Full Answer
What percentage of hospitals receive Medicare and Medicaid payments?
In 2019, 63 percent of hospitals received Medicare payments less than cost, while 58 percent of hospitals received Medicaid payments less than cost. 1. Medicare and Medicaid payments include all applicable payment adjustments (Disproportionate Share, Indirect Medical Education, etc.).
Do not-for-profit hospitals have to provide care for Medicare and Medicaid?
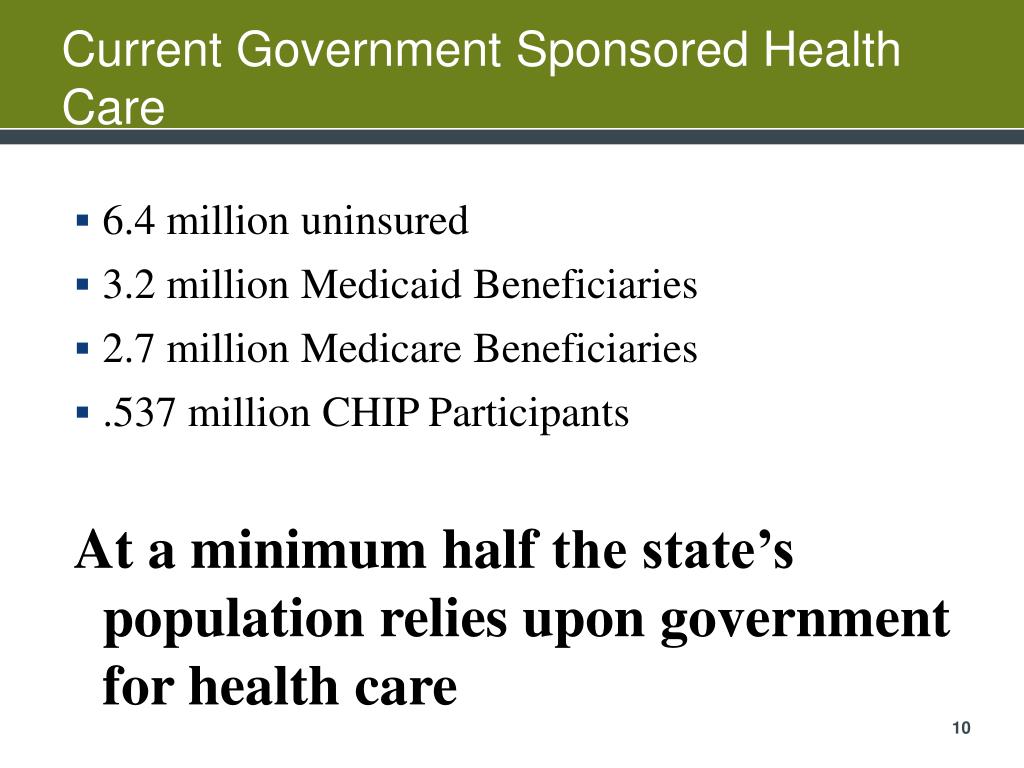
However, as a condition for receiving federal tax exemption for providing health care to the community, not-for-profit hospitals are required to care for Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries. Also, Medicare and Medicaid account for more than 60 percent of all care provided by hospitals.
Are hospital payment rates set below the costs of providing care?
These payment rates are currently set below the costs of providing care, resulting in underpayment. Payments made by managed care plans contracting with the Medicare and Medicaid programs are generally negotiated with the hospital.
How much did Medicare and Medicaid underpayments fall below costs in 2019?
In the aggregate, both Medicare and Medicaid payments fell below costs in 2019: Combined underpayments were $75.8 billion in 2019. This includes a shortfall of $56.8 billion for Medicare and $19.0 billion for Medicaid. For Medicare, hospitals received payment of only 87 cents for every dollar spent by hospitals caring for Medicare patients in 2019.

Does Medicare cover 100 percent of hospital?
According to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), more than 60 million people are covered by Medicare. Although Medicare covers most medically necessary inpatient and outpatient health expenses, Medicare reimbursement sometimes does not pay 100% of your medical costs.
What percentage of hospital costs does Medicare cover?
Everyone with Medicare is entitled to a yearly wellness visit that has no charge and is not subject to a deductible. Beyond that, Medicare Part B covers 80% of the Medicare-approved cost of medically necessary doctor visits. The individual must pay 20% to the doctor or service provider as coinsurance.
What percentage of US hospitals accept Medicare?
40.9 percentThe majority of patients treated by hospitals are covered by Medicare (40.9 percent of patients treated in U.S. hospitals). The average payer mix of a U.S. hospital is as follows: Medicare: 40.9 percent. Medicaid: 17.2 percent.
What is the Medicare two midnight rule?
The Two-Midnight rule, adopted in October 2013 by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, states that more highly reimbursed inpatient payment is appropriate if care is expected to last at least two midnights; otherwise, observation stays should be used.
How Does Medicare pay for hospitals?
Inpatient hospitals (acute care): Medicare pays hospitals per beneficiary discharge, using the Inpatient Prospective Payment System. The base rate for each discharge corresponds to one of over 700 different categories of diagnoses—called Diagnosis Related Groups (DRGs)—that are further adjusted for patient severity.
Do all hospitals accept Medicare?
Medicare is accepted at over 7,000 hospitals, which must meet Medicare's safety and care standards. In most cases, you can go to any doctor, healthcare provider, hospital or facility that's enrolled in Medicare. In fact, more than 7,000 hospitals in the U.S. provide services to Medicare patients.
Why do hospitals participate in Medicare?
Hospital participation in Medicare and Medicaid is voluntary. However, as a condition for receiving federal tax exemption for providing health care to the community, not-for-profit hospitals are required to care for Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries.
Why do doctors opt out of Medicare?
There are several reasons doctors opt out of Medicare. The biggest are less stress, less risk of regulation and litigation trouble, more time with patients, more free time for themselves, greater efficiency, and ultimately, higher take home pay.
How many hospitals in the US participate in Medicare?
About 7,000 hospitals provide services to Medicare patients.
What does code 44 mean in a hospital?
A Condition Code 44 is a billing code used when it is determined that a traditional Medicare patient does not meet medical necessity for an inpatient admission.
What surgeries are not covered by Medicare?
However, services such as elective cosmetic surgery, some dental procedures and laser eye surgery are not listed on the MBS....What Medicare doesn't coverAmbulance services.Most dental services (unless deemed medically necessary)Optometry (glasses, LASIK, etc)Audiology (hearing aids)Physiotherapy.Cosmetic Surgery.
What happens when your Medicare runs out?
For days 21–100, Medicare pays all but a daily coinsurance for covered services. You pay a daily coinsurance. For days beyond 100, Medicare pays nothing. You pay the full cost for covered services.
What are Medicare covered services?
Medicare-covered hospital services include: Semi-private rooms. Meals. General nursing. Drugs as part of your inpatient treatment (including methadone to treat an opioid use disorder) Other hospital services and supplies as part of your inpatient treatment.
How many days of inpatient care is in a psychiatric hospital?
Inpatient mental health care in a psychiatric hospital is limited to 190 days in a lifetime.
What is an inpatient hospital?
Inpatient hospital care. You’re admitted to the hospital as an inpatient after an official doctor’s order, which says you need inpatient hospital care to treat your illness or injury. The hospital accepts Medicare.
How many days in a lifetime is mental health care?
Things to know. Inpatient mental health care in a psychiatric hospital is limited to 190 days in a lifetime.
Why are hospitals required to make public charges?
Hospitals are required to make public the standard charges for all of their items and services (including charges negotiated by Medicare Advantage Plans) to help you make more informed decisions about your care.
Who approves your stay in the hospital?
In certain cases, the Utilization Review Committee of the hospital approves your stay while you’re in the hospital.
How many people are on Medicare in 2019?
In 2019, over 61 million people were enrolled in the Medicare program. Nearly 53 million of them were beneficiaries for reasons of age, while the rest were beneficiaries due to various disabilities.
What is Medicare inpatient?
Hospital inpatient services – as included in Part A - are the service type which makes up the largest single part of total Medicare spending. Medicare, however, has also significant income, which amounted also to some 800 billion U.S. dollars in 2019.
Which state has the most Medicare beneficiaries?
With over 6.1 million, California was the state with the highest number of Medicare beneficiaries . The United States spent nearly 800 billion U.S. dollars on the Medicare program in 2019. Since Medicare is divided into several parts, Medicare Part A and Part B combined were responsible for the largest share of spending.
What is Medicare 2020?
Research expert covering health, pharma & medtech. Get in touch with us now. , May 15, 2020. Medicare is a federal social insurance program and was introduced in 1965. Its aim is to provide health insurance to older and disabled people. In 2018, 17.8 percent of all people in the United States were covered by Medicare.
How many hospitals lose accreditation?
Typically, 10 to 15 (0.6 to 0.8 percent) of the 1,800 hospitals surveyed each year by the Joint Commission either lose their accreditation or close voluntarily. The trend over the past few years shows an increase in this percentage. Hospitals that lose accreditation can and many do apply for certification from HCFA in order to stay in the Medicare program; however, the number of hospitals that lose accreditation and subsequently are certified is not currently available from HCFA's survey and certification data system. There are also cases in which hospitals are decertified by HCFA but retain Joint Commission accreditation. Generally, 1 to 2 percent of the approximately 800 hospitals inspected for HCFA each year by the state survey agencies are decertified involuntarily [9 in fiscal year (FY) 1987, 20 in FY 1986, and 8 in FY 1985] and most are recertified within a short time. Past comparisons of state surveyor and Joint Commission surveyor findings in the same facilities, however, have found low levels of agreement on specific deficiencies (DHHS, 1988).
What are the three aspects of patient care?
In 1966, at the time the Conditions of Participation were first drafted, Donabedian (1966) identified three aspects of patient care that could be measured in assessing the quality of care: structure, process, and outcome . Theoretically, structure, process, and outcome are related, and, ideally, a good structure for patient care (e.g., safe and sanitary building, necessary equipment, qualified personnel, and properly organized staff) increases the likelihood of a good process of patient care (e.g., the right diagnosis and best treatment available), and a good process increases the likelihood of a good outcome (e.g., the highest health status possible) (Donabedian, 1988).1
What is deemed status in Medicare?
Since 1965, under authority of Section 1865 of the Social Security Act, hospitals accredited by the Joint Commission on the Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (Joint Commission) or the American Osteopathic Association (AOA) have been automatically “deemed” to meet all the health and safety requirements for participation except the utilization review requirement, the psychiatric hospital special conditions, and the special requirements for hospital providers of long term care. As a result of this deemed status provision, most hospitals participating in Medicare do so by meeting the standards of a private body governed by representatives of the health providers themselves (i.e., the Joint Commission or the AOA). Both the federal conditions and the Joint Commission standards also require hospitals to be licensed by their states. (A more detailed discussion of the Conditions of Participation and deemed status is provided in Volume II, Chapter 7, from which much of the information in this chapter was taken. Options covering the Conditions of Participation program, and their respective implications, considered by the committee in developing its conclusions on the certification and accreditation of hospitals are delineated in the Volume II chapter.)
Who is responsible for health and safety regulations in hospitals?
Federal responsibility for applying health and safety regulations in hospitals participating in Medicare is delegated, on the one hand, to the Joint Commission, and, on the other hand, to the state survey agencies. Since 1972, HCFA has been required to have the state agencies conduct validation surveys of a random sample of accredited hospitals each year to ensure that the Joint Commission's surveying of accredited hospitals is equivalent to state agency surveying of unaccredited hospitals. As of late 1989 HCFA was considering a revision of its sampling methodology to improve the effectiveness of its validation efforts (HCFA, personal communication, 1989). HCFA is also authorized to have state inspectors investigate allegations of substantial deficiencies in accredited hospitals. HCFA concludes in its annual reports that the two systems are equivalent, because the percentage of Joint Commission-accredited hospitals found out of compliance with one or more Conditions of Participation (including about 400 a year inspected on the basis of complaints) has been roughly equal to the percentage of unaccredited hospitals found out of compliance (DHHS, 1988).
Does Medicare have a PRO program?
Although the Office of Survey and Certification and the Office of Medical Review, which administers the Utilization and Quality Control Peer Review Organization (PRO) program, are both in HSQB and deal with the same Medicare hospitals, they do not interact in terms of information sharing or coordinated action. At the state level, numerous obstacles exist (e.g., legal and administrative) to deter information sharing about a facility or practitioner between a Medicare PRO and the state survey agency.
Can a hospital be certified by the HCFA?
In HCFA's state certification process, a hospital cannot be certified if it fails to meet any Condition of Participation, but decisions on compliance with conditions and standards are left to the judgment of the surveyors, as are decisions concerning the adequacy of plans of correction. If inspectors decide to initiate decertification procedures, hospitals may and usually do remedy the deficiencies in time to avoid actual decertification. Facilities also have extensive legal due process protections that serve as a deterrent to enforcement attempts, as do the difficulties encountered by the surveyors in documenting quality problems (Vladeck, 1988).
Is Medicare condition of participation consistent with quality assurance?
The study committee concluded that the Medicare Conditions of Participation and procedures for enforcing them should become a more significant component of and be more consistent with the overall federal quality assurance effort. This position was taken after weighing other options and their respective implications, many of which are stated in Volume II, Chapter 7.
How much is the Medicare shortfall?
This includes a shortfall of $56.8 billion for Medicare and $19.0 billion for Medicaid. For Medicare, hospitals received payment of only 87 cents for every dollar spent by hospitals caring for Medicare patients in 2019. For Medicaid, hospitals received payment of only 90 cents for every dollar spent by hospitals caring for Medicaid patients in 2019.
How are Medicare and Medicaid payments reported?
Gross charges for these services are then translated into costs. This is done by multiplying each hospital’s gross charges by each hospital’s overall cost-to-charge ratio, which is the ratio of a hospital’s costs (total expenses exclusive of bad debt) to its charges (gross patient and other operating revenue).
What is underpayment in healthcare?
Underpayment occurs when the payment received is less than the costs of providing care, i.e., the amount paid by hospitals for the personnel, technology and other goods and services required to provide hospital care is more than the amount paid to them by Medicare or Medicaid for providing that care.
Is Medicare voluntary for hospitals?
Hospital participation in Medicare and Medicaid is voluntary. However, as a condition for receiving federal tax exemption for providing health care to the community, not-for-profit hospitals are required to care for Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries. Also, Medicare and Medicaid account for more than 60 percent of all care provided by hospitals.
Is Medicare underpayment voluntary?
Hospital participation in Medicare and Medicaid is voluntary. However, as a condition for receiving federal tax ...
Is Medicare and Medicaid bridging the gaps?
Bridging the gaps created by government underpayments from Medicare and Medicaid is only one of the benefits that hospitals provide to their communities. In a separate fact sheet, AHA has calculated the cost of uncompensated hospital care (financial assistance and bad debt), which also are benefits to the community.
How Much Do Hospitals Lose On Medicare Patients?
Hospital administrators, who include some of the country’s most renowned medical centers, will lose 1% of their Medicare funding for one year.
What Percent Of Medicare Is Spent On Last Year Of Life?
Nearly 30 percent of the Medicare budget is spent on patients nearing the end of their lives, while more than half is spent on patients who die within two months of receiving Medicare.
How Much Of Medicare Is Spent On End Of Life Care?
As a major source of payments for Medicare, beneficiaries aged 50 or older have significant expenses in the last year of life. Estimates vary significantly depending on the methods and assumptions used.
How Does Medicare Bill For Hospice Services?
Using CPT E/M code, only attenders not employed by hospices can bill Medicare Part B for hospice services. In the case where the hospice physician serves as the attending physician, Medicare pays hospice charges for everything related to a terminal condition.
Does Medicare Penalize Hospitals For Readmissions?
From the start of Medicare’s hospital readmissions incentive in the 1970s, hospitals have been fined heavily for excessive discharge rates. Medicare will end the incentive in mid-2010 with most of America’s hospitals receiving much less.
What Type Of Patient Is Most Likely Under Hospice Care?
For patients at risk of dying if their natural course of treatment continues, hospice provides them with medical care so they can live as long as possible.
Where Do Most Patients Receive Hospice Care?
There are in addition hospice facilities for individuals receiving medical care within hospitals, nursing homes, assisted living facilities, and dedicated hospice.
How many days can you use Medicare in one hospital visit?
Medicare provides an additional 60 days of coverage beyond the 90 days of covered inpatient care within a benefit period. These 60 days are known as lifetime reserve days. Lifetime reserve days can be used only once, but they don’t have to be used all in one hospital visit.
How much does Medicare Part A cost in 2020?
In 2020, the Medicare Part A deductible is $1,408 per benefit period.
How long does Medicare Part A deductible last?
Unlike some deductibles, the Medicare Part A deductible applies to each benefit period. This means it applies to the length of time you’ve been admitted into the hospital through 60 consecutive days after you’ve been out of the hospital.
What is the Medicare deductible for 2020?
Even with insurance, you’ll still have to pay a portion of the hospital bill, along with premiums, deductibles, and other costs that are adjusted every year. In 2020, the Medicare Part A deductible is $1,408 per benefit period.
What is Medicare Part A?
Medicare Part A, the first part of original Medicare, is hospital insurance. It typically covers inpatient surgeries, bloodwork and diagnostics, and hospital stays. If admitted into a hospital, Medicare Part A will help pay for:
How long do you have to work to qualify for Medicare Part A?
To be eligible, you’ll need to have worked for 40 quarters, or 10 years, and paid Medicare taxes during that time.
Does Medicare cover hospital stays?
Medicare Part A can help provide coverage for hospital stays. You’ll still be responsible for deductibles and coinsurance. A stay at the hospital can make for one hefty bill. Without insurance, a single night there could cost thousands of dollars. Having insurance can help reduce that cost.
Why do hospitals charge more?
Some hospitals argue they charge more because they deliver better care , and there does seem to be some association. “What we see is quality and the ability to charge high prices are intrinsically related,” said Craig Garthwaite, a health economist at the Kellogg School of Management at Northwestern University, who says some hospitals may be taking the extra money to invest in ways of improving quality.
Which hospital is the most expensive in Massachusetts?
Mass General Brigham, formerly Partners Healthcare, was the most expensive system in Massachusetts, but Massachusetts General, one of its premier hospitals, charged private insurers nearly three times what Medicare paid in 2016 through 2018, compared to roughly two times for the system’s Newton-Wellesley Hospital, according to the study.
Can hospitals be shuttered if Medicare is lower?
Hospitals warn that they might not be able to function if they were paid Medicare rates. “There is certainly a cost shift, because the government knowingly underpays,” said Tom Nickels, an executive vice president for the American Hospital Association, a trade group. He warned that hospitals would lose billions of dollars in revenue. Some could be shuttered if forced to operate at lower Medicare payments.
Do employers pay more than Medicare?
A study shows that employers in many states are paying much more than Medicare prices for hospital services. The study, which exposes the aggressive pricing by mega-hospital systems that have gained enormous market power through widespread consolidation, is sure to kick-start the debate over the U.S. health care system and the need to overhaul it.
Is Parkview Health the most expensive insurance?
In Indiana, Parkview Health, based in Fort Wayne, also remained one of the most expensive, charging private insurers in 2018 three times what Medicare paid for an overnight hospital stay and more than four times the Medicare rate for outpatient care. Employers pressured Anthem, the state’s largest insurer, to force Parkview to lower prices by threatening to drop it from the plan’s network.
How is uncompensated care calculated?
Uncompensated care is first calculated on a hospital by hospital basis. Bad debt and charity care are reported as charges in the AHA Annual Survey. These two numbers are added together and then multiplied by the hospital's cost-to-charge ratio, or the ratio of total expenses to gross patient and other operating revenue.
How does a hospital provide financial assistance?
Hospitals provide varying levels of financial assistance, which must be budgeted for and financed by the hospital depending on the hospital’s mission, financial condition, geographic location and other factors. Hospitals have processes in place to identify who can and cannot afford to pay, in advance of billing, in order to anticipate whether the patient’s care needs to be funded through an alternative source. Hospitals also continue efforts to identify patients who are unable to pay during the billing and any collection process. Depending on a variety of factors, including whether a patient completes an application for financial assistance, care may be classified as either financial assistance or bad debt. Bad debt is often generated by medically indigent and/or uninsured patients, making the distinctions between the two categories arbitrary at best.
Why combine bad debt and financial assistance to arrive at the hospital’s total uncompensated care cost?
Combining bad debt and financial assistance to arrive at the hospital’s total uncompensated care cost allows for comparability across hospitals.
Is uncompensated care a charge?
Uncompensated care data are sometimes expressed in terms of hospital charges, but charge data can be misleading, particularly when comparisons are being made among types of hospitals, or hospitals with very different payer mixes. For this reason, the AHA data on hospitals’ uncompensated care are expressed in terms of costs not charges.
Does AHA include Medicaid?
For this reason, the AHA data on hospitals’ uncompensated care are expressed in terms of costs not charges. It should be noted that the uncompensated care figures do not include Medicaid or Medicare underpayment costs.
