
Will Medicare run a surplus of $526 billion?
According to the White House, Medicare will run a trust-fund surplus of $526 billion over the next ten years. Excluding interest, its cash surplus of earmarked tax revenue over outlays will be just $277 billion.
Is Medicare’s trust-fund surplus really a savings?
Trust-fund accounting obscures the fiscal bottom line by counting prior-year surpluses, together with the interest-earned thereon, as genuine savings. In reality, these assets are simply claims on future taxpayers. According to the White House, Medicare will run a trust-fund surplus of $526 billion over the next ten years.
Is Medicare in deficit or surplus?
Within the trust-fund framework, Medicare is running a large surplus. Within the cash accounting framework adopted in the White House budget, Medicare is deep in deficit. The Concord Coalition supports this change because it has always believed that cash accounting provides a more honest measure of Medicare's fiscal burden.
What is a gross-up in a compensation plan?
Reviewed by Adam Hayes. Updated Aug 18, 2019. A gross-up is an additional amount of money added to a payment to cover the income taxes the recipient will owe on the payment. The gross-up is most often seen in executive compensation plans.
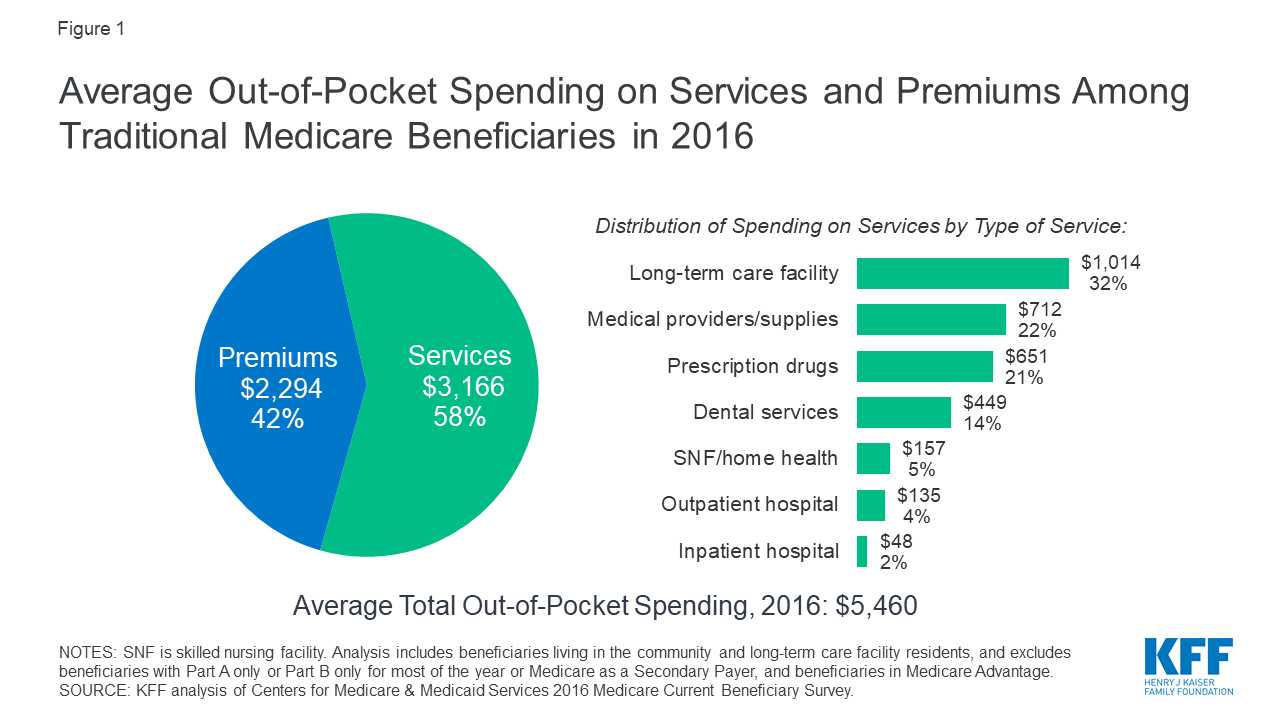
Can I get a refund for excess Medicare tax withheld?
Therefore, you need to file Form 8959, Additional Medicare Tax, to document the withholding and to receive a refund of any tax that was withheld in excess of the total tax owed on your individual income tax return.
Does the 3.8 Medicare tax apply to capital gains?
What Types of Income Are Subject to the Medicare Surtax? Income sources like interest, dividends, capital gains, rental income, royalties, and even some other passive investment income will be counted.
How do I calculate excess Medicare withholding?
Based on the Additional Medicare Tax law, all income for an individual above $200,000 is subject to an additional 0.9% tax. Therefore, his Additional Medicare Tax bill is $50,722 X 0.9% = $456. He has already paid (1.45% X $199,558) + (2.9% X $51,164) = $2,893.59 + $1,483.7 = $4,377.29 in Medicare taxes already.
Who pays excess Medicare tax?
Everyone who earns income pays some of that income back into Medicare. The standard Medicare tax is 1.45 percent, or 2.9 percent if you're self-employed. Taxpayers who earn above $200,000, or $250,000 for married couples, will pay an additional 0.9 percent toward Medicare.
Does additional Medicare tax apply to capital gains?
The Medicare surtax applies to the following gross investment income types: Interest. Dividends. Capital gains.
Is Medicare charged on capital gains?
The Medicare surtax applies to taxpayers above certain income thresholds. If the surtax applies to you, you'll owe an additional 3.8% tax rate on your investment income.
Where does additional Medicare tax go on w2?
This new tax is calculated on Federal Form 8959 Additional Medicare Tax and that form also reconciles the amount of tax owed against what an employer has already withheld from an employee's paycheck (and so is included as withholding in box 6 of the Form W-2 along with the regular Medicare tax withholding).
What is the 3.8 Medicare surtax?
The Medicare tax is a 3.8% tax, but it is imposed only on a portion of a taxpayer's income. The tax is paid on the lesser of (1) the taxpayer's net investment income, or (2) the amount the taxpayer's AGI exceeds the applicable AGI threshold ($200,000 or $250,000).
What triggers additional Medicare tax?
An employer must begin withholding Additional Medicare Tax in the pay period in which the wages or railroad retirement (RRTA) compensation paid to an employee for the year exceeds $200,000. The employer then continues to withhold it each pay period until the end of the calendar year.
How do I avoid paying the Medicare levy surcharge?
How do I avoid paying the Medicare Levy Surcharge (MLS)? If your income is less than $90,000 (singles) or $180,000 (couples, families and single parents), then you won't need to pay the MLS at all.
How much bad debt can be recovered from Medicare?
Hundreds of millions of dollars of unrealized Medicare bad debt revenue can be recovered at scale if reporting and analysis are performed efficiently with automation — whether via a fully outsourced consulting service or by using a SaaS solution. Recoveries can be close to a half a million dollars per provider (TransUnion Healthcare proprietary data).
What is Medicare bad debt?
Medicare bad debt is defined as Medicare coinsurance and deductible amounts that are unpaid and uncollectable from the patient. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) pays hospitals 65% of their gross Medicare bad debt if ...
How to deal with uncompensated care?
When tackling uncompensated care, specifically as it relates to Medicare bad debt, it is important to address the problem holistically, to ensure all your earned revenue is realized. Sophisticated analysis of all the relevant data must validate the thousands of opportunities. This can be a burdensome process, detracting from the primary goal of the billers and follow-up team to ship out claims and audit reimbursement. It is critical to evaluate assistance from third parties in this process in order to help free time for revenue cycle management staff to focus on other important issues. Cost report filing time is stressful for reimbursement departments, but external software and consultation can off-load weeks or even months of work.
How much of a hospital's annual revenue is patient financial responsibility?
Patient financial responsibility represents more than 30% of a hospital’s annual revenues. When tackling uncompensated care, specifically as it relates to Medicare bad debt, it is important to address the problem holistically, to ensure all your earned revenue is realized. Healthcare is becoming increasingly unaffordable to many, ...
What does every dollar of payment mean for a hospital?
To a hospital, every dollar of payment means a better opportunity to deliver excellent patient care. By finding the right partner and tools, hospitals can accurately and efficiently recover Medicare-bad-debt revenue. The money is waiting — go get it.
Does Medicare give back money?
Secure defendable documentation. Medicare doesn’t like giving money back, so reports need to be defensible on audit. Ensure the process delivers results with the full documentation required for submission to Medicare.
Do people on Medicare have to pay for healthcare?
Although many people struggle to pay for healthcare, the issue is particularly prevalent among Medicare beneficiaries, who are often retired and on a fixed income.
What is Medicaid surplus?
The “Medicaid Surplus” program allows New York Medicaid applicants (seniors aged 65 and over, blind and disabled residents, persons aged 21 and under, pregnant women, and parents with a child under 21 years of age) who are over Medicaid’s income limit, to still qualify for Medicaid. To be clear, this program is not relevant to assets, which means if a NY Medicaid applicant has assets over the asset limit, it won’t help in lowering an applicant’s countable assets. (For information on how to spend down excess assets, click here ).
What are some examples of medical expenses that can be applied to the “spend down”?
Examples of bills that might be applied towards one’s “spend down” include a hospitalization, prescription medications, physician / dental / vision appointments, eyeglasses, hearing aids, Medicare and Medicaid co-payments / deductibles, chiropractor services, and long-term care costs , such as in-home personal care assistance, home health aides, adult day care, etc. A married Medicaid beneficiary can apply his / her spouse’s medical bills towards his / her “spend down” amount.
Can a married person on medicaid pay down his/her spouse's medical bills?
A married Medicaid beneficiary can apply his / her spouse’s medical bills towards his / her “spend down” amount. For those who do not have medical expenses from which to “spend down” their excess income, there is another option, the Pay-In program.
What happens if you open a Medicaid case with excess income?
If your Medicaid case is opened with excess income, you will get a notice telling you the amount of your excess income.
What happens if you have excess income on medicaid?
If your monthly income is over the Medicaid level, you may still be able to get help with your medical bills. The amount your income is over the Medicaid level is called excess income. It is like a deductible. If you are eligible for Medicaid except for having excess income and you can show that you have medical bills equal to your excess income in a particular month, Medicaid will pay your additional medical bills beyond that for the rest of that month. This includes outpatient care, doctor and dental visits, lab tests, prescription drugs, and long-term care in the community such as home care and assisted living. There are special rules for hospital stays which is explained further below.
What is the Medicaid Excess Income program?
The Medicaid Excess Income program is sometimes referred to as the "Spenddown program" or the "Surplus Income program". Here we will be referring to it as the Excess Income program.
How is the amount of my excess income determined?
The amount is the difference between the monthly Medicaid income limit and your countable income. When we count your income, we take your gross monthly income and then subtract certain deductions. There are different deductions depending on whether you are certified disabled or blind or age 65 or older, or whether you are under age 21, pregnant, or a parent of a child under age 21.
What if I don't have bills that are equal to or exceed my excess income?
If you do not have medical bills but you need medical care, there is another option called the Pay-In Program. You can pay your monthly excess income amount for any month to your local department of social services. You should only do this if you need services in that month. Ask your local department of social services about this option.
Do I have to pay a bill in order for it to count toward meeting my excess income?
No. Bills can be paid or unpaid. Once the provider bills you for a medical service, you can submit that bill to count toward your excess income, even if you do not pay it.
How long can you get Medicaid outpatient?
If you have medical bills that are equal to or more than your monthly excess income, you can get Medicaid outpatient services for one month at a time. You must bring in, send or fax your medical bills to your local department of social services when they are at least equal to your excess income amount.
How is Medicare financed?
1-800-557-6059 | TTY 711, 24/7. Medicare is financed through two trust fund accounts held by the United States Treasury: Hospital Insurance Trust Fund. Supplementary Insurance Trust Fund. The funds in these trusts can only be used for Medicare.
Who can help with Medicare enrollment?
If you’d like more information about Medicare, including your Medicare enrollment options, a licensed insurance agent can help.
How Much Is the Medicare Tax Rate in 2021?
The 2021 Medicare tax rate is 2.9%. You’re typically responsible for paying half of this amount (1.45%), and your employer is responsible for the other half. Learn more.
How much Medicare tax do self employed pay?
Medicare taxes for the self-employed. Even if you are self-employed, the 2.9% Medicare tax applies. Typically, people who are self-employed pay a self-employment tax of 15.3% total – which includes the 2.9% Medicare tax – on the first $142,800 of net income in 2021. 2. The self-employed tax consists of two parts:
How is the Hospital Insurance Trust funded?
The Hospital Insurance Trust is largely funded by Medicare taxes paid by employees and employers , but is also funded by: The Hospital Insurance Trust Fund pays for Medicare Part A benefits and Medicare Program administration costs. It also pays for Medicare administration costs and fighting Medicare fraud and abuse.
What is Medicare Part A?
Medicare Part A premiums from people who are not eligible for premium-free Part A. The Hospital Insurance Trust Fund pays for Medicare Part A benefits and Medicare Program administration costs. It also pays for Medicare administration costs and fighting Medicare fraud and abuse.
How many parts are there in self employed tax?
The self-employed tax consists of two parts:
When grossing up, are taxes included in the employee's taxable income?
When grossing up, the taxes paid by the employer are included in the employee’s taxable income.
How much bonus do salespeople get?
A salesperson receives a $100 bonus. The sales manager wants the salesperson to receive $100 in cash (after withholding taxes), so the gross amount of the bonus will be more than $100. The employer decides to pay the employee’s taxes on taxable relocation expenses. The value of excess group-term life insurance for a terminated employee is ...
What is the tax rate for a $100 bonus?
For example, calculate the gross-up on the salesperson’s $100 bonus. Bonuses are taxed at the supplemental tax rate of 28% ; in addition, social security tax of 6.2% and Medicare tax of 1.45% are due. Assume that there is no state or local income tax and the salesperson will not meet the social security limit. Thus the tax percentage (step 1) is 35.65% (28% + 6.2% + 1.45% = 35.65%).
How much is a bonus taxed?
Bonuses are taxed at the supplemental rate of 28%; in addition, only $50 of the bonus is subject to social security tax while the entire bonus is subject to the Medicare tax. Assume that there is no state or local income tax. $100 + ( ($87,900-87,850) x 6.2%) / 70.55% = $100 + $3.10 / 70.55% = $146.14.
Does gross up work for Social Security?
In most circumstances, the gross-up formula works when paying the employee’s taxes. However, if the payment of the taxes causes the employee’s year-to-date social security wages to cross the social security wage base, the formula must be revised.
How to calculate gross up?
The formula to calculate a tax gross-up is: Gross-up = [Net Amount / (1 – Tax Rate)].
What boxes do you add FICA to W-2C?
The additional employee FICA tax paid by the employer should be reported in boxes 4 (Social security tax withheld) and 6 (Medicare tax withheld). However, the federal income tax paid by the employer should not be reported in box 2 as federal income tax withholdings because the employer did not withhold the tax from employee wages.
How much FICA tax was paid in 2018?
However, if the employer chooses not to collect the 2016 employee FICA tax from the employee in 2018, the PMTA concludes that the $765 of employee FICA tax paid by the employer in 2018 is additional wages and is subject to employment taxes. With respect to these additional wages, the employer can:
Is there a gross up obligation for 2016?
Tax Gross-Up Takeaways. In sum, the PMTA provides that (1) there is no tax gross-up obligation with respect to the additional 2016 wages but (2) there could be a tax gross-up obligation in 2018 with respect to the employer’s 2018 payment of the 2016 employee FICA taxes, if that payment constitutes additional wages in 2018.
Is fringe benefit taxable income?
In 2018, the IRS examined an employer’s 2016 employment tax returns and discovered that the employer gave $10,000 in taxable fringe benefits to an employee but, problematically, did not report the fringe benefits that year as taxable income to the employee or withhold employment taxes.
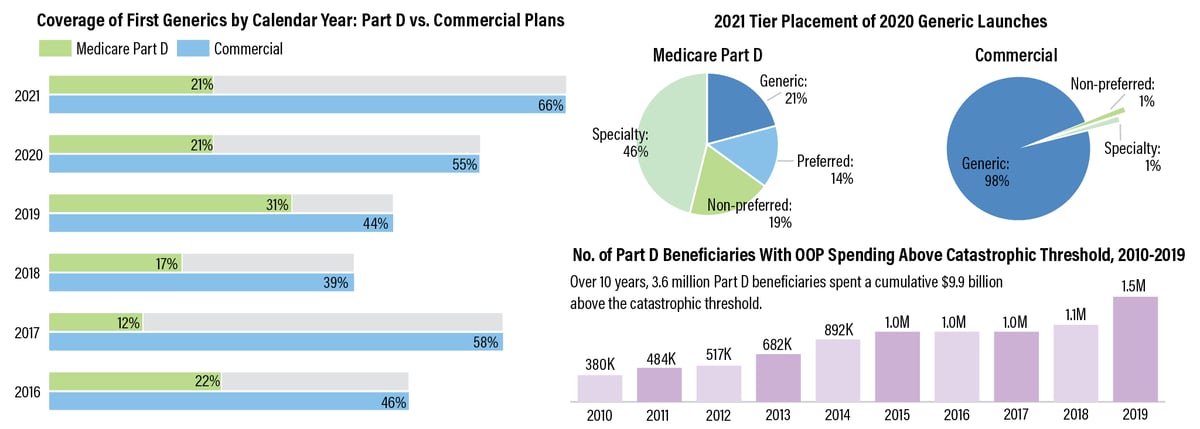
What Is A Gross-Up?
How A Gross-Up Works
- Grossing up a paycheck is essentially computing a paycheck but in reverse. Usually, employees are initially paid a gross paycheck amount from which deductions are thus withheld (such as taxes, retirement contributions, and social security) and the employees are paid the remainder as net pay. In a gross-up situation, the desired net pay is arranged in advance and the gross is suffi…
Example of Grossing-Up
- As an example, consider a company offering an employee who has an income tax rate of 20% a net salary of $100,000 annually. The formula for grossing up is as follows: 1. Gross pay= net pay / (1 - tax rate) The employer must gross-up the salary paid to the employee to $125,000 in order to account for the required 20% paid on income—because $125,000 ...
The Gross-Up Controversy
- With executive pay coming under increased scrutiny in light of the 2008 financial crisis, grossing up has grown as an increasingly popular way to pay executives. Companies can efficiently increase executive pay by 30% or more, without it being apparent in their financial statements since those statements show only what employees net. Nonetheless, several compa…