What is a Medicare Advantage RAF score?
The Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ (CMS) Hierarchical Condition Category (HCC) risk adjustment model assigns a risk score, also called the Risk Adjustment Factor or RAF medical abbreviation “RAF score”, to each eligible Medicare Advantage (MA) beneficiary.
What is a Medicare risk adjustment factor (RAF)?
What is a “Medicare Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF)?” The purpose for the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to conduct Risk Adjustment Factors is to pay plans for the risk of the beneficiaries they enroll, instead of calculating an average amount of Medicare/Medicare Advantage beneficiaries.
What is a Medicare Advantage plan?
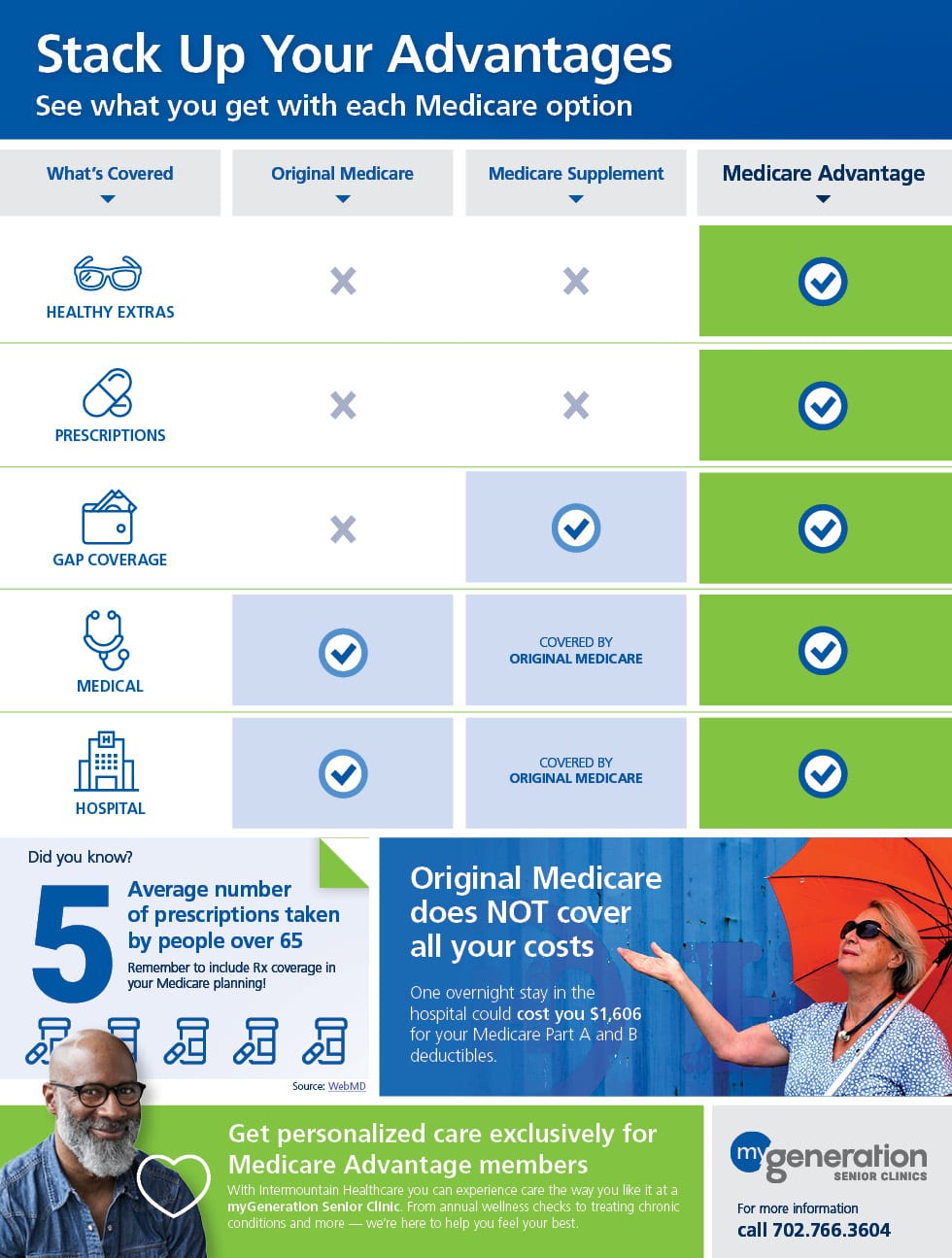
Medicare Advantage Plans are a type of Medicare health plan offered by a private company that contracts with Medicare to provide all your Part A and Part B benefits. Most Medicare Advantage Plans also offer prescription drug coverage. If you’re enrolled in a Medicare Advantage Plan, most Medicare services are covered through the plan.
What is the Medicare risk adjustment model?
Payment: Medicare risk adjustment is considered a prospective model. The current year’s demographics and diagnoses predict the following year’s payments. While MAOs receive a per-member per-month (PMPM) capitation payment based on predicted risk scores, final payment from CMS based on actual risk scores could take up to two years.

What is RAF in Medicare?
What is a Medicare Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF)? In 2003, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) implemented Risk Adjustment Factors (RAF) and Hierarchical Condition Category (HCC) coding to identify individuals with serious and/or chronic illnesses and assign them a risk factor score that is based on a combination ...
How does ICD-10 work?
How it works: Diagnoses are reported using ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes and submitted by providers. The higher the number of chronic conditions listed, the more care is assumed—thus a greater cost for delivering that care.
Why do you keep your Medicare card?
Keep your red, white, and blue Medicare card in a safe place because you’ll need it if you ever switch back to Original Medicare. Below are the most common types of Medicare Advantage Plans. An HMO Plan that may allow you to get some services out-of-network for a higher cost.
What is MSA plan?
Medicare Medical Savings Account (Msa) Plan. MSA Plans combine a high deductible Medicare Advantage Plan and a bank account. The plan deposits money from Medicare into the account. You can use the money in this account to pay for your health care costs, but only Medicare-covered expenses count toward your deductible.
Does Medicare Advantage include drug coverage?
Most Medicare Advantage Plans include drug coverage (Part D). In many cases , you’ll need to use health care providers who participate in the plan’s network and service area for the lowest costs.
Why do Medicare Advantage Organizations invest in retrospective risk adjustment chart reviews?
Why do Medicare Advantage Organizations invest in retrospective risk adjustment chart reviews? RAF scores determine how MAOs get paid— so ensuring accuracy is crucial. Retrospective chart reviews can help MAOs improve the accuracy of risk-adjustment payments by allowing them to add and delete diagnoses in the encounter data based on a patient’s medical records in the EMR. This helps ensure that MAOs that enroll sicker beneficiaries are appropriately compensated for their more costly levels of care.
Why is risk adjustment coding review important?
A stronger risk adjustment coding review before claims are sent to the payer will ensure correct HCC coding the first time. Many refer to this as a concurrent coder review. It results in more accurate payments from payers and will help groups avoid a lot of unnecessary back and forth in the form of paperwork and record pulling. Capturing the information correctly the first time will ensure groups have the information they need for continual year-after-year recapture. To be successful in the long run, medical groups need a comprehensive view of their patients’ HCC data.
Does Medicare Advantage have risk adjustment coding?
As Medicare Advantage Organizations have known for years, providers often have robust documentation but lack in risk adjustment coding. There’s a significant opportunity for medical groups to create a stronger HCC coding review process to avoid having to rely on the retrospective review process used by MAOs.
Who performs risk adjustment calculations?
While this information about hierarchies is interesting to risk adjustment coders, these calculations and hierarchy groupings are performed by CMS. Official risk scores are reported to the MAO, but the health plan may run their own analysis to aid in predicting costs. Risk adjustment coders will rarely need to perform these calculations, but seeing how risk scores are calculated is helpful to fully grasp the need for accurate and complete diagnosis reporting.
How do risk adjustment programs work?
The programs use a person’s Social Security number, permanent address, and medical and financial questionnaires to establish enrollment.
What is risk adjustment in medical billing?
While most medical coders are familiar with the fee-for-service (FFS) payment methodology in which insurers pay providers based on the procedures or services performed for a patient, risk adjustment is instead how insurance companies participating in specific programs get payment for managing the healthcare needs of members based on their diagnoses.
When was commercial risk adjustment created?
Commercial risk adjustment was created by the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) of 2010 and implemented in 2014. This type of payment model serves individuals and small groups who purchase insurance through the online insurance exchange called the Health Insurance Marketplace.
Is HCC 19 added to risk score?
The risk value of HCC 19 is added only once for an individual member’s risk score calculation. But if the member also had a diagnosis from outside that diabetes family, such as stroke (HCC 100), the risk value for HCC 100 also would be used in the risk score.
Can a patient see multiple providers?
A patient may see multiple providers throughout the year with each submitting a claim for services. Not all providers will document details of a condition identically, which may result in the hierarchical system coming into play. Only the HCC value of the most severe condition in the hierarchy would be used for risk score calculation for that member. Calculation occurs once the state or federal government agency overseeing the program receives all diagnoses for each member for that calendar year.
Does Medicare use HCC risk score?
Also keep in mind that the CMS-HCC model is additive. If a provider submits other diagnoses outside of a family at any time in a calendar year, Medicare also uses those diagnoses when calculating the HCC risk score. For instance, note how the Calculator Results section in Figure 4 shows multiple HCC scores added together (for HCCs 54, 57, and 19) and also lists when an HCC is not used for calculation (for instance, the score for HCC 55 is not included because HCC 54 takes precedence).