
How much does Medicare cost the government per person?
That's $11,582 per person. This figure accounted for 17.7% of gross domestic product (GDP) that year. If we look at each program individually, Medicare spending grew 6.7% to $799.4 billion in 2019,...
Is Medicare funded by state or government?
That means Medicare is primarily funded by taxpayers through general federal tax revenue, payroll tax revenue from the Medicare tax, and premiums paid by its beneficiaries. How Medicare is funded Funding for Medicare comes from the Medicare Trust Funds, which are two separate trust fund accounts held by the U.S. Treasury:
Is Medicare considered private or government?
Medicare is a Private–Public Partnership Most people think Medicare is a government program. That’s only partly true. While Congress created Medicare, and continues to develop Medicare coverage and appeal rules, decisions to pay claims are actually made by private companies. The government does not make those decisions.
Does the government pay for Medicaid?
While every state receives at least an FMAP of 50% (the federal government pays 50% of Medicaid costs, i.e. $1 for every $1 spent by the state), other states will receive higher percentages.
Is Medicare paid for by the federal government?
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is the federal agency that runs Medicare. The program is funded in part by Social Security and Medicare taxes you pay on your income, in part through premiums that people with Medicare pay, and in part by the federal budget.
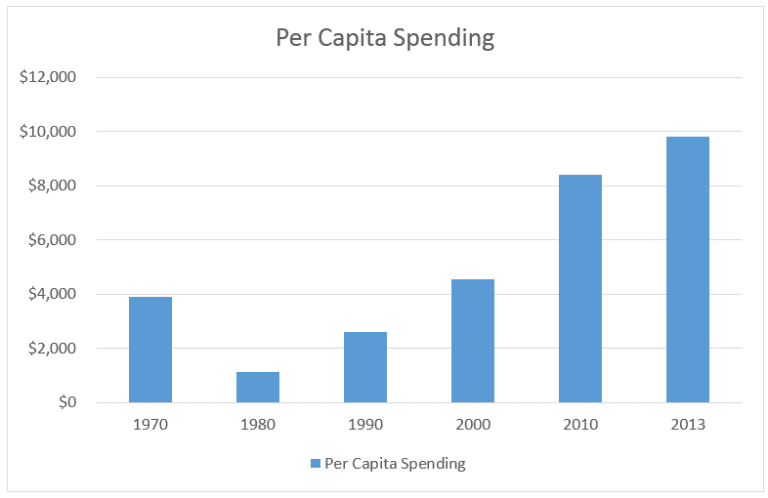
How much does the government spend per person on Medicare?
Historical NHE, 2020: NHE grew 9.7% to $4.1 trillion in 2020, or $12,530 per person, and accounted for 19.7% of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Medicare spending grew 3.5% to $829.5 billion in 2020, or 20 percent of total NHE.
Why does Medicare cost so much?
Medicare Part B covers doctor visits, and other outpatient services, such as lab tests and diagnostic screenings. CMS officials gave three reasons for the historically high premium increase: Rising prices to deliver health care to Medicare enrollees and increased use of the health care system.
Why are Medicare costs rising?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) announced the premium and other Medicare cost increases on November 12, 2021. The steep hike is attributed to increasing health care costs and uncertainty over Medicare's outlay for an expensive new drug that was recently approved to treat Alzheimer's disease.
How much did Medicare spend?
Medicare spending increased 6.4% to $750.2 billion, which is 21% of the total national health expenditure. The rise in Medicaid spending was 3% to $597.4 billion, which equates to 16% of total national health expenditure.
What is the agency that administers Medicare?
To grasp the magnitude of the government expenditure for Medicare benefits, following are 2018 statistics from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), which is the agency that administers Medicare:
What is the largest share of health spending?
The biggest share of total health spending was sponsored by the federal government (28.3%) and households (28.4%) while state and local governments accounted for 16.5%. For 2018 to 2027, the average yearly spending growth in Medicare (7.4%) is projected to exceed that of Medicaid and private health insurance.
Does Medicare pay payroll taxes?
Additionally, Medicare recipients have seen their share of payroll taxes for Medicare deducted from their paychecks throughout their working years.
How much does Medicare pay for outpatient therapy?
After your deductible is met, you typically pay 20% of the Medicare-approved amount for most doctor services (including most doctor services while you're a hospital inpatient), outpatient therapy, and Durable Medical Equipment (DME) Part C premium. The Part C monthly Premium varies by plan.
What is Medicare Advantage Plan?
A Medicare Advantage Plan (Part C) (like an HMO or PPO) or another Medicare health plan that offers Medicare prescription drug coverage. Creditable prescription drug coverage. In general, you'll have to pay this penalty for as long as you have a Medicare drug plan.
How much is coinsurance for days 91 and beyond?
Days 91 and beyond: $742 coinsurance per each "lifetime reserve day" after day 90 for each benefit period (up to 60 days over your lifetime). Beyond Lifetime reserve days : All costs. Note. You pay for private-duty nursing, a television, or a phone in your room.
How much is coinsurance for 61-90?
Days 61-90: $371 coinsurance per day of each benefit period. Days 91 and beyond: $742 coinsurance per each "lifetime reserve day" after day 90 for each benefit period (up to 60 days over your lifetime) Beyond lifetime reserve days: all costs. Part B premium.
What happens if you don't buy Medicare?
If you don't buy it when you're first eligible, your monthly premium may go up 10%. (You'll have to pay the higher premium for twice the number of years you could have had Part A, but didn't sign up.) Part A costs if you have Original Medicare. Note.
Do you pay more for outpatient services in a hospital?
For services that can also be provided in a doctor’s office, you may pay more for outpatient services you get in a hospital than you’ll pay for the same care in a doctor’s office . However, the hospital outpatient Copayment for the service is capped at the inpatient deductible amount.
Does Medicare cover room and board?
Medicare doesn't cover room and board when you get hospice care in your home or another facility where you live (like a nursing home). $1,484 Deductible for each Benefit period . Days 1–60: $0 Coinsurance for each benefit period. Days 61–90: $371 coinsurance per day of each benefit period.
Get help paying costs
Learn about programs that may help you save money on medical and drug costs.
Part A costs
Learn about Medicare Part A (hospital insurance) monthly premium and Part A late enrollment penalty.
Part B costs
How much Medicare Part B (medical insurance) costs, including Income Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA) and late enrollment penalty.
Costs for Medicare health plans
Learn about what factors contribute to how much you pay out-of-pocket when you have a Medicare Advantage Plan (Part C).
Compare procedure costs
Compare national average prices for procedures done in both ambulatory surgical centers and hospital outpatient departments.
Ways to pay Part A & Part B premiums
Learn more about how you can pay for your Medicare Part A and/or Medicare Part B premiums. Find out what to do if your payment is late.
Costs at a glance
Medicare Part A, Part B, Part C, and Part D costs for monthly premiums, deductibles, penalties, copayments, and coinsurance.
How much does Medicare pay for inpatient care?
Here’s how much you’ll pay for inpatient hospital care with Medicare Part A: Days 1-60 : $0 per day each benefit period, after paying your deductible. Days 61-90 : $371 per day each benefit period. Day 91 and beyond : $742 for each "lifetime reserve day" after benefit period. You get a total of 60 lifetime reserve days until you die.
What are the out-of-pocket expenses of Medicare?
Medicare costs. Beneficiaries face the same three major out-of-pocket expenses associated with any health insurance plan, which include: Premiums : The monthly payment just to have the plan. Deductible : The amount you must pay on your own before insurance starts to cover the costs.
How much does Medigap cost?
The average Medigap premiums can be anywhere from $20 to over $500. Essentially, you are paying an extra monthly cost to have more coverage later on if Original Medicare falls short. Deductibles range from $203 (the deductible you pay for Medicare Part B) to $6,220, if you opt for a high-deductible Medigap plan.
How much is the deductible for Medicare Part A?
The deductible for Medicare Part A is $1,484 per benefit period. A benefit period begins the day you’re admitted to a hospital and ends once you haven’t received in-hospital care for 60 days. The Medicare Part A coinsurance amount varies, depending on how long you’re in the hospital.
How much is Medicare Part B 2021?
The premium for Medicare Part B in 2021 is $148.50 per month. You may pay less if you’re receiving Social Security benefits. You also may pay more — up to $504.90 — depending on your income. The higher your income, the higher your premium. The deductible for Medicare Part B is $203 per year.
What is Medicare Part D?
Medicare Part D is prescription drug coverage. It is provided by Medicare-approved private insurers. Premium costs vary by plan, state and income, but the average basic monthly premium for a Medicare Part D plan in 2020 was about $43, according to data from the CMS compiled by Policygenius.
How much is the late enrollment penalty for Medicare?
The penalties are added to your monthly premium. Part A late enrollment penalty : 10% higher premium for twice the number of years you didn’t sign up. Part B late enrollment penalty : 10% higher premium for every 12 months you don’t sign up after becoming eligible, for as long as you have the plan.
How many people did Medicare cover in 2017?
programs offered by each state. In 2017, Medicare covered over 58 million people. Total expenditures in 2017 were $705.9 billion. This money comes from the Medicare Trust Funds.
What is the CMS?
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services ( CMS) is the federal agency that runs the Medicare Program. CMS is a branch of the. Department Of Health And Human Services (Hhs) The federal agency that oversees CMS, which administers programs for protecting the health of all Americans, including Medicare, the Marketplace, Medicaid, ...
What is Medicare Part B?
Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) Part B covers certain doctors' services, outpatient care, medical supplies, and preventive services. and. Medicare Drug Coverage (Part D) Optional benefits for prescription drugs available to all people with Medicare for an additional charge.
What is covered by Part A?
Part A covers inpatient hospital stays, care in a skilled nursing facility, hospice care, and some home health care. The health care items or services covered under a health insurance plan. Covered benefits and excluded services are defined in the health insurance plan's coverage documents.
Who pays payroll taxes?
Payroll taxes paid by most employees, employers, and people who are self-employed. Other sources, like these: Income taxes paid on Social Security benefits. Interest earned on the trust fund investments. Medicare Part A premiums from people who aren't eligible for premium-free Part A.
Does Medicare cover home health?
Medicare only covers home health care on a limited basis as ordered by your doctor. , and. hospice. A special way of caring for people who are terminally ill. Hospice care involves a team-oriented approach that addresses the medical, physical, social, emotional, and spiritual needs of the patient.
How is Medicare funded?
Medicare is financed by two trust funds: the Hospital Insurance (HI) trust fund and the Supplementary Medical Insurance (SMI) trust fund. The HI trust fund finances Medicare Part A and collects its income primarily through a payroll tax on U.S. workers and employers. The SMI trust fund, which supports both Part B and Part D, ...
What percentage of Medicare is from the federal government?
The federal government’s general fund has been playing a larger role in Medicare financing. In 2019, 43 percent of Medicare’s income came from the general fund, up from 25 percent in 1970. Looking forward, such revenues are projected to continue funding a major share of the Medicare program.
What percentage of Medicare is home health?
Medicare is a major player in our nation's health system and is the bedrock of care for millions of Americans. The program pays for about one-fifth of all healthcare spending in the United States, including 32 percent of all prescription drug costs and 39 percent of home health spending in the United States — which includes in-home care by skilled nurses to support recovery and self-sufficiency in the wake of illness or injury. 4
How much of Medicare was financed by payroll taxes in 1970?
In 1970, payroll taxes financed 65 percent of Medicare spending.
How is Medicare self-financed?
One of the biggest misconceptions about Medicare is that it is self-financed by current beneficiaries through premiums and by future beneficiaries through payroll taxes. In fact, payroll taxes and premiums together only cover about half of the program’s cost.
What are the benefits of Medicare?
Medicare is a federal program that provides health insurance to people who are age 65 and older, blind, or disabled. Medicare consists of four "parts": 1 Part A pays for hospital care; 2 Part B provides medical insurance for doctor’s fees and other medical services; 3 Part C is Medicare Advantage, which allows beneficiaries to enroll in private health plans to receive Part A and Part B Medicare benefits; 4 Part D covers prescription drugs.
How much did Medicare cost in 2019?
In 2019, it cost $644 billion — representing 14 percent of total federal spending. 1. Medicare has a large impact on the overall healthcare market: it finances about one-fifth of all health spending and about 40 percent of all home health spending. In 2019, Medicare provided benefits to 19 percent of the population. 2.
What is the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015?
The Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA) amends the cost plan competition requirements specified in section 1876 (h) (5) (C) of the Social Security Act (the Act).
What is cost contract?
A Cost Contract provides the full Medicare benefit package. Payment is based on the reasonable cost of providing services. Beneficiaries are not restricted to the HMO or CMP to receive covered Medicare services, i.e. services may be received through non-HMO/CMP sources and are reimbursed by Medicare intermediaries and carriers.
When do transition plans have to notify CMS?
Plans are responsible for following all contracting, enrollment, and other transition guidance released by CMS. In its initial, December 7, 2015 guidance, CMS specified that transitioning plans must notify CMS by January 31 of the year preceding the last cost contract year. In its May 17, 2017 guidance, CMS revised this date to permit ...
How is Medicare funded?
How Medicare Is Funded. Medicare is funded by two trust funds that can only be used for Medicare. The hospital insurance trust fund is funded by payroll taxes paid by employees, employers, and the self-employed. These funds are used to pay for Medicare Part A benefits. 11 .
How much did Medicare spend in 2019?
If we look at each program individually, Medicare spending grew 6.7% to $799.4 billion in 2019, which is 21% of total NHE, while Medicaid spending grew 2.9% to $613.5 billion in 2019, which is 16% of total NHE. 3 . The CMS projects that healthcare spending is estimated to grow by 5.4% each year between 2019 and 2028.
What is CMS and Medicaid?
CMS works alongside the Department of Labor (DOL) and the U.S. Treasury to enact insurance reform. The Social Security Administration (SSA) determines eligibility and coverage levels. Medicaid, on the other hand, is administered at the state level.
How is Medicare supplemental insurance fund funded?
Medicare's supplementary medical insurance trust fund is funded by Congress, premiums from people enrolled in Medicare, and other avenues, such as investment income from the trust fund. These funds pay for Medicare Part B benefits, Part D benefits, and program administration expenses.
What is Medicare contribution tax?
It is known as the unearned income Medicare contribution tax. Taxpayers in this category owe an additional 3.8% Medicare tax on all taxable interest, dividends, capital gains, annuities, royalties, and rental properties that are paid outside of individual retirement accounts or employer-sponsored retirement plans .
What is the Medicare tax rate for 2013?
On Jan. 1, 2013, the ACA also imposed an additional Medicare tax of 0.9% on all income above a certain level for high-income taxpayers. Single filers have to pay this additional amount on all earned income they receive above $200,000 and married taxpayers filing jointly owe it on earned income in excess of $250,000.
What is Medicare 2021?
Updated Jun 29, 2021. Medicare, and its means-tested sibling Medicaid, are the only forms of health coverage available to millions of Americans today. They represent some of the most successful social insurance programs ever, serving tens of millions of people including the elderly, younger beneficiaries with disabilities, ...
How many people are covered by Medicare?
Today, Medicare provides this coverage for over 64 million beneficiaries, most of whom are 65 years and older.
What percentage of Medicare deductible is paid?
After your deductible is paid, you pay a coinsurance of 20 percent of the Medicare-approved amount for most services either as an outpatient, inpatient, for outpatient therapy, and durable medical equipment.
How many parts of Medicare are there?
The four parts of Medicare have their own premiums, deductibles, copays, and/or coinsurance costs. Here is a look at each part separately to see what your costs may be at age 65.
How much does Medicare Part B cost?
Medicare Part B has a monthly premium. The amount you pay depends on your yearly income. Most people pay the standard premium amount of $144.60 (as of 2020) because their individual income is less than $87,000.00, or their joint income is less than $174,000.00 per year.
How much is Part A deductible for 2020?
If you purchase Part A, you may have to also purchase Part B and pay the premiums for both parts. As of 2020, your Part A deductible for hospital stays is $1408.00 for each benefit period. After you meet your Part A deductible, your coinsurance costs are as follows: • Days 1 – 60: $0 coinsurance per benefit period.
