Full Answer
Does Someone on Medicaid automatically qualify for Medicare?
Feb 11, 2022 · One must be a U.S. Citizen or a legal U.S. resident residing in the states for a minimum of 5 years immediately preceding one’s Medicare application. One must also be a minimum of 65 years old OR disabled OR have end-stage renal disease OR have Lou Gehrig’s disease (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis).
How much can you make to qualify for Medicare?
How to apply for Medicaid. Each state has different rules about eligibility and applying for Medicaid. Call your State Medical Assistance (Medicaid) office for more information and to see if you qualify. You can also call 1-800-MEDICARE (1-800-633-4227) to get the phone number for your state's Medicaid office. TTY users can call 1-877-486-2048.
How does Medicare compare to Medicaid?
Nov 11, 2021 · To qualify for Medicare, individuals generally need to be 65 or older or have a qualifying disability. There are several levels of assistance an individual can receive as a dual eligible beneficiary. The term full dual eligible refers to individuals who are enrolled in Medicare and receive full Medicaid benefits.
What's the income level requirement to qualify for Medicaid?
The Medicare eligibility requirement is that you must be 65 years old or older. If you or your spouse are 65 years old or older and have paid enough Medicare taxes through previous employment, you or your spouse may be eligible for premium-free Part A of the Medicare program (hospital coverage).
What is dual eligible for Medicare?
Eligibility for the Medicare Savings Programs, through which Medicaid pays Medicare premiums, deductibles, and/or coinsurance costs for beneficiaries eligible for both programs (often referred to as dual eligibles) is determined using SSI methodologies..
What is Medicaid coverage?
Medicaid is the single largest source of health coverage in the United States. To participate in Medicaid, federal law requires states to cover certain groups of individuals. Low-income families, qualified pregnant women and children, and individuals receiving Supplemental Security Income (SSI) are examples of mandatory eligibility groups (PDF, ...
How many people are covered by medicaid?
Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that, together with the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), provides health coverage to over 72.5 million Americans, including children, pregnant women, parents, seniors, and individuals with disabilities. Medicaid is the single largest source of health coverage in the United States.
What is MAGI for Medicaid?
MAGI is the basis for determining Medicaid income eligibility for most children, pregnant women, parents, and adults. The MAGI-based methodology considers taxable income and tax filing relationships to determine financial eligibility for Medicaid. MAGI replaced the former process for calculating Medicaid eligibility, ...
How long does medicaid last?
Benefits also may be covered retroactively for up to three months prior to the month of application, if the individual would have been eligible during that period had he or she applied. Coverage generally stops at the end of the month in which a person no longer meets the requirements for eligibility.
Do you have to be a resident to get medicaid?
Medicaid beneficiaries generally must be residents of the state in which they are receiving Medicaid. They must be either citizens of the United States or certain qualified non-citizens, such as lawful permanent residents. In addition, some eligibility groups are limited by age, or by pregnancy or parenting status.
Can you get medicaid if you are medically needy?
Medically Needy. States have the option to establish a “medically needy program” for individuals with significant health needs whose income is too high to otherwise qualify for Medicaid under other eligibility groups. Medically needy individuals can still become eligible by “spending down” the amount of income that is above a state's medically ...
What is medicaid?
Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that: 1 Helps with medical costs for some people with limited income and resources 2 Offers benefits not normally covered by Medicare, like nursing home care and personal care services
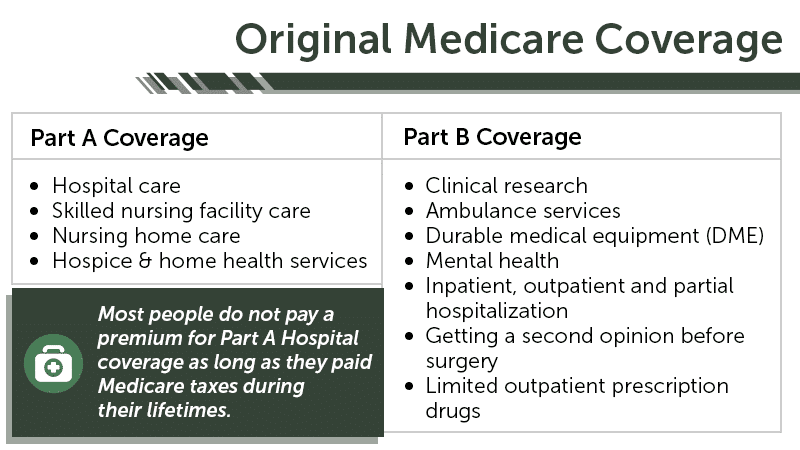
What is original Medicare?
Original Medicare. Original Medicare is a fee-for-service health plan that has two parts: Part A (Hospital Insurance) and Part B (Medical Insurance). After you pay a deductible, Medicare pays its share of the Medicare-approved amount, and you pay your share (coinsurance and deductibles). or a.
What is extra help?
And, you'll automatically qualify for. Extra Help. A Medicare program to help people with limited income and resources pay Medicare prescription drug program costs, like premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance. paying for your.
Does Medicare cover prescription drugs?
. Medicaid may still cover some drugs and other care that Medicare doesn’t cover.
Does medicaid pay first?
Medicaid programs vary from state to state, but most health care costs are covered if you qualify for both Medicare and Medicaid. pays second. Medicaid never pays first for services covered by Medicare. It only pays after Medicare, employer group health plans, and/or Medicare Supplement (Medigap) Insurance have paid.
Does Medicare have demonstration plans?
Medicare is working with some states and health plans to offer demonstration plans for certain people who have both Medicare and Medicaid and make it easier for them to get the services they need. They’re called Medicare-Medicaid Plans. These plans include drug coverage and are only in certain states.
Can you get medicaid if you have too much income?
Even if you have too much income to qualify, some states let you "spend down" to become eligible for Medicaid. The "spend down" process lets you subtract your medical expenses from your income to become eligible for Medicaid. In this case, you're eligible for Medicaid because you're considered "medically needy."
Who are the dual-eligible recipients?
People who are dual-eligible for Medicare and Medicaid are referred to as dual-eligible beneficiaries. Moreover, each state determines Medicaid coverage, and as a result, Medicaid benefits may differ.
Medicare Ineligibility
The Medicare eligibility requirement is that you must be 65 years old or older. If you or your spouse are 65 years old or older and have paid enough Medicare taxes through previous employment, you or your spouse may be eligible for premium-free Part A of the Medicare program (hospital coverage).
Medicaid Ineligibility
Medicaid eligibility varies depending on where a person resides, as various states have different qualifications.
Dual eligibility
A person must qualify for either partial-dual or full-dual coverage to be eligible for both Medicare and Medicaid.
Variations in geography
Medicaid benefits and coverage vary from one state to the next, and there are differences between them. Depending on the state, Medicaid coverage may be available to those who earn more than the standard income limits.
Medicare Part D Extra Assistance Program
Aside from Medicaid, many other programs assist with medical expenses, and government sponsors them. Extra Help, a program that assists Medicare Part D enrollees with their prescription drug costs, can be applied for by a qualified individual.
Summary
A person’s health and income level may qualify them for both Medicare and Medicaid.
What is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid?
The benefit is the plan will have very low copays and very few additional fees. Medicare is for those aged 65 and older or those with disabilities or specific medical conditions. Medicaid is for people of any age, with or without medical conditions, so long as they meet the state’s economic conditions.
What is Medicare for 65?
Medicare coverage is for adults 65 and older and those with certain qualifying medical conditions or disabilities. To qualify, you would need proof of age, proof of income (to determine how much your deductible is), residency or citizenship documentation, and more. Since Medicare is a government insurance program, ...
How are Medicare premiums paid?
Premiums are typically paid on a monthly basis. In the federal Medicare program, there are four different types of premiums. ... , deductibles, copays, and more. Medicaid assists with these costs, but you may be required to use an approved Medicaid health plan.
Does Medicare cover skilled nursing?
Medicare covers most of the costs associated with skilled nursing after an inpatient stays in the hospital. If you have both Medicare and Medicaid, a stay at a skilled nursing facility will cost very little. After inpatient treatment, many patients need more outpatient care in the home setting.
What is Medicare Advantage?
Medicare Advantage (MA), also known as Medicare Part C, are health plans from private insurance companies that are available to people eligible for Original Medicare ( Medicare Part A and Medicare Part B).... . Some smaller, rural counties may not have SNP plans but will have a local Medicaid plan.
What is deductible insurance?
A deductible is an amount a beneficiary must pay for their health care expenses before the health insurance policy begins to pay its share. ... Coinsurance is a percentage of the total you are required to pay for a medical service. ... , and copays, are the beneficiary’s responsibility.
Is Medicaid a federal or state program?
While Medicaid is both a state and federal program, it is administered at the state level and each state has its own rules and benefits. All Medicaid programs must follow the same federal guidelines while being directed and managed at the local state level.
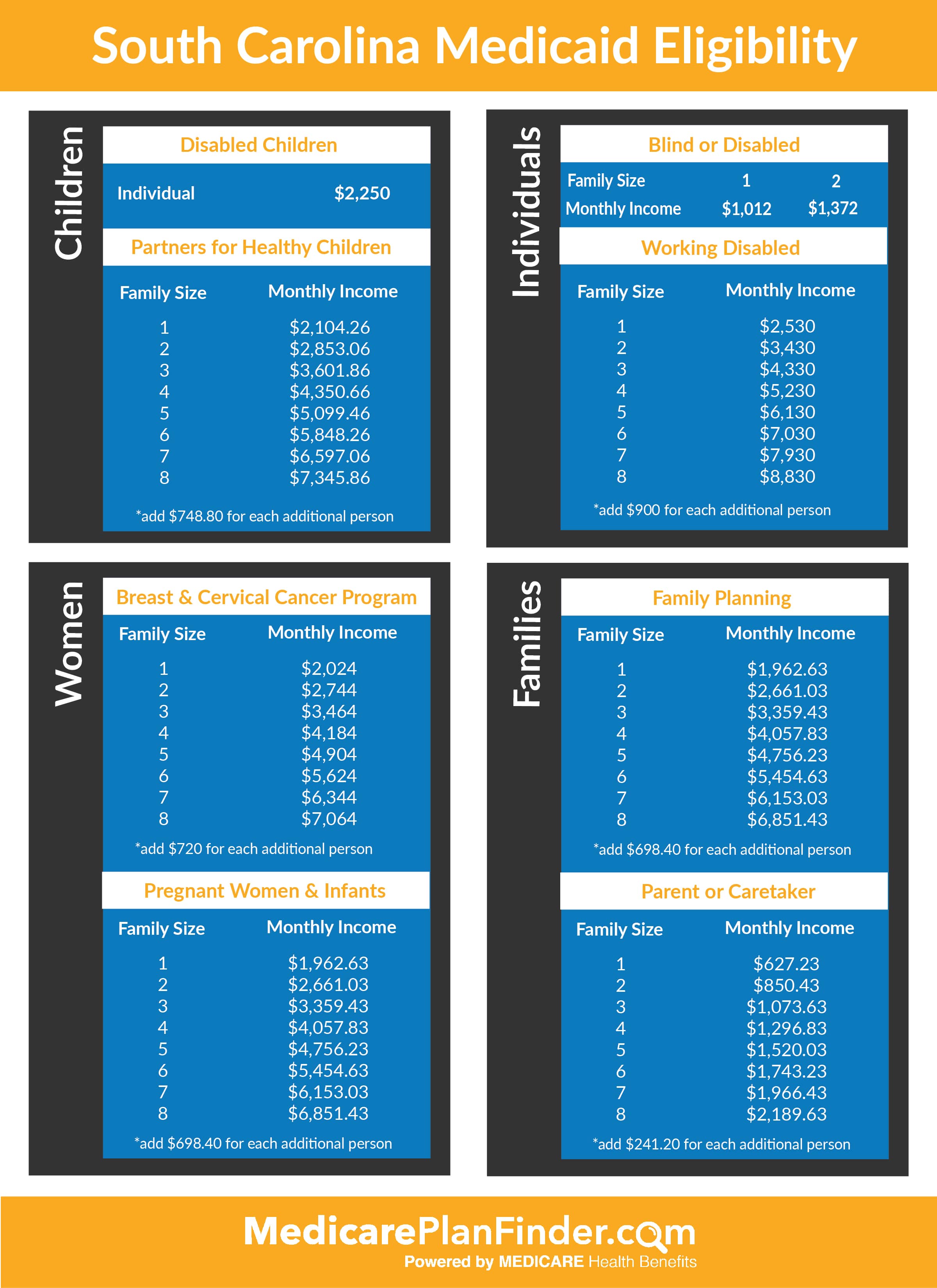
Determining Eligibility For Medicaid
- Financial Eligibility
The Affordable Care Act established a new methodology for determining income eligibility for Medicaid, which is based on Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI). MAGI is used to determine financial eligibility for Medicaid, CHIP, and premium tax credits and cost sharing reductions avail… - Non-Financial Eligibility
To be eligible for Medicaid, individuals must also meet certain non-financial eligibility criteria. Medicaid beneficiaries generally must be residents of the state in which they are receiving Medicaid. They must be either citizens of the United States or certain qualified non-citizens, suc…
Medically Needy
- States have the option to establish a “medically needy program” for individuals with significant health needs whose income is too high to otherwise qualify for Medicaid under other eligibility groups. Medically needy individuals can still become eligible by “spending down” the amount of income that is above a state's medically needy income standard. Individuals spend down by incu…
Appeals
- States must provide individuals the opportunity to request a fair hearing regarding a denial, an action taken by the state agency that he or she believes was erroneous, or if the state has not acted with reasonable promptness. States have options for how to structure their appeals processes. Appeals may be conducted by the Medicaid agency or delegated to the Exchange or …
Related Topics
- Spousal Impoverishment: Protects the spouse of a Medicaid applicant or beneficiary who needs coverage for long-term services and supports (LTSS), in either an institution or a home or other community-based setting, from becoming impoverished in order for the spouse in need of LTSS to attain Medicaid coverage for such services. Treatment of Trusts: When an individual, his or her s…