
"Cost Share Protection" (CSP) is provided through Medicare Savings Programs (MSPs) and state Medicaid programs. Basically, the carrier pays some, and Medicaid pays some or all of the beneficiary's portion. CSP applies ONLY to Medicare and/or Medicaid covered services.
Full Answer
What are my Medicare cost sharing obligations?
Sep 18, 2021 · Medicare’s cost-sharing is the out-of-pocket costs Out-of-Pocket Costs for Medicare are the remaining costs that are not covered by the beneficiary's health insurance plan. These costs can come from the beneficiary's monthly premiums, deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments. that beneficiaries pay to receive medical services or supplies, like a doctor’s …
What is Medicare Part a cost sharing?
Jan 19, 2012 · QMBs as well as other people with Medicare and Medicaid are also protected from any charges above the Medicare-approved amount, that is, charges beyond cost-sharing. (For example, the doctor charges $125, Medicare approves $100 and pays $80, the cost-sharing is $20, but even when that is paid, the doctor has not received the full $125 that she or he billed.
What is the average cost of Medicare per month?
MEDICARE COST-SHARING BENEFITS Medicaid may pay the following for Medicaid recipients who are entitled to Medicare: • Medicare Part A premiums. • Medicare Part B premiums. • Part of Medicare Part B premiums. • Medicare deductibles and coinsurances. The type of Medicare cost-sharing benefits depends on the type of Medicaid eligibility.
What is the monthly premium for Medicare Part B?
Feb 22, 2008 · States have the option to charge premiums and to establish out of pocket spending (cost sharing) requirements for Medicaid enrollees. Out of pocket costs may include copayments, coinsurance, deductibles, and other similar charges. Maximum out of pocket costs are limited, but states can impose higher charges for targeted groups of somewhat higher ...
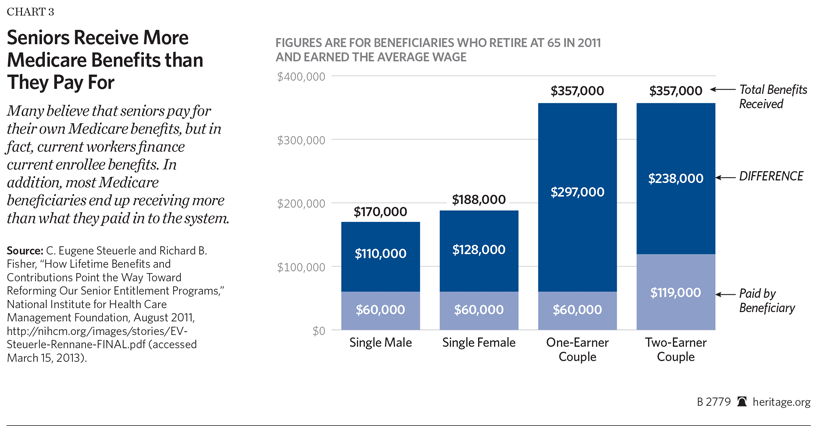
What is the purpose of cost sharing in Medicare?
The share of costs covered by your insurance that you pay out of your own pocket. This term generally includes deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments, or similar charges, but it doesn't include premiums, balance billing amounts for non-network providers, or the cost of non-covered services.
What is a Medicare cost share plan?
Medicare Cost Plans are a type of Medicare health plan available in certain, limited areas of the country. • In general, you can join even if you only have Part B. • If you have Part A and Part B and go to a non-network provider, Original Medicare covers the services. You'll pay the Part A and Part B.
What is Medicare cost protection?
Medicare Part B Annual Deductible and Share of Cost: This program will pay your Medicare Part B deductible which is $233 in 2022. It will also pay your share (20%) of the cost of services when you receive services from a Medicare provider.
What are the benefits of cost sharing?
Plans with lower cost-sharing (ie, lower deductibles, copayments, and total out-of-pocket costs when you need medical care) tend to have higher premiums, whereas plans with higher cost-sharing tend to have lower premiums. Cost-sharing reduces premiums (because it saves your health insurance company money) in two ways.Apr 10, 2021
What is the Irmaa for 2021?
C. IRMAA tables of Medicare Part B premium year for three previous yearsIRMAA Table2021More than $111,000 but less than or equal to $138,000$297.00More than $138,000 but less than or equal to $165,000$386.10More than $165,000 but less than $500,000$475.20More than $500,000$504.9012 more rows•Dec 6, 2021
How is share price calculated?
To do this, divide the total cost share obligation by 1.52. (22,280 / 1.52 = 14,658 TDC)....Example:Cost CategoryAmount (example)Total Project Costs111,400X .20Cost share (20% Match on Total Project)22,280Request from Sponsor (80% of Total Project)89,1207 more rows
Do Medicare beneficiaries have cost sharing?
The Qualified Medicare Beneficiary (QMB) program provides Medicare coverage of Part A and Part B premiums and cost sharing to low-income Medicare beneficiaries.Dec 1, 2021
What is not covered by Medicare?
Medicare does not cover: medical exams required when applying for a job, life insurance, superannuation, memberships, or government bodies. most dental examinations and treatment. most physiotherapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, eye therapy, chiropractic services, podiatry, acupuncture and psychology services.Jun 24, 2021
Which of the following refers to a cost sharing amount with the insurance company?
All health insurance requires consumers to pay some of the cost of covered health care services. This is called "cost sharing" or "out-of-pocket" costs. Cost sharing varies with different types of health plans, but most will have a copayment, coinsurance or deductible amount.Sep 28, 2018
What is an example of cost sharing?
A term used to describe the practice of dividing the cost of healthcare services between the patient and the insurance plan. For example, if a plan pays 80% of the cost of a service, then the patient pays the remaining 20% of the cost.
Is cost share the same as copay?
What is a co-payment or co-pay? A co-‐payment (also called a “co-‐pay”) is a form of cost-‐sharing. It is a set amount of money you will pay for a service ($3, $15, $40 etc). The amount is the same no matter how much the doctor or hospital charges for the service.
What are the 3 main types of cost sharing in private insurance and how do they work?
Cost sharing lowers costs for everyone. There are three basic types of cost sharing everyone needs to understand: deductibles, copayments and coinsurance. Here's your guide to understanding these basics so you can plan your care better.Jun 23, 2017
What is the law that states that Medicare is paid in full?
Two sections of the law require this result. The first is 42 U.S.C. § 1396a (n) (3) (A), which says that the amount paid by Medicare and the amount, if any, paid by the state shall be considered payment in full.
How much does Medicare pay for a physician visit?
For example, if Medicare allows $100 for a visit to a physician's office, Medicare will pay 80% of that amount, or $80. If the state Medicaid program pays only $70 for the same service, it would make no payment for that service delivered to a QMB. The authority (but not a requirement) for states to limit their QMB cost-sharing obligations ...
What is a QMB in Medicare?
Qualified Medicare Beneficiaries (QMBs) are people with Medicare who have incomes at or below 100% of the Federal Poverty Level , or a higher level set by their state, and very few resources. [1] . The QMB benefit is administered by State Medicaid programs. QMBs can be eligible for Medicare cost-sharing protections only, ...
Does Medicare have a cross-over billing agreement?
The MLN piece reminds providers that most states have "cross-over" billing agreements with Medicare whereby any Medicare claim for a person also receiving Medicaid is sent to the state for the state's share of payment.
Can you pay Medicare with QMB?
People with QMB are excused, by law, from paying Medicare cost-sharing, and providers are prohibited from charging them. [2] . All cost-sharing (premiums, deductibles, co-insurance and copayments) related to Parts A and B is excused, meaning that the individual has no liability . The state has responsibility for these payments for QMBs regardless ...
Can advocates work with states to increase the state's cost sharing payment to the full Medicare rate?
Advocates can work with their states to increase the state's cost-sharing payment to the full Medicare rate. Perhaps it is time for Congress to revisit the question of whether limited cost-sharing payments adversely impact beneficiaries.
Do states have to pay Medicare premiums?
States can, but are not required to, pay premiums for Medicare Advantage plans' basic and supplemental benefits; states do have responsibility for MA co-payments for Part A and B services. The State's responsibility, however, is limited.
What is cost sharing in Medicaid?
Cost Sharing. States have the option to charge premiums and to establish out of pocket spending (cost sharing) requirements for Medicaid enrollees. Out of pocket costs may include copayments, coinsurance, deductibles, and other similar charges.
Can you charge out of pocket for coinsurance?
Certain vulnerable groups, such as children and pregnant women, are exempt from most out of pocket costs and copayments and coinsurance cannot be charged for certain services.
Does Medicaid cover out of pocket charges?
Prescription Drugs. Medicaid rules give states the ability to use out of pocket charges to promote the most cost-effective use of prescription drugs. To encourage the use of lower-cost drugs, states may establish different copayments for generic versus brand-name drugs or for drugs included on a preferred drug list.
Can you get higher copayments for emergency services?
States have the option to impose higher copayments when people visit a hospital emergency department for non-emergency services . This copayment is limited to non-emergency services, as emergency services are exempted from all out of pocket charges. For people with incomes above 150% FPL, such copayments may be established up to the state's cost for the service, but certain conditions must be met.
What is Medicare Cost-Sharing?
When you use Medicare, you share the cost of your care by paying premiums, deductibles, copayments, co-insurance, and out-of-pocket maximums. If you receive a paycheck, part of your check will be set aside for Medicare. You pay for the program when you work and pay again when you use it.
We Explain Cost-Sharing Terms
Cost-Sharing includes your cost of premiums, deductibles, copayments, co-insurance, and out-of-pocket maximums. You share the cost of your medical services with your insurance company.
What is cost sharing?
What is cost-sharing? Cost-sharing refers to the patient’s portion of costs for healthcare services covered by their health insurance plan. The patient is responsible to pay cost-sharing amounts out-of-pocket.
How much will Medicare cost share in 2021?
Medicare Advantage plans cannot require members to pay cost-sharing in excess of $7,550 in 2021, although many plans have cost-sharing limits below this (note that the out-of-pocket limits for Medicare Advantage plans do not include the cost of prescription drugs, which are covered separately and have separate — and unlimited — cost-sharing).
What is the certificate of insurance?
The certificate of insurance will list the amount of your individual and/or family deductible as well as copayments or coinsurance amounts you will be required to pay for covered services.
What is out of pocket medical insurance?
But under private health insurance or Medicaid, “out-of-pocket costs” generally only refer to cost-sharing incurred when a person has medical claims (even though premiums are also paid out-of-pocket).
Does the ACA cover grandfathered plans?
The ACA’s limits on out-of-pocket costs only applies to in-network services that fall within the umbrella of essential health benefits. And it does not apply to grandmothered or grandfather ed plans, or to plans that aren’t regulated by the ACA at all, such as short-term health insurance.
Is health insurance a cost sharing amount?
Health insurance premiums – the monthly payments you must make to keep your coverage in force, regardless of whether or not you use a healthcare service – are not considered cost-sharing amounts.
Can you be higher on out of pocket limits?
Many plans have out-of-pocket limits below this level, but they cannot be higher. Once your cost-sharing amounts have reached your plan’s maximum out-of-pocket limit for the year, the health insurance plan will pay 100% of your remaining covered costs that year. The ACA’s limits on out-of-pocket costs only applies to in-network services ...
