Why has Medicare spending increased so much?
That increase in spending is largely due to the retirement of the baby boomers (those born between 1944 and 1964), longer life expectancies, and healthcare costs that are growing faster than the economy. Medicare finances an array of health services.
What is the impact of Medicare on the economy?
Medicare has a large impact on the overall healthcare market: it finances about one-fifth of all health spending and 39 percent of all home health spending. In 2020, Medicare provided benefits to 19 percent of the population.
What is the future of Medicare spending?
Medicare spending is a major driver of long-term federal spending and is projected to rise from 4 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) in fiscal year 2020 to about 6 percent in fiscal year 2051 due to the retirement of the baby-boom generation and the rapid growth of per capita healthcare costs. What Are the Components of Medicare?
What happens when the government increases the fiscal deficit?
This gap between income and spending is subsequently closed by government borrowing, increasing the national debt. An increase in the fiscal deficit, in theory, can boost a sluggish economy by giving more money to people who can then buy and invest more.

Does Medicare run a deficit?
Last year, the Medicare Part A fund ran a deficit of $5.8 billion, and that excess of spending over revenue is expected to continue until it finally runs dry.
How much does Medicare cost the federal government?
$776 billionMedicare accounts for a significant portion of federal spending. In fiscal year 2020, the Medicare program cost $776 billion — about 12 percent of total federal government spending.
How does Medicare affect the economy?
In addition to financing crucial health care services for millions of Americans, Medicare benefits the broader economy. The funds disbursed by the program support the employment of millions of workers, and the salaries paid to those workers generate billions of dollars of tax revenue.
How does healthcare affect the federal budget?
How much does the federal government spend on health care? The federal government spent nearly $1.2 trillion in fiscal year 2019. In addition, income tax expenditures for health care totaled $234 billion. The federal government spent nearly $1.2 trillion on health care in fiscal year 2019 (table 1).
Is Medicare subsidized by the federal government?
As a federal program, Medicare relies on the federal government for nearly all of its funding. Medicaid is a joint state and federal program that provides health care coverage to beneficiaries with very low incomes.
Is Medicare underfunded?
Politicians promised you benefits, but never funded them.
How does Medicare affect us today?
Providing nearly universal health insurance to the elderly as well as many disabled, Medicare accounts for about 17 percent of U.S. health expenditures, one-eighth of the federal budget, and 2 percent of gross domestic production.
What are the cons of Medicare for All?
Cons of Medicare for All:Providers can choose only private pay options unless mandated differently.Doesn't solve the shortage of doctors.Health insurance costs may not disappear.Requires a tax increase.Shifts costs of employer coverage.
What would happen if we had free healthcare?
Most agree that if we had universal healthcare in America, we could save lives. A study from Harvard researchers states that not having healthcare causes around 44,789 deaths per year. 44,789 deaths per year means that there is a 40% increased risk of death for people who are uninsured.
What percentage of the federal budget is health care?
In 2014, California's personal health care spending was highest in the nation ($295.0 billion), representing 11.5 percent of total U.S. personal health care spending.
Why are Medicare costs rising?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) announced the premium and other Medicare cost increases on November 12, 2021. The steep hike is attributed to increasing health care costs and uncertainty over Medicare's outlay for an expensive new drug that was recently approved to treat Alzheimer's disease.
How might citizens be affected if the government reduced funding for Medicaid?
The most significant impact of these Medicaid cuts would be the disruption of health care services for working families, seniors, children, and people with disabilities. States that want to avoid deep cuts in health programs would have to either raise taxes or cut other programs.
How much does Social Security cost the government?
The federal government spent nearly $910 billion on Social Security benefits in 2016. Together, Social Security's programs account for nearly one-quarter of all federal spending in 2016. Social Security is the largest among the three major entitlement programs.
How much did the government spend on Medicare in 2021?
$696 billionWhat is the spending on Medicare? In FY 2021 the federal government spent $696 billion on Medicare.
How much does the Affordable Care Act cost taxpayers?
Also prior to this year, ACA subsidies cost taxpayers about $50 billion a year. And yet they led to only about 2 million people gaining exchange-plan coverage. That's a small number in a nation of 330 million.
What percent of the total federal budget is spent on the Social Security program relative to other programs?
Today, Social Security is the largest program in the federal budget and typically makes up almost one-quarter of total federal spending.
What percentage of prescriptions were brand name drugs in 2015?
In 2015, brand-name specialty drugs accounted for about 30 percent of net spending on prescription drugs under Medicare Part D and Medicaid, but they accounted for only about 1 percent of all prescriptions dispensed in each program.
What is Medicare recurring?
Recurring Publications. Medicare is the second-largest federal program and provides subsidized medical insurance for the elderly and certain disabled people. CBO’s work on Medicare includes projections of federal spending under current law, cost estimates for legislative proposals, and analyses of specific aspects of the program ...
What is the only income protection for older people?
Social Security is the only inflation-protected, guaranteed source of income people can count on when they retire. It is the principal source of income for more than 34 million older households, and roughly 10 million individuals age 65 and older depend on it for nearly all of their income. Medicare provides the critical health coverage ...
What percentage of people over 50 oppose Social Security?
A full 85 percent of those 50 and over strongly oppose reducing Social Security and Medicare to help reduce the federal budget deficit. While older Americans care about the nation’s long-term fiscal health, we also know they want to make sure the promises made to all Americans regarding Social Security and Medicare are honored.
Can you participate in AmeriSpeak surveys?
Households without conventional internet access but having web access via smartphones are allowed to participate in AmeriSpeak surveys by web. AmeriSpeak panelists participate in NORC studies or studies conducted by NORC on behalf of governmental agencies, academic researchers, and media and commercial organizations.
Do Americans get Social Security and Medicare?
Americans have earned their Social Security and Medicare benefits after years of working and paying taxes into the two programs. These programs are critical to tens of millions of workers and retirees who rightfully expect Congress to be careful stewards of their earned benefits.
What Are the Components of Medicare?
Medicare is a federal program that provides health insurance to people who are age 65 and older, blind, or disabled. Medicare consists of four "parts":
How Much Does Medicare Cost and What Does It Cover?
Medicare accounts for a significant portion of federal spending. In fiscal year 2020, the Medicare program cost $776 billion — about 12 percent of total federal government spending. Medicare was the second largest program in the federal budget last year, after Social Security.
How much of Medicare was financed by payroll taxes in 1970?
In 1970, payroll taxes financed 65 percent of Medicare spending.
How is Medicare self-financed?
One of the biggest misconceptions about Medicare is that it is self-financed by current beneficiaries through premiums and by future beneficiaries through payroll taxes. In fact, payroll taxes and premiums together only cover about half of the program’s cost.
How is Medicare funded?
Medicare is financed by two trust funds: the Hospital Insurance (HI) trust fund and the Supplementary Medical Insurance (SMI) trust fund. The HI trust fund finances Medicare Part A and collects its income primarily through a payroll tax on U.S. workers and employers. The SMI trust fund, which supports both Part B and Part D, ...
What percentage of GDP will Medicare be in 2049?
In fact, Medicare spending is projected to rise from 3.0 percent of GDP in 2019 to 6.1 percent of GDP by 2049. That increase in spending is largely due to the retirement of the baby boomers (those born between 1944 and 1964), longer life expectancies, and healthcare costs that are growing faster than the economy.
What percentage of Medicare is from the federal government?
The federal government’s general fund has been playing a larger role in Medicare financing. In 2019, 43 percent of Medicare’s income came from the general fund, up from 25 percent in 1970. Looking forward, such revenues are projected to continue funding a major share of the Medicare program.
How is Medicare Financed?
Medicare is funded primarily from general revenues (43 percent), payroll taxes (36 percent), and beneficiary premiums (15 percent) (Figure 7) .
How much does Medicare cost?
In 2018, Medicare spending (net of income from premiums and other offsetting receipts) totaled $605 billion, accounting for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1).
Why is Medicare spending so slow?
Slower growth in Medicare spending in recent years can be attributed in part to policy changes adopted as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Budget Control Act of 2011 (BCA). The ACA included reductions in Medicare payments to plans and providers, increased revenues, and introduced delivery system reforms that aimed to improve efficiency and quality of patient care and reduce costs, including accountable care organizations (ACOs), medical homes, bundled payments, and value-based purchasing initiatives. The BCA lowered Medicare spending through sequestration that reduced payments to providers and plans by 2 percent beginning in 2013.
What is the average annual growth rate for Medicare?
Average annual growth in total Medicare spending is projected to be higher between 2018 and 2028 than between 2010 and 2018 (7.9 percent versus 4.4 percent) (Figure 4).
What has changed in Medicare spending in the past 10 years?
Another notable change in Medicare spending in the past 10 years is the increase in payments to Medicare Advantage plans , which are private health plans that cover all Part A and Part B benefits, and typically also Part D benefits.
What is excess health care cost?
Over the next 30 years, CBO projects that “excess” health care cost growth—defined as the extent to which the growth of health care costs per beneficiary, adjusted for demographic changes, exceeds the per person growth of potential GDP (the maximum sustainable output of the economy)—will account for half of the increase in spending on the nation’s major health care programs (Medicare, Medicaid, and subsidies for ACA Marketplace coverage), and the aging of the population will account for the other half.
What percentage of Medicare is spending?
Key Facts. Medicare spending was 15 percent of total federal spending in 2018, and is projected to rise to 18 percent by 2029. Based on the latest projections in the 2019 Medicare Trustees report, the Medicare Hospital Insurance (Part A) trust fund is projected to be depleted in 2026, the same as the 2018 projection.
Why are deficits considered negative?
While macroeconomic proposals under the Keynesian school argue that deficits are sometimes necessary to stimulate aggregate demand after a monetary policy has proven ineffective, other economists argue that deficits crowd out private borrowing and distort the marketplace.
How much is the deficit for 2020?
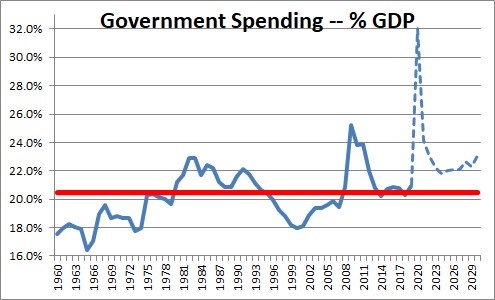
The U.S. federal shortfall for fiscal year 2020 was to be $3.1 trillion (due in large part to the coronavirus pandemic). Such a deficit occurs because the U.S. government currently spends way more than it earns. The fiscal year 2019 budget deficit came in at $984 billion. 4
What is the current account deficit?
This imbalance—sometimes called the current accounts deficit or the budget deficit—is common among contemporary governments all over the world. Since 1970, the U.S. government has had higher expenditures than revenues for all but four years with recent years each year showing a fiscal deficit in the U.S. of more than $1 trillion. 1 .
How much will the Trump tax cuts increase the deficit?
The Trump tax cuts will reduce revenue and increase the deficit; tax cuts total $1.5 trillion over the next 10 years. While the Joint Committee on Taxation expects that the cuts should stimulate growth by 0.7% annually offsetting some of the lost income, the deficit will increase $1 trillion over the next decade. 7 Lastly, Social Security is another contributor to the deficit. According to the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation, Medicare spending accounted for 15% of total federal spending in 2018 and is expected to reach 18% by 2029. 8
What was Keynes's view on the economy?
Governments could borrow money and increase spending as part of a targeted fiscal policy. Keynes rejected the idea that the economy would return to a natural state of equilibrium. Instead, he argued that once an economic downturn sets in, for whatever reason, the fear and gloom that it engenders among businesses and investors will tend to become self-fulfilling and can lead to a sustained period of depressed economic activity and unemployment.
Why do politicians rely on fiscal deficits?
Politicians and policymakers rely on fiscal deficits to expand popular policies, such as welfare programs and public works, without having to raise taxes or cut spending elsewhere in the budget. In this way, fiscal deficits also encourage rent-seeking and politically motivated appropriations.
How does an increase in the fiscal deficit help the economy?
An increase in the fiscal deficit, in theory, can boost a sluggish economy by giving more money to people who can then buy and invest more.