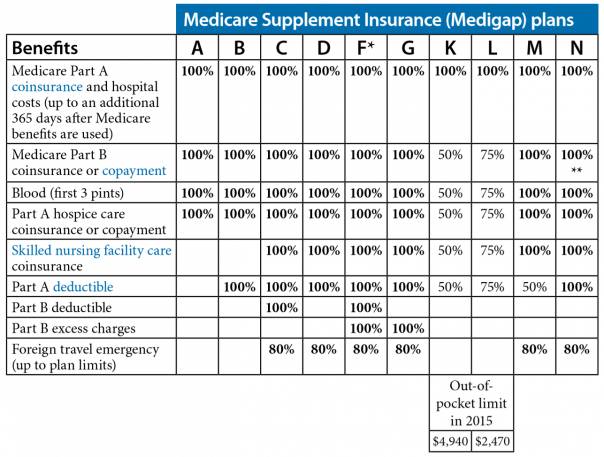
For most services, Part B medical insurance pays only 80% of what Medicare decides is the approved charge for a particular service or treatment. You are responsible for paying the other 20% of the approved charge, called your coinsurance amount.
How much does Medicare pay for Medicare Part B?
Medicare uses the modified adjusted gross income reported on your IRS tax return from 2 years ago. This is the most recent tax return information provided to Social Security by the IRS. The standard Part B premium amount in 2020 is $144.60.
What is the medical loss ratio (MLR) requirement for Medicare Advantage?
One of the earliest reforms of the ACA for the commercial market was the medical loss ratio (MLR) requirement. 1 Effective January 1, 2011, carriers must meet an 85% MLR for large group and an 80% MLR for individual and small group. Three years later, the MLR requirement 2 for Medicare Advantage (MA) is now here.
What does Part B of the Medicare card cover?
Part B covers things like: Clinical research Ambulance services Durable medical equipment (DME) Mental health Inpatient Getting a second opinion before surgery Limited outpatient prescription drugs
How much does Medicare Part B cost in 2020?
In 2020, you pay $198 ($203 in 2021) for your Part B Deductible [glossary]. After you meet your deductible for the year, you typically pay 20% of the Medicare-approved amount for these: Most doctor services (including most doctor services while you're a hospital inpatient) Outpatient therapy; Durable medical equipment (DME) [Glossary]
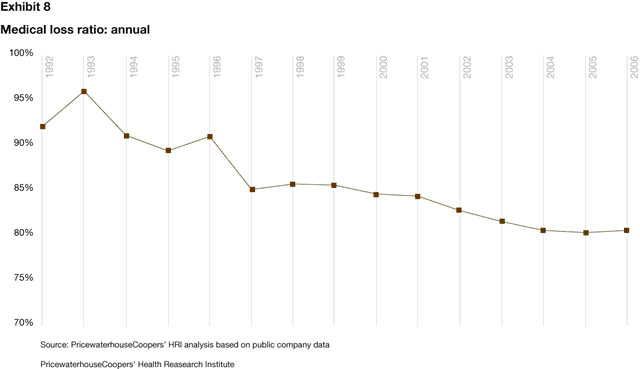
What is a good medical loss ratio?
An insurer's MLR is determined by adding total paid medical service claims and all quality improvement activities together, then dividing that number by the total premium revenue minus all allowable deductions. As insurers are likely already aware, a good MLR is 80 or 85 percent (depending on the organization size).
What is the MLR threshold?
In general, the higher the MLR, the more value a policyholder receives for his or her premium dollar. The ACA requires an annual, minimum 80% MLR for individual and small group insurance plans, and an annual, minimum 85% MLR for large group plans.
How is medical loss ratio determined?
MLR is calculated by dividing the cost of medical services (incurred claims paid, plus expenses for health care quality improvement activities) for a period of time by the premium collected, minus federal or state taxes and licensing and regulatory fees, for the same period.
What is a minimum loss ratio?
The minimum medical loss ratio requirement provides that, beginning with 2011, health insurers must spend a minimum percentage (80 percent in the individual and small group market and 85 percent in the large group market) of their adjusted premium revenues on health care claims and quality improvement expenses.
Will there be a MLR rebate in 2022?
We find that insurers estimate they will issue a total of about $1 billion in MLR rebates across all commercial markets in 2022, using preliminary data reported by insurers to state regulators and compiled by Mark Farrah Associates. Final rebate data will be available later this year.
How do I calculate my MLR rebate?
In its simplest form, MLR rebates are calculated by taking the amount spent on medical claims and qualified health quality initiatives and dividing it by the premiums collected, minus certain federal and state taxes and fees.
Who is subject to MLR?
MLR Standards under the ACA The Medical Loss Ratio provision of the ACA requires most insurance companies that cover individuals and small businesses to spend at least 80% of their premium income on health care claims and quality improvement, leaving the remaining 20% for administration, marketing, and profit.
What is a bad medical loss ratio?
Large-group insurers must do the same for loss ratios less than 85 percent, or when overhead and profits average more than 15 percent of premium dollars based on a three-year average. The ACA's MLR rule took effect in 2011.
Medical Loss Ratios Explained
Lorraine Roberte is an insurance writer for The Balance. As a personal finance writer, her expertise includes money management and insurance-related topics. She has written hundreds of reviews of insurance products.
Definition of a Medical Loss Ratio
An insurer’s medical loss ratio is generally the amount it spends on claims and other expenses that improve the quality of its healthcare divided by the net premiums received from the participants enrolled in its health plans: 2 MLR = Claims costs + quality improvement expenditures ÷ premiums received
How the Medical Loss Ratio Works
The minimum medical loss ratio requirements are designed to hold insurance providers accountable for how they spend health insurance premiums, and to keep health insurance costs down. More specifically, these requirements attempt to put a cap on insurance companies’ profits and administrative costs.
What the Medical Loss Ratio Means for You
If your healthcare insurance provider fails to meet their minimum required medical loss ratio, you or your employer may receive a rebate. Rebates may be issued in one of the following ways:
What is Part B?
Part B covers 2 types of services. Medically necessary services: Services or supplies that are needed to diagnose or treat your medical condition and that meet accepted standards of medical practice. Preventive services : Health care to prevent illness (like the flu) or detect it at an early stage, when treatment is most likely to work best.
What are the factors that determine Medicare coverage?
Medicare coverage is based on 3 main factors 1 Federal and state laws. 2 National coverage decisions made by Medicare about whether something is covered. 3 Local coverage decisions made by companies in each state that process claims for Medicare. These companies decide whether something is medically necessary and should be covered in their area.
What does Medicare Part B cover?
Medicare Part B helps cover medical services like doctors' services, outpatient care, and other medical services that Part A doesn't cover. Part B is optional. Part B helps pay for covered medical services and items when they are medically necessary. Part B also covers some preventive services like exams, lab tests, ...
What is Part B insurance?
Part B also covers some preventive services like exams, lab tests, and screening shots to help prevent, find, or manage a medical problem. Cost: If you have Part B, you pay a Part B premium each month. Most people will pay the standard premium amount.
CY 2014 MLR
Public Use File for CY 2014 (ZIP) - This release contains data submitted by MAOs, Part D sponsors, and cost plans in their CY 2014 MLR reports.
MLR Reporting Q&As
CMS Guidance Regarding MLR Reporting Requirements: Q&A (PDF) (last updated: 10/19/2015) Medical Loss Ratio and Expenditures Related to COVID-19 Permissive Actions – Questions and Answers (PDF) (dated: 7/10/2020)
What is Medicare Part B?
Some people automatically get. Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) Part B covers certain doctors' services, outpatient care, medical supplies, and preventive services. , and some people need to sign up for Part B. Learn how and when you can sign up for Part B. If you don't sign up for Part B when you're first eligible, ...
How much is Part B deductible in 2021?
Part B deductible & coinsurance. In 2021, you pay $203 for your Part B. deductible. The amount you must pay for health care or prescriptions before Original Medicare, your prescription drug plan, or your other insurance begins to pay. . After you meet your deductible for the year, you typically pay 20% of the.
What is the standard Part B premium for 2021?
The standard Part B premium amount in 2021 is $148.50. Most people pay the standard Part B premium amount. If your modified adjusted gross income as reported on your IRS tax return from 2 years ago is above a certain amount, you'll pay the standard premium amount and an Income Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA). IRMAA is an extra charge added to your premium.
How much do you pay for Medicare after you meet your deductible?
After you meet your deductible for the year, you typically pay 20% of the. Medicare-Approved Amount. In Original Medicare, this is the amount a doctor or supplier that accepts assignment can be paid. It may be less than the actual amount a doctor or supplier charges.
What happens if you don't get Part B?
Your Part B premium will be automatically deducted from your benefit payment if you get benefits from one of these: Social Security. Railroad Retirement Board. Office of Personnel Management. If you don’t get these benefit payments, you’ll get a bill. Most people will pay the standard premium amount.
Do you pay Medicare premiums if your income is above a certain amount?
If your modified adjusted gross income is above a certain amount, you may pay an Income Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA). Medicare uses the modified adjusted gross income reported on your IRS tax return from 2 years ago.
What is the key to properly reporting MLRs?
Clearly identifying and supporting fraud reduction expenses, healthcare quality expenses, and federal and state taxes and licensing or regulatory fees are keys to properly reporting MLRs and minimizing MLR rebates.
Do financial statements show the MLR formula?
In addition, the financial statements do not clearly show certain components of the MLR formula. For example, MA/PDP costs related to improving health care quality expenses or taxes and fees are not reported separately, and the Part D federal reinsurance subsidy is not separately identified.
