How to spot and report Medicare fraud?
· Medicare Fraud Costs $65 Billion a Year. You Can Help. Nov 12, 2021 Medicare Fraud Costs $65 Billion a Year. You Can Help. In addition to costing taxpayers billions of dollars, Medicare fraud also lowers the quality of healthcare. Medicare processed more than $909 billion in Medicare benefits in 2020.
What constitutes Medicaid or Medicare fraud?
Fraud costs Medicare an estimated $60 billion a year and contributes to the rising cost of health care for all Americans. Once you understand what is involved, you can help prevent fraud. …
How to spot Medicaid fraud?
· The reporting period for the Fiscal Year (FY) 2020 Medicare FFS improper payment rate included claims submitted during the 12-month period from July 1, 2018 through June 30, …
What is the most common forms of Medicare fraud?
· According to the letter, “The Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services’ (CMS) own numbers show that in Fiscal Year (FY) 2019, Medicaid made $57.36 billion in improper …

What is the cost of Medicaid fraud?
The FY 2019 national Medicaid improper payment rate estimate is 14.90 percent, representing $57.36 billion in improper payments. The FY 2019 national CHIP improper payment rate estimate is 15.83 percent, totaling $2.74 billion in improper payments.
How much U.S. healthcare is lost to fraud?
3 percentThe National Heath Care Anti-Fraud Association estimates conservatively that health care fraud costs the nation about $68 billion annually — about 3 percent of the nation's $2.26 trillion in health care spending. Other estimates range as high as 10 percent of annual health care expenditure, or $230 billion.
How much money is stolen from Medicare?
$60 billionThe federal government admits that a staggering $60 billion is stolen from tax payers through Medicare scams every year.
What is the charge for Medicare fraud?
Professionals who are accused of submitting false medical claims, engaging in fraudulent medical billing or creating false records may face various penalties under the False Claims Act. These include incarceration for up to five years and criminal fines worth up to $250,000, according to the CMS.
How does healthcare fraud affect taxpayers?
The Effects on Your Organization Fraud perpetrated against the Medicare and Medicaid systems directly drains the taxpayers of this country. Medicare is funded through a payroll tax on both the employer and employee. As more funds are needed, taxes are raised. Thus, everyone employed is affected.
Is medical fraud common?
Unfortunately, healthcare fraud is a common occurrence and the amount of healthcare fraud is on the rise. The U.S. Justice Department recovered more than $2.6 billion in 2019 from lawsuits involving healthcare fraud and false claims, federal data released Thursday show.
What is the overall Medicare claims improper payment amount each year?
In total, Medicare improper payments were estimated to be $43 billion in fiscal year 2020. However, the amount of improper payments made in Medicare are significant, accounting for over one-quarter of the total amount of improper payments made government-wide in fiscal year 2019.
What is the purpose of the Stark law?
The Physician Self-Referral Law, commonly referred to as the Stark law, prohibits physicians from referring patients to receive "designated health services" payable by Medicare or Medicaid from entities with which the physician or an immediate family member has a financial relationship, unless an exception applies.
What does heat stand for in Medicare?
The Health Care Fraud Prevention and Enforcement Action Team (HEAT), a joint initiative between HHS, OIG, and DOJ, has played a critical role in the fight against health care fraud.
What agency fights Medicare fraud?
the Office of the Inspector GeneralHave your Medicare card or Medicare Number and the claim or MSN ready. Contacting the Office of the Inspector General. Visit tips.oig.hhs.gov or call 1-800-HHS-TIPS (1-800-447-8477). TTY users can call 1-800-377-4950.
Who enforces Stark Law?
Government agencies, including the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ), the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services (HHS), the HHS Office of Inspector General (OIG), and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), enforce these laws. The civil FCA, 31 United States Code (U.S.C.)
What is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid?
Medicare is a federal program that provides health coverage if you are 65+ or under 65 and have a disability, no matter your income. Medicaid is a state and federal program that provides health coverage if you have a very low income.
What was the federal deficit in 2015?
The federal budget deficit in 2015 was $439 billion; that’s down about two-thirds from where it was in 2010. For all those radio ranters and cable-news mouthholes asking what electing Republicans ever has accomplished, there’s your answer.
Does Medicaid help with poverty?
RELATED: Medicaid Doesn’t Alleviate Poverty — So Why Do We Keep Spending More On It?
Is 12 percent an error rate?
12 percent in improper payments isn’t an error rate — it’s a malfeasance rate.
Medicare Fraud Stats
According to federal law, frauds are recognized as criminal acts. They don’t harm only the organization they are targeted at. They may have a much wider impact and harm the entire industry or system, and therefore its direct and indirect beneficiaries.
How does fraud and abuse impact the costs of healthcare?
Scams are extremely expensive. An inconceivable amount of cash is wasted, without any alternative to rebound it. Medicare fraud costs are estimated at a whopping $50 billion a year. In other words, this is $1 billion per week spent.
The Bottom Line: How Much Fraud Is There in Medicare
Medicare covers around 60 million people in the US, which accounts for over 18% of the population. The program is funded by users’ premiums, payroll tax, and general revenues, so the Medicare fraud numbers are nothing to be scoffed at.
Which states have the highest number of Medicaid fraud cases?
7. The five states with the highest number of fraud cases include California, Texas, New York, Ohio and Kentucky. 8.
When was the Medicare fraud strike force formed?
The Medicare Fraud Strike Force was formed by federal officials in 2007. The group visited some 1600 businesses in Miami at random, following up on billing to Medicare for durable medical equipment. Of those businesses, nearly one-third did not exist although they had billed Medicare for $237 million in the past year.
Why is the Affordable Care Act criticized?
Some have criticized the Affordable Care Act because it widens the requirements to receive Medicaid or Medicare, whereas others have praised it for working hard to crack down on these frauds.
How much money was stolen from Medicare in 2010?
2. In 2010 federal officials arrested some 94 people who had filed false claims through Medicare and Medicaid, for a total of $251 million in fraudulent claims. 3. The Medicare Fraud Strike Force was formed by federal officials in 2007.
How much was Medicare in 2010?
In 2010 the Government Accountability Office or GAO reported that they had found some $48 billion in “improper payments” during the past year for Medicaid and Medicare. This amount was roughly 10% of the $500 billion that was paid out during the year. 11.
How much money did the Consumer Protection Branch get in 2012?
In 2012 the Civil Division Consumer Protection Branch, which files civil suits against those convicted of Medicaid and Medicare fraud, obtained almost $1.5 billion in judgments, fines, and other forfeitures against those convicted of such frauds.
How much did the federal government recover from fraud in 2011?
In 2011, state governments recovered some $1.7 billion from fraudulent payouts. They spent an estimated $208 million to accomplish this. 9. In that same year, the federal government also recovered some $4.1 billion from fraudulent activity, but they too needed to spend hundreds of millions of dollars to do this. 10.
How is Medicaid improper payment calculated?
CMS estimates Medicaid and CHIP improper payments through the Payment Error Rate Measurement (PERM) program. The improper payment rates are based on reviews of the FFS, managed care, and eligibility components of Medicaid and CHIP in the year under review. The PERM program uses a 17-state rotational approach to measure the 50 states and the District of Columbia over a three-year period. By this approach, CMS measures each state once every three years and national improper payment rates include findings from the most recent three-year cycle measurements. Each time a cycle of states is measured, CMS utilizes the new findings and removes the respective cycle’s previous findings. The review period for the FY 2020 Medicaid and CHIP improper payment rate included claims submitted from July 1, 2018 through June 30, 2019.
What is Medicare Part D improper payment estimate?
The Medicare Part D improper payment estimate measures the payment error related to inaccurately submitted prescription drug event (PDE) data, where the majority of errors for the program exists . CMS measures the inconsistencies between the information reported on PDEs and the supporting documentation submitted by Part D sponsors including prescription record hardcopies (or medication orders, as appropriate), and detailed claims information. The FY 20202020 Part D improper payment data is representative of PDE data generated from the Calendar Year 2018 payment year.
What is the Medicare FFS rate for 2020?
The FY 2020 Medicare FFS estimated improper payment rate is 6.27 percent , representing $25.74 billion in improper payments. This compares to the FY 2019 estimated improper payment rate of 7.25 percent, representing $28.91 billion in improper payments. The decrease was driven by reductions in the improper payment rates for home health and skilled nursing facility claims.
What is the Payment Integrity Information Act?
The Payment Integrity Information Act of 2019 requires CMS to periodically review programs it administers, identify programs that may be susceptible to significant improper payments, estimate the amount of improper payments, and report on the improper payment estimates and the Agency’s actions to reduce improper payment s in ...
What is improper payment?
Instead, improper payments are payments that did not meet statutory, regulatory, administrative, or other legally applicable requirements and may be overpayments or underpayments. Additionally, improper payments do not necessarily represent expenses that should not have occurred. For example, current OMB guidance states that when an agency’s review is unable to discern whether a payment was proper as a result of insufficient or missing documentation, this payment should be considered an improper payment. A significant amount of improper payments is due to instances where a lack of documentation or errors in the documentation limits CMS’s ability to verify the payment was paid correctly. However, had the documentation been submitted or properly maintained, then the payments might have been determined to be proper. A smaller proportion of improper payments are payments that should not have been made or should have been made in different amounts and are considered a monetary loss to the government (e.g., medical necessity, incorrect coding, beneficiary ineligible for program or service, and other errors).
What is a smaller proportion of improper payments?
A smaller proportion of improper payments are payments that should not have been made or should have been made in different amounts and are considered a monetary loss to the government (e.g., medical necessity, incorrect coding, beneficiary ineligible for program or service, and other errors).
How much was the decrease in home health payments in 2016?
Home Health - $5.90 billion decrease in estimated improper payments (2016 to 2020) due to corrective actions such as policy clarification and Targeted Probe and Educate (TPE) for home health agencies.
How much was Medicaid improperly paid in 2019?
According to the letter, “The Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services’ (CMS) own numbers show that in Fiscal Year (FY) 2019, Medicaid made $57.36 billion in improper payments representing 32.8 percent of all improper payments across the federal government. According to CMS, in FY 2020, improper payments rose to $86.9 billion, meaning more than 1 out of every 5 Medicaid payments were improper. This is an unacceptable waste of American taxpayer dollars.”
Which federal program is the most fraud ridden?
According to a new report by the Government Accountability Office (GAO), Medicaid is the most fraud-ridden program in the entire federal government.
How much did Medicaid cost in 2020?
As the report notes, “In fiscal year 2020, Medicaid covered an estimated 77 million low-income and medically needy individuals at a cost of $673 billion, of which $419 billion was financed by the federal government. … Medicaid improper payments represented about 21.4 percent of federal program spending—more than $85 billion—in fiscal year 2020, an increase of nearly $30 billion from 2019.”
What are some ways to reform medicaid?
These include the introduction of health savings accounts, implementing minimal co-pays, enforcing work requirements for able-bodied adults without dependents, and many more.
Is Medicaid considered a high risk program?
Unfortunately, in the 18 years that Medicaid has been deemed a “high risk” program, little progress has been made in combating the improper payments that have become rampant throughout the program.
Is Medicaid rife with improper payments?
It should come as no surprise that Medicaid is rife with improper payments, given how much the program has expanded in recent years.
Is Medicaid a government program?
In other words, Medicaid—one of the largest government programs in existence— is fraught with waste, fraud, and abuse.
Why is Medicaid improperly paid?
Medicaid and CHIP eligibility improper payments are mostly due to insufficient documentation to verify eligibility, related primarily to income or resource verification for both situations where the required verification was not done at all and where there is indication the verification was initiated but there was no documentation to validate the verification process was completed, and non-compliance with eligibility redetermination requirements.
How does CMS calculate Medicaid payments?
CMS estimates Medicaid and CHIP improper payments through the Payment Error Rate Measurement (PERM) program. The improper payment rates are based on reviews of the FFS, managed care, and eligibility components of Medicaid and CHIP in the year under review. The PERM program uses a 17-state rotational approach to measure the 50 states and the District of Columbia over a three-year period. By this approach, CMS measures each state once every three years and national improper payment rates include findings from the most recent three year cycle measurements. Each time a cycle of states is measured, CMS utilizes the new findings and removes the respective cycle’s previous findings.
What is Medicare Part D improper payment estimate?
The Medicare Part D improper payment estimate measures the payment error related to inaccurately submitted prescription drug event (PDE) data, where the majority of errors for the program exists. CMS measures the inconsistencies between the information reported on PDEs and the supporting documentation submitted by Part D sponsors including prescription record hardcopies (or medication orders, as appropriate), and detailed claims information.
What is a Part C estimate?
The Part C improper payment estimate measures improper payments resulting from errors in beneficiary risk scores. The primary component of most beneficiary risk scores is based on clinical diagnoses submitted by plans for risk adjusted payment. If medical records do not support the diagnoses submitted to CMS, the risk scores may be inaccurate and result in payment errors. The Part C estimate is based on medical record reviews conducted annually, where CMS identifies unsupported diagnoses and calculates corrected risk scores.
What is the purpose of the Improper Payments Information Act of 2002?
The Improper Payments Information Act of 2002 (IPIA), as amended by the Improper Payments Elimination and Recovery Act of 2010 and the Improper Payments Elimination and Recovery Improvement Act of 2012, requires CMS to periodically review programs it administers, identify programs that may be susceptible to significant improper payments, estimate the amount of improper payments, and report on the improper payment estimates and the Agency’s actions to reduce improper payments in the Department of Health & Human Services (HHS) annual Agency Financial Report (AFR).
What is the Medicare improper payment rate for 2019?
The FY 2019 Medicare FFS estimated improper payment rate is 7.25 percent, representing $28.91 billion in improper payments, compared to the FY 2018 estimated improper payment rate of 8.12 percent, representing $31.62 billion in improper payments. This decrease was driven by reductions in the improper payment rates for home health, other Part B services, and Durable Medical Equipment, Prosthetics, Orthotics and Supplies (DMEPOS) claims as a result of provider burden and policy clarification initiatives. Specifically,
What is improper payment?
Instead, improper payments are payments that did not meet statutory, regulatory, administrative, or other legally applicable requirements and may be overpayments or underpayments. Additionally, improper payments do not necessarily represent expenses that should not have occurred. For example, current OMB guidance states that when an agency’s review is unable to discern whether a payment was proper as a result of insufficient or missing documentation, this payment should be considered an improper payment. A significant amount of improper payments is due to instances where a lack of documentation or errors in the documentation limits CMS’s ability to verify the payment was paid correctly. However, if the documentation had been submitted or properly maintained, then the payments may have been determined to be proper. A smaller proportion of improper payments are payments that should not have been made or should have been made in different amounts and are considered a monetary loss to the government (e.g., medical necessity, incorrect coding, beneficiary ineligible for program or service, and other errors).
What is Health Care Fraud?
Fraud in our nation’s health care system, including that in the Western District of Michigan, results in losses of millions of dollars every year from the Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance programs.
What Can You Do About Health Care Fraud?
For approximately five years, fiscal intermediaries and carriers for Medicare have been required, in virtually all circumstances, to send notices and explanations of benefits to Medicare users and patients.
General Contact Information
If you believe that a health care provider has engaged in any of the conduct or practices described above, you should promptly contact the insurance carrier that sent the payment notice to you.
What does FWA stand for in Medicare?
Waste is enough a problem that it is part of an acronym used by the federal Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services: FWA, for fraud, waste and abuse. In a training manual for employees, CMS says with bold type and an exclamation point that "combating FWA is everyone’s responsibility!"
What is improper payment?
Under federal law, an improper payment is one "that should not have been made or that was made in an incorrect amount, including overpayments and underpayments." These could range from coding errors in the billing process to fraud, such as companies billing Medicare for services that were never provided.
How much was Ryan's budget?
Of the $52 billion Ryan alluded to, $45 billion consisted of overpayments and $7 billion, underpayments, Badoyan told us.
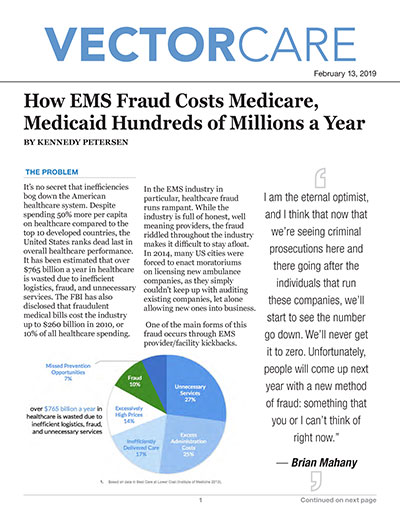
Statistics of Medicaid Fraud That Will Shock You
The Purpose of Medicaid
- Medicaid is meant for families and individuals who have low incomes regardless of their age, whereas Medicare is reserved for seniors. Medicaid is the largest source of funding for this type of coverage for those with low incomes in the U.S. Medicaid is jointly funded by both the federal government and individual states, who manage their portion of Medicaid dollars. States are not r…
The Cost of Fraud
- Medicaid scams or fraud cost the U.S. government and in turn, taxpayers footing the bill for this program, literally tens of millions if not hundreds of millions of dollars every single year. Some news reports find small fraudulent claims such as individuals who do not reveal their entire income when applying for the program, but other sources repo...
Rising Costs
- As healthcare costs and expenditures continue to rise, many assume that frauds and scams will also continue to flourish. The number of claims processed every day along with the lack of oversight makes Medicare and Medicaid easy targets for an experienced scam artist, and for fraudulent claims. Anyone able to skirt the system by claiming just enough to go unnoticed may …