Under the 2010 “pay-as-you-go” law known as PAYGO, that increase to the deficit would have triggered automatic spending cuts to programs, including a $25 billion cut to Medicare in 2018 alone. But in an AARP-supported move, the House and Senate on Thursday waived the required cuts as part of a temporary spending bill to prevent a government shutdown.
Full Answer
What Medicare cuts are being considered?
2018 Medicare payment cuts for clinical testing Payment reductions could be severe. For tests that are commonly performed in a physician’s office, the payment amounts... Patient access could be impacted. It is widely assumed that many, if not …
What happens if Medicare is cut?
Income thresholds will change in 2018. For people who earn above $85,000, the categories for higher Part B IRMAA surcharges will change in the middle tiers as follows: Up to $85,000 for single filers; up to $170,000 for joint filers. $85,001 to $107,000 for single; $170,001 to $214,000 for joint.
How much does Medicare pay for a haircut?
· Under the 2010 “pay-as-you-go” law known as PAYGO, that increase to the deficit would have triggered automatic spending cuts to programs, including a $25 billion cut to Medicare in 2018 alone. But in an AARP-supported move, the House and Senate on Thursday waived the required cuts as part of a temporary spending bill to prevent a government shutdown.
How will Medicare cuts affect seniors?
· Medicare Advantage, formally known as Medicare Part C, was created as a way for the private insurance industry to help control the cost of Medicare. But instead of saving taxpayers money, these ...

How much is the penalty for Medicare Part B?
For Part B, the penalty is 10 percent of your premium (charged on top of the premium rate) for each 12-month period that you didn’t have Part B coverage when you could have. The penalty lasts for as long as you have Part B. Medicare Part B has other costs as well.
How much is Medicare premium in 2017?
The standard premium in 2017 is $134 a month for new enrollees, but this number actually only applies to about 30 percent of Part B beneficiaries. The remaining majority pay about $109 a month – but this will change in 2018. The standard premium applies to:
What is the donut hole in Medicare?
If you have Medicare Part D, then you may face a situation known as the donut hole (or coverage gap). This happens when you hit your plan’s initial coverage limit ($3,750 in 2018) but still need to buy prescriptions. Until you hit the catastrophic coverage limit – i.e., the other side of the “donut” – you’ll be responsible for the full cost of your medications.
How much does Medicare Part B cost?
Medicare Part B covers medical care, including regular trips to the doctor and anything considered “medically necessary” for you. How much you pay for Part B coverage depends on different factors, such as when you enroll and your yearly income. The standard premium in 2017 is $134 a month for new enrollees, but this number actually only applies to about 30 percent of Part B beneficiaries. The remaining majority pay about $109 a month – but this will change in 2018. The standard premium applies to:
Why do people pay less on Social Security?
Most people pay less than the standard amount in 2017 because of the hold harmless provision under the Social Security Act. Usually, Social Security beneficiaries get a cost-of-living adjustment (COLA) to their payments each year, but in 2016, there was no COLA. The hold harmless clause protects people getting Social Security from rising Medicare costs. In 2017, there was a very small COLA of about 0.3 percent, which kept people in the hold harmless group protected from the higher standard premium. This rule doesn’t apply to new enrollees or people who don’t have Part B premiums deducted from Social Security payments.
What is Medicare Part A?
Medicare Part A is the hospital portion, covering services related to hospital stays, skilled nursing facilities, nursing home care, hospice and home healthcare. Under the Affordable Care Act, Part A alone counts as minimum essential coverage, so if this is all you sign up for, you’ll meet the law’s requirements. Most people don’t pay a premium for Part A because it’s paid for via work-based taxes. If, over the course of your working life, you’ve accumulated 40 quarter credits, then you won’t pay a premium for Part A. This applies to nearly all enrollees, but some do pay a premium as follows:
Does Medicare Advantage cover Part B?
If you have Medicare Advantage, then you will pay the Part B premium as well as any premiums that your plan charges. Medicare Advantage must cover Part B services. Income thresholds will change in 2018.
How much does Medicare Advantage pay?
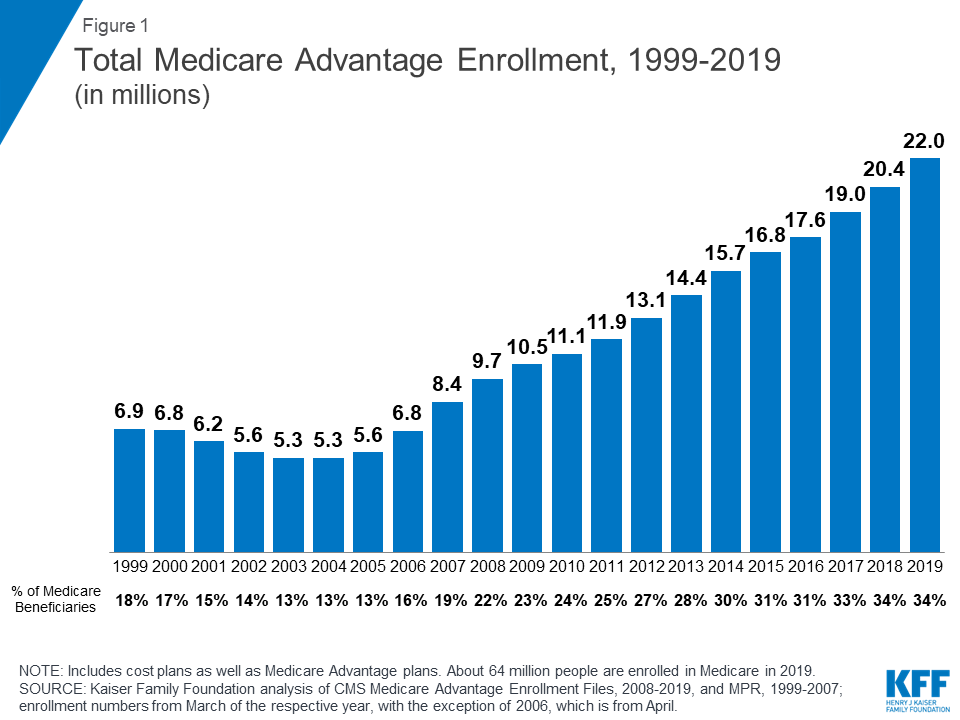
Between upcoding and other schemes, Medicare Advantage plans are paid an average of 105 percent of what comparable patients would cost the traditional Medicare program. Medicare Advantage is an increasingly popular choice among seniors, and now attracts more than 18 million members.
What percentage of Medicare beneficiaries are on Advantage plans?
Medicare Advantage plans continue to grow in popularity, now attracting 31 percent of all Medicare beneficiaries. People make this choice because most Advantage plans offer reductions in copays and deductibles, along with enhanced benefits like membership in gym clubs or including a Medicare Part D pharmacy benefit.
How much does Medicare spend on prescription drugs?
Prices here are roughly double what patients in other countries pay for the same drugs. Over the next ten years, Medicare is projected to spend $1.5 trillion on prescription drugs.
Why was Medicare Advantage created?
Medicare Advantage, formally known as Medicare Part C, was created as a way for the private insurance industry to help control the cost of Medicare.
Can an Advantage plan exclude unprofitable patients?
Although Advantage plans aren ’t allowed to overtly exclude costly (read: unprofitable) patients, they have found ways to push high-cost patients back into traditional Medicare by charging high copayments for drugs and services that are mostly used by high-cost patients.
Does Medicare pay for heart failure?
For example, Medicare pays Advantage plans several thousand dollars extra for patients with heart failure. But insurers know that heart failure ranges from nearly undetectable (and inexpensive to care for) to overwhelming (and very expensive to care for). Insurers have become remarkably effective at attracting the undetectable and shunning ...
What percentage of Medicare beneficiaries are covered by Part B?
Part B coverage is voluntary, and about 91 percent of all Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in Part B. Approximately 25 percent of Part B costs are financed by beneficiary premiums, with the remaining 75 percent covered by general revenues.
How much is Medicare Part D deductible?
Medicare Part D offers a standard prescription drug benefit with a 2017 deductible of $400 and an average estimated monthly premium of $35.
What is the Medicare Part D coverage gap?
The Medicare Part D coverage gap, or “donut hole, ” is being closed through a combination of manufacturer discounts and gradually increasing Federal subsidies. Beneficiaries fall into the coverage gap once their total drug spending exceeds an initial coverage limit ($3,700 in 2017), until they reach the threshold for qualified out-of-pocket spending ($4,950 in 2017), at which point they are generally responsible for five percent of their drug costs. Previously beneficiaries were responsible for 100 percent of their drug costs in the coverage gap. In 2018, non-low income subsidy beneficiaries who reach the coverage gap will pay 35 percent of the cost of covered Part D brand drugs and biologics and 44 percent of the costs for all generic drugs in the coverage gap. Cost-sharing in the coverage gap will continue to decrease each year until beneficiaries are required to pay only 25 percent of the costs of covered Part D drugs in 2020 and beyond.
How many people are on Medicare Advantage in 2018?
In 2018, Medicare Advantage enrollment will total approximately 20.8 million, or approximately 38 percent of all Medicare beneficiaries. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) data confirm that 99 percent of Medicare beneficiaries will have access to at least one Medicare Advantage plan in 2018.
How much is Medicare Part C?
Part C ($203.0 billion gross spending in 2018) Medicare Part C, the Medicare Advantage Program, pays plans a capitated monthly payment to provide all Part A and B services, and Part D services if offered by the plan.
What is the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services?
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services ensure s availability of effective, up-to-date health care coverage and promotes quality care for beneficiaries.
What is expedited procedure for claims with no material fact in dispute?
Expedite Procedures for Claims with No Material Fact in Dispute: This proposal allows the Office of Medicare Hearings and Appeals to issue decisions without holding a hearing if there is no material fact in dispute. These cases include appeals, for example, in which Medicare does not cover the cost of a particular drug or the Administrative Law Judge cannot find in favor of an appellant due to binding limits on authority. [No budget impact]
How much does Medicare cost in 2020?
In 2020, US federal government spending on Medicare was $776.2 billion.
How many people have Medicare?
In 2018, according to the 2019 Medicare Trustees Report, Medicare provided health insurance for over 59.9 million individuals —more than 52 million people aged 65 and older and about 8 million younger people.
What is the CMS?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), administers Medicare, Medicaid, the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), and parts of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) ("Obamacare"). Along with the Departments of Labor and Treasury, the CMS also implements the insurance reform provisions of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) and most aspects of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010 as amended. The Social Security Administration (SSA) is responsible for determining Medicare eligibility, eligibility for and payment of Extra Help/Low Income Subsidy payments related to Parts C and D of Medicare, and collecting most premium payments for the Medicare program.
What is Medicare and Medicaid?
Medicare is a national health insurance program in the United States, begun in 1965 under the Social Security Administration (SSA) and now administered by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). It primarily provides health insurance for Americans aged 65 and older, ...
How is Medicare funded?
Medicare is funded by a combination of a specific payroll tax, beneficiary premiums, and surtaxes from beneficiaries, co-pays and deductibles, and general U.S. Treasury revenue. Medicare is divided into four Parts: A, B, C and D.
When did Medicare Part D start?
Medicare Part D went into effect on January 1, 2006. Anyone with Part A or B is eligible for Part D, which covers mostly self-administered drugs. It was made possible by the passage of the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003. To receive this benefit, a person with Medicare must enroll in a stand-alone Prescription Drug Plan (PDP) or public Part C health plan with integrated prescription drug coverage (MA-PD). These plans are approved and regulated by the Medicare program, but are actually designed and administered by various sponsors including charities, integrated health delivery systems, unions and health insurance companies; almost all these sponsors in turn use pharmacy benefit managers in the same way as they are used by sponsors of health insurance for those not on Medicare. Unlike Original Medicare (Part A and B), Part D coverage is not standardized (though it is highly regulated by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services). Plans choose which drugs they wish to cover (but must cover at least two drugs in 148 different categories and cover all or "substantially all" drugs in the following protected classes of drugs: anti-cancer; anti-psychotic; anti-convulsant, anti-depressants, immuno-suppressant, and HIV and AIDS drugs). The plans can also specify with CMS approval at what level (or tier) they wish to cover it, and are encouraged to use step therapy. Some drugs are excluded from coverage altogether and Part D plans that cover excluded drugs are not allowed to pass those costs on to Medicare, and plans are required to repay CMS if they are found to have billed Medicare in these cases.
When did Medicare+Choice become Medicare Advantage?
These Part C plans were initially known in 1997 as "Medicare+Choice". As of the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003, most "Medicare+Choice" plans were re-branded as " Medicare Advantage " (MA) plans (though MA is a government term and might not even be "visible" to the Part C health plan beneficiary).