But, she said, it could reduce Medicare payments to providers such as hospitals, physicians, and skilled nursing facilities. One of the key things the tax cut bill is keeping is the medical expense deduction. This provision allows families to deduct extraordinary medical expenses that eat up more than 10 percent of their income.
How would a payroll tax cut affect social security and Medicare?
Full details on how the Trump administration could implement a payroll tax cut are still not known. Particularly, it’s unclear how that cut would affect levies for Social Security or Medicare or both. Currently, employees and employers are each subject to a 6.2% tax for Social Security and 1.45% for Medicare.
How did tax reform affect Medicare tax treatment?
While the recently passed Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) did repeal the individual health coverage mandate under the Affordable Care Act, it left in place the 0.9% Additional Medicare tax on high-income individuals. The takeaway here is that there were no changes to the tax treatment of Medicare benefits or rules due to tax reform.
What does the tax cuts and Jobs Act mean for Medicare?
Editor’s Note: This article was originally published on April 09, 2018. While the recently passed Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) did repeal the individual health coverage mandate under the Affordable Care Act, it left in place the 0.9% Additional Medicare tax on high-income individuals.
Are Medicare benefits taxable?
Basic Medicare benefits under part A (hospital benefits) are not taxable. Supplementary Medicare benefits under part B (coverage of doctors’ services and other items) are not taxable unless the premiums were previously deducted. That being said, social security benefits used to purchase Medicare Part B remain taxable.

What affects Medicare tax?
An individual will owe Additional Medicare Tax on wages, compensation and self-employment income (and that of the individual's spouse if married filing jointly) that exceed the applicable threshold for the individual's filing status.
Who is impacted by a payroll tax cut?
The payroll tax cut applies to individual employees who earn less than $4,000, before taxes, during any bi-weekly paycheck period. This equates to $104,000 per year for a salaried employee.
How much tax is taken out for Medicare?
1.45%The FICA tax includes the Social Security tax rate at 6.2% and the Medicare tax at 1.45% for a total of 7.65% deducted from your paycheck.
Why are taxes taken out for Medicare?
Social Security taxes fund Social Security benefits and the Medicare tax goes to pay for the Medicare Hospital Insurance (HI) that you'll get when you're a senior.
Will I have to pay back the payroll tax cut?
IRS Notice 2020-65PDF allowed employers to defer withholding and payment of the employee's Social Security taxes on certain wages paid in calendar year 2020. Employers must pay back these deferred taxes by their applicable dates.
Is Social Security still being taken out of paychecks?
The Social Security taxable maximum is $142,800 in 2021. Workers pay a 6.2% Social Security tax on their earnings until they reach $142,800 in earnings for the year. READ: How Much You Will Get From Social Security. ]
What is the Medicare tax rate for 2021?
1.45%FICA tax includes a 6.2% Social Security tax and 1.45% Medicare tax on earnings. In 2021, only the first $142,800 of earnings are subject to the Social Security tax ($147,000 in 2022). A 0.9% Medicare tax may apply to earnings over $200,000 for single filers/$250,000 for joint filers.
What is the Medicare rate for 2021?
For 2021, the Medicare Part B monthly premiums and the annual deductible are higher than the 2020 amounts. The standard monthly premium for Medicare Part B enrollees will be $148.50 for 2021, an increase of $3.90 from $144.60 in 2020.
What is the Medicare tax limit for 2020?
There is no limit on the amount of earnings subject to Medicare (hospital insurance) tax. The Medicare tax rate applies to all taxable wages and remains at 1.45 percent with the exception of an “additional Medicare tax” assessed against all taxable wages paid in excess of the applicable threshold (see Note).
Who pays additional Medicare tax 2021?
The Additional Medicare Tax applies to people who are at predetermined income levels. For the 2021 tax year, those levels are: Single tax filers: $200,000 and above. Married tax filers filing jointly: $250,000 and above.
Can I opt out of paying Medicare tax?
To do that, you'll use IRS Form 4029, Application for Exemption From Social Security and Medicare Taxes and Waiver of Benefits.
Who is exempt from paying Medicare tax?
The Code grants an exemption from Social Security and Medicare taxes to nonimmigrant scholars, teachers, researchers, and trainees (including medical interns), physicians, au pairs, summer camp workers, and other non-students temporarily present in the United States in J-1, Q-1 or Q-2 status.
When will Medicare run out of money?
The Medicare Part A trust fund is projected to run out of money in 2026. Meanwhile, the latest estimate projects Social Security’s trust funds will be insolvent in 2035.
Why is payroll tax cut important?
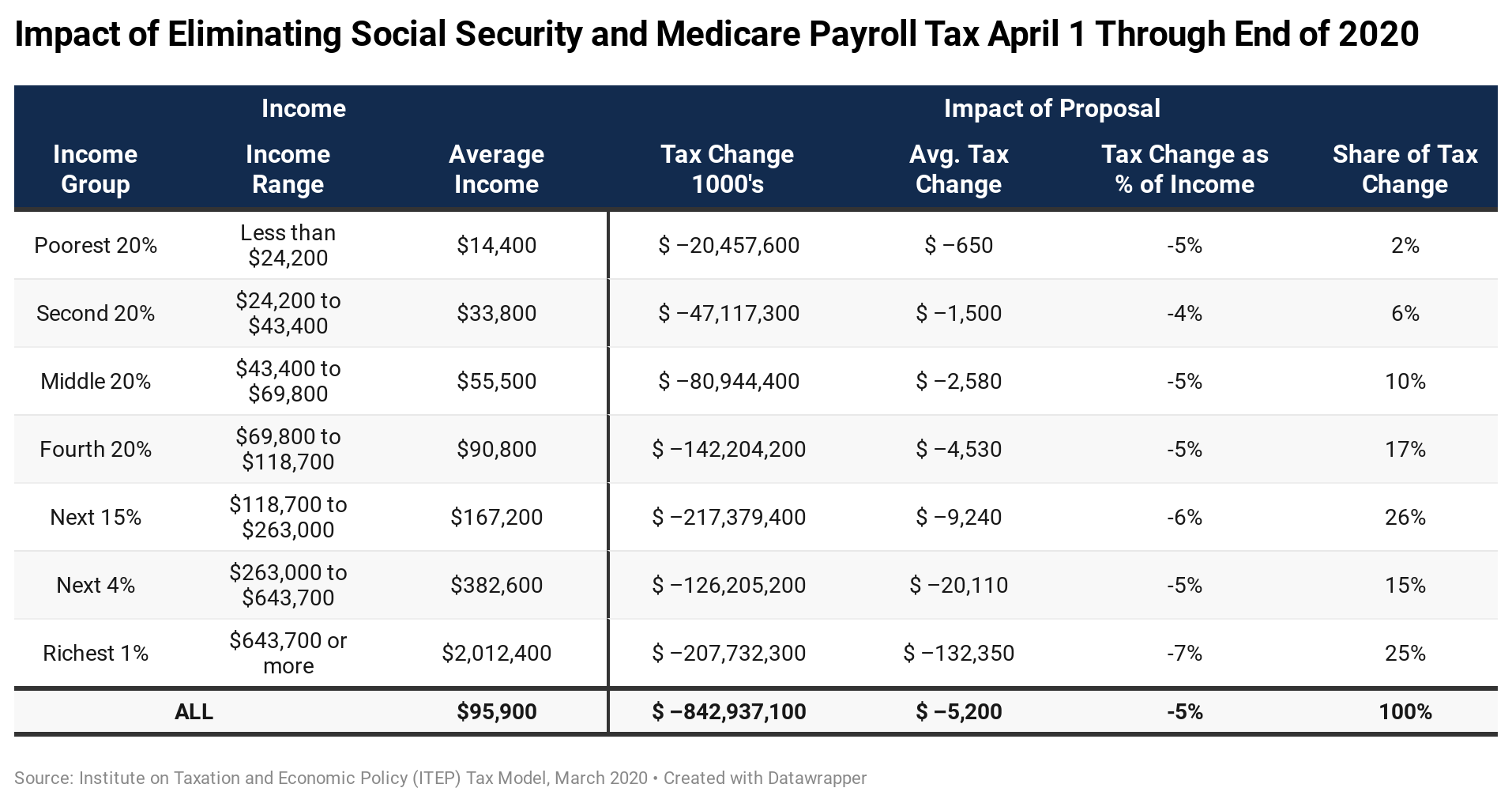
A payroll tax cut is one idea President Donald Trump is considering in response to the negative effects of coronavirus on the U.S. economy. Experts say such a move would not necessarily be a magic bullet. One reason why: It could impair funding to Medicare and Social Security, which rely on payroll taxes for funding and are already facing looming ...
How much tax do you pay on Social Security?
Currently, employees and employers are each subject to a 6.2% tax for Social Security and 1.45% for Medicare. Self-employed individuals, meanwhile, make the full contributions on their own, 12.4% for Social Security and 2.9% for Medicare. In addition, if you earn over $200,000 individually, or $250,000 if you’re married and file jointly, ...
When was the last time there was a payroll tax cut?
That could be accomplished as it was the last time there was a payroll tax cut, in 2011, when money was moved from the general fund to the trust funds. However, halting payroll taxes for up to a year, which has been mentioned as a potential strategy, would be very expensive.
Will people who lose their jobs get a payroll tax cut?
Those who lose their jobs because of the negative impacts of the coronavirus will not benefit from a payroll tax cut. “They’re the ones who are going to have the biggest drops in income, and yet they’re not going to get anything from a payroll tax holiday,” Greszler said.
Does the pullback in consumer spending affect Social Security?
Plus, because the pullback in consumer spending is related to health concerns, not financial worries, it might not result in increased spending, experts say.
Is payroll tax regressive?
The other problem is that payroll taxes are regressive, so it’s a bigger chunk for people with low or moderate incomes than high income workers. And big earners are unlikely to spend that extra cash. “We know when high -income people get a tax cut, they don’t spend as much as low-income people do,” Gleckman said.
How is Medicare funded?
Medicare is funded by a payroll tax, premiums and surtaxes from beneficiaries, and general revenue.
What does Medicare Part B cover?
Medicare Part B helps cover: services from doctors and other health care providers; outpatient care; home health care; durable medical equipment; and some preventive services. Part B is optional and may be deferred if the beneficiary or their spouse is still working and has health coverage through their employer.
Who does the Social Security Administration provide health insurance to?
It provides health insurance for Americans aged 65 and older who have worked and paid into the system through the payroll tax. It also provides health insurance to younger people with some disability status as determined by the Social Security Administration.
Did Medicare change tax form?
The takeaway here is that there were no changes to the tax treatment of Medicare benefits or rules due to tax reform. While there are no changes to Medicare rules because of tax form, understanding how Medicare works can be helpful in understanding your overall financial picture.
How much will Medicare be reduced?
It’s estimated that would create an annual reduction of $25 billion in Medicare spending, starting next year.
What percentage of medical expenses are deducted in the tax cut?
This provision allows families to deduct extraordinary medical expenses that eat up more than 10 percent of their income. The original House bill proposed eliminating this deduction.
Why is the ACA mandate necessary?
Experts have told Healthline that the mandate is necessary because it forces healthier consumers into the insurance pool overseen by ACA marketplaces.
What are the provisions that will have the biggest impact on the healthcare industry?
Without a doubt, the provisions that will have the biggest impact on the healthcare industry are the repeal of the individual mandate and the potential cuts in Medicare spending. The individual mandate is a key component of the Affordable Care Act (ACA). It requires everyone to have health insurance.
What is the deduction for 2017?
During those tax years, the deduction will kick in at 7.5 percent of a household’s annual income. After that, it returns to the 10 percent threshold.
Why is the American Hospital Association opposing the tax waiver?
The bill keeps the tax waiver for reduced tuition for graduate students. Medical schools had pushed to preserve this break because it helps make graduate medical studies more affordable.
What programs are exempt from the 2010 tax cuts?
Programs such as Social Security and unemployment benefits are exempt from the cuts.
How much Medicare tax do self employed pay?
Medicare taxes for the self-employed. Even if you are self-employed, the 2.9% Medicare tax applies. Typically, people who are self-employed pay a self-employment tax of 15.3% total – which includes the 2.9% Medicare tax – on the first $142,800 of net income in 2021. 2. The self-employed tax consists of two parts:
How is Medicare financed?
1-800-557-6059 | TTY 711, 24/7. Medicare is financed through two trust fund accounts held by the United States Treasury: Hospital Insurance Trust Fund. Supplementary Insurance Trust Fund. The funds in these trusts can only be used for Medicare.
What is the Medicare tax rate for 2021?
Together, these two income taxes are known as the Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) tax. The 2021 Medicare tax rate is 2.9%. Typically, you’re responsible for paying half of this total Medicare tax amount (1.45%) and your employer is responsible for the other 1.45%.
What is Medicare Part A?
Medicare Part A premiums from people who are not eligible for premium-free Part A. The Hospital Insurance Trust Fund pays for Medicare Part A benefits and Medicare Program administration costs. It also pays for Medicare administration costs and fighting Medicare fraud and abuse.
When was the Affordable Care Act passed?
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) was passed in 2010 to help make health insurance available to more Americans. To aid in this effort, the ACA added an additional Medicare tax for high income earners.
How is the Hospital Insurance Trust funded?
The Hospital Insurance Trust is largely funded by Medicare taxes paid by employees and employers , but is also funded by: The Hospital Insurance Trust Fund pays for Medicare Part A benefits and Medicare Program administration costs. It also pays for Medicare administration costs and fighting Medicare fraud and abuse.
How did the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act affect healthcare?
The Tax Cuts and Jobs act will affect health care in various ways. The dramatic vote cast by Sen. John McCain (R-Ariz.) against the Health Care Freedom Act on July 28, 2017, which sealed the bill’s defeat, seemed to put an end to the efforts of congressional Republicans and the Trump administration to repeal and replace the Affordable Care Act ...
What is the impact of the tax reform law?
Given the Trump administration’s stated legislative priorities of infrastructure and immigration for this year, the tax reform law will likely have the biggest impact on healthcare legislation passed under this administration over the next two years. For hospitals, the TCJA may mean slightly higher uncompensated care starting in 2019, a continued push for value-based care, and downward pressure on utilization. Faced with these pressures, hospitals more than ever must innovate to successfully navigate increasingly challenging waters.
Why is it so hard to repeal the ACA?
Congressional Republicans found it more difficult than expected to repeal and replace the ACA primarily because of opposition to a pullback of the Medicaid expansion.
How much will the TCJA increase the federal debt?
According to the Joint Committee on Taxation, the TCJA will increase the federal debt by $1.0 trillion from 2018 to 2027, after taking into account increased federal revenues resulting from added economic growth. d The projected increase to the nation’s debt will put pressure on Congress to rein in federal expenditures, in turn shining a spotlight on the need to curb healthcare spending. Toward the end of 2017, Speaker of the House Paul Ryan (R-Wisc.) said, “Frankly, it’s the healthcare entitlements that are the big drivers of our debt, so we spend more time on the healthcare entitlements—because that’s really where the problem lies, fiscally speaking.” e
Why did the Federation of American Hospitals oppose the TCJA?
Nonetheless, the Federation of American Hospitals, the trade association for investor-owned hospitals in the United States, opposed the TCJA primarily because of concerns about the potential adverse financial impact on hospitals of the repeal of the individual mandate, the more significant of the two provisions of the TCJA affecting health care.
Is single payer healthcare dimmer?
In like manner, the prospects of a single-payer healthcare system would appear to be dimmer because such a major expansion of the federal government would require not only the repeal of the TCJA’s tax breaks for individuals and corporations, but also the imposition of additional tax increases.
Will the TCJA increase the number of uninsured Americans?
Thus, the actual extent to which the TCJA will increase the number of uninsured Americans is unclear. Of course, any rise in the number of uninsured Americans would contribute to increased uncompensated care (charity care and bad debt) for hospitals and health systems.