How much does Medicare pay for residency?
To make things more complex, Medicare will only pay fully for the number of years it would normally take a resident to complete their first residency; Medicare covers anything over that at 50% (eg, fellowship years, residents that need to repeat a year, etc.).
How is Medicare funded?
How is Medicare funded? The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is the federal agency that runs the Medicare Program. CMS is a branch of the
Who pays for the residents of a hospital?
If your hospital has residents, someone has to pay them. Ultimately, it is the American taxpayers. For the purposes of this post, when I use the word “resident”, I’m referring to interns, residents, and fellows all bundled together.
How do hospitals with no residency programs get Medicare training slots?
SOURCE: Mullan et al., 2013. Hospitals without residency programs can obtain Medicare-funded training slots if they develop newly accredited teaching programs. After 5 years, Medicare then caps the hospital's slots at the highest total number of residents for all specialty programs during that period.
How do residency programs make money?
The training of residents is funded by GME payments made to hospitals and health systems, largely through Medicare and Medicaid.
How is GME funding allocated?
Available funds are allocated to individual hospitals based on the Medicare GME payment formulae (HRSA Bureau of Health Professions, 2011). There are separate DGME and IME funding streams: DGME payments cover the direct cost of GME such as stipends and benefits for residents and faculty.
How Does Medicare pay GME?
Medicare direct GME payments are calculated by multiplying the PRA times the weighted number of full-time equivalent (FTE) residents working in all areas of the hospital (and non-hospital sites, when applicable), and the hospital's Medicare share of total inpatient days.
What is a GME payment?
• Direct GME (DGME) is the amount. Medicare pays the hospital for Medicare's. share of the direct cost of the residency. – Resident salaries, faculty teaching, administration, building maintenance, personnel, etc.
How is medical education funded in the US?
Sources of funds include federal and state governments, families or individuals that pay tuition, insurance companies that pay for patient care, and philanthropy. Organizations involved in medical education include medical schools and numerous patient care sites in which students gain clinical experience.
How are teaching hospitals typically reimbursed?
How are teaching hospitals typically reimbursed? Rationale: For teaching hospitals, the services of the resident are typically paid through Direct Graduate Medical Education (DGME) and Indirect Medical Education (IME) payment or reasonable cost payments made by the Part A MAC.
What is residency cap?
The limitation in funding has essentially put a cap on the number of residencies that can take place in the United States – and since a doctor cannot go into practice without a residency, this is essentially a cap on the number of new, American-trained physicians who are allowed to practice in this country.
What is IME and GME?
Medicare reimburses teaching hospitals for the costs of GME on a cost per resident basis. Indirect medical education (IME) costs, on the other hand, are additional patient care costs associated with the training of interns and residents.
How is IME payment calculated?
The additional payment is based on the IME adjustment factor. The IME adjustment factor is calculated using a hospital's ratio of residents to beds, which is represented as r, and a multiplier, which is represented as c, in the following equation: c x [(1 + r). 405 - 1]. The multiplier c is set by Congress.
How do you calculate GME?
In general, Medicare direct GME payments are calculated by multiplying the hospital's updated Per Resident Amount (PRA) by the weighted number of Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) residents working in all areas of the hospital complex (and at nonprovider sites, when applicable), and the hospital's ratio of Medicare inpatient ...
What is the federal government's role in federal GME?
The federal government offers operational funding subsidies to programs in California. This funding comes to GME programs through the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) in the form of Direct Graduate Medical Education (DGME) payments and Indirect Medical Education (IME) payments.
How long is GME program?
GME stands for “graduate medical education,” more commonly referred to as ”residency” and “fellowship” training. The 3 to 9 years of training allows physicians to specialize and practice independently following medical school.
How many people did Medicare cover in 2017?
programs offered by each state. In 2017, Medicare covered over 58 million people. Total expenditures in 2017 were $705.9 billion. This money comes from the Medicare Trust Funds.
Who pays payroll taxes?
Payroll taxes paid by most employees, employers, and people who are self-employed. Other sources, like these: Income taxes paid on Social Security benefits. Interest earned on the trust fund investments. Medicare Part A premiums from people who aren't eligible for premium-free Part A.
What is the CMS?
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services ( CMS) is the federal agency that runs the Medicare Program. CMS is a branch of the. Department Of Health And Human Services (Hhs) The federal agency that oversees CMS, which administers programs for protecting the health of all Americans, including Medicare, the Marketplace, Medicaid, ...
What is Medicare Part B?
Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) Part B covers certain doctors' services, outpatient care, medical supplies, and preventive services. and. Medicare Drug Coverage (Part D) Optional benefits for prescription drugs available to all people with Medicare for an additional charge.
What is SNF in nursing?
Skilled nursing care and rehabilitation services provided on a daily basis, in a skilled nursing facility (SNF). Examples of SNF care include physical therapy or intravenous injections that can only be given by a registered nurse or doctor. , home health care.
What is covered by Part A?
Part A covers inpatient hospital stays, care in a skilled nursing facility, hospice care, and some home health care. The health care items or services covered under a health insurance plan. Covered benefits and excluded services are defined in the health insurance plan's coverage documents.
Does Medicare cover home health?
Medicare only covers home health care on a limited basis as ordered by your doctor. , and. hospice. A special way of caring for people who are terminally ill. Hospice care involves a team-oriented approach that addresses the medical, physical, social, emotional, and spiritual needs of the patient.
How does Medicare get money?
Medicare gets money from two trust funds : the hospital insurance (HI) trust fund and the supplementary medical insurance (SMI) trust fund. The trust funds get money from payroll taxes, as allowed by the Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) enacted in 1935.
What is Medicare for adults?
Medicare is the federal healthcare program for adults aged over 65, adults with disabilities, and people with end stage renal disease. The program provides coverage for inpatient and outpatient services, and prescription drugs. Medicare gets money from two trust funds: the hospital insurance (HI) trust fund and the supplementary medical insurance ...
How much is the Medicare deductible for 2020?
A person enrolled in Part A will also pay an inpatient deductible before Medicare covers services. Most recently, the deductible increased from $1,408 in 2020 to $1,484 in 2021. The deductible covers the first 60 days of an inpatient hospital stay.
What is the best Medicare plan?
We may use a few terms in this piece that can be helpful to understand when selecting the best insurance plan: 1 Deductible: This is an annual amount that a person must spend out of pocket within a certain time period before an insurer starts to fund their treatments. 2 Coinsurance: This is a percentage of a treatment cost that a person will need to self-fund. For Medicare Part B, this comes to 20%. 3 Copayment: This is a fixed dollar amount that an insured person pays when receiving certain treatments. For Medicare, this usually applies to prescription drugs.
How much is Medicare spending in 2019?
According to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, Medicare expenditures in 2019 totaled $796.2 billion. This article looks at the ways in which Medicare is funded. It also discusses changes in Medicare costs.
How much will Part D premiums be in 2021?
The adjusted monthly fee for 2021 ranges from $12.30 to a maximum of $77.10.
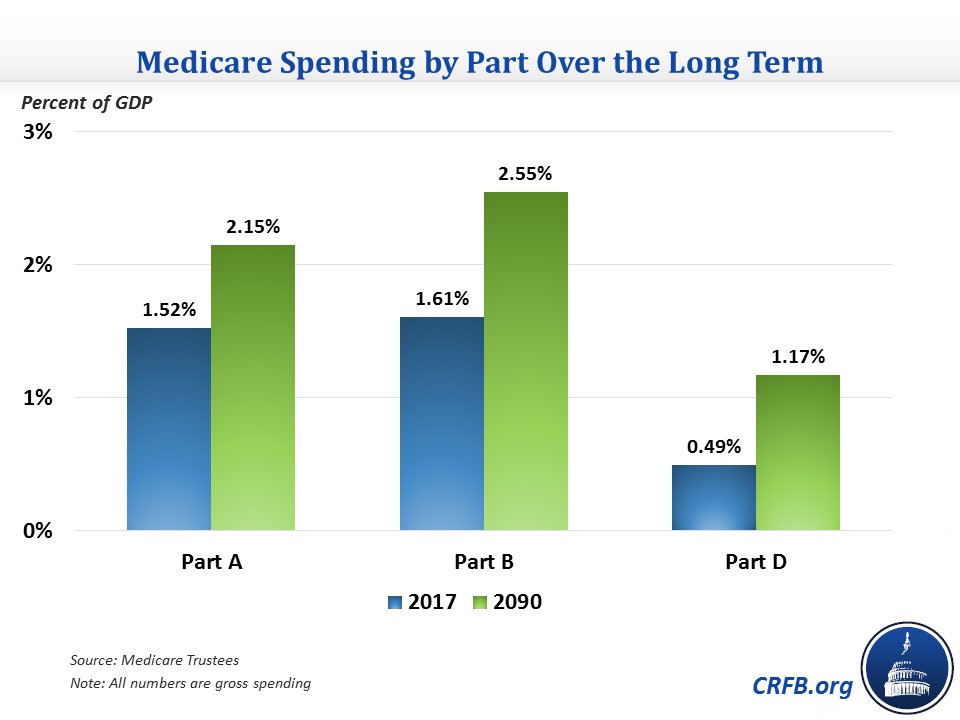
Why is it so hard to predict the future of Medicare?
According to the 2020 Medicare Trustees Report, it is difficult to predict future Medicare costs because of the uncertainty of changes and advances in technology and medicine. Each Medicare part has different costs, which help fund Medicare services.
How does Medicare Part A finance?
Medicare Part A Financing: Financing for the Hospital Insurance Program is primarily through a mandatory payroll deduction, the "FICA tax." Currently, the FICA tax is 1.45% of earnings paid by each employee and their employer, or 2.90% for the self-employed. The money is paid into a trust fund that is a special account in the U.S. Treasury. The trust fund also receives income from a portion of income taxes levied on Social Security benefits paid to high income beneficiaries, premiums from those who are not otherwise entitled Medicare benefits and choose to enroll voluntarily, and interest earnings. The taxes paid each year are used primarily to pay benefits for current beneficiaries. The hospital insurance funds can be used only to pay for the Medicare Part A, and Part B funds cannot be transferred for Part A use.
When did outpatient physicians get paid?
Beginning in 1992, outpatient physicians were paid an "allowed charge" defined as the lesser of (1) submitted charges or (2) a fee schedule based on a relative value scale (RVS). If a physician agrees to accept the approved payment rate, it becomes payment in full for services rendered to Medicare beneficiaries.
What are Medicare Part C and B liabilities?
Beneficiary Payment Liabilities and Medicare Part C: Beneficiaries are responsible for charges not covered by the Medicare Program and for the various cost-sharing aspects of Parts A and B . These liabilities may be paid "out of pocket" by the beneficiary, or by a third party insurance company as part of a "medigap" coverage plan.
What is Medicare Part D?
Medicare Part D: Various commercial health companies offer Medicare prescription drug coverage plans. These plans have premiums that are in addition to the medicare part B premium. Premiums vary according to the plan selected as well as the income of the beneficiary.
How long does it take for Medicare to stop paying?
Medicare payments stop after 100 days. Home health care has no deductible or co-insurance payments. For Part B, the beneficiary pays one annual deductible of $198, the monthly premiums, and co-insurance payments of 20% of the medically allowed charges. Medicare Part D: Various commercial health companies offer Medicare prescription drug coverage ...
How much does Medicare pay for prescription drugs in 2020?
Once the beneficiary and the plan have spent $4,020 on covered drugs in 2020, the beneficiary pays 25% of the cost of prescription drugs until $6,350 of spending is reached. At this point, catastrophic coverage takes over and Medicare pays 95% of drug costs.
What is a Medigap plan?
Medigap refers to private insurance policies that will pay most of the health care charges not covered by Parts A or B. These plans are also called Medicare Advantage Plans or Medicare Part C.
