
What happened to Medicare in the 1980s?
These developments produced two consequences for Medicare. First, driven by budget deficit politics, the 1980s saw the adoption of major new cost containment policies for Medicare payments to doctors and hospitals.
How did Medicare reform get passed in the House?
On June 17 the House Ways and Means Committee approved, by a margin of 25 to 15, its Medicare reform proposal, which prompted “an impassioned partisan debate over the proper roles of government and private industry in delivering health care to the elderly. …
What led to Medicare cost containment in the 1980s?
First, driven by budget deficit politics, the 1980s saw the adoption of major new cost containment policies for Medicare payments to doctors and hospitals. Those policies had bipartisan support from Republican presidents (first Reagan and later George H. W. Bush) and Democratic Congresses seeking budgetary savings.
What were the main proposals of the 1999 Medicare reform bill?
The main proposals in 1999 called for the broad restructuring and privatization of the program, thus building on the Medicare+Choice approach.

What payment method did Congress institute in 1983 as a way to control increases in Medicare spending?
The Social Security Amendments of 1983 (Public Law 98-21), passed by Congress and enacted by the President in the spring of that year, established the statutory framework for the Medicare hospital prospective payment system (PPS).
What is Medicare payment reform?
Medicare payment reform aims to increase quality health care for Medicare beneficiaries and improve the program's financial sustainability. This briefing provided background on Medicare payment reform, including new value-based models that have evolved over the past decade.
What did the Medicare Act change?
Nixon signed into the law the first major change to Medicare. The legislation expanded coverage to include individuals under the age of 65 with long-term disabilities and individuals with end-stage renal disease (ERSD).
What was passed by Congress in 1965 designed to assist in the payment of medical bills for the elderly?
On July 30, 1965, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed the Medicare and Medicaid Act, also known as the Social Security Amendments of 1965, into law. It established Medicare, a health insurance program for the elderly, and Medicaid, a health insurance program for people with limited income.
How can health care payment policies be reformed to improve quality?
Quality could be rewarded by using direct payment mechanisms or by redirecting volume to health plans and providers recognized for providing high-quality care by offering stronger incentives for people to seek out better quality care (e.g., adjustments to out-of-pocket costs).
What did the Medicare program provide?
The Medicare program, providing hospital and medical insurance for Americans age 65 or older, was signed into law as an amendment to the Social Security Act of 1935. Some 19 million people enrolled in Medicare when it went into effect in 1966.
When was Medicare Part D enacted?
2006The MMA also expanded Medicare to include an optional prescription drug benefit, “Part D,” which went into effect in 2006.
Which state health care reform law most influenced the approach taken by the Affordable Care Act?
California provides one example of state-influenced improvements. California expanded eligibility for Medicaid, established its own marketplace, and adopted state-specific policies and operational approaches.
Why was 1965 such an important year for policy issues?
On July 30, 1965, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed the Social Security Amendments of 1965 into law. With his signature he created Medicare and Medicaid, which became two of America's most enduring social programs. The signing ceremony took place in Independence, Missouri, in the presence of former President Harry S.
Why was Medicare passed?
The Medicare program was signed into law in 1965 to provide health coverage and increased financial security for older Americans who were not well served in an insurance market characterized by employment-linked group coverage.
What did the Medicare program provide quizlet?
Medicare: A federal program established in 1965 to provide hospital and medical services to older people through the Social Security system.
How much did Medicare spend in 1985?
Between 1975 and 1985, annual Medicare spending per beneficiary rose from $472 to $1,579 —a growth rate of 12.8 percent per year, or 5.3 percent when adjusted for economywide inflation. 6.
When did Medicare Advantage start?
In 1997 and again in 2003, Congress expanded the number and scope of private plans available through this program, now called Medicare Advantage. Medicare Advantage plans receive a monthly payment for each Medicare beneficiary enrolled in the plan, based on the location, age, and health status of the beneficiary.
What is Medicare Shared Savings Program?
The ACA created the Medicare Shared Savings Program (MSSP) for accountable care organizations ( ACOs), which are groups of providers who accept joint responsibility for the quality and cost of the Medicare patients they treat and can share in the savings they generate as compared with a cost target. 21 The ACA also created the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation (CMMI) to develop and test value-based alternative payment methods. 22,23 Many of those initiatives represent more far-reaching reforms, and put providers at financial risk for a portion or all of the cost of providing Medicare services. Among the most prominent activities being conducted by the CMMI are several aimed at transforming primary care, and several of its models involve a bundled payment for specified sets of hospital and/or postacute care related to specific procedures or conditions. 24
What is Medicare payment policy?
Medicare payment policy has evolved from the cost- and charge-reimbursement approach that was the predominant model when the program was enacted to the establishment of prospective payment systems in the 1980s and 1990s and, more recently, to movement toward value-based payment. 1 The enactment of the Affordable Care Act of 2010 (ACA) and the recent announcement of value-based payment goals for Medicare, along with the enactment of the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA), have accelerated that movement and provided Medicare with the means to accomplish the goals of better health care, smarter spending, and a healthier population. 2,3 The first two papers in this series focused on Medicare’s accomplishments over its first 50 years, the impact of the ACA on the program, and the challenges that remain; this paper focuses on the evolution of Medicare payment policy and the potential of payment reform to help address those challenges. 4,5
How does the Affordable Care Act help Medicare?
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has provided the Medicare program with an array of tools to improve the quality of care that beneficiaries receive and to increase the efficiency with which that care is provided. Notably, the ACA has created the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation, which is developing and testing promising new models to improve the quality of care provided to Medicare beneficiaries while reducing spending. These new models are part of an effort by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to increase the proportion of traditional Medicare payments tied to quality or value to 85 percent by 2016 and 90 percent by 2018. This issue brief, one in a series on Medicare’s past, present, and future, explores the evolution of Medicare payment policy, the potential of value-based payment to improve care for beneficiaries and achieve savings, and strategies for accelerating its adoption.
What is the HHS Secretary's authority?
One powerful tool that the HHS secretary possesses is the authority , granted by the ACA, to adopt innovations found to save money and improve quality for use throughout the Medicare program. In addition to continuing to test how well different incentives improve value, HHS is focused on improving the way care is delivered through learning networks such as the recently announced Health Care Payment Learning and Action Network. 40 It also aims to increase the availability of information to guide decision-making, by increasing the use of health information technology, enhancing transparency, and generating information through the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute that can guide care decisions.
What would be a major step toward improving the financial sustainability of the Medicare program in particular?
Reducing or eliminating avoidable, unnecessary, and ineffective care, and redeploying those savings to provide better financial protection and lower federal outlays, would be a major step toward improving the financial sustainability of the Medicare program in particular, and the U.S. health system in general.
When did Medicare start?
Amends title XVIII of the Social Security Act to require the Secretary of Health and Human Services to promulgate the monthly actuarial rates and premiums for Medicare enrollees in September of each year, beginning in 1983.
What are the 1983 Social Security Amendments?
Social Security Amendments of 1983 - Title I: Provisions Affecting the Financing of the Social Security System - Part A: Coverage - Amends title II (Old Age, Survivors and Disability Insurance) of the Social Security Act and the Internal Revenue Code to provide mandatory coverage under the Old Age, Survivors and Disability Insurance program as of January 1, 1984, for: (1) all Federal employees hired on or after January 1, 1984; (2) the President; (3) the Vice President; (4) all elected officials and political appointees ; (5) judges; (6) Members of Congress; and (7) all legislative branch employees who are not participating in the Civil Service Retirement System as of December 31, 1983.
What is modified adjusted gross income?
Defines "modified adjusted gross income" as adjusted gross income: (1) determined without regard to this part or to certain deductions and exemptions; and (2) increased by any tax-exempt interest received by the taxpayer during the taxable year.
What is the repeal of the child's insurance?
Repeals the requirement that an individual's wife's, child's, widow's, mother's, or parent's insurance benefit entitlement be terminated if such individual marries a person entitled to child's insurance benefits and such person ceases to be so entitled.
When did the OASDI increase?
Revises the OASDI tax rates on employees and employers so as to: (1) increase the tax rate for 1984; (2) keep the current tax rate for 1985 through 1987; and (3) increase the tax rate for 1988-1989.
When was the Social Security Act amended?
Amends title II of the Social Security Act to revise the allocations of wages and self-employment income from the Treasury to the Federal Disability Insurance Trust Fund, beginning in 1983.
What is the title IV of the Social Security Act?
Title IV: Supplemental Security Income Benefits - Amends title XVI (Supplemental Security Income) of the Social Security Act to provide for a $20 increase in the Federal SSI benefit standard for an individual and a $30 increase in the Federal SSI benefit standard for a married couple.
When did Medicare start paying the $30 enrollment fee?
The voluntary interim program would begin in mid-2004. Medicare would pay the $30 enrollment fee and provide a $600 credit for those beneficiaries with a household income below 135 percent of poverty (in 2003, $12,123 for an individual and $16,362 for a couple) who do not qualify for Medicaid or have other coverage.
How much did Medicare cut in 1997?
Nonetheless, reducing the budget deficit remained a high political priority, and two years later, the Balanced Budget Act of 1997 (Balanced Budget Act) cut projected Medicare spending by $115 billion over five years and by $385 billion over ten years (Etheredge 1998; Oberlander 2003, 177–83).
How many Medicare beneficiaries will have private prescription coverage?
At that time, more than 40 million beneficiaries will have the following options: (1) they may keep any private prescription drug coverage they currently have; (2) they may enroll in a new, freestanding prescription drug plan; or (3) they may obtain drug coverage by enrolling in a Medicare managed care plan.
How much does Medicare pay for Part D?
The standard Part D benefits would have an estimated initial premium of $35 per month and a $250 annual deductible. Medicare would pay 75 percent of annual expenses between $250 and $2,250 for approved prescription drugs, nothing for expenses between $2,250 and $5,100, and 95 percent of expenses above $5,100.
What was the Task Force on Prescription Drugs?
Department of Health, Education and Welfare (HEW; later renamed Health and Human Services) and the White House.
What was the Byrnes bill?
The counterproposal offered by Republicans, the Byrnes bill, called for voluntary enrollment in a health insurance program financed by premiums paid by the beneficiaries and subsidized by general revenues. It had more benefits, including physician services and prescription drugs.
How long have seniors waited for Medicare?
Seniors have waited 38 years for this prescription drug benefit to be added to the Medicare program. Today they are just moments away from the drug coverage they desperately need and deserve” (Pear and Hulse 2003). In fact, for many Medicare beneficiaries, the benefits of the new law are not so immediate or valuable.
When did Medicare become a bipartisan program?
In 1988, the Reagan administration and Congress did agree on bipartisan legislation that produced the largest expansion in Medicare benefits since the program’s enactment (though the Medicare Catastrophic Coverage Act was repealed in 1989).
Who proposed Medicare Part C?
Congressman Pete Stark, for example, proposed a Medicare Part C to cover the uninsured. But the Clinton administration itself did not embrace such ideas, and Medicare’s primary role in the Clinton plan was to serve as a piggy bank to help fund the costs of expanded coverage for the uninsured.
What did the Clinton administration and Congress do to regulate the health insurance market and expand coverage?
Advertisement: The Clinton administration and Congress did pursue incremental measures to regulate the health insurance market and expand coverage, including enacting the State Children’s Health Insurance Program (SCHIP) in 1996.
What was the ACA model like?
Advertisement: Instead, the ACA’s health reform model resembled what was previously advanced by the Nixon and Clinton administrations, with a reliance on private plans, consumer choice, means-tested subsidies, and employer financing. (Obamacare, notably, did call for a substantial expansion of Medicaid eligibility.)
What was the main policy of the 1980s?
First, driven by budget deficit politics, the 1980s saw the adoption of major new cost containment policies for Medicare payments to doctors and hospitals. Those policies had bipartisan support from Republican presidents (first Reagan and later George H. W. Bush) and Democratic Congresses seeking budgetary savings.
What was Reagan's goal in 1980?
The Reagan administration sought to cut taxes, privatize the welfare state, and constrain federal expenditures on domestic programs, all while increasing military spending.
What was the political agenda after the Clinton Plan?
Following the 1994 demise of the Clinton plan, the national political agenda turned away from universal health insurance. After winning majority control of both houses of Congress for the first time in 40 years, in 1995 Republicans proposed substantial overhauls to Medicare and Medicaid.
What was the Medicare catastrophe coverage act of 1988?
Medicare Catastrophic Coverage Act of 1988. Passed new supplemental premium tax on all persons eligible for Medicare. Premium rate was 15 percent of individual income tax liability in excess of $150, increased to 28 percent in 1993. Premium limited to $800 in 1989, raised to $1,050 in 1993, with future premium cap dependent on medical care costs ...
What was the Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act of 1986?
Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act of 1986. Enacted excise tax of 8.2 cents per barrel on domestic crude oil and 11.7 cents per barrel on imported petroleum products. Enacted new broad-based tax on all corporations equal to 0.12 percent of alternative minimum taxable income in excess of $2 million.
When did Medicare start?
But it wasn’t until after 1966 – after legislation was signed by President Lyndon B Johnson in 1965 – that Americans started receiving Medicare health coverage when Medicare’s hospital and medical insurance benefits first took effect. Harry Truman and his wife, Bess, were the first two Medicare beneficiaries.
When did Medicare start limiting out-of-pocket expenses?
In 1988 , Congress passed the Medicare Catastrophic Coverage Act, adding a true limit to the Medicare’s total out-of-pocket expenses for Part A and Part B, along with a limited prescription drug benefit.
How much was Medicare in 1965?
In 1965, the budget for Medicare was around $10 billion. In 1966, Medicare’s coverage took effect, as Americans age 65 and older were enrolled in Part A and millions of other seniors signed up for Part B. Nineteen million individuals signed up for Medicare during its first year. The ’70s.
How much will Medicare be spent in 2028?
Medicare spending projections fluctuate with time, but as of 2018, Medicare spending was expected to account for 18 percent of total federal spending by 2028, up from 15 percent in 2017. And the Medicare Part A trust fund was expected to be depleted by 2026.
What is the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act?
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010 includes a long list of reform provisions intended to contain Medicare costs while increasing revenue, improving and streamlining its delivery systems, and even increasing services to the program.
How many people will have Medicare in 2021?
As of 2021, 63.1 million Americans had coverage through Medicare. Medicare spending is expected to account for 18% of total federal spending by 2028. Medicare per-capita spending grew at a slower pace between 2010 and 2017. Discussion about a national health insurance system for Americans goes all the way back to the days ...
What was Truman's plan for Medicare?
The plan Truman envisioned would provide health coverage to individuals, paying for such typical expenses as doctor visits, hospital visits, ...
What was the health care reform bill of 1993?
The 1993 Clinton health care plan included mandatory enrollment in a health insurance plan, subsidies to guarantee affordability across all income ranges, and the establishment of health alliances in each state. Every citizen or permanent resident would thus be guaranteed medical care. The bill faced withering criticism by Republicans, led by William Kristol, who communicated his concern that a Democratic health care bill would "revive the reputation of... Democrats as the generous protector of middle-class interests. And it will at the same time strike a punishing blow against Republican claims to defend the middle class by restraining government." The bill was not enacted into law.
When did the health care bill end?
Roosevelt ended up removing the health care provisions from the bill in 1935. Fear of organized medicine's opposition to universal health care became standard for decades after the 1930s. During this time, individual hospitals began offering their own insurance programs, the first of which became Blue Cross.
What was the first prepaid medical plan in the United States?
This was the first prepaid medical care plan in the United States. The monies were used for the care of sick seamen and the building of seamen's hospitals. This act created the Marine Hospital Service under the Department of the Treasury.
How did progressivism affect the 20th century?
In the first 10–15 years of the 20th century Progressivism was influencing both Europe and the United States. Many European countries were passing the first social welfare acts and forming the basis for compulsory government-run or voluntary subsidized health care programs.
What was the first public health law?
On July 16, 1798, President John Adams signed the first Federal public health law, " An act for the relief of sick and disabled Seamen ." This assessed every seaman at American ports 20 cents a month. This was the first prepaid medical care plan in the United States. The monies were used for the care of sick seamen and the building of seamen's hospitals. This act created the Marine Hospital Service under the Department of the Treasury. In 1802 Marine Hospitals were operating in Boston; Newport; Norfolk; and Charleston, S.C. and medical services were contracted in other ports.
When was the first national health insurance bill introduced?
Congress. In February 1970 , Representative Martha Griffiths ( D - MI) introduced a national health insurance bill—without any cost sharing —developed with the AFL–CIO. In April 1970, Senator Jacob Javits ( R - NY) introduced a bill to extend Medicare to all—retaining existing Medicare cost sharing and coverage limits—developed after consultation with Governor Nelson Rockefeller ( R - NY) and former Johnson administration HEW Secretary Wilbur Cohen. In August 1970, Senator Ted Kennedy ( D - MA) introduced a bipartisan national health insurance bill—without any cost sharing—developed with the Committee for National Health Insurance founded by United Auto Workers (UAW) president Walter Reuther, with a corresponding bill introduced in the House the following month by Representative James Corman ( D - CA ). In September 1970, the Senate Labor and Public Welfare Committee held the first congressional hearings in twenty years on national health insurance.
When did the Health Security Express start?
The "Health Security Express," a cross-country tour by multiple buses carrying supporters of President Clinton's national health care reform, started at the end of July 1994.
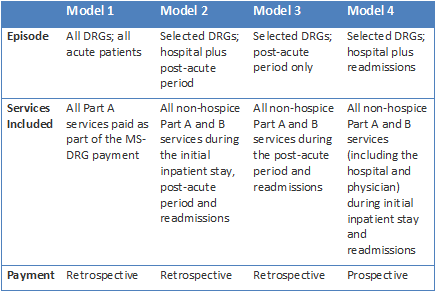
Background
Evolution of Medicare Payment Policy
- When Medicare was first established, it adopted the payment methods used by Blue Cross and Blue Shield plans at the time. Hospitals were paid on the basis of their own costs, and physicians were paid on the basis of the fees they charged. These payment systems provided no incentive to control costs—in effect rewarding higher hospital costs and physician fees—and did not take int…
Moving The Focus of Payment Policy from Volume to Value
- Medicare has made significant improvements in the original payment methods modeled on the private insurance payment practices of the 1960s, and recent actions by Congress and the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) have focused on accelerating that change. The ACA includes an array of provisions that are laying the foundation for fundamental Medicare pay…
Strategies For Expanding Value-Based Payment
- One powerful tool that the HHS secretary possesses is the authority, granted by the ACA, to adopt innovations found to save money and improve quality for use throughout the Medicare program. In addition to continuing to test how well different incentives improve value, HHS is focused on improving the way care is delivered through learning networks such as the recently announced …