Full Answer
What are unfunded liabilities?
Unfunded liabilities are debt obligations that do not have sufficient funds set aside to pay the debt.
How do you calculate unfunded liabilities for Medicare and Social Security?
Both Medicare and Social Security have substantial unfunded liabilities, which are calculated by subtracting the value of future taxes and the trust fund balance from the value of future benefit payments. UNFUNDED LIABILITIES
What will $157 trillion unfunded liabilities mean in 2023?
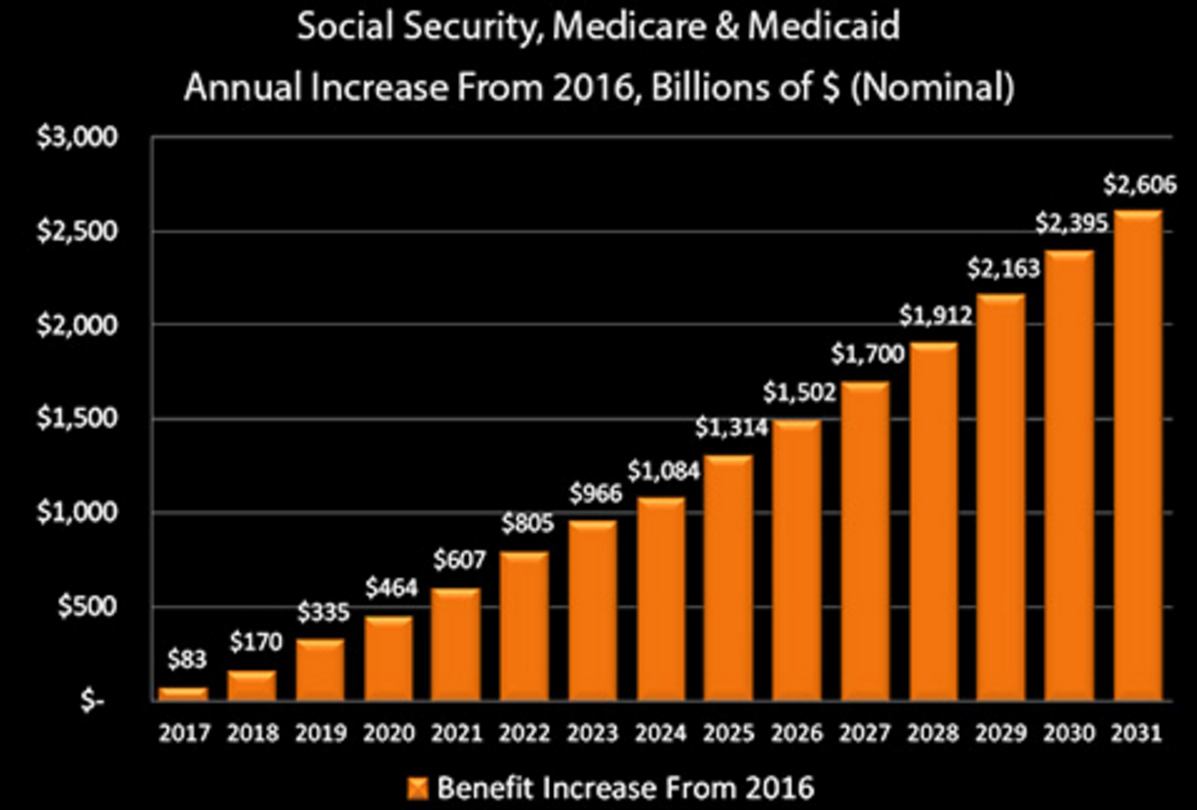
But now, get ready to gag because in 2023 the “Debt Clock Time Machine” projects unfunded liabilities will be $157 trillion, a $35 trillion increase in only four years. I would wager that a majority of citizens have no concept of what “just” $1 trillion looks like or even means. For the record, one trillion is 1,000 times 1 billion.
What are the effects of unfunded liabilities of Pensions?
For example, taxpayers feel the effects of unfunded liabilities of pensions because they are funding the revenue to pay the wages and benefits of government employees. The rising number of unfunded liabilities creates the need for higher payments, which means more funds go to pensions that could go to other resources and services.

What are unfunded liabilities?
Unfunded pension liability – which is more formally referred to as unfunded actuarial accrued liability (UAAL) in financial statements – is the difference between a retirement system's assets and the value of benefits already accrued.
Is Medicare an unfunded liability?
Both Medicare and Social Security have substantial unfunded liabilities, which are calculated by subtracting the value of future taxes and the trust fund balance from the value of future benefit payments.
What does unfunded payment mean?
Unfunded Obligation means those payment amounts associated with a Covered Obligation but for which no coverage is provided under the Liquidation Plan.
What does unfunded debt mean?
Funded vs. While funded debt is a long-term borrowing, unfunded debt is a short-term financial obligation that comes due in a year or less. Many companies that use short-term or unfunded debt are those that may be strapped for cash when there isn't enough revenue to cover routine expenses.
Is Medicare underfunded?
Politicians promised you benefits, but never funded them.
How much is Medicare in debt?
Medicare accounts for a significant portion of federal spending. In fiscal year 2020, the Medicare program cost $776 billion — about 12 percent of total federal government spending. Medicare was the second largest program in the federal budget last year, after Social Security.
How are unfunded liabilities paid?
This shortfall in pension funding — the unfunded liabilities — is money that is owed to the pension fund by the relevant state or local government. Employers make 'amortization' payments into the pension fund that are regular, additional contributions made until there is no more funding shortfall.
What is funded liability?
Funded Liability. A source of funds that a firm must take overt action to arrange and that carries an interest cost.
What is the meaning of unfunded account?
adjective. not provided with a fund or money; not financed. Finance.
What is the difference between funded and unfunded loan?
Funded loans are those loans where there is an actual transfer of funds from the bank to the borrower whereas non-funded facilities are those which do not involve such transfer. Examples of funded loans are term loans and overdraft. Examples of non-funded loans are letters of credit, bank guarantees, etc.
Is Social Security unfunded?
Thus, Social Security's unfunded liability over the next 75 years — in other words, its shortfall divided by the potential resources available to pay for it — equals 3.4 percent of taxable payroll and 1.2 percent of GDP.)
What is the US government's largest unfunded liability?
The total unfunded liability of the PBGC for single-employer defined benefit pension plans can therefore be estimated as $b 16 billion. The largest part is the estimate of Hirtle and Estrella for the unfunded cost of future plan terminations, $15 billion.
How much is Uncle Sam owed in Medicare?
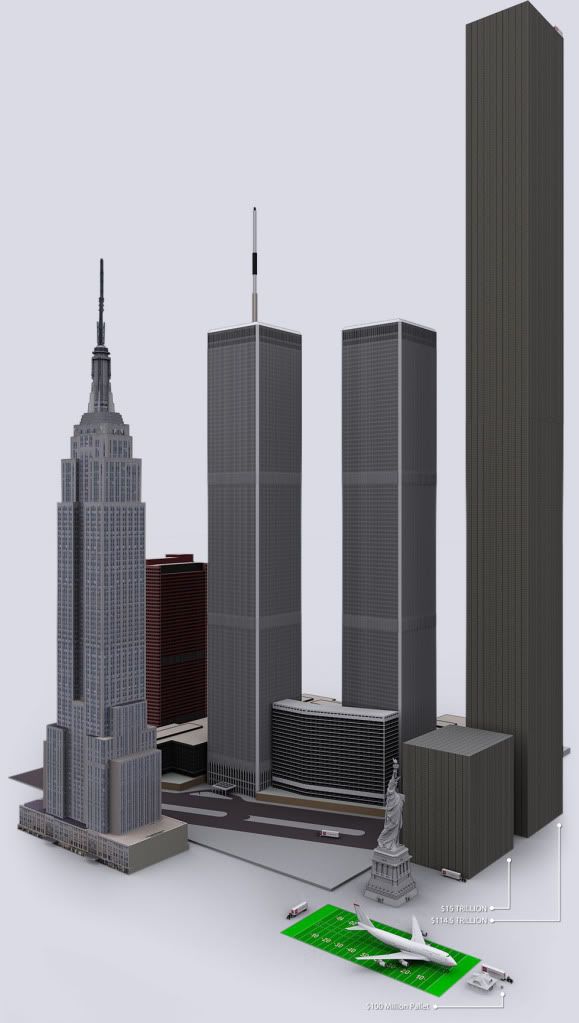
That’s according to truthinaccounting.org, which noted that there’s $96.3 trillion owed in promised but unfunded Medicare and Social Security benefits — $55.1 trillion for Medicare and $41.2 trillion for Social Security. While Uncle Sam has $5.9 trillion in assets, the $129 trillion owed in bills — including military and civilian retirement ...
How much is Uncle Sam's debt?
While Uncle Sam has $5.9 trillion in assets, the $129 trillion owed in bills — including military and civilian retirement benefits — means the U.S. is in the hole for $123 trillion. Just the unfunded liabilities in Medicare and Social Security add up to $96 trillion.
What is an unfunded liability?
An unfunded liability is a debt that is not covered by the value of assets, savings or investments that have been allocated to pay the debt. What this means is that Australian state and federal governments have a debt that is now more than $200 billion in size, yet is not directly related to the budget debt that these governments are trying ...
What happens to unfunded liabilities every year?
Every year, some portion of the unfunded liabilities become due for payment. If the government cannot pay, then the only option is to borrow to pay. This adds to the overall size of the unfunded liabilities and means the cost of servicing this debt is constantly growing.
What are the hidden costs associated with unfunded liabilities?
One of the hidden costs associated with unfunded liabilities is the cost of indexing the public service and military superannuation and pension benefits. The public service and military superannuation and pensions are currently indexed using the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
What is the largest contributor to the current unfunded liability debt?
Superannuation and pensions. Superannuation and pension benefits are by far the largest contributors to the current unfunded liability debt. In the early 1970s, when Gough Whitlam was Prime Minister, significant changes were made to how superannuation and pensions were funded.
Why is the future fund bigger than the unfunded liabilities?
The problem is that until the Future Fund grows to be larger than the unfunded liabilities debt, there is the cost of servicing the debt itself, inflation and debt increase due to increases in the size of the current and retired public service and military.
What happens if the government cannot pay off unfunded liabilities?
If the government cannot pay off unfunded liabilities they must borrow more, adding to the cost of servicing debt. shutterstock. What governments do not want is for the public to become concerned about future liabilities, so they simply do not mention them when talking about the next budget.
Who created the Future Fund?
The Future Fund was created by the government led by John Howard in 2006 to “assist future Australian governments [to] meet the cost of public sector superannuation liabilities by delivering investment returns on contributions to the Fund”.
Why is it so hard to fund Medicare?
Of course, estimating the economic and budgetary effects of putting Medicare on a firmer financial footing is difficult because of the high degree of uncertainty surrounding long-term trends in life expectancy, birth rates, productivity, and wage growth.
Is Medicare a threat to Social Security?
However, Medicare, the other major program intended to ensure the well-being of older Americans, represents an equal if not greater threat to the long-term fiscal health of the federal government.
