This premium is paid by enrollees age 65 and over who are not otherwise eligible for benefits under Medicare Part A (hereafter known as the “uninsured aged”) and by certain individuals with disabilities who have exhausted other entitlement. The monthly Part A premium for the 12 months beginning January 1, 2021 for these individuals will be $471.
Who qualifies for premium-free Medicare Part A?
If you are over 65 and qualify for Medicare, you are eligible for premium-free Part A if you or your spouse have at least 40 calendar quarters of work in a job where you paid payroll taxes to Social Security, or are eligible for Railroad Retirement benefits.
Will I have to pay for part an of Medicare?
Medicare Part A, which covers hospitalization, is free for anyone eligible for Social Security, even if they have not claimed benefits yet. If enrolled in Part B but not yet collecting Social Security benefits, you’ll be billed quarterly by Medicare.
Is there a deductible for Medicare Part A?
The Qualified Medicare Beneficiary Program pays your premiums, deductibles, coinsurance and copayments for Parts A and B and Medicare Advantage plans. For those in original Medicare, it operates like a Medigap plan. In most states, you can qualify if your gross monthly income in 2021 doesn’t exceed $1,094 for individuals or $1,472 for couples.
What do Medicare Parts A, B, C, D mean?
Medicare parts A and B together are known as original Medicare. Medicare Part C plans cover everything that original Medicare does and often include additional coverage options. Medicare Part D is prescription drug coverage.
Does everyone get Medicare Part A for free?
Most people get Part A for free, but some have to pay a premium for this coverage. To be eligible for premium-free Part A, an individual must be entitled to receive Medicare based on their own earnings or those of a spouse, parent, or child.
Why would a patient not have Medicare Part A?
Unless they meet other requirements, such as a qualifying disability, they cannot get Medicare Part A benefits before this age. Some people may be 65 but ineligible for premium-free Medicare Part A. For instance, a person who did not work for 40 quarters and pay Medicare taxes would not be eligible.
Why do I need Medicare Part A?
Medicare Part A (Hospital Insurance) Part A helps cover your inpatient care in hospitals. Part A also includes coverage in critical access hospitals and skilled nursing facilities (not custodial or long-term care). It also covers hospice care and home health care. You must meet certain conditions to get these benefits.
Can you just get Medicare Part A only?
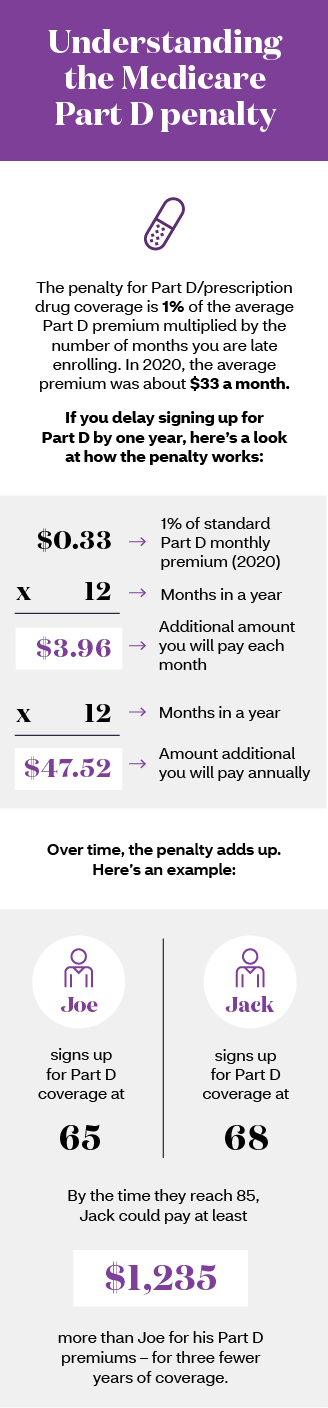
Just the Essentials... Eligible people can choose to join Medicare Part A only, but it covers only hospital stay expenses. Delayed enrollment in Part A can mean a 10% increase to your premium when you do sign up. If you sign up for Part A only, a similar penalty applies to delayed enrollment in Part B.
What happens if you don't enroll in Medicare Part A at 65?
If you don't have to pay a Part A premium, you generally don't have to pay a Part A late enrollment penalty. The Part A penalty is 10% added to your monthly premium. You generally pay this extra amount for twice the number of years that you were eligible for Part A but not enrolled.
What is the difference between Medicare Part A and Part B?
If you're wondering what Medicare Part A covers and what Part B covers: Medicare Part A generally helps pay your costs as a hospital inpatient. Medicare Part B may help pay for doctor visits, preventive services, lab tests, medical equipment and supplies, and more.
Does Medicare Part A cover 100 percent?
Most medically necessary inpatient care is covered by Medicare Part A. If you have a covered hospital stay, hospice stay, or short-term stay in a skilled nursing facility, Medicare Part A pays 100% of allowable charges for the first 60 days after you meet your Part A deductible.
Does Medicare Part A cover surgery?
Medicare Part A hospital insurance covers inpatient hospital care, skilled nursing facility, hospice, lab tests, surgery, home health care.
How does Medicare Part A work?
Part A covers inpatient hospital stays, care in a skilled nursing facility, hospice care, and some home health care. coverage if you or your spouse paid Medicare taxes for a certain amount of time while working. This is sometimes called "premium-free Part A." Most people get premium-free Part A.
Do you have to pay for Medicare Part B?
Part B premiums You pay a premium each month for Part B. Your Part B premium will be automatically deducted from your benefit payment if you get benefits from one of these: Social Security. Railroad Retirement Board.
What is Medicare Part A deductible for 2021?
Medicare Part A Premiums/Deductibles The Medicare Part A inpatient hospital deductible that beneficiaries will pay when admitted to the hospital will be $1,484 in 2021, an increase of $76 from $1,408 in 2020.
Do you have to enroll in Medicare Part B every year?
I Want to Keep My Current Medicare Coverage It works the same whether you have Original Medicare (Parts A and B), a Medicare Advantage plan (Part C) or a Medicare prescription drug plan (Part D). You simply do nothing and your current coverage choices stay in place for another year.
What is Medicare Part A?
Medicare Part A, or Medicare hospital coverage, pays for care at a hospital, skilled nursing facility, or nursing home, and for home health services. Enrollees who paid Medicare taxes during their working years or people whose spouse paid these taxes don’t pay premiums for Medicare Part A once they’re 65 years old.
Why doesn't Medicare cover my expenses?
The three reasons why Medicare Part A might not cover something are: 1 . General federal and state laws.
How much is the deductible for Medicare in 2021?
People insured under Medicare still have to pay deductibles, too. For 2021, deductibles for inpatient hospital stays are $1,484. This payment covers the first 60 days of a patient's stay in the hospital. Copays kick in after the 61st day. Patients are responsible for a $371 copay for the 61st to 90th day in the hospital. 9 .
How long do you have to be on Medicare before you turn 65?
You may, for example, be enrolled automatically in Medicare Part A and Medicare Part B if you: 11 . Have received benefits from Social Security or the Railroad Retirement Board for at least four months before you turn 65. Have received Social Security benefits for at least 24 months.
How long do you have to be on Social Security to get Medicare?
Have received Social Security benefits for at least 24 months. Have amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also called Lou Gehrig's disease. You will automatically get Medicare Parts A and B when your disability benefits start.
How old do you have to be to get Medicare?
In general, you're eligible for Medicare Part A if you meet the citizenship and residency requirements and you: 10. Are age 65 or older. Get disability benefits from Social Security or the Railroad Retirement Board for at least 25 months.
Does Medicare cover custodial care?
Local Medicare claims processors’ assessment of whether a service is medically necessary. One example of a service Medicare does not usually cover is custodial care in a skilled nursing facility—help with basic activities of daily living, such as getting dressed, bathing, and eating—if it’s the only care you need.
What is national coverage?
National coverage decisions made by Medicare about whether something is covered. Local coverage decisions made by companies in each state that process claims for Medicare. These companies decide whether something is medically necessary and should be covered in their area.
Is Medicare Advantage the same as Original Medicare?
What's covered? Note. If you're in a Medicare Advantage Plan or other Medicare plan, your plan may have different rules. But, your plan must give you at least the same coverage as Original Medicare. Some services may only be covered in certain settings or for patients with certain conditions.
How much is Medicare Part A monthly?
Part A monthly premium. 40 quarters or more. $0. 30–39 quarters. $259. fewer than 30 quarters. $471. Of course, a free premium doesn’t mean you won’t pay anything for hospital care. There are other costs involved with Medicare Part A, several of which have increased for 2021.
What is Medicare Part A 2021?
What You Need to Know About Medicare Part A in 2021. Medicare Part A is the hospital coverage portion of Medicare. For many people who worked and paid Medicare taxes, Medicare Part A is free of charge, starting when you reach age 65.
How long does Medicare cover inpatient hospital care?
After 90 days of inpatient hospital care, you enter what Medicare calls lifetime reserve days. Medicare covers 60 lifetime reserve days in total over your lifetime. After you meet your lifetime reserve days, you’re expected to pay all costs.
How much is a deductible for Medicare 2021?
A deductible is the amount you pay out of pocket before Part A starts covering the costs of your care. In 2021, you’ll pay $1,484 for each benefit period. A benefit period starts the day you’re admitted as an inpatient to a hospital, skilled nursing facility, or any other inpatient facility.
How long does it take to get Medicare Part A?
For the most part, signing up for Medicare Part A depends on when you turn age 65. You have a 7-month time period during which you can enroll. You can enroll as early as 3 months before your birth month, during your birth month, and up to 3 months after your 65th birthday.
How old do you have to be to get Medicare?
Typically, you must be age 65 to enroll in Medicare. To receive Medicare Part A free of charge, you must meet the following criteria: You’ve worked and paid Medicare taxes at least 40 quarters or roughly 10 years. If your spouse worked, but you did not, you can still qualify.
Do all people on Medicare have to be enrolled in Medicare?
While the Social Security Administration automatically enrolls many beneficiaries in Medicare parts A and B, not all people are automatically enrolled. There are several ways to accomplish this if you or a loved one is approaching age 65 when your open enrollment period occurs.
What is Medicare Part A?
While Part B generally covers doctor's appointments and preventive care, Medicare Part A is hospital insurance and generally covers:
What happens after Medicare coverage ends?
After your coverage ends, you’ll get a special enrollment period, at which time you can enroll in Medicare and choose plans without late penalties. (If you were to enroll and keep your employer coverage, your Medicare would be secondary and your employer coverage would be primary.)
What is inpatient hospital care?
This covers hospital services you get when you’re admitted to a hospital on doctor’s orders, including semiprivate rooms, meals, general nursing and drugs for inpatient treatments. The hospital must accept Medicare. Medicare Part A covers inpatient hospital care in a variety of facilities, including: Acute care hospitals.
How much is the deductible for hospital care in 2021?
In 2021, that deductible for hospital care is $1,484 per benefit period, which starts on the day you’re admitted and ends when you haven’t received inpatient hospital care or care in a skilled nursing facility for 60 days. If your hospital stay exceeds 60 days, you'll have to start paying coinsurance.
How long do you have to wait to get Medicare?
So, for example, if you were to realize on April 1 that you needed to sign up for Medicare during the general enrollment period, you'd have to wait over a year to actually get that coverage — even if you signed up as soon as possible during the general enrollment period the following January.
How old do you have to be to qualify for Medicare?
Generally, you're eligible for Medicare Part A if you meet one of the following requirements, according to Medicare: You are age 65 or older. You've gotten disability benefits from Social Security or the Railroad Retirement Board for at least 25 months.
What is hospice care?
Hospice is the end-of-life care you receive if you're terminally ill, for example. Covered services include care from doctors, nurses and aides; medical equipment (such as wheelchairs); certain prescription drugs; occupational therapy; physical therapy; and grief and loss counseling for you and your family.
Why does Bill have Medicare?
Example: Bill has Medicare coverage because of permanent kidney failure. He also has group health plan coverage through the company he works for. His group health coverage will be his primary payer for the first 30 months after Bill becomes eligible for Medicare. After 30 months, Medicare becomes the primary payer.
How long is a person eligible for Medicare?
Everyone eligible for Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) benefits is also eligible for Medicare after a 24-month qualifying period. The first 24 months of disability benefit entitlement is the waiting period for Medicare coverage. During this qualifying period for Medicare, the beneficiary may be eligible for health insurance ...
How long can you keep Medicare after you return to work?
Answer: As long as your disabling condition still meets our rules, you can keep your Medicare coverage for at least 8 ½ years after you return to work. (The 8 ½ years includes your nine month trial work period.) Question: I have Medicare hospital Insurance (Part A) and medical insurance (Part B) coverage.
What is a large group health plan?
If the employer has 100 employees or more, the health plan is called a large group health plan. If you are covered by a large group health plan because of your current employment or the current employment of a family member, Medicare is the secondary payer (see example below).
How to order a publication from Medicare?
Answer: You can view, print, or order publications online or by calling 1-800-MEDICARE (1-800-633-4227). The fastest way to get a publication is to use our search tool and then view and print it. If you order online or through 1-800-MEDICARE, you will receive your order within 3 weeks. The link to search publications is at: http://www.medicare.gov/Publications/home.asp
Is Medicare a secondary payer?
Answer: Medicare may be the "secondary payer" when you have health care coverage through your work. See the information under "Coordination of Medicare and Other Coverage for Working Beneficiaries with Disabilities" about when Medicare is a "secondary payer or primary payer".
Does Medicare pay for non-VA hospital?
If the VA authorizes services in a non-VA hospital, but doesn't pay for all of the services you get during your hospital stay, then Medicare may pay for the Medicare-covered part of the services that the VA does not pay for. Example: John, a veteran, goes to a non-VA hospital for a service that is authorized by the VA.
What is A13 in Medicare?
A13: Again, this is a decision to be made by the hospital. If a hospital decides that it wants the special Medicare reimbursement allowing for payment of Medicare bad debts, however, then it must engage in uniform collection efforts for all patients, both Medicare and non-Medicare.
Does Medicare pay for bad debt?
A9: Yes. In the case of Medicare patients generally, the program reimburses a hospital for a percentage of the “bad debt” of a Medicare beneficiary (i.e., unpaid deductibles or coinsurance) as long as the hospital sends a bill to a patient and engages in reasonable, consistent collection efforts.
Does Medicare require documentation for indigency determination?
For Medicare patients, however, if a provider wants to claim Medicare bad debt reimbursement CMS does require documentation to support the indigency determination. To claim Medicare bad debt reimbursement, the provider must follow the guidance stated in the Provider Reimbursement Manual. A hospital should examine a patient’s total resources, which could include, but are not limited to, an analysis of assets, liabilities, income and expenses and any extenuating circumstances that would affect the determination. The provider should document the method by which it determined the indigency and include all backup information to substantiate the determination. Medicare also requires documentation where a collection effort is made. The effort should be documented in the patient’s file with copies of the bill(s), follow-up letters, and reports of telephone and personal contacts. In the case of a dually-eligible patient (i.e., a patient entitled to both Medicare and Medicaid), the hospital must include a denial of payment from the State with the bad debt claim.
Can a hospital write off uncollected medical bills?
A15: Yes. If a hospital does not want to collect, but wants to write off the uncollected debt regardless of income level, as “charity care” or as a “courtesy allowance,” Medicare rules don’t prohibit that, but Medicare will also not reimburse these amounts.