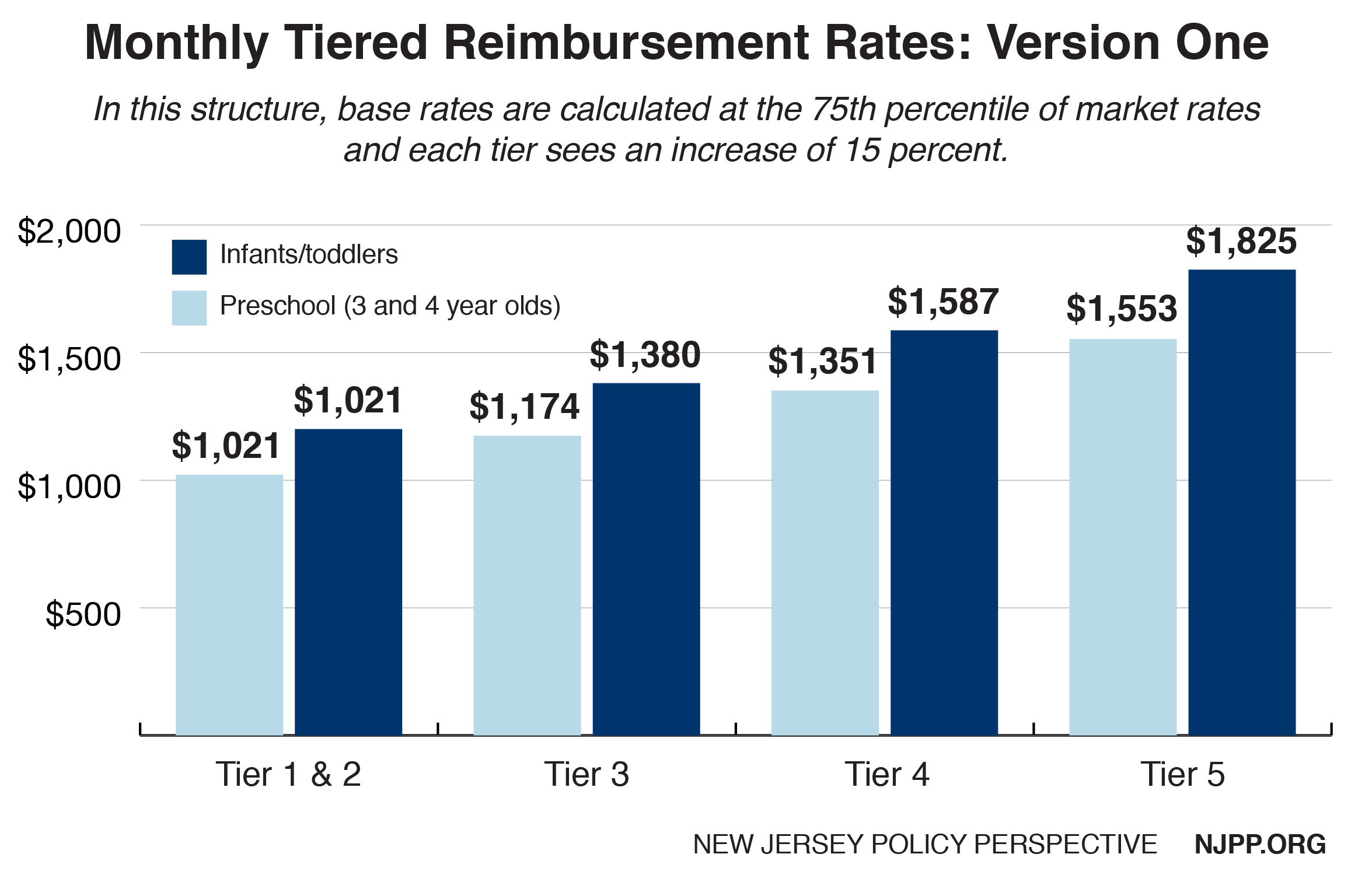
Value-Based payment programs reward healthcare providers with incentive payments for the quality of care they give to people with Medicare. These programs are part of CMS’s larger quality strategy to reform how healthcare is delivered and paid for.
Full Answer
What is CMS doing to advance value-based care?
• CMS has already made a strong commitment to advancing value-based care to over 61 million enrollees in Medicare. • This guidance is designed to ensure that this same commitment can continue at the state level to the nearly 74 million beneficiaries in Medicaid.
What is the percentage of value-based Medicare spending?
The percentage of value-based Medicare spending is around 30%. CMS is moving to achieve a 100% value-based system and hopes to reach that goal by 2025. They also expect to bring commercial and Medicaid spending to 25% by 2022 and 50% by 2025. Currently, it is around 15%.
What does value-based care mean for physicians and physicians in training?
Moving to a system of value-based health care requires that physicians and physicians-in-training learn to think differently about their role within the larger care team, about what constitutes an effective care solution, and about the importance of measuring the health outcomes that matter most to patients.
How does reimbursement work in value-based care?
Value-based reimbursements are calculated by using numerous quality measures and determining the overall health of populations. Unlike the traditional model, value-based care is driven by data because providers must report to payers on specific metrics and demonstrate improvement.
How do value based programs work?
Value-Based Care (VBC) is a health care delivery model under which providers — hospitals, labs, doctors, nurses and others — are paid based on the health outcomes of their patients and the quality of services rendered. Under some value-based contracts, providers share in financial risk with health insurance companies.
What is value-based care reimbursement model?
Value-Based Reimbursement Models Aim to Improve Care Providers are paid based on the number of patients they have and the number of tests and procedures they order. The more tests ordered, the higher the payment. Value-based care emphasizes high-quality, lower cost, and preventive patient care.
What is CMS value-based care?
CMS currently defines value-based care as paying for health care services in a manner that directly links performance on cost, quality and the patient's experience of care.
What are the four main methods of reimbursement?
Here are the five most common methods in which hospitals are reimbursed:Discount from Billed Charges. ... Fee-for-Service. ... Value-Based Reimbursement. ... Bundled Payments. ... Shared Savings.
Who benefits the most from value based reimbursement?
patientsPerhaps the primary way patients benefit from value-based care is that they will experience better health outcomes, not just in one isolated area of illness, but across the full spectrum of comorbidities and side effects that accompany their illness.
How is value-based care measured?
The simplest definition of value in health care is: Value = Quality / Cost. Typically, experts meet and develop a group of quality measures.
What are the components of value-based care?
An ideal high-value health care system features six key components: a clear, shared vision with the patient at the center; leadership and professionalism of health care workers; a robust IT infrastructure; broad access to care; and payment models that reward quality improvement over volume.
What are the 5 original value based programs?
There are 5 original value-based programs; their goal is to link provider performance of quality measures to provider payment: End-Stage Renal Disease Quality Incentive Program (ESRD QIP) Hospital Value-Based Purchasing (VBP) Program. Hospital Readmission Reduction Program (HRRP)
What factors are part of the CMS value based programs?
What measures are used in the Hospital VBP Program?Mortality and complications.Healthcare-associated infections.Patient safety.Patient experience.Efficiency and cost reduction.
What is the goal of value-based care?
Value in health care is the measured improvement in a patient's health outcomes for the cost of achieving that improvement. The goal of value-based care transformation is to enable the health care system to create more value for patients.
What is an outcome of value based healthcare?
Value-based healthcare is about linking how much money is spent on healthcare programs or services over a patient's journey to the outcomes that matter most to patients – rather than focusing primarily on the amount of services, or on specific processes or products. Value. Outcomes that. matter to patients.
What does CMS encourage states to request?
CMS encourages states to request technical assistance from CMS to learn more about the models discussed in the letter and receive feedback on concepts in development. States should direct inquiries to their CMCS state leads.
Why is value based care important?
Value-based care has particular promise in helping the United States and its healthcare system ...
What is alternative payment methodology?
“Alternative payment methodologies (APM)” refers to a variety of ways to pay healthcare providers for delivering value over volume that are not simply tied to fee-for-service reimbursements for services rendered to patients. Alternative payment methodologies aim to create greater provider accountability for care of defined populations by attributing patients to providers and linking payment to outcomes. This State Medicaid Director Letter (SMDL) references APMs described in the Health Care Payment Learning and Action Network (HCP-LAN) APM Framework and clarifies how state Medicaid agencies can adopt them.
What is CMS 1115?
CMS acknowledges that there may be instances when a state requires additional flexibility to adopt an approach to value-based care or pursue other delivery system reforms that are not available through the Medicaid state plan or section 1915 waiver authorities. These instances generally should be limited to when a state wants to pilot a geographically limited payment or delivery system model, limit benefits to certain populations, and/or offer benefits not available under any other Medicaid authority. In such circumstances, CMS welcomes the opportunity to work with states on state-driven section 1115 demonstration proposals that take into account their unique needs and capabilities.
What does CMS believe about VBC?
CMS believes that VBC represents a way to improve health outcomes, lower costs, and promote provider flexibility. CMS understands that states face unique circumstances in their healthcare landscapes, and what works for one state may not necessarily work for another state.
What is VBC in healthcare?
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is releasing guidance for states on how to advance value-based care (VBC) across their healthcare systems, with a particular emphasis on Medicaid populations, and to share pathways for adoption of such approaches.
Does CMS require states to adhere to any specific approaches or payment methodologies?
CMS is not requiring states to establish or adhere to any specific approaches or payment methodologies. CMS does encourage states to move toward value-based care and to set targets for expanding value-based payments, consistent with the targets established by the HCP-LAN.
What is value based payment?
Value-Based payment programs reward healthcare providers with incentive payments for the quality of care they give to people with Medicare. These programs are part of CMS’s larger quality strategy to reform how healthcare is delivered and paid for. Value-Based programs support better care for individuals, better health for populations, and lower cost.
Why is value based care important?
It helps: improve patients’ quality of life.
What is an advanced alternative payment model?
Advanced Alternative Payment Models (Advanced APMs) are a kind of APM designated by MACRA that allow practices to earn more – through the Quality Payment Program – for taking on additional risk related to their patients’ outcomes . Clinicians who participate to a sufficient extent in Advanced APMs earn Qualifying APM Participant (QP) status through which they receive added incentives and an exclusion from the requirements of the Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS).
What is a small practice in Medicare?
Small practices (defined as 15 or fewer clinicians), especially those in rural or Health Professional Shortage Areas (HPSAs), play a vital role in caring for Medicare patients with diverse needs. The Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA) provides support to help solo Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) eligible clinicians and small practices participate in the Quality Payment Program.
What is the purpose of Medicare?
To improve beneficiary population health. To improve the care received by Medicare beneficiaries . To lower costs to the Medicare program through improvement of care and health. To advance the use of healthcare information between allied providers and patients.
What is CPC+ in healthcare?
Comprehensive Primary Care Plus (CPC+) is a national advanced primary care model that aims to strengthen primary care through state-based multi-payer payment reform and care delivery transformation. CPC+ was built on the foundation and lessons learned from the original Comprehensive Primary Care (CPC) model.
What is value based care?
Chan goes on to explain that in a value-based care model, providers are rewarded for things like successful surgical procedures, reduced effects and incidences of chronic disease, and measurably healthier lives. In value-based care models, it’s all about the quality of care rather than the quantity of services provided. It’s a patient-centered approach that has its benefits as well as drawbacks.
What are the potential pitfalls of value based care?
A potential pitfall of value-based care is that high-risk patients could be turned away. Similar to actuarially based insurance, doctors would need to outweigh a high-risk patient with enough healthy ones, Dr. Jorgensen explains.#N#Additionally, some areas of health care need further advancement before value-based care can fully take hold. Take for instance, how patient outcomes are measured. A value-based care system would rely on this information in order to evaluate services and billing.#N#“At its core, value-based health care should be highly data-driven,” Chan says. He adds that health systems and insurers need to improve their ability to collect data, measure outcomes, and optimize for this to truly drive cost reduction while improving care. “Health care needs to continue adding measurement and analytics capabilities to accelerate value-based care,” he believes.
Is health care an industry?
Health care is an expanding and convoluted industry. There are many moving parts coming together to help patients, providers, and health care professionals behind the scenes. From appointment scheduling and health care data to prescriptions and health insurance, the health care industry encompasses more than many may realize.
Is value based care a hot topic?
Value-based care has become a hot topic of discussion and debate. But health care models are not the only topics of conversation. The medical field is facing another challenge in the coming years: doctor shortages.
How does value based care improve patient outcomes?
By improving patients’ health outcomes, value-based health care reduces the compounding complexity and disease progression that drive the need for more care.
What is the goal of value based health care?
The goal of value-based health care is better health outcomes. Value and patient satisfaction are also commonly confused. While the patient satisfaction movement has brought a much-needed emphasis on treating people with dignity and respect, the essential purpose of health care is improving health.
What is value in health care?
Value in health care is the measured improvement in a person’s health outcomes for the cost of achieving that improvement. While some descriptions conflate value-based health care and cost reduction, quality improvement, or patient satisfaction, those efforts—while important—are not the same as value, which focuses primarily on improving patient ...
What is the purpose of measuring health outcomes?
Recognizing that the essential purpose of health care is improving the health of patients, it is axiomatic that health care teams must measure the health results as well as the costs of delivering care for each patient .
Is measuring health outcomes complex?
Measuring health outcomes is not as complex as it is often perceived to be. Routine clinical practice does not dictate, nor can it support, the voluminous health outcome measure sets used in clinical research. Instead, clinicians need to focus on measuring the outcomes that define health for their patients.
How much is healthcare in 2019?
In 2019, healthcare costs neared the $4-trillion mark and made up almost 18% of the United States economy. As the Baby Boomer and Gen X generations age into seniors, these figures are expected to rise even more.
Is value based reimbursement easy?
Value-based reimbursement – next steps. Moving to a value-based reimbursement system is usually not easy, but it is not impossible either. By using a systematic approach and taking it a step at a time, you can make that transition to higher-quality care much smoother and easier.
