
How do I pay taxes on my stock options?
How you’ll pay taxes on stock options largely depends on whether you receive NQSOs or ISOs. Either way, you’ll pay income tax or capital gains tax when you sell the shares on the open market. With NQSOs, you’ll also pay income tax on the difference between the share value and your grant price when you actually exercise the option.
What are FICA taxes on stock options?
FICA taxes provide funds for Social Security and Medicare. You pay these taxes on wage income. When you receive and exercise stock options from your employer, some of their value might be treated like wages, in which case FICA taxes will apply.
Do I have to pay taxes on NQ stock options?
Your payroll taxes on gains from exercising your NQ stock options will be 1.45% for Medicare only if and when your earned income exceeds the wage base for the given tax year. You won't pay more than 6.2% of your wage base in taxes for Social Security if you earn more than that amount.
Should you exercise stock options based on tax decisions?
You should not exercise employee stock options strictly based on tax decisions. However, if you have held a stock with options and decide to exercise when you have no other earned income, you will pay payroll taxes on it. This might be one time when you decide to exercise based on taxes.
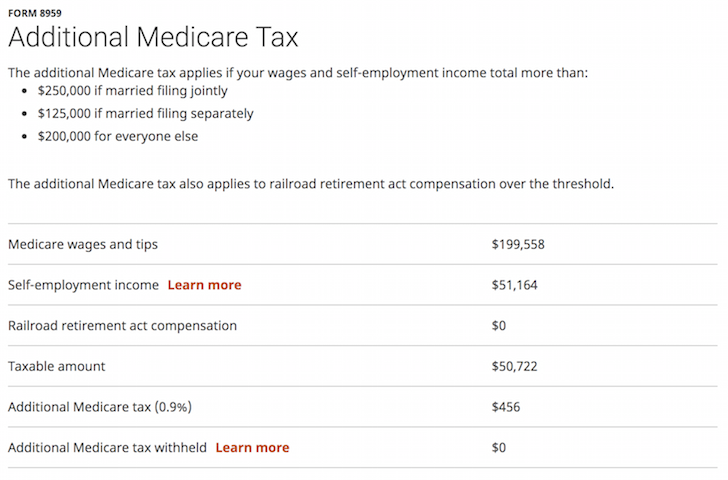
Do you pay Medicare tax on stock options?
With NSOs, you are taxed when you exercise the stock options. You pay ordinary income and Medicare taxes and are subject to Social Security tax if you have not paid the yearly maximum on the difference between the fair market value at exercise and the grant price.
How do you pay taxes on options trading?
When you buy an open-market option, you're not responsible for reporting any information on your tax return. However, when you sell an option—or the stock you acquired by exercising the option—you must report the profit or loss on Schedule D of your Form 1040.
Does FICA apply to stock options?
At exercise: The excess of the stock's fair market value over the option price is taxed as ordinary income and is subject to FICA and income tax withholding (if the option holder is an employee).
Do you pay taxes twice on stock options?
1. Double-counting income. When you exercise non-qualified stock options, the discount you receive or the “spread” — market value at exercise minus the price you paid — becomes part of annual compensation, levied at regular income tax rates and reported on your W-2.
How do I file taxes on a stock trade?
Security traders can declare 6% of the turnover), then you will be required to file ITR 4. However, you will be required to file ITR-3 if you declare your F&O income as presumptive business with capital gains. When we declare F&O income as presumptive business and we have capital gains ITR-3 is applicable.
What happens if you don't report stocks on taxes?
If you fail to report the gain, the IRS will become immediately suspicious. While the IRS may simply identify and correct a small loss and ding you for the difference, a larger missing capital gain could set off the alarms.
Are stock options subject to withholding tax?
Tax Implications of Nonqualified Stock Options and is subject to withholding. applicable state tax withholding. If shares are sold immediately, withholding can be taken from sales proceeds. If shares are not sold, employee must deliver a check to payroll department for withholding amounts.
How much taxes do you pay on options?
Non-equity options taxation 60% of the gain or loss is taxed at the long-term capital tax rates. 40% of the gain or loss is taxed at the short-term capital tax rates.
How can I avoid double tax on stocks?
Alert: If the cost basis is not reported on Form 1099-B, avoid double taxation by listing the market price on the date of exercise as your cost basis in the stock. The basis should be the exercise price plus the amount of ordinary income you already paid taxes on.
Do you get a 1099 for stock options?
If you sold stock, you'll receive Form 1099-B and the Supplemental Information form during the tax season. The information on your 1099-B is reported to the IRS, but the Supplemental Information form includes adjustments to a capital gain or loss necessary to avoid overpaying taxes.
What are the two types of options?
You don't have to buy the shares. It's your choice whether to do so, which is why they're called "options.". Employers typically give out two kinds of options: statutory and nonstatutory.
What are nonstatutory options?
Nonstatutory options are those that don't qualify for special treatment. They're also called nonqualified options.
Do you have to pay FICA on nonstatutory options?
The legal distinctions between statutory and nonstatutory options are somewhat technical and are based on such things as who receives the options, how the strike price is set and the rules for exercising the options. Your employer can tell you which kind you have. When it comes to FICA and stock options, the important thing to know is that you do not have to pay FICA taxes on statutory stock options, but you probably will pay them on nonstatutory options.
Do stock options pay FICA taxes?
FICA taxes provide funds for Social Security and Medicare. You pay these taxes on wage income. When you receive and exercise stock options from your employer, some of their value might be treated like wages, in which case FICA taxes will apply. It depends on the kind of stock option you receive.
Is exercise of stock option taxable?
Taxable Income at Exercise. It makes sense to exercise a stock option only if the strike price is lower than the actual share price of the stock. It would be a costly blunder to exercise an option to buy shares at, say, $10 a share if the stock was selling for only $9.
What is a 427 stock option?
427 Stock Options. If you receive an option to buy stock as payment for your services, you may have income when you receive the option, when you exercise the option, or when you dispose of the option or stock received when you exercise the option. There are two types of stock options:
What is nonstatutory stock option?
If your employer grants you a nonstatutory stock option, the amount of income to include and the time to include it depends on whether the fair market value of the option can be readily determined.
What is a Form 3922?
Employee Stock Purchase Plan - After your first transfer or sale of stock acquired by exercising an option granted under an employee stock purchase plan, you should receive from your employer a Form 3922, Transfer of Stock Acquired Through an Employee Stock Purchase Plan under Section 423 (c). This form will report important dates and values needed to determine the correct amount of capital and ordinary income to be reported on your return.
Is an option without a fair market value taxable?
For nonstatutory options without a readily determinable fair market value, there's no taxable event when the option is granted but you must include in income the fair market value of the stock received on exercise, less the amount paid, when you exercise the option. You have taxable income or deductible loss when you sell ...
What happens to stock options when a company is acquired?
Company Acquisition: If your company gets acquired, your stock options may be compensated or converted into shares of the acquiring company. You might be able to exercise your options during or after the acquisition deal.
What is incentive stock option?
Incentive stock options are similar to NQSOs but they include a special tax provision, discussed below, which makes them more attractive for employees. Executives or other high-ranking officials at a company are more likely to receive ISOs.
How long do you have to exercise stock options after leaving a company?
At that moment, your employer will offer you a post-termination exercise (PTE) period, or a limited timeframe of up to three months to exercise your options.
What happens if you don't hold stock for a year?
But keep in mind that if you do not hold on to your stock for at least one year, your gains will be taxed at a higher rate as ordinary income. Company Acquisition: If your company gets acquired, your stock options may be compensated or converted into shares of the acquiring company.
Is stock profit a capital gain?
Any profit counts as a capital gain. Stocks sold within a year are subject to income tax. If you wait at least a year, they are subject to the lower long-term capital gains rate. Taxes for Incentive Stock Options. Incentive stock options, on the other hand, are much more tax-friendly for employees.
Do you pay taxes on stock sales?
You will still have to pay tax on the money you make from selling the actual stock units though. The long-term capital gains tax applies to sales made two years after the grant and one year after exercising the option. The regular income tax applies to earlier sales.
Why are incentive stock options preferred to non-qualified stock options?
Incentive stock options are often preferred to non-qualified stock options because you have the potential to pay long term capital gains rates on the bargain element of the stock should you meet specific holding requirements:
What is an incentive stock option?
Similar to non-qualified stock options, incentive stock options (ISOs) allow for the purchase of a stock at a predetermined share price. If the current share price of the stock is above the price at which you can exercise your right to buy the share, you have an “in the money” option. But if the current market price of the stock is below ...
What is AMT in stock options?
AMT is the result of a secondary tax calculation that occurs every year when you file your tax return. As a taxpayer, you generally pay the higher of the regular tax calculation or the tentative minimum tax calculation. The difference you pay if the tentative minimum tax is higher is the AMT. When you exercise and hold incentive stock options past ...
What is the first taxable event?
The first taxable event occurs when you exercise your ISOs. When you exercise your incentive stock options, you create a reportable tax event that is based on the spread between the grant price of the option and the fair market value of the stock when you exercise, multiplied by the number of shares you exercise.
How long does it take to sell stock after the exercise date?
The final sale of the stock must be at least 1 year from the exercise date.
What happens if the stock price is below the price at which you can buy the stock?
But if the current market price of the stock is below the price at which you can buy the share, you likely pass on your right to exercise the option and buy the shares.
Do you pay taxes on ISOs?
Generally speaking, ISOs aren’t taxed until you exercise the option to buy the share – but over the lifespan of an incentive stock option, you may find yourself dealing with several types of taxes along the way.
What form do you get when you sell stocks?
In the year you sell the stocks, the employee would get a form 1099-B which reports all the capital gain or loss from the transactions in their tax return. In this case, they would have to analyze the investment records for verifying the cost basis amount on the form 1099-B, which is based on the details on the employee’s brokerage. In case the details are not complete, the cost basis amount might be incorrect.
What is box 1 in a tax return?
Box 1: Displays the gross wage, prizes, bonuses, tips, stock options, and other compensation that is taxable for the year in question . The amount is deducted from specific elective deferrals like payroll deductions, pre-tax benefits, and 401 (k) plans.
What is restricted stock unit?
The restricted stock units are another form of employee compensation. But in this plan, the employee does not get the stock during the grant. It has a particular vesting scheme that is outlined for the employee and how they would get the stock. When the stock is vested, the employee gets the shares and the FMV of the stock that the employee got on the same day is regarded as income.
What is Form 3921?
This form is used for ISOs during the year in which the employee receives it. It holds the details that accurately reports everything about the sale. Hence, this form has to be saved with the investment records. And it is important to note that the details would be entered from the form 3921 into the tax return only when you sell the shares.
What box is 1040?
Boxes 2 and 17 are used by the employer to share the amount that was withheld by the company for federal and state income tax.
How much discount is allowed on ESPP?
The maximum discount permitted in this plan is up to 15% lower than the actual market price.
How are non qualified stock options taxed?
When you exercise your non-qualified stock options, the value of the bargain element will be treated as earned income that is reported on your tax return the same way as your regular earned income. The bargain element is calculated as the difference between the grant price ...
How are stock shares taxed?
The period for which you retain ownership, and the value of the shares dictate how they will be taxed. Stock shares are subject to capital asset tax rates. Short term capital assets (assets that are held for less than one year) are taxed as ordinary income and long term capital gains (assets that are held for one year or greater) ...
What happens when you exercise non qualified stock options?
When you exercise your options, the spread between the grant price and the exercise price is taxed the same as compensation income subject to Medicare and Social Security tax. Any subsequent gain or loss from the date you exercise your options is taxed as a capital asset subject to capital asset rates.
What is the lifespan of options?
The lifespan of your options includes the period beginning when your shares are granted and ending when you sell the stock. During this time, you need to consider two different types of tax you may need to pay: Earned Income Tax: Earned income is taxed as ordinary income and is subject to Social Security and Medicare wage taxes.
What does advanced planning for non-qualified stock options mean?
Advanced planning for non-qualified stock options may also mean exercising in calendar years when you are also exercising or selling incentive stock options as a means to increase or decrease the alternative minimum tax.
Is long term capital gains tax better than short term?
Long term capital gains offers a more favorable rate, considering it creates a tax bill that is over 50% lower. (While this illustration indicates that long term capital gains rates are better than short term capital gains rates, it does not mean that you should always hold your stock for one year or more.
Is capital gains taxed as ordinary income?
Capital Gains Tax: Capital gains are taxed as ordinary income (for short term capital gains) or as long-term capital gains, depending on the holding period of the stock. The amount of gain subject to earned income tax and the amount subject to capital gains depends on several factors. Some of these include the exercise price ...
What are the two types of stock options?
There are two main types of stock options that you could receive as part of your compensation gift: incentive stock options and nonqualified stock options. The main difference between these two is how they are treated for tax purposes when you exercise the options. Incentive stock options (ISOs), also known as statutory stock options, ...
What is an incentive stock option?
Incentive stock options (ISOs), also known as statutory stock options, are granted under a stock purchase plan. However, nonqualified stock options (NSOs) are granted without a specific type of plan and are often referred to as nonstatutory stock options. As we'll see below, NSOs don't qualify for the same tax benefits that ISOs receive.
Why is it important to have a tax strategy when exercising NSOs?
It's important to have a tax strategy when exercising NSOs because you'll be hit with a tax twice, and it can get a bit complicated.
When you exercise stock options, do you have to be aware of the exercise?
When you have employee stock options, there are three special occasions you need to be aware of: the date your company granted you the options, when you exercised them, and how long you hold the shares you receive on exercise before you sell them. These moments play an important role in your tax calculation.
Can you tap into stock options?
Simply put, you cannot tap into your stock option benefits until you've been at your company for a certain period of time. After you are vested, then you can exercise the options at any time before they expire.
Can employees buy stock at a discount?
Often, employees are able to buy the company stock at a discount, providing a great opportunity to accumulate wealth if the stock performs well. But the other piece of the puzzle is trying to grasp how taxes for employee stock options work. It could easily become a nightmare if you've never dealt with stock options before.
Do you pay capital gains tax on shares you sell?
The IRS considers this as compensation income even though you haven't actually made any money. Then, you'll pay capital gains tax if you sell the shares at a profit. If the sale results in a loss, you'll report a capital loss for the difference between your tax basis and what you received.

Taxation of Non-Qualified Stock Options
Taxation of Incentive Stock Options
- Unlike NQ stock options, a gain on incentive stock options is not subject to payroll taxes, but it is subject to income tax. It's a preference item for the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) calculation.5 There can be two tax outcomes when you exercise an ISO.
The Bottom Line
- Tax rules can be complex. A good tax professional or financial planner can help you estimate the taxes and show you how much you'll have left after all taxes are paid if you choose any of these options. They can provide guidance on ways to time the exercise of your options to pay the least tax possible.