Why is my Medicare so expensive?
These include obesity, hypertension, heart disease, diabetes, chronic lung disease, cancer and many others. Chronic diseases are inherently difficult to manage, will last a lifetime (some cancers excepted) and are expensive to treat. Chronic illness …
How much does Medicare cost at age 65?
Mar 22, 2013 · Whatever else happens with the Medicare program, increased aging and greater longevity guarantee higher taxpayer costs. True Administrative Costs. It is conventionally assumed that Medicare is more...
Will My Medicare premiums increase?
Mar 04, 2022 · One reason for rising healthcare costs is government policy. Since the inception of Medicare and Medicaid —programs that help people without health insurance—providers have been able to increase...
How much is Medicare increasing?
60 rows · Mar 26, 2021 · From 1974 to 1982, health care prices rose by an average of 14.1% a year for three reasons. First, prices rebounded after the wage-price controls expired in 1974. Second, Congress enacted the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974. It exempted corporations from state regulations and taxes if they self-insured.
What is one of the reasons why Medicare costs have been rising?
One reason for rising healthcare costs is government policy. Since the inception of Medicare and Medicaid—programs that help people without health insurance—providers have been able to increase prices.
What are the two biggest factors that causes the Medicare costs to increase?
There were two causes of this massive increase: government policy and lifestyle changes. First, the United States relies on company-sponsored private health insurance. The government created programs like Medicare and Medicaid to help those without insurance. These programs spurred demand for healthcare services.
What are the 5 main reasons for rising health care costs?
Five factors contribute to the rise in health care costs in the US: (1) more people; (2) an aging population; (3) changes in disease prevalence or incidence; (4) increases in how often people use health care services; and (5) increases in the price and intensity of services.Nov 7, 2017
What are 3 reasons for high health care costs?
Cutler explored three driving forces behind high health care costs—administrative expenses, corporate greed and price gouging, and higher utilization of costly medical technology—and possible solutions to them.
Are healthcare costs rising?
Total national health expenditures, US $ per capita, 1970-2020. On a per capita basis, health spending has increased sharply in the last five decades, from $353 per person in 1970 to $12,531 in 2020. In constant 2020 dollars, the increase was from $1,875 in 1970 to $12,531 in 2020.Feb 25, 2022
What is a reason that healthcare costs are rising quizlet?
Three factors contribute to the rising healthcare costs; a fragmented system that multiplies administrative costs (track patient expenses and bills to multiple insurers), the power that health care providers have over consumers, and the for-profit basis of the health care system.
What are some of the reasons for increased health care costs that are attributed to the providers of medical care?
A 2018 JAMA study suggests that three key factors contribute to inflated healthcare prices in the United States:Physician salaries.Administrative costs, and.Prescription drug prices.Jun 26, 2019
What are major market factors in healthcare?
In its annual report to Congress this month, MedPAC identified the following five notable spending trend influencers.Technology. ... Healthcare product and service prices. ... Market power. ... Health insurance coverage. ... Demographics and patient characteristics. ... More Articles on Healthcare Spending:Mar 28, 2014
What are the effects of rising healthcare costs?
higher health care spending, they have less income to spend on other goods and services. High health care costs could reduce access to health care, bankrupt consumers and deplete retirement savings.
When did healthcare costs start rising?
Within the United States, medical care prices increased much more rapidly between 1980 and 1988 than did prices of other major categories of expenditures.
What factors determine the cost of healthcare services?
To quantify changes in spending associated with 5 fundamental factors related to health care spending in the United States: population size, population age structure, disease prevalence or incidence, service utilization, and service price and intensity.Nov 7, 2017
Why should we lower healthcare costs?
Workplace health programs will not impact many of the drivers of healthcare costs, but they can impact unhealthy behaviors and this is why reducing health care costs is one of the main benefits of wellness. By helping employees adopt and maintain healthy behaviors, they improve their health and avoid chronic diseases.Feb 22, 2022
What are the factors that contribute to the inflated healthcare prices in the United States?
A 2018 JAMA study suggests that three key factors contribute to inflated healthcare prices in the United States: Physician salaries. Administrative costs, and. Prescription drug prices.
How much did Medicare spend in 2018?
Because Medicare is a publicly funded program, this enrollment growth will also impact national health expenditures. According to CMS, the U.S. spent $750.2 billion on Medicare in 2018. As a result of enrollment growth, CMS projects that Medicare spending will increase by 7.6 percent per year through 2028.
How much can healthcare providers reduce administrative costs?
According to a 2019 McKinsey & Company report, the U.S. could reduce administrative spending by 30 percent by automating and streamlining BIR processes.
How much will healthcare cost in 2027?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) estimate that national health expenditures will rise to $6.0 trillion by 2027.
What percentage of older adults have chronic conditions?
The National Council on Aging reports that 80 percent of older Americans have a chronic condition. Seventy-seven percent of older adults have two or more chronic conditions. The most common of these conditions include:
Why is medical claims data important?
Medical claims data is an important tool for understanding chronic disease prevalence in the United States. All-payor claims data can provide insight into comorbidities, common procedures, or areas with a high volume of specific chronic disease diagnoses. Chronic conditions often require long-term medical attention.
How much does a C section cost?
According to Definitive Healthcare data, the average cost of a c-section was $5,305 in 2019.
What percentage of Medicare will increase over the next 25 years?
Under the most realistic scenario, the Congressional Budget Office estimates that the aging population is responsible for 52 percent of Medicare’s rapid spending increase.
How much is Medicare spending?
In 2012, Medicare’s aggregate spending reached $557 billion, and it is expected to nearly double in just 10 years, reaching over a trillion dollars by 2023. [4] Medicare spending accounted for 3.67 percent of the entire economy, measured as gross domestic product (GDP), in 2011. It will be an estimated 5.8 percent of GDP in 2030, according to the Medicare Actuary’s full alternative scenario, which uses the most realistic assumptions. By 2080, under the same assumptions, Medicare spending will account for 9.97 percent of the entire economy. [5]
How much of Medicare is funded by taxpayers?
In Medicare Parts B and D, taxpayers already fund 75 percent of the standard total premium costs, a sharp departure from the original Medicare law, which in 1966 required taxpayers to finance 50 percent of Part B program costs.
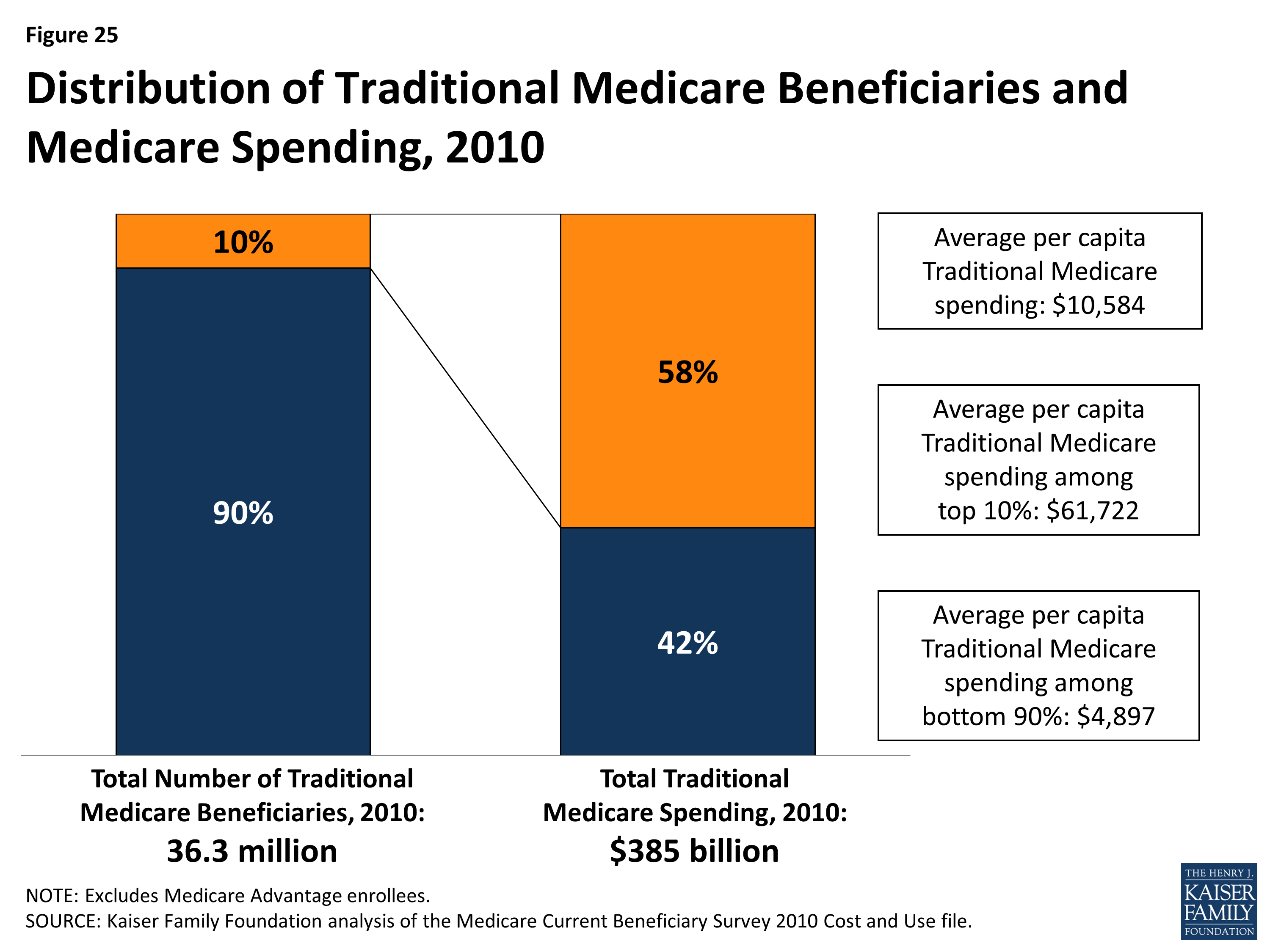
How many Medicare patients are in traditional Medicare?
Today, roughly three of four Medicare patients are enrolled in the traditional Medicare program. [1] Price Controls. Traditional Medicare relies on conventional methods of “cost control”—ratcheting down reimbursements for doctors and hospitals and tightening the program’s price controls on payments for their services.
How many baby boomers are eligible for medicare?
There are roughly 77 million baby boomers—who will be eligible for Medicare at the rate of 10,000 per day over the next 19 years. [14] .
What percentage of the economy is Medicare?
Medicare spending accounted for 3.67 percent of the entire economy, measured as gross domestic product (GDP), in 2011. It will be an estimated 5.8 percent of GDP in 2030, according to the Medicare Actuary’s full alternative scenario, which uses the most realistic assumptions.
When was Medicare enacted?
Since the enactment of Medicare in 1965, government actuaries have historically underestimated the true cost of Medicare. Outside of calculating on the basis of hard data, such as the age of those eligible or the size of enrollment, forecasting in Medicare (and health care in general) is inherently difficult.
Why are healthcare costs rising?
One reason for rising healthcare costs is government policy. Since the inception of Medicare and Medicaid —programs that help people without health insurance—providers have been able to increase prices. Still, there's more to rising healthcare costs than government policy.
Why is healthcare so expensive?
Healthcare gets more expensive when the population expands —as people get older and live longer. Therefore, it’s not surprising that 50% of the increase in healthcare spending comes from increased costs for services, especially inpatient hospital care.
How much of healthcare costs are chronic diseases?
Chronic diseases constitute 85% of healthcare costs, and more than half of all Americans have a chronic illness. 2 9 . Demand for medical services has increased because of Medicare and Medicaid, resulting in higher prices.
How much does healthcare cost in the US?
Healthcare costs in the U.S. have been rising for decades and are expected to keep increasing. The U.S. spent more than $3.8 trillion on healthcare in 2019 and was expected to exceed $4 trillion in 2020, according to a study by the Peterson and Kaiser Foundations. A JAMA study found five factors that affect the cost of healthcare: ...
Why do people avoid medical care?
People avoiding needed medical care due to concerns about costs has been a problem for several years. A 2019 survey by the Physicians Advocacy Institute (PAI) found patients avoiding care due to an inability to afford covering deductibles under their HDHPs. 12
Why is it so hard to know the cost of healthcare?
Thanks to a lack of transparency and underlying inefficiency, it’s difficult to know the actual cost of healthcare. Most people know the cost of care is going up, but with few details and complicated medical bills, it’s not easy to know what you're getting for the price.
What was the biggest increase in spending in the JAMA study?
The authors of the JAMA study point to diabetes as the medical condition responsible for the greatest increase in spending over the study period. The increased cost of diabetes medications alone was responsible for $44.4 billion of the $64.4 billion increase in costs to treat that disease. 4
What are the causes of rising health care costs?
The second cause of rising health care costs is an epidemic of preventable diseases. The four leading causes of death are heart disease, cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder, and stroke. Chronic health conditions cause most of them. They can either be prevented or would cost less to treat if caught in time. Risk factors for heart disease and strokes are poor nutrition and obesity. Smoking is a risk factor for lung cancer (the most common type) and COPD. Obesity is also a risk factor for other common forms of cancer. 23
Why did the government create programs like Medicare and Medicaid?
The government created programs like Medicare and Medicaid to help those without insurance. These programs spurred demand for health care services. That gave providers the ability to raise prices.
How much did Medicare cost in 2008?
By 2009, rising health care costs were consuming the federal budget. Medicare and Medicaid cost $671 billion in 2008. 25 Payroll taxes cover less than half of Medicare and none of Medicaid.
How much did people pay for medical care in 1965?
By 1965, households paid out-of-pocket for 44% of all medical expenses. Health insurance paid for 24%. From 1966 to 1973, health care spending rose by an average of 11.9% a year. Medicare and Medicaid covered more people and allowed them to use more health care services.
How did health insurance companies control costs in the 1990s?
In the early 1990s, health insurance companies tried to control costs by spreading the use of HMOs once again. Congress then tried to control costs with the Balanced Budget Act in 1997. Instead, it forced many health care providers out of business.
How much did the Affordable Care Act increase in 2010?
Since 2010, when the Affordable Care Act was signed, health care costs rose by 4.3% a year. It achieved its goal of lowering the growth rate of health care spending. 27. In 2010, the government predicted that Medicare costs would rise by 20% in just five years.
How much did health care cost in 1960?
It equals 17.7% of gross domestic product. 1 In comparison, health care cost $27.2 billion in 1960, just 5% of GDP. 2 That translates to an annual health care cost of $11,172 per person in 2018 versus just $147 per person in 1960. Health care costs have risen faster than the median annual income.
Why are healthcare costs rising?
Seven reasons for rising healthcare costs. 1. Medical providers are paid for quantity, not quality. Most insurers—including Medicare—pay doctors, hospitals, and other medical providers under a fee-for-service system that reimburses for each test, procedure, or visit. That means the more services provided, the more fees are paid.
Why do organizations have incentives to purchase more expensive healthcare plans?
Organizations have an incentive to purchase more expensive healthcare plans because the amount employers pay toward coverage is tax deductible for the organization and tax exempt to the employee. In addition, low deductibles or small office co-payments can encourage overuse of care, driving both demand and cost. 5.
How much of healthcare costs are chronic?
A staggering 85% of healthcare costs in the U.S. are for the care of a chronic condition. What’s more, recent data from the Center for Disease Control and Prevention finds that over 40% of adults in the U.S. are either overweight or obese, which also leads to chronic illness and inflated medical spending.
Why do doctors prescribe unnecessary tests?
Fear of malpractice lawsuits. Oftentimes called “defensive medicine,” some doctors will prescribe unnecessary tests or treatment out of fear of facing a lawsuit. The cost for these treatments add up over time—a study done by JAMA estimates that an annual $46 billion are wasted in defensive medicine practices.
How many Americans get health insurance through their employer?
Data from the KFF finds that roughly 49% of the U.S. population gets their insurance through their employer. That means nearly half of Americans don’t actually make any true consumer decisions about the cost of their care or coverage, because it was already made for them by their employer.
How much did healthcare spending drop in 2020?
At the beginning of 2020, the outbreak of COVID-19 led health services spending to drop 8.6% in the second quarter of 2020 compared to the second quarter of 2019. This was largely due to social distancing and many Americans delaying or canceling their elective procedures.
How much did the US spend on health care in 1970?
have been on the rise. In 1970, health spending totaled $74.1 billion, but by 2019 that number had rocketed to $3.8 trillion.
