
MEDICARE PART D: The estimate for the average 2012 Part D premium for basic coverage is $30. This is slightly lower than the actual average for 2011 of $30.76. The estimate for the average 2012 Part D premium for supplemental coverage is $8.
What is the average cost of Part D insurance for 2012?
Oct 27, 2011 · MEDICARE PART D: The estimate for the average 2012 Part D premium for basic coverage is $30. This is slightly lower than the actual average for 2011 of $30.76. The estimate for the average 2012 Part D premium for supplemental coverage is $8. The estimate for the average 2012 total Part D premium is $38. MEDICARE ADVANTAGE PLANS:
What is the cost of Medicare Part A for 2012?
will increase from $2,840 in 2011 to $2,930 in 2012. Out-of-Pocket Threshold: will increase from $4,550 to $4,700 in 2012. Coverage Gap (donut hole): begins once you reach your Medicare Part D plan’s initial coverage limit ($2,930 in 2012) and ends when you spend a total of $4,700 in 2012.
What is Medicare Part D (Medicare drug coverage)?
For the hypothetical applicant above, if I chose the cheapest Part D plan, opted for traditional Medicare and stuck with name brands at my local pharmacy, my total cost would be …
Can the amount of Medicare Part D premiums change?
Costs for Medicare drug coverage. You'll make these payments throughout the year in a Medicare drug plan: Premium. Yearly deductible. Copayments or coinsurance. Costs in the coverage gap. Costs if you get Extra Help. Costs if you pay a late enrollment penalty. Your actual drug coverage costs will vary depending on:
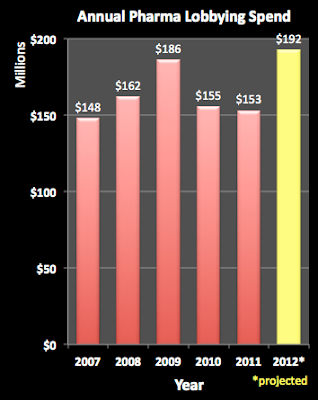
What was Medicare premium in 2013?
Today we announced that the actual rise will be lower—$5.00—bringing 2013 Part B premiums to $104.90 a month. By law, the premium must cover a percent of Medicare's expenses; premium increases are in line with projected cost increases.Nov 16, 2012
How much did Medicare cost in 2011?
This premium will be $450 for 2011, a decrease of $11 from 2010....Fact sheet. MEDICARE PREMIUMS, DEDUCTIBLES FOR 2011.Beneficiaries who file an individual tax return with income:Beneficiaries who file a joint tax return with income:Income-related monthly adjustment amountGreater than $214,000Greater than $428,000$69.104 more rows•Nov 4, 2010
What is the annual cost of Medicare Part D?
Want to make changes to your Part D coverage? Discuss your options with a licensed Medicare advisor at 1-844-309-3504. The maximum annual deductible in 2021 for Medicare Part D plans is $445, up from $435 in 2020.
What were Medicare Part D premiums in 2018?
The average monthly premium for Medicare Advantage plans in 2018 was $12 and in 2019, the amount was $8. Prescription drug plan premiums also decreased slightly, from $26 in 2018 to $25 in Medicare costs 2019.Dec 30, 2021
What was Medicare Part B premium in 2015?
How much will Medicare premiums cost in 2015? Medicare Part B premiums will be $104.90 per month in 2015, which is the same as the 2014 premiums. The Part B deductible will also remain the same for 2015, at $147.Oct 10, 2014
How much did Medicare cost in 2000?
$45.50Appendix ATable 1: Historical and Projected Social Security Cost-of-Living Adjustment, Average Monthly Social Security Benefits, and Medicare Part B and Part D Premiums and Deductibles, 1975-2024YearSocial Security Cost-of-Living Adjustment1Monthly Part B Premium320003.5%$45.5020012.6%$50.0020021.4%$54.0048 more rows•Nov 11, 2015
What is the most popular Medicare Part D plan?
Best-rated Medicare Part D providersRankMedicare Part D providerMedicare star rating for Part D plans1Kaiser Permanente4.92UnitedHealthcare (AARP)3.93BlueCross BlueShield (Anthem)3.94Humana3.83 more rows•Mar 16, 2022
Who has the cheapest Part D drug plan?
SilverScript Medicare Prescription Drug Plans Although costs vary by zip code, the average nationwide monthly premium cost of the SmartRX plan is only $7.08, making it the most affordable Medicare Part D plan on the market.
What is the maximum out of pocket for Medicare Part D?
A Medicare Part D deductible is the amount you must pay every year before your plan begins to pay. Medicare requires that Medicare Part D deductibles cannot exceed $445 in 2021, but Medicare Part D plans may have deductibles lower than this. Some Medicare Part D plans don't have deductibles.
What are 2021 Medicare premiums?
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has announced that the standard monthly Part B premium will be $148.50 in 2021, an increase of $3.90 from $144.60 in 2020.
What is the premium for Medicare Part B for 2019?
$135.50The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has announced that the standard monthly Part B premium will be $144.60 in 2020, an increase from $135.50 in 2019. However, some Medicare beneficiaries will pay less than this amount.
CMS Part D 2012 Standard Benefit Model Plan Details
Here are the highlights for the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) defined Standard Benefit Plans for 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011 and 2012. This "Standard Benefit Plan" is the minimum allowable plan to be offered.
Brand Drug Coverage Gap Discount Program
Pharmaceutical manufacturers will be required to provide certain beneficiaries access to discount prices for certain brand drugs purchased under Medicare Part D. The manufacturer discount prices will be equal to 50% of the plan’s negotiated price defined (minus any applicable dispensing fees).
Reduced Cost sharing for Generic Drugs in the Coverage Gap
The coinsurance under basic prescription drug coverage for certain beneficiaries will be reduced for generic covered Part D drugs purchased during the coverage gap (donut hole) phase of the Part D benefit. The coinsurance charged to eligible beneficiaries will be equal to 86% (or actuarially equivalent to an average expected payment of 86%).
LIS Benchmarks - lack of qualifying plans
In some Medicare Part D regions, low income beneficiaries would have a very limited choice of zero-premium prescription drug plans under the statutory methodology for calculating the maximum government premium subsidy.
What is Medicare Part D?
Medicare Part D, also called the Medicare prescription drug benefit, is an optional United States federal-government program to help Medicare beneficiaries pay for self-administered prescription drugs.
How much of Medicare is covered by Part D?
In 2019, about three-quarters of Medicare enrollees obtained drug coverage through Part D. Program expenditures were $102 billion, which accounted for 12% of Medicare spending. Through the Part D program, Medicare finances more than one-third of retail prescription drug spending in the United States.
What is Medicare Part D cost utilization?
Medicare Part D Cost Utilization Measures refer to limitations placed on medications covered in a specific insurer's formulary for a plan. Cost utilization consists of techniques that attempt to reduce insurer costs. The three main cost utilization measures are quantity limits, prior authorization and step therapy.
How many Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in Part D?
Medicare beneficiaries who delay enrollment into Part D may be required to pay a late-enrollment penalty. In 2019, 47 million beneficiaries were enrolled in Part D, which represents three-quarters of Medicare beneficiaries.
How much coinsurance do you pay for 2020?
For example, under the 2020 standard benefit, beneficiaries first pay a 100% coinsurance amount up to a $435 deductible. Second, beneficiaries pay a 25% coinsurance amount up to an Out-of-Pocket Threshold of $6,350. In the final benefit phase, beneficiaries pay the greater of a 5% coinsurance amount or a nominal co-payment amount.
What is excluded from Part D?
Excluded drugs. While CMS does not have an established formulary, Part D drug coverage excludes drugs not approved by the Food and Drug Administration, those prescribed for off-label use, drugs not available by prescription for purchase in the United States, and drugs for which payments would be available under Part B.
When did Medicare Part D go into effect?
Part D was enacted as part of the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003 and went into effect on January 1, 2006. Under the program, drug benefits are provided by private insurance plans that receive premiums from both enrollees and the government.
What is Medicare drug coverage?
You'll make these payments throughout the year in a Medicare drug plan: A list of prescription drugs covered by a prescription drug plan or another insurance plan offering prescription drug benefits. Also called a drug list. ).
Why are my out-of-pocket drug costs less at a preferred pharmacy?
Your out-of-pocket drug costs may be less at a preferred pharmacy because it has agreed with your plan to charge less. A Medicare program to help people with limited income and resources pay Medicare prescription drug program costs, like premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance. paying your drug coverage costs.
What is formulary in insurance?
Your prescriptions and whether they’re on your plan’s list of covered drugs (. formulary. A list of prescription drugs covered by a prescription drug plan or another insurance plan offering prescription drug benefits. Also called a drug list.
When will Medicare start paying for insulin?
Look for specific Medicare drug plan costs, and then call the plans you're interested in to get more details. Starting January 1, 2021, if you take insulin, you may be able to get Medicare drug coverage that offers savings on your insulin.
When is open enrollment for insulin?
Find a plan that offers this savings on insulin in your state. You can join during Open Enrollment (October 15 – December 7, 2020). Note. If your drug costs are higher than what you paid last year, talk to your doctor.
What is Medicare premium?
premium. The periodic payment to Medicare, an insurance company, or a health care plan for health or prescription drug coverage. . If you're in a. Medicare Advantage Plan (Part C) A type of Medicare health plan offered by a private company that contracts with Medicare. Medicare Advantage Plans provide all of your Part A and Part B benefits, ...
Does Social Security pay Part D?
Social Security will contact you if you have to pay Part D IRMAA, based on your income . The amount you pay can change each year. If you have to pay a higher amount for your Part D premium and you disagree (for example, if your income goes down), use this form to contact Social Security [PDF, 125 KB].
Is Medicare paid for by Original Medicare?
Medicare services aren’t paid for by Original Medicare. Most Medicare Advantage Plans offer prescription drug coverage. or. Medicare Cost Plan. A type of Medicare health plan available in some areas. In a Medicare Cost Plan, if you get services outside of the plan's network without a referral, your Medicare-covered services will be paid for ...
Do you have to pay Part D premium?
Most people only pay their Part D premium. If you don't sign up for Part D when you're first eligible, you may have to pay a Part D late enrollment penalty. If you have a higher income, you might pay more for your Medicare drug coverage.
Do you have to pay extra for Part B?
This doesn’t affect everyone, so most people won’t have to pay an extra amount. If you have Part B and you have a higher income, you may also have to pay an extra amount for your Part B premium, even if you don’t have drug coverage. The chart below lists the extra amount costs by income.
Do you pay extra for Medicare?
If you have questions about your Medicare drug coverage, contact your plan. The extra amount you have to pay isn’t part of your plan premium. You don’t pay the extra amount to your plan. Most people have the extra amount taken from their Social Security check.
How to get prescription drug coverage
Find out how to get Medicare drug coverage. Learn about Medicare drug plans (Part D), Medicare Advantage Plans, more. Get the right Medicare drug plan for you.
What Medicare Part D drug plans cover
Overview of what Medicare drug plans cover. Learn about formularies, tiers of coverage, name brand and generic drug coverage. Official Medicare site.
How Part D works with other insurance
Learn about how Medicare Part D (drug coverage) works with other coverage, like employer or union health coverage.
When will Medicare Part D enrollment start in 2022?
If you would like for us to send you an email as additional 2022 Medicare Part D plan information comes online and when enrollment begins (October 15th), please complete the form below. We will NOT share your information with any third-parties.
Does Part D increase the number of pharmacies?
Also, CMS may request that Part D plans increase the number of pharmacies offering preferred, or lower, cost sharing as CMS is concerned that some plans that offer preferred cost sharing do not provide beneficiaries with sufficient access to the lower cost sharing at select network pharmacies.

Overview
Criticisms
The federal government is not permitted to negotiate Part D drug prices with drug companies, as federal agencies do in other programs. The Department of Veterans Affairs, which is allowed to negotiate drug prices and establish a formulary, has been estimated to pay between 40% and 58% less for drugs, on average, than Part D. On the other hand, the VA only covers about half the brands that a typical Part D plan covers.
Program specifics
To enroll in Part D, Medicare beneficiaries must also be enrolled in either Part A or Part B. Beneficiaries can participate in Part D through a stand-alone prescription drug plan or through a Medicare Advantageplan that includes prescription drug benefits. Beneficiaries can enroll directly through the plan's sponsor or through an intermediary. Medicare beneficiaries who delay enrollment into Part D may be required to pay a late-enrollment penalty. In 2019, 47 million benef…
History
Upon enactment in 1965, Medicare included coverage for physician-administered drugs, but not self-administered prescription drugs. While some earlier drafts of the Medicare legislation included an outpatient drug benefit, those provisions were dropped due to budgetary concerns. In response to criticism regarding this omission, President Lyndon Johnsonordered the forma…
Program costs
In 2019, total drug spending for Medicare Part D beneficiaries was about 180 billion dollars. One-third of this amount, about 120 billion dollars, was paid by prescription drug plans. This plan liability amount was partially offset by about 50 billion dollars in discounts, mostly in the form of manufacturer and pharmacy rebates. This implied a net plan liability (i.e. net of discounts) of roughly 70 billion dollars. To finance this cost, plans received roughly 50 billion in federal reinsur…
Cost utilization
Medicare Part D Cost Utilization Measures refer to limitations placed on medications covered in a specific insurer's formulary for a plan. Cost utilization consists of techniques that attempt to reduce insurer costs. The three main cost utilization measures are quantity limits, prior authorization and step therapy.
Quantity limits refer to the maximum amount of a medication that may be dispensed during a gi…
Implementation issues
• Plan and Health Care Provider goal alignment: PDP's and MA's are rewarded for focusing on low-cost drugs to all beneficiaries, while providers are rewarded for quality of care – sometimes involving expensive technologies.
• Conflicting goals: Plans are required to have a tiered exemptions process for beneficiaries to get a higher-tier drug at a lower cost, but plans must grant medically-necessary exceptions. However, the rule denies beneficiaries the right to reques…
Impact on beneficiaries
A 2008 study found that the percentage of Medicare beneficiaries who reported forgoing medications due to cost dropped with Part D, from 15.2% in 2004 and 14.1% in 2005 to 11.5% in 2006. The percentage who reported skipping other basic necessities to pay for drugs also dropped, from 10.6% in 2004 and 11.1% in 2005 to 7.6% in 2006. The very sickest beneficiaries reported no reduction, but fewer reported forgoing other necessities to pay for medicine.