative Payment Model (APM) is a payment approach that gives added incentive payments to provide high-quality and cost-efficient care. APMs can apply to a specific clinical condition, a care episode, or a population.
What is an advanced APM entity?
Physicians participate in an Advanced APM through an APM Entity. There is flexibility in how an APM Entity could be formed. It could be comprised of: A solo practitioner. A group practice of physicians and other eligible clinicians with a single tax identification number (TIN)
Why was Qpp created?
To improve the care received by Medicare beneficiaries. To lower costs to the Medicare program through improvement of care and health.
What are the 4 MIPS categories?
MIPS adjusts Medicare Part B payments based on performance in four performance categories: quality, cost, promoting interoperability, and improvement activities.
What are MIPS requirements?
2022 Low Volume Threshold Participation in MIPS is required if, in both 12-month segments of the MIPS Determination Period if: Excluded individuals or groups must have ≤ $90,000 Part B allowed charges OR ≤ 200 Part B patients OR ≤ 200 covered professional Part B services.
What are alternative payment methods?
Alternative payment methods are defined as a way of paying for goods or services which are not made via cash or major card schemes (Visa, MasterCard, American Express). This includes prepaid cards, mobile payments, e-wallets, bank transfers, and 'buy now, pay later' instant financing.
What does insurance APM mean?
An alternative payment model (APM) is an approach to paying for medical care through Medicare that incentivizes quality and value.
Is Medicare Advantage an APM?
Other Payer Advanced APMs are non-Medicare Fee For Service (FFS) payment arrangements with other payers such as Medicaid, Medicare Health Plans (including Medicare Advantage, Medicare-Medicaid Plans, 1876 Cost Plans, and Programs of All Inclusive Care for the Elderly (PACE) plans), payers with payment arrangements in ...
What is Medicare Alt?
An Alternative Payment Model (APM) is a payment approach that gives added incentive payments to provide high-quality and cost-efficient care. APMs can apply to a specific clinical condition, a care episode, or a population.
Parts of Medicare
Learn the parts of Medicare and what they cover. Get familiar with other terms and the difference between Medicare and Medicaid.
General costs
Discover what cost words mean and what you’ll pay for each part of Medicare.
How Medicare works
Follow 2 steps to set up your Medicare coverage. Find out how Original Medicare and Medicare Advantage work.
Working past 65
Find out what to do if you’re still working & how to get Medicare when you retire.
Medicare basics
Start here. Learn the parts of Medicare, how it works, and what it costs.
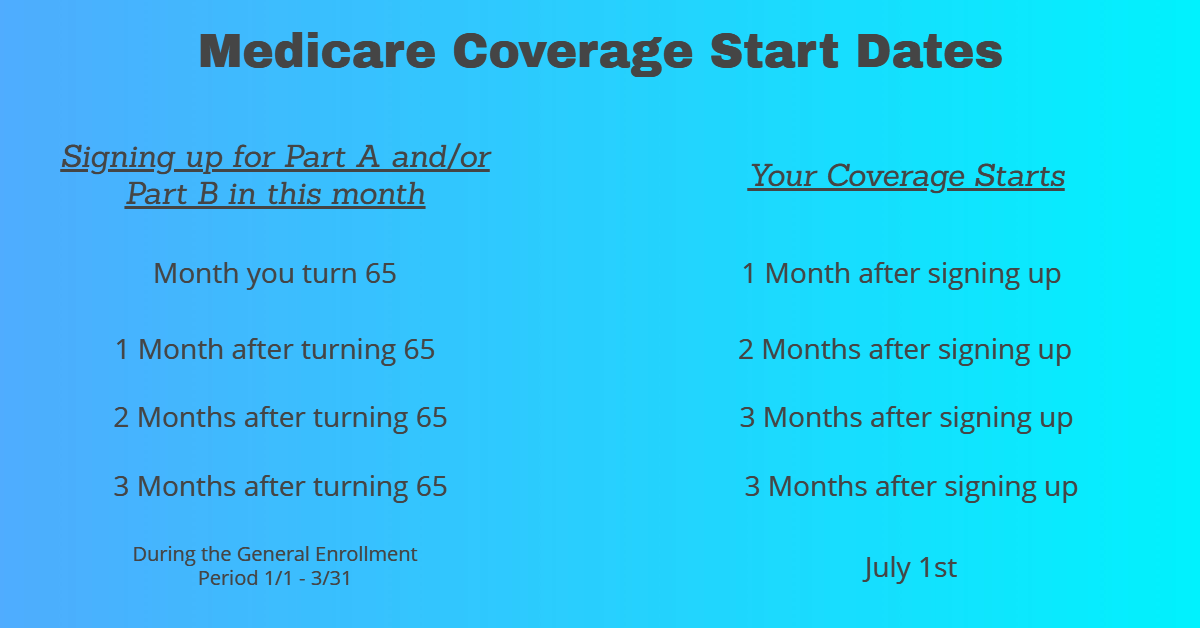
Sign up
First, you’ll sign up for Parts A and B. Find out when and how to sign up, and when coverage starts.
How to become a Medicare provider?
Become a Medicare Provider or Supplier 1 You’re a DMEPOS supplier. DMEPOS suppliers should follow the instructions on the Enroll as a DMEPOS Supplier page. 2 You’re an institutional provider. If you’re enrolling a hospital, critical care facility, skilled nursing facility, home health agency, hospice, or other similar institution, you should use the Medicare Enrollment Guide for Institutional Providers.
How long does it take to change your Medicare billing?
To avoid having your Medicare billing privileges revoked, be sure to report the following changes within 30 days: a change in ownership. an adverse legal action. a change in practice location. You must report all other changes within 90 days. If you applied online, you can keep your information up to date in PECOS.
How to get an NPI?
If you already have an NPI, skip this step and proceed to Step 2. NPIs are issued through the National Plan & Provider Enumeration System (NPPES). You can apply for an NPI on the NPPES website.
Do you need to be accredited to participate in CMS surveys?
ii If your institution has obtained accreditation from a CMS-approved accreditation organization, you will not need to participate in State Survey Agency surveys. You must inform the State Survey Agency that your institution is accredited. Accreditation is voluntary; CMS doesn’t require it for Medicare enrollment.
Can you bill Medicare for your services?
You’re a health care provider who wants to bill Medicare for your services and also have the ability to order and certify. You don’t want to bill Medicare for your services, but you do want enroll in Medicare solely to order and certify.
What is QMB in Medicare?
The Qualified Medicare Beneficiary ( QMB) program provides Medicare coverage of Part A and Part B premiums and cost sharing to low-income Medicare beneficiaries. In 2017, 7.7 million people (more than one out of eight people with Medicare) were in the QMB program.
Can a QMB payer pay Medicare?
Billing Protections for QMBs. Federal law forbids Medicare providers and suppliers, including pharmacies, from billing people in the QMB program for Medicare cost sharing. Medicare beneficiaries enrolled in the QMB program have no legal obligation to pay Medicare Part A or Part B deductibles, coinsurance, or copays for any Medicare-covered items ...
How many measures are required for CMS?
General reporting requirements (for those not reporting through the CMS Web Interface): You’ll typically need to submit collected data for at least 6 measures (including 1. outcome measure. or high-priority measure in the absence of an applicable outcome measure), or a complete. specialty measure set.
When does CMS Web Interface end?
The CMS Web Interface will no longer be an available collection and submission type beginning with the 2022 performance period.
How many measures are required to submit for a specialty measure set?
Specialty Measure Sets. If you choose to submit a specialty measure set, you must submit data on at least 6 measures within that set. If the set contains fewer than 6 measures, you should submit each measure in the set.
What is a QAPI plan?
The QAPI plan will guide your organization’s performance improvement efforts. Prior to developing your plan, complete the Guide to Develop Purpose, Guiding Principles, and Scope for QAPI. Your QAPI plan is intended to assist you in achieving what you have identified as the purpose, guiding principles and scope for QAPI, therefore this information is needed before you begin working on your plan. This is a living document that you will continue to refine and revisit. Use these step-by-step instructions to create your QAPI plan. This plan should reflect input from caregivers representing all roles and disciplines within your organization.
What is QAPI based on?
Based on the Guide to Develop Purpose, Guiding Principles, and Scope for QAPI, indicate the QAPI goals that your plan will strive to meet. Goals should be specific, measurable, actionable, relevant, and have a time line for completion. (See Goal Setting Worksheet).
What is QMB in Medicare?
Qualified Medicare Beneficiary (QMB) Program. If you’re a Medicare beneficiary, you know that health care costs can quickly add up. These costs are especially noticeable when you’re on a fixed income. If your monthly income and total assets are under the limit, you might be eligible for a Qualified Medicare Beneficiary program, or QMB.
What is QMB insurance?
The QMB program pays: The Part A monthly premium (if applicable) The Part B monthly premium and annual deductible. Coinsurance and deductibles for health care services through Parts A and B. If you’re in a QMB program, you’re also automatically eligible for the Extra Help program, which helps pay for prescription drugs.
What is a qualified Medicare beneficiary?
The Qualified Medicare Beneficiary program is a type of Medicare Savings Program (MSP). The QMB program allows beneficiaries to receive financial help from their state of residence with the costs of Medicare premiums and more. A Qualified Medicare Beneficiary gets government help to cover health care costs like deductibles, premiums, and copays.
How much money do you need to qualify for QMB?
To be eligible for a QMB program, you must qualify for Part A. Your monthly income must be at or below $1,084 as an individual and $1,457 as a married couple. Your resources (money in checking and/or savings accounts, stocks, and bonds) must not total more than $7,860 as an individual or $11,800 as a married couple.
Can QMB members pay for coinsurance?
Providers can’t bill QMB members for their deductibles , coinsurance, and copayments because the state Medicaid programs cover these costs. There are instances in which states may limit the amount they pay health care providers for Medicare cost-sharing. Even if a state limits the amount they’ll pay a provider, QMB members still don’t have to pay Medicare providers for their health care costs and it’s against the law for a provider to ask them to pay.
Does Medicare Advantage cover dual eligibility?
A Medicare Advantage Special Needs Plan for dual-eligible individuals could be a fantastic option. Generally, there is a premium for the plan, but the Medicaid program will pay that premium. Many people choose this extra coverage because it provides routine dental and vision care, and some come with a gym membership.
Is Medigap coverage necessary for QMB?
Medigap coverage isn’t necessary for anyone on the QMB program. This program helps you avoid the need for a Medigap plan by assisting in coverage for copays, premiums, and deductibles. Those that don’t qualify for the QMB program may find that a Medigap plan helps make their health care costs much more predictable.
What's MACRA?
The Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA) is a bipartisan legislation signed into law on April 16, 2015.
Quality Payment Program
You can learn more about the Quality Payment Program at qpp.cms.gov and on our CMS.gov pages. On 11/1/17, we moved the Quality Payment Program content you’re used to finding here to our new CMS.gov Quality Payment Program pages.
What's new?
On September 21, 2018, we selected 7 applicants to receive cooperative agreement awards through the “Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA) Funding Opportunity: Measure Development for the Quality Payment Program.”
New Medicare cards
MACRA required us to remove Social Security Numbers (SSNs) from all Medicare cards. Replacing SSNs on all Medicare cards helps to better protect:
