
You can start Social Security at 62, but your benefit will be permanently reduced (at 70% of full benefit) to reflect the early start. Also, if you keep working your benefit checks will be reduced by $1 for every $2 you earn over a certain amount, which in 2019 is $17,640. At 67, you will get 100% of your retirement benefit.
Full Answer
Should the Medicare eligibility age be changed to 67?
Under this option, the eligibility age for Medicare would remain below Social Security’s FRA until 2029, when both would be 67 for people born in 1962; from that point on, the two eligibility ages would be identical. A change in the eligibility age for Medicare would affect people’s sources of health insurance coverage, including Medicaid.
What happens to your social security when you turn 62?
Workers with an older retirement age get smaller Social Security payments throughout retirement. The full retirement age will further increase until it hits 67 for everyone born in 1960 or later. (Getty Images) While you can start Social Security payments at age 62, your monthly checks are reduced if you begin collecting benefits at this age.
Will the Social Security age ever be raised to 67?
It would remain at 67 thereafter. Social Security’s full retirement age, or FRA (the age at which workers become eligible for full retirement benefits), has already been increased from 65 to 66 and is scheduled to rise further during the coming decade, reaching 67 for people born in 1960; they will turn 67 in 2027.
What is the full retirement age for a widow in 1962?
Full Retirement Age for Survivors If You Were Born In 1962 or Later | SSA Full Retirement Age for Survivors Born In 1962 or Later: 67 The earliest a widow or widower can start receiving Social Security survivors benefits based on age is age 60. If you start receiving survivors benefits at age
When can I get full Social Security if I was born in 1962?
67Full Retirement Age for Survivors Born In 1962 or Later: 67 (En español)
What is full retirement born 1962?
Full retirement age for survivors is 66 for people born in 1956 and gradually increases to age 67 for people born in 1962 or later.
What is the difference between taking Social Security at 62 and 63?
Monthly Social Security payments are reduced if you sign up at age 63, but by less than if you claim payments at age 62. A worker eligible for $1,000 monthly at age 66 would get $800 per month at age 63, a 20% pay cut. If your full retirement age is 67, you will get 25% less by signing up at age 63.
How much does Social Security go up between 62 and 67?
Retirees who begin collecting Social Security at 62 instead of at the full retirement age (67 for those born in 1960 or later) can expect their monthly benefits to be 30% lower. So, delaying claiming until 67 will result in a larger monthly check.
Can I retire at 62 if I was born in 1962?
If you were born between 1960 your full retirement age is 67 (En español) You can start your Social Security retirement benefits as early as age 62, but the benefit amount you receive will be less than your full retirement benefit amount.
What is the $16 728 Social Security secret?
1:266:46My Review: Motley Fool's $16,728 Social Security Bonus - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIf you've read any of their articles you've probably seen this it says the sixteen thousand sevenMoreIf you've read any of their articles you've probably seen this it says the sixteen thousand seven hundred and twenty eight dollar social security bonus most retirees completely overlook.
Can I draw Social Security at 62 and still work full time?
You can get Social Security retirement or survivors benefits and work at the same time. But, if you're younger than full retirement age, and earn more than certain amounts, your benefits will be reduced.
At what age is Social Security no longer taxed?
between 65 and 67 years oldHowever once you are at full retirement age (between 65 and 67 years old, depending on your year of birth) your Social Security payments can no longer be withheld if, when combined with your other forms of income, they exceed the maximum threshold.
Why retiring at 62 is a good idea?
Probably the biggest indicator that it's really ok to retire early is that your debts are paid off, or they're very close to it. Debt-free living, financial freedom, or whichever way you choose to refer it, means you've fulfilled all or most of your obligations, and you'll be under much less strain in the years ahead.
Is it better to collect Social Security at 62 or 67?
Key takeaways. If you claim Social Security at age 62, rather than wait until your full retirement age (FRA), you can expect a 30% reduction in monthly benefits. For every year you delay claiming Social Security past your FRA up to age 70, you get an 8% increase in your benefit.
What is the average Social Security benefit at age 62 in 2021?
At age 62: $2,364. At age 65: $2,993. At age 66: $3,240. At age 70: $4,194.
What are the pros and cons of taking Social Security at age 62?
The advantage of taking retirement benefits early is that you start to collect the money that you've been paying over to the government monthly since you started working. The downside to that, however, is that it causes a permanent reduction in your Social Security retirement benefit.
What Policy Option Did CBO Analyze?
The option that CBO analyzed would raise the age of eligibility for Medicare by two months every year, beginning with people who were born in 1951...
What Is CBO's New Estimate?
Implementing this option would reduce federal budget deficits by $19 billion between 2016 and 2023, according to estimates by CBO and the staff of...
How Much Did CBO's Estimate Change and Why?
CBO’s current estimate of the savings to Medicare from this option is much lower than its earlier estimates for proposals to raise Medicare’s eligi...
When will Medicare be 67?
The option that CBO analyzed would raise the age of eligibility for Medicare by two months every year, beginning with people who were born in 1951 (who will turn 65 in 2016), until the eligibility age reached 67 for people born in 1962 (who will turn 67 in 2029). Thereafter, the eligibility age would remain at 67.
What would happen if the eligibility age for Medicare changed?
A change in the eligibility age for Medicare would affect people’s sources of health insurance coverage, including Medicaid. States have the option under current law to expand their Medicaid programs to people with income below 138 percent of the federal poverty guidelines. Although that optional Medicaid expansion applies only to people ...
How many people will lose Medicare in 2023?
For example, CBO estimates that of the 5.5 million people who would be affected by this option in 2023, about 50 percent would obtain insurance from their (or their spouse’s) employer or former employer, about 15 percent would continue to qualify for Medicare on the basis of their eligibility for disability benefits, about 15 percent would buy insurance through the exchanges or in the nongroup market, about 10 percent would receive coverage through Medicaid, and about 10 percent would become uninsured. To develop those estimates, CBO examined data on the patterns of health insurance coverage among people a few years younger than Medicare’s current eligibility age. CBO then adjusted those figures to account for changes in sources of health insurance coverage and in participation in the labor force as people age.
How much will Medicare be cut in 2038?
Looking farther into the future, CBO estimates that by 2038, spending on Medicare would be about 3 percent less under this option than it would be under current law—4.7 percent of gross domestic product rather than 4.9 percent. On the basis of its estimates for 2016 through 2023, CBO projects that roughly two-thirds of those long-term savings from this option would be offset by the increases in federal spending for Medicaid and exchange subsidies and the reduction in revenues described above.
How much would the federal budget deficit be reduced?
Implementing this option would reduce federal budget deficits by $19 billion between 2016 and 2023, according to estimates by CBO and the staff of the Joint Committee on Taxation (see Table 1). That figure represents the net effect of a $23 billion decrease in outlays and a $4 billion decrease in revenues over that period. The decrease in outlays includes a reduction in federal spending for Medicare as well as a slight reduction in outlays for Social Security retirement benefits. However, those savings would be substantially offset by increases in federal spending for Medicaid and for subsidies to purchase health insurance through the new insurance exchanges and by the decrease in revenues.
Why would Social Security retirement benefits decline?
In addition, outlays for Social Security retirement benefits would decline slightly because raising the eligibility age for Medicare would induce some people to delay applying for retirement benefits. One reason is that some people apply for Social Security at the same time that they apply for Medicare; another reason is ...
What is the eligibility age for Medicare?
Under this option, the eligibility age for Medicare would remain below Social Security’s FRA until 2029, when both would be 67 for people born in 1962; from that point on, the two eligibility ages would be identical.
How long do you have to be on Social Security to get Medicare?
You will need to find a way to maintain coverage until you turn age 65 and become eligible for Medicare.You can receive Medicare at any age if you have been receiving Social Security disability benefits for two years.
How long is the special enrollment period for Medicare Advantage?
Whenever you do leave your group coverage, you will get a 63 day special enrollment period to choose whatever medigap or Medicare advantage plan you would like… and not have to answer any underwriting questions.
What is a retirement estimate?
Description. The Retirement Estimator is one of 11 online calculators available from SSA that address various aspects of retirement planning. It uses an individual's actual earnings history to estimate the future value of his or her Social Security retirement benefits under various claiming-age scenarios. The Retirement Estimator had o
What does it mean to retire early?
The truth is for a lot of people in the United States “retiring” early means losing health insurance and not getting it back until you hit 65. Assuming you live to 65. Which you might now, because you lost your health insurance when you “retired”.
Can you get Medicare if you are 65?
Medicare is only for people who are 65+ or under 65 but disabled. If you aren’t disabled, your Medicare won’t start until you turn 65.
Do you have to pay bills when retiring on your own?
Now, retiring on you own, you’re going to have pay that for yourself above board: it’s no longer hidden, the bills roll in and you’ve got to pay them.
Does Medicare cut out private insurance?
It would not cut out private insurers since private insurers actually provide and administer the insurance through the Medicare program. It’s a workable solution. We just need to get both sides of government on board.
Who proposed the Medicare at 50 Act?
The most prominent proposal is the Medicare at 50 Act sponsored by Senator Sherrod Brown. Asking for the age to be lowered by 15 years may be too much of a stretch; other proposals call for a more moderate age 60 or 62 as the age of eligibility.
What is the earliest age to sign up for Medicare?
Under current law, absent certain exceptions, age 65 is the earliest age you can sign up for Medicare. This age has been set since the inception of Medicare in 1965. The discussion of lowering the age of initial eligibility has come up in the past, but it never had the necessary support to advance through the legislative process.
Why are health insurance companies pushing back?
The health insurance companies are going to push back as well because not only will they lose the revenue from this enormous group of the population, but they see this as a slippery slope to a single-payer system where insurance companies are no longer needed.
When will Medicare insolvency happen?
The Part A account that funds the hospitalization and related services faces insolvency by 2026. Insolvency means that Medicare wouldn’t be able to fully reimburse hospitals, nursing homes, and home health agencies for promised benefits.
Can Medicare cut provider payments?
There’s no way around this. You cannot cut provider payments for medical services without impacting the beneficiaries of those services .
Is there a difference between Medicare and private insurance?
There is a big difference between the reimbursement rate between a Medicare patient and a patient with private health insurance. There was another Kaiser study that found that private insurers paid nearly double the Medicare rates for the same hospital services.
When will Social Security be 67?
In 2000, the Social Security Amendments of 1983 began pushing back the standard age for full Social Security benefits. The progressive changes are nearing their conclusion: Beginning in 2022, the standard age for full benefits will be 67 for anyone born after 1960.
When did Medicare become law?
In the summer of ‘65, President Lyndon Johnson signed Medicare into law, establishing the age of eligibility at 65. The eligibility age for Medicare remains the same to this day.
Why do people not get Medicare at 65?
These days, fewer people are automatically enrolled in Medicare at age 65 because they draw Social Security benefits after 65. If you do not receive Social Security benefits, you will not auto-enroll in Medicare.
What is the age limit for Medicare?
Most older adults are familiar with Medicare and its eligibility age of 65. Medicare Part A and Medicare Part B are available based on age or, in some cases, health conditions, including:
How long do you have to be on Social Security to get Medicare?
Individuals under 65 and already receiving Social Security or Railroad Retirement Board benefits for 24 months are eligible for Medicare. Still, most beneficiaries enroll at 65 when they become eligible for Medicare.
How old do you have to be to get medicare?
While some specific circumstances can impact at what age you are eligible for Medicare, most people must wait until 65 as things currently stand.
Does Medicare Part B have a premium?
While Medicare Part B has a standard monthly premium, 99 out of 100 people don’t have to pay a premium for Medicare Part A. Still, no part of Medicare can genuinely be called “free” because of associated costs you have to pay, like deductibles, coinsurance and copays.
What is the Social Security benefit reduction for 1959?
Workers born in 1959 will see their monthly payments reduced by 29.17% if they sign up for Social Security at age 62, compared to a 28.33% benefit reduction for those born in 1958 and a 25% decrease for those born in 1954.
How much is Social Security at 62?
For a worker eligible for a $1,000 monthly Social Security benefit at his full retirement age, claiming at age 62 will reduce his monthly payment to $750 if his birth year is 1954 and $708 if he was born in 1959.
What age do you have to be to get Medicare?
While the Social Security full retirement age has increased over the past several years, the age when workers qualify for Medicare has remained age 65 . Those who delay claiming Social Security until their full retirement age or later still need to sign up for Medicare at age 65 or maintain other group health insurance based on current employment to avoid hefty Medicare late enrollment penalties. While many retirees have their Medicare premiums withheld from their Social Security checks, those who enroll in Medicare before starting Social Security will have to pay premiums out of pocket.
What is the full retirement age for Social Security at 62 in 2021?
"If you turn 62 in 2021, your full retirement age is 66 and 10 months. You get less if you start early or more if you delay until later," says Andy Landis, author of "Social Security: The Inside Story.". "Starting at 62 in 2021 gets you ...
How long can you delay Social Security?
However, those who have an older retirement age have fewer months to delay claiming Social Security and less of an opportunity to earn delayed retirement credits. "If a person files at age 70, if they had a full retirement age of 66, that means they waited 48 months beyond full retirement age, so they would get 132% of their primary insurance ...
What is the retirement age for a person born in 1937?
The full retirement age used to be 65 for those born in 1937 or earlier. Those born between 1943 and 1954 have a full retirement age of 66. The full retirement age further increases in two-month increments each year to 66 and 10 months for those born in 1959, up from 66 and 8 months for those with a birth year of 1958.
When will Social Security retirement age increase?
The Social Security Retirement Age Increases in 2021. Workers with an older retirement age get smaller Social Security payments throughout retirement. The full retirement age will further increase until it hits 67 for everyone born in 1960 or later.
When will Medicare be 67?
That trend, which results in higher program costs, will almost certainly continue. This option would raise the age of eligibility for Medicare by two months each year, starting in 2020 (people born in 1955 will turn 65 that year), until it reaches 67 for people born in 1966 (who would become eligible for Medicare benefits in 2033).
How much will Medicare be delayed in 2026?
By calendar year 2026, the benefits of 3.7 million people would be delayed by 14 months. Total spending on Medicare as a result would be $55 billion lower between 2020 and 2026 than under current law. CBO anticipates that most people who become eligible for Medicare after age 65 under this option would continue their existing coverage ...
How much of the Medicare savings will be offset by Social Security?
On the basis of its estimates for 2020 through 2026, CBO projects that roughly three-fifths of the long-term savings from Medicare under this option would be offset by changes in federal outlays for Social Security, Medicaid, and subsidies for coverage through the marketplaces as well as by reductions in revenues.
What is the maximum age for medicaid?
Under this option, federal outlays for Medicaid would increase for two groups of people between the age of 65 and the new Medicare eligibility age: dual-eligible beneficiaries (Medicare enrollees who also are eligible for full benefits under Medicaid) and enrollees who would be Medicaid beneficiaries before turning 65 but who, under current law, would lose that eligibility once they qualified for Medicare at age 65. For this option, CBO assumed that the age limit for Medicaid would increase in tandem with Medicare’s eligibility age. Hence, this option would cause Medicaid to remain the primary source of coverage for members of both groups until they reached the new eligibility age for Medicare. As a result, federal outlays for Medicaid between 2020 and 2026 would be $20 billion higher under this option, CBO projects.
Why is the CBO predicting retirement benefits to be less linked to Medicare eligibility age?
CBO also expects future decisions about claiming retirement benefits to be less linked to Medicare’s eligibility age than has historically been the case because of greater access to health insurance through Medicaid and through the nongroup market.
How many people will be eligible for Medicare in 2020?
In calendar year 2020, when this option would take effect, about 3.4 million people will become eligible for Medicare coverage on the basis of their age, CBO estimates. Under this option, that group would see its benefits delayed by two months. By calendar year 2026, the benefits of 3.7 million people would be delayed by 14 months.
How much will Social Security be reduced in 2026?
The option also would reduce outlays for Social Security retirement benefits by an estimated $5 billion over the 2020–2026 period because raising the eligibility age for Medicare would induce some people to delay claiming retirement benefits. In CBO’s estimation, the reduction in Social Security spending would be fairly small because raising ...
When will Social Security beneficiaries receive their benefits?
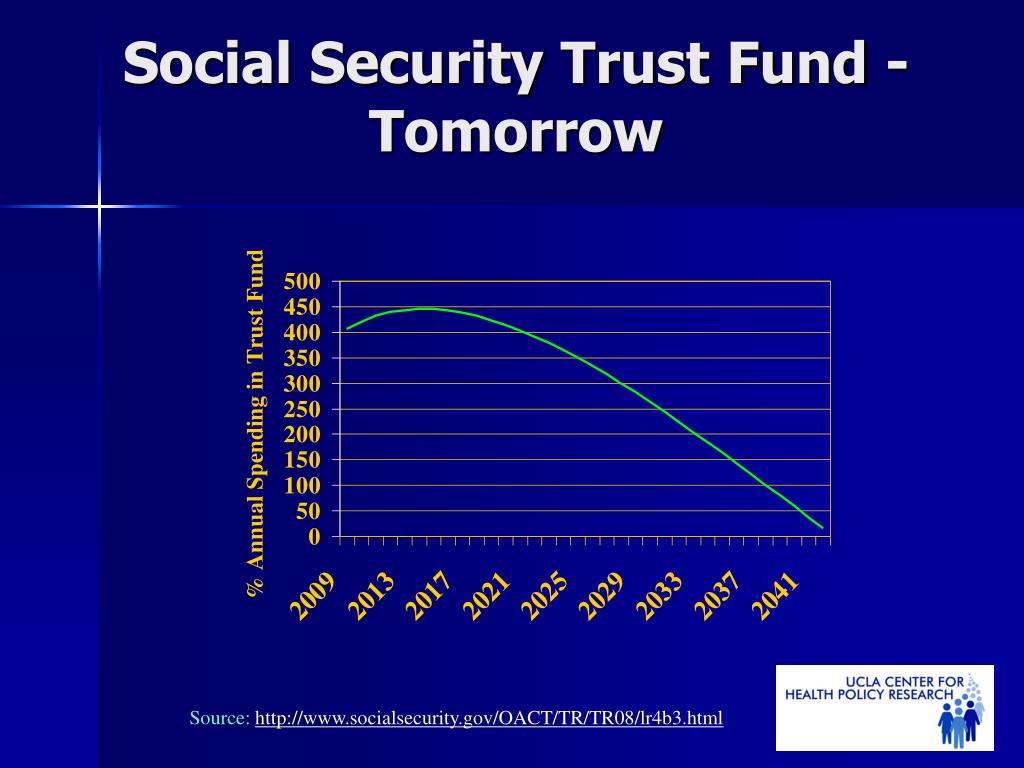
Looking Ahead to 2035. According to the most recent Social Security and Medicare Boards of Trustees annual report, both trust funds will be depleted as of 2035. If these predictions hold, beginning in 2035, beneficiaries will receive about three-quarters (75%) of their scheduled benefit until at least 2093.
When will Social Security change?
Every October, the Social Security Administration (SSA) announces its annual changes to the Social Security program for the coming year. 1 Here are the Social Security changes that were announced in Oct. 2020 to take effect on Jan. 1, 2021, according to the SSA's annual fact sheet. Keep them in mind when you update your Social Security ...
What is the maximum taxable earnings for 2020?
2. Maximum Taxable Earnings Rose to $142,800. In 2020, employees were required to pay a 6.2% Social Security tax (with their employer matching that payment) on income of up to $137,700. Any earnings above that amount were not subject to the tax. In 2021, the tax rate remains the same at 6.2% (12.4% for the self-employed), ...
How much will the COLA increase in 2022?
As we've seen, 2022's 5.9% bump is much higher than most years; in 2021 the COLA increase was just 1.3%. 1 The average monthly benefit for all retired workers will increase by $92 in 2022, from $1,565 to $1,657. 2
What will happen to Social Security in 2022?
Other changes for 2022 include an increase in how much money working Social Security recipients can earn before their benefits are reduced and a slight rise in disability benefits.
How much is the Cola increase for Social Security?
In 2019, the COLA was 2.8%, the largest increase since 2012. 3 For the average Social Security recipient, the 1.3% raise amounts to just $20 per month on an average monthly payout of $1,543 vs. $1,523 in 2020. 4 . 2.
What is the maximum amount of Social Security income in 2021?
Maximum earnings subject to the Social Security tax also increased—from $137,700 a year to $142,800. Other changes for 2021 included an increase in how much money working Social Security recipients can earn before their benefits are reduced and a slight rise in disability benefits.
