Full Answer
How does CMS conduct annual analyses of its hospital outcome measures?
In addition to calculating the above measures for public reporting, CMS also conducts annual analyses of its hospital outcome measures to provide greater insight into measure trends and variation. These additional analyses use calculations reported annually on Hospital Compare and are compiled in the Chartbook as described below.
What is the EHR Incentive Program?
The EHR Incentive Program asks providers to use the capabilities of their EHRs to achieve benchmarks that can lead to improved patient care. It’s important to know that the EHR Incentive Program is NOT a reimbursement program for purchasing or replacing an EHR. Providers have to meet speciic requirements in order to receive incentive payments.
What is the value of an incentive payment?
The value of an incentive payment cannot exceed $20 per qualifying service. The ACO may indicate that it will adjust the amount of the incentive payment annually by the percentage increase in the consumer price index for all urban consumers.
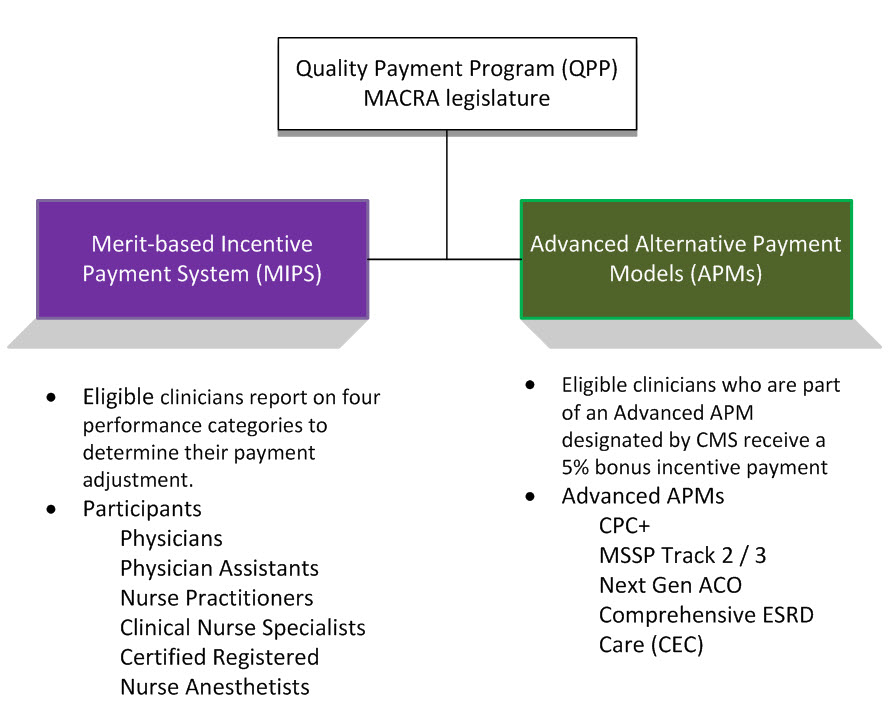
What is the merit based incentive payment system (MIPS)?
Medicare's legacy quality reporting programs were consolidated and streamlined into the Merit-based Incentive Payment System, referred to as "MIPS." This consolidation reduced the aggregate level of financial penalties physicians otherwise faced, and it also provides a greater potential for bonus payments.

What are the quality measures for MIPS?
Traditional MIPS, established in the first year of the Quality Payment Program, is the original framework available to MIPS eligible clinicians for collecting and reporting data to MIPS. Your performance is measured across 4 areas – quality, improvement activities, Promoting Interoperability, and cost.
What are the 4 main goals of the meaningful use program?
They were: Improve quality, safety, efficiency, and reduce health disparities.
How are CQMs measured?
What is a Clinical Quality Measure (CQM)? CQMs can be measures of processes, experiences and/or outcomes of patient care, observations or treatment that relate to one or more quality aims for health care such as effective, safe, efficient, patient-centered, equitable, and timely care.
What are the CMS quality measures?
These goals include: effective, safe, efficient, patient-centered, equitable, and timely care.
What are the meaningful use measures?
1) The use of certified EHRs in a meaningful manner, such as e-prescribing, 2) The use of certified EHR technology for electronic exchange of health information to improve quality of health care, and. 3) The use of certified EHR technology to submit clinical quality and other measures for monitoring.
What are the 5 pillars support of health outcomes policy priorities were important in developing the concept of meaningful use?
According to the CDC, there are five "pillars" of health outcomes that support the concept of Meaningful Use: Improving quality, safety, and efficiency while reducing health disparities. Engaging patients and families. Improving care coordination.
What is an outcome measure in healthcare?
Outcome measures reflect the impact of the health care service or intervention on the health status of patients. For example: The percentage of patients who died as a result of surgery (surgical mortality rates). The rate of surgical complications or hospital-acquired infections.
What are process measures and outcome measures?
Process measures can determine the volume at which cost-effective preventive services are performed, while outcome measures give a payer insight into the relationship between preventive services and healthier outcomes.
What are the eight measurements for the patient and caregiver centered experience?
Research by the Picker Institute has delineated 8 dimensions of patient-centered care, including: 1) respect for the patient's values, preferences, and expressed needs; 2) information and education; 3) access to care; 4) emotional support to relieve fear and anxiety; 5) involvement of family and friends; 6) continuity ...
What are the 4 core measures?
These measures specify best clinical practice in four areas: Heart Failure, Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI, i.e. Heart Attack), Pneumonia, and Surgical Site Infection prevention. Health organizations' performance on the Core Measures is assessed by examining documentation in patients' medical records.
What is an outcome measure in MIPS?
MIPS quality measures are tools that help us measure or quantify health care processes, outcomes, and patient perceptions that go with being able to give high quality health care. MIPS quality measures help link outcomes that relate to one or more of the following CMS quality goals for health care: •
What are CMS core measures?
Core measures are national standards of care and treatment processes for common conditions. These processes are proven to reduce complications and lead to better patient outcomes. Core measure compliance shows how often a hospital provides each recommended treatment for certain medical conditions.
What is MIPS in Medicare?
Medicare's legacy quality reporting programs were consolidated and streamlined into the Merit-based Incentive Payment System, referred to as "MIPS." This consolidation reduced the aggregate level of financial penalties physicians otherwise faced, and it also provides a greater potential for bonus payments.
Does Medicaid include CDS?
However, the Medicaid Meaningful Use program continues to include CPO E and CDS measures. While CPOE and CDS functionality will still be included in EHRs, CMS will no longer require a certain number of orders, that a physician enter the orders, and that physicians implement a certain number of CDS tools.
Is the severity of penalties and size of potential bonuses under prior law unknown?
* The severity of penalties and size of potential bonuses under prior law is "unknown" because annual regulations pertaining to the VBM were no longer issued following MACRA'S passage. However, Medicare law on the VBM included no ceiling or floors; and in the first three years it was applied, CMS doubled the size of the potential cuts each year. Incentives for the MU and PQRS Medicare programs were no longer available in 2017.
Does Medicare have CPOE?
Following years of advocacy by the AMA, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) has removed the computerized physician order entry (CPOE) and clinical decision support (CDS) measures from the Medicare MU program and the ACI component of the Quality Payment Program (QPP). However, the Medicaid Meaningful Use program continues to include CPOE and CDS measures.
What is the Promoting Interoperability Program?
Beginning in 2011, the Promoting Interoperability (formerly the Medicare and Medicaid EHR Incentive Programs) were developed to encourage eligible professionals (EPs) and eligible hospitals and critical access hospitals (CAHs) to adopt, implement, upgrade (AIU), ...
How many measures must an EP report?
If no outcome measures are relevant, EPs must report on at least one high-priority measure. If there are no outcome or high priority measures relevant to an EP’s scope of practice, they may report on any six relevant measures.
What level of Medicare is eligible for incentive payments?
Any beneficiary assigned to an ACO that is participating under Levels C, D, or E of the BASIC track, or the ENHANCED track is eligible to receive an incentive payment under that ACO’s CMS-approved BIP. If a beneficiary opts out of Medicare claims data sharing, they are still eligible to receive incentive payments. Please note that even if a beneficiary opts out of Medicare claims data sharing, Medicare will still use their information for some purposes, and the ACO would be able to identify this beneficiary because they would still appear on the assignment lists and Claim and Claim Line Feed (CCLF) files.
How long does an ACO have to maintain a BIP?
Each year during Yearly ACO Signing Event, an ACO establishing a BIP and an ACO that seeks to continue operating its BIP beyond the initial 12-month term must certify that it intends to continue operating its BIP for the entirety of the relevant performance year and that its BIP continues to meet all applicable requirements.
When does an ACO need to establish a BIP?
An ACO that is approved to establish a BIP must operate its CMS-approved BIP for an initial period of 12 months beginning on January 1st of the relevant performance year.
Can an ACO terminate a BIP?
CMS may require an ACO to terminate its BIP at any time for failure to comply with the requirements of the Shared Savings Program or for any of the grounds for ACO termination set forth in 42 CFR § 425.218(b). There is no administrative or judicial review of CMS’ decision to terminate an ACO’s BIP. Any ACO that wishes to reestablish a BIP after termination must reapply in accordance with 42 CFR § 425.304(c)(2). The ACO would need to wait until the application period commences and would need to follow the same procedures as an ACO that is establishing a BIP for the first time.
Can a fee for service beneficiary receive an incentive payment under a BIP?
No. Per 42 CFR § 425.304(c)(3)(ii), a fee-for- service (FFS ) beneficiar y is eligible to receive an incentive payment under a BIP if the beneficiary is assigned to the ACO through either preliminary prospective assignment, as described in
Does an ACO have to pay BIP?
A qualifying service is defined as a primary care service (as defined in 42 CFR § 425.20) with respect to which coinsurance applies under Part B. An ACO cannot limit its BIP to a subset of qualifying services. In addition, CMS encourages ACOs to review the regulatory language under
Can ACOs make cash incentives?
No. ACOs are prohibited from distributing incentive payments to beneficiaries in the form of cash. Cash incentive payments are inherently difficult to track for reporting and auditing purposes since they are not necessarily tied to documents providing written evidence that a cash incentive payment was furnished to an eligible beneficiary for a qualifying service. CMS cannot trace a cash incentive to ensure that an ACO has uniformly furnished incentive payments to all eligible beneficiaries and has not made excessive payments or otherwise used incentive payments to improperly attract “healthier” beneficiaries while disadvantaging beneficiaries who are less healthy or who have a disability. Incentive payments must be in the form of a cash equivalent, which includes instruments convertible to cash or widely accepted on the same basis as cash, such as checks and debit cards.
