Key Takeaways
- Single-payer health insurance is a system in which a single entity pays healthcare providers on behalf of all people in the country.
- Many countries have some form of a single-payer system, though there are differences among their systems.
- In the U.S., which does not have a single-payer system, this concept is also known as "Medicare for All."
What are the pros and cons of single payer healthcare?
Pros of Single Payer Health Care
- Equitable distribution of healthcare cost. ...
- No surprise billing. ...
- No provider networks. ...
- It reduces the administrative costs. ...
- Easy system for consumers. ...
- Access to care. ...
- Affordability at point of services. ...
- It is equal. ...
- Universal coverage. ...
- Wider choice of doctors. ...
What countries have a single payer health care system?
There are currently 17 countries that offer single-payer healthcare:
- Norway
- Japan
- United Kingdom
- Kuwait
- Sweden
- Bahrain
- Brunei
- Canada
- United Arab Emirates
- Denmark
Why do we need single payer health care?
- Does the plan deliver better health care to you or deliver more profits to the private insurance industry?
- Does the plan eliminate different levels of of care for different classes of people?
- Does the plan prevent the shift of health care costs from business to working families?
Would single payer healthcare cost more?
Single-payer coverage could lower healthcare costs because administrative expenses are much lower for a government-funded system than for a private insurer. Also, with no competing insurance companies, there's less money spent on marketing and advertising.
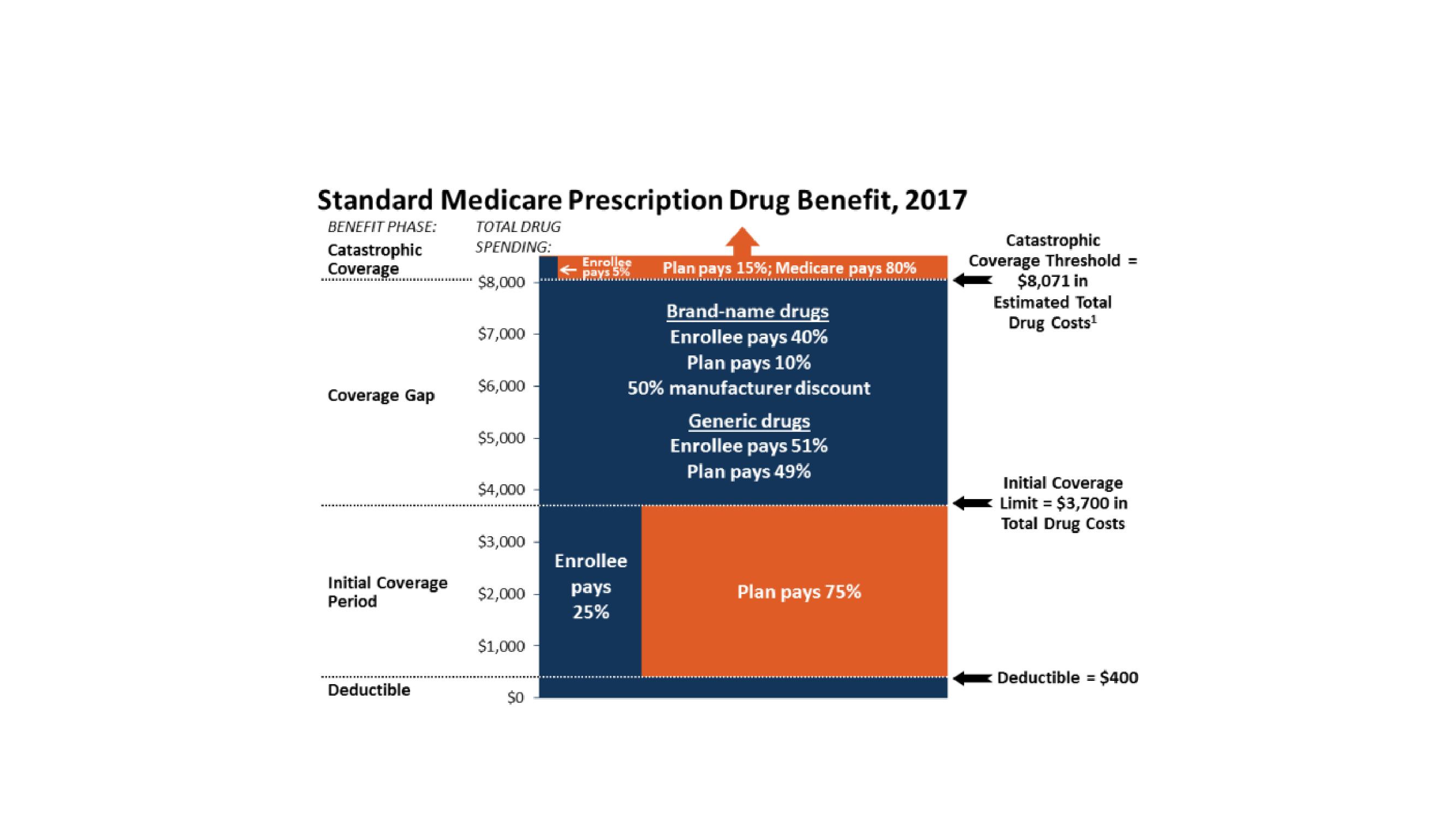
What does single-payer Medicare mean?
Single payer refers to a healthcare system in which only the government pays. The term “Medicare for All” means the same thing. Therefore, in this case, the two terms are interchangeable. However, in the broader sense, single payer could refer to healthcare that a government other than the U.S. government finances.
Is Medicare an example of a single-payer system?
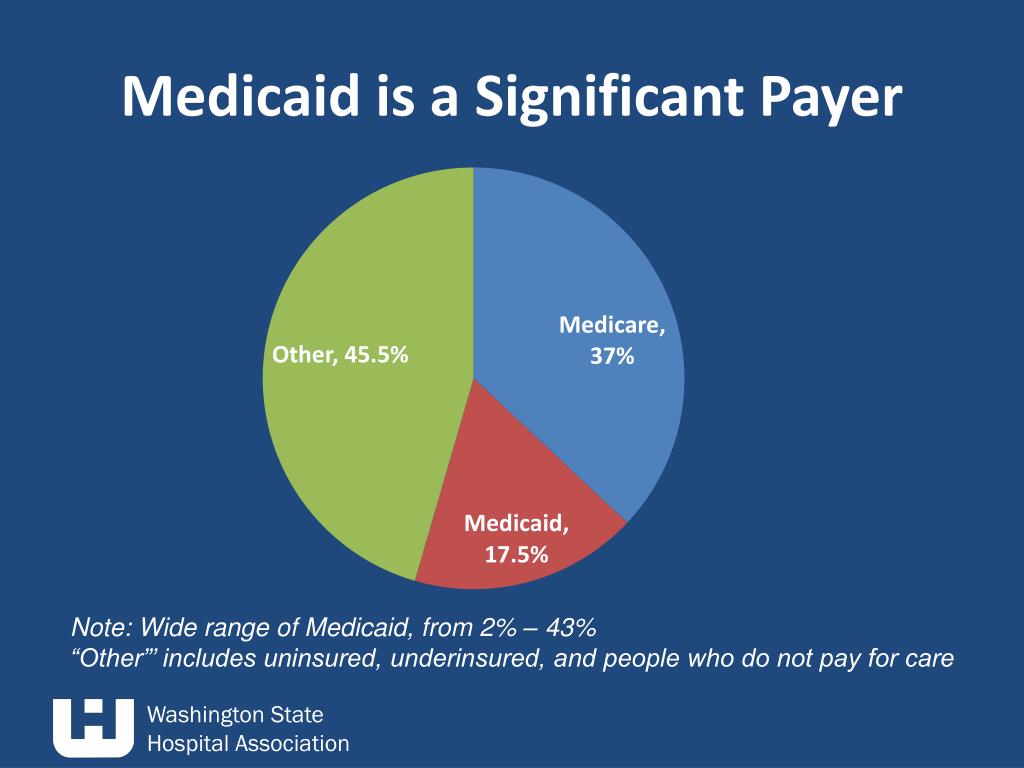
In the U.S., Medicare and the Veterans Health Administration are examples of single-payer systems. Medicaid is sometimes referred to as a single-payer system, but it is actually jointly funded by the federal government and each state government.
What is the meaning of single-payer?
Definition of single-payer : of, relating to, or being a system in which health-care providers are paid for their services by the government rather than by private insurers.
How does single payer healthcare work?
Single-payer health insurance is a healthcare system mostly or wholly funded by one entity (like a government agency, using tax dollars). The system takes the place of private health insurance companies and patient co-payments.
Is US healthcare a single-payer?
Health care in the United States is currently a unique hybrid, multiple-payer system, but with elements of single payer (i.e., Medicare, although beneficiaries also contribute through premiums), publicly subsidized private payers (e.g., employer-sponsored health insurance), socialized medicine (e.g., Department of ...
What is the difference between universal healthcare and single-payer?
Answer: "Universal coverage" refers to a health care system where every individual has health coverage. On the other hand, a "single-payer system" is one in which there is one entity—usually the government— responsible for paying health care claims.
What are the disadvantages of a single-payer system?
Reduction in Government Spending: The government would be financially strained by a single-payer healthcare system. Not only would more money be provided, but the government would have to spend more money and hire more people to oversee and manage the healthcare system.
Why a single-payer system is good?
The most prominent benefit of single payer is that patients will be able to access health care with minimal financial barriers. This improved access will increase health by increasing preventive/primary care and allowing patients to afford their treatment regimens. Free choice of provider.
Is Canada a single-payer?
Canada is a single-payer system, though, here, each of the 13 provinces and territories control their own system. Doctor and hospital care is covered, but major gaps exist.
Do doctors support single-payer?
A NEW SURVEY finds that a majority of physicians (56%) now say they either strongly or somewhat support a single-payer health care system. That's a sharp turnaround from a similar survey conducted in 2008 by the same physician staffing firm, Merritt Hawkins.
What countries use single-payer health care?
There are currently 17 countries that offer single-payer healthcare: Norway, Japan, United Kingdom, Kuwait, Sweden, Bahrain, Canada, United Arab Emirates, Denmark, Finland, Slovenia, Italy, Portugal, Cyprus, Spain, and Iceland. The United Kingdom has both universal healthcare and a single-payer healthcare system.
What is single payer health insurance?
Single-payer national health insurance, also known as “Medicare for all,” is a system in which a single public or quasi-public agency organizes health care financing, but the delivery of care remains largely in private hands. Under a single-payer system, all residents of the U.S.
What is the Medicare for All Act?
The Medicare for All Act of 2019, H.R. 1384, based on PNHP’s AJPH-published Physicians’ Proposal, would establish an American single-payer health insurance system.
What is unfair financing of healthcare?
The law continues the unfair financing of health care, whereby costs are disproportionately borne by middle- and lower-income Americans and those families facing acute or chronic illness.
How does Obamacare affect people?
The Affordable Care Act (“Obamacare”) aims to expand coverage to about 30 million Americans by requiring people to buy private insurance policies (partially subsidizing those policies by government payments to private insurers) and by expanding Medicaid. However: 1 About 30 million people will still be uninsured in 2023, and tens of millions will remain underinsured. 2 Insurers will continue to strip down policies, maintain restrictive networks, limit and deny care, and increase patients’ co-pays, deductibles and other out-of-pocket costs. 3 The law preserves our fragmented financing system, making it impossible to control costs. 4 The law continues the unfair financing of health care, whereby costs are disproportionately borne by middle- and lower-income Americans and those families facing acute or chronic illness.
How many people will be uninsured in 2023?
About 30 million people will still be uninsured in 2023, and tens of millions will remain underinsured.
What countries have single payer health care?
Other countries with single-payer health care systems include the following: 1 Taiwan - Started in 1995, coverage reached 99 percent of the population by 2004. Paid for through a combination of payroll taxes and direct government funding. 2 South Korea - Federal reforms started in the 1970s resulted in universal coverage by 1989, with all medical coverage paid through a single entity after reforms made in 2000. 3 United Kingdom - England, Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales have separate systems of publicly funded health care, supplemented with voluntary private insurance for coverage of additional services. 4 Australia - Australia's Medicare system is funded by a 2 percent income tax and operates in tandem with a private health care system for those who elect (and can afford) additional coverage. 5 Spain - Beginning in 1986, Spain established a publicly funded health care system, with management delegated to the country's various autonomous regions. Spain also allows for private insurers, which covers nearly 15 percent of the population.
Is Medicare a single payer system?
The prospect of a single-payer system in the United States is often referred to as " Medicare for all," which is a fairly apt description. Like Medicare, the government is the single payer of services, replacing insurance companies, but these services would continue to be provided by a combination of private and public entities.
What is single payer healthcare?
Single-payer healthcare systems refer to health insurance programs that are governed by one organization. These single-payer systems, which can be found worldwide, may vary by how they are funded, who is eligible, what benefits they offer, and more.
What is Medicare provider payment?
Provider payment. Services administered by Medicare for All providers would be paid for on a fee-for-service basis using a fee schedule.
What services would be affected by switching to single payer healthcare?
rehabilitation and substance abuse services. Switching to a single-payer healthcare system would likely affect the current government-funded healthcare options, such as Medicare and Medicaid.
What is Medicare for All?
The Medicare for All proposal would be an expansion of Medicare, the health insurance program that covers Americans age 65 and older. Medicare is currently broken into different parts: Part A, Part B, Part C, and Part D. There is also Medicare supplement insurance, also known as Medigap.
What is Medicare coverage?
providing coverage for all individuals, regardless of age or health status. offering original Medicare coverage, including inpatient and outpatient medical insurance. adding additional coverage, such as reproductive, maternity, and pediatric care.
How is Medicare for All funded?
Revenue and contributions. Medicare for All would be funded through income tax increases, premiums, and contributions.
Is Medicare for All a single payer system?
Medicare for All is only one type of single-payer system. There are a variety of single-payer healthcare systems that are currently in place in countries all around the world, such as Canada, Australia, Sweden, and others.
When did California start single payer health care?
California attempted passage of a single-payer health system by initiative in 1994, as Proposition 186, which got 27% of the vote.
When did universal health insurance become a single payer system?
This new service became a single-payer healthcare system in 2004.
What is Medicare for All?
For the United States Congressional bill known as the Expanded and Improved Medicare for All Act, see United States National Health Care Act. For the US Congressional caucus supporting single-payer healthcare, see Medicare for All Caucus.
How many times has the New York Health Act been passed?
New York State has been attempting passage of the New York Health Act, which would establish a statewide single-payer health plan, since 1992. The New York Health Act passed the Assembly four times: once in 1992 and again in 2015, 2016, and 2017, but has not yet advanced through the Senate after referrals to the Health Committee. On all occasions, the legislation passed the Assembly by an almost two-to-one ratio of support.
How many deaths are caused by lack of health insurance?
A study done at Harvard Medical School with Cambridge Health Alliance showed that nearly 45,000 annual deaths are associated with a lack of patient health insurance.
What is the difference between the NHS and the Canadian healthcare system?
The term was coined in the 1990s to characterize the differences between the Canadian healthcare system with those such as the United Kingdom's NHS. In the Cana dian healthcare system , the government pays private agencies to provide healthcare for qualifying individuals. In other systems, the government both funds and delivers care.
How does India pay for healthcare?
India has a universal multi-payer health care model that is paid for by a combination of public and private health insurances along with the element of almost entirely tax-funded public hospitals. The public hospital system is essentially free for all Indian residents except for small, often symbolic co-payments in some services. At the federal level, a national health insurance program was launched in 2018 by the Government of India, called Ayushman Bharat. This aimed to cover the bottom 50% (500 million people) of the country's population working in the unorganized sector (enterprises having less than 10 employees) and offers them free treatment even at private hospitals. For people working in the organized sector (enterprises with more than 10 employees) and earning a monthly salary of up to Rs 21000 are covered by the social insurance scheme of Employees' State Insurance which entirely funds their healthcare (along with pension and unemployment benefits), both in public and private hospitals. People earning more than that amount are provided health insurance coverage by their employers through the many public or private insurance companies. As of 2020, 300 million Indians are covered by insurance bought from one of the public or private insurance companies by their employers as group or individual plans. Unemployed people without coverage are covered by the various state insurance schemes if they do not have the means to pay for it. In 2019, the total net government spending on healthcare was $36 billion or 1.23% of its GDP. Since the country's independence, the public hospital system has been entirely funded through general taxation.
What is single payer system?
Single-payer system is a health care system in which one entity – a single payer – collects all health care fees and pays for all health care costs.
What would happen if all health care providers were single payer?
Instead, all health care providers in a single-payer system would bill one entity for their services. Within a single-payer system, all citizens would receive high-quality, comprehensive medical care PLUS the freedom to choose providers to a greater extent than most network-based health plans allow. Paperwork would also be dramatically reduced.
Is Medicare a socialized system?
A single-payer system – like the Canadian health system and the United States’ Medicare system – is NOT socialized medicine. Read more about the difference between a single-payer system and socialized medicine.
Why is Medicare called Medicare for All?
It’s called “Medicare for All” because it vastly improves and then scales up Medicare to pay for everyone’s healthcare. Medicare for All replaces all private insurance.
Who supports Medicare for All?
The only Democratic candidate who supports single-payer Medicare for All—a.k.a. “the real deal”—is Bernie Sanders. He’s fought for it for decades.
Why do healthcare corporations increase costs?
We have two things: an inefficient private insurance model, and sky-high medical prices. Large healthcare corporations increase costs because nobody can stop them. Insurance companies can’t profit from insuring people who are sick or who need healthcare, so they find ways to restrict their care, drop their coverage, or otherwise slough them off to public insurance.
What is public option insurance?
The public option is a public insurance plan which operates alongside private insurance plans, and it is designed to keep private insurance companies profitable. It is a rotten plan that does very little to help people.
Does Medicare for All have negotiating power?
Medicare for All has all the negotiating power, so it can set fair prices for care while making sure to compensate your doctors, nurses, and social workers fairly. Because we’re not dealing with the massive, bloated bureaucracy of profit-seeking insurance companies and their army of middlemen, we’ve built something more efficient and more humane.

Single-Payer Health Care and Medicare For All
- The prospect of a single-payer system in the United States is often referred to as "Medicarefor all," which is a fairly apt description. Like Medicare, the government is the single payer of services, replacing insurance companies, but these services would continue to be provided by a combination of private and public entities. In the current system...
Single-Payer Health Care in Other Countries
- The vast majority of industrialized nations, many of which guarantee the right to health carein their constitutions, offer some form of single-payer health care. Canada, for instance, has a system consisting of 13 provincial and territorial health insurance plans. They're administered within each territory or province in accordance with federal regulations, similar to the U.S. Medic…
Attempts at Creating Single-Payer Health Care in The U.S.
- The most notable attempt at legislation creating a single-payer health care system in the United States was forged by now-retired U.S. Representative John Conyers (D-MI) in 2003 (and reintroduced each year until his departure in 2017). The Expanded and Improved Medicare for All Act (H.R. 676), modeled after the systems used in Canada and Taiwan, would replace private ins…
Get Legal Guidance on Your Important Health Care Decisions
- Since the United States doesn't have a single-payer health care system, there are a lot of players involved, including health management organizations (HMOs) and private insurers. This means patients really need to do their homework and read the fine print. If you have questions about coverage or need representation, your best option is to meet with an experienced health care att…