Is Medicare funded by state or government?
That means Medicare is primarily funded by taxpayers through general federal tax revenue, payroll tax revenue from the Medicare tax, and premiums paid by its beneficiaries. How Medicare is funded Funding for Medicare comes from the Medicare Trust Funds, which are two separate trust fund accounts held by the U.S. Treasury:
What are the four Medicare savings programs?
- Most MSPs pay Medicare Part B premiums and some help with additional Part A and B costs
- MSPs don’t cover costs from Medicare Part C plans (Medicare Advantage)
- Medicare beneficiaries who qualify for an MSP also receive Medicare Extra Help to help pay for prescription drugs
Is Medicare the same in every state?
To determine the county with the worst health insurance coverage in every ... using the same definition. We selected the under 65 age group because Americans become eligible for Medicare at ...
What is Medicaid buy in program?
- Be a resident of New York State;
- Be at least 16 years of age (coverage up to 65 years of age);
- Have a disability as defined by the Social Security Administration;
- Be engaged in paid work (includes part-time and full-time work);
- Have a gross income that may be as high as $65,436 for an individual and $88,140 for a couple; and
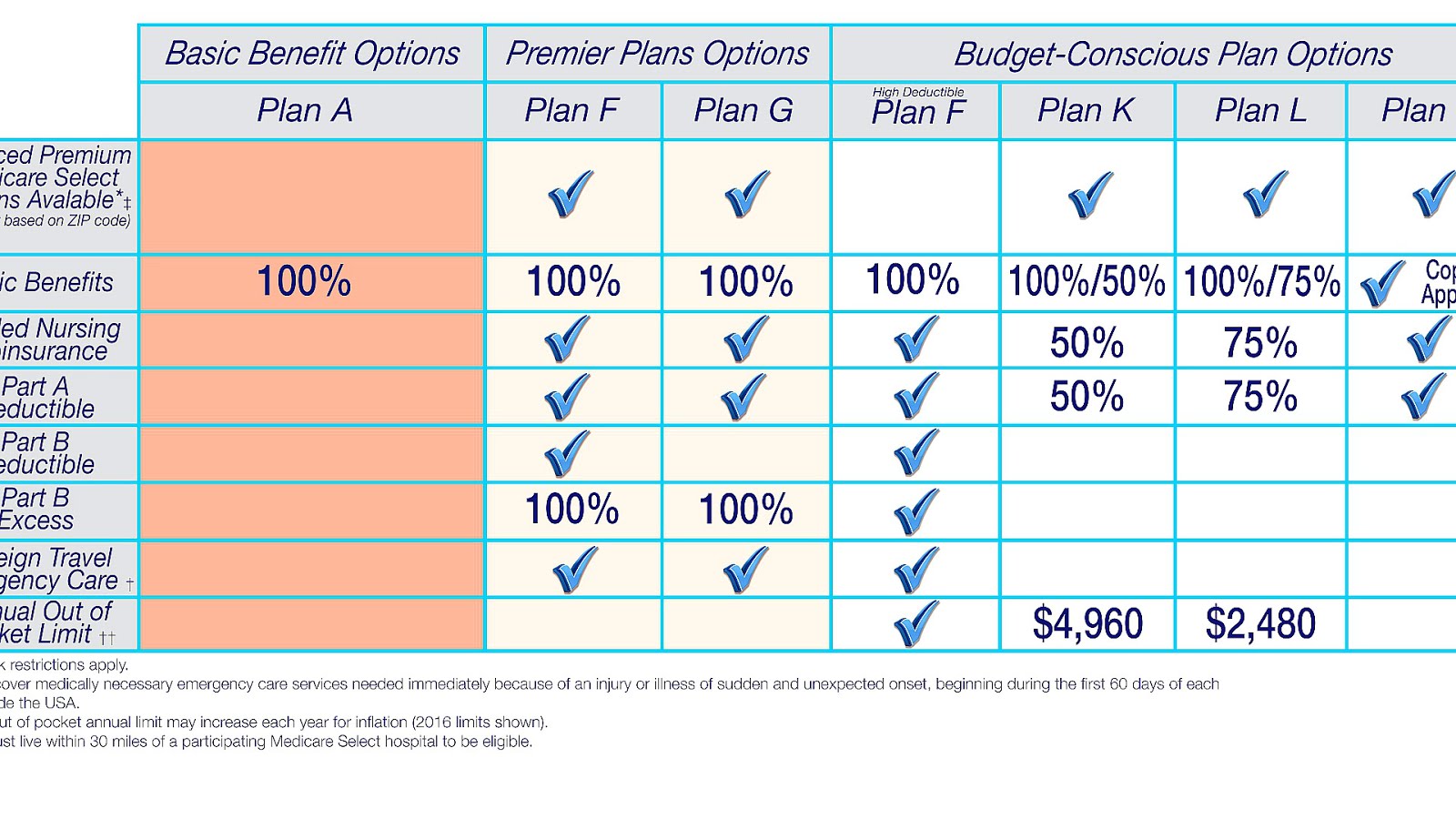
Is Medicare Part A buy-in available in all states?
According to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), the Medicare buy-in program enables states to help more than 10 million Americans pay their monthly Medicare Part B premiums and more than 700,000 people pay their Part A premiums. All states offer buy-in for Part B, but fewer states offer Part A buy-in.
What is a buy-in program?
The Medicaid “buy-in” program is the nickname used to collectively refer to the Medicaid eligibility groups that serve workers with disabilities who are earning income and against whom states may charge premiums as a condition of Medicaid eligibility.
Do states pay into Medicare?
Is Medicare funded by the state or federal government? Medicare is a federal program, and as a result, the vast majority of Medicare funding comes from the federal government. However, state governments do make a small contribution for enrollees who qualify for both Medicare and Medicaid.
Where does the money for Medicare go?
How is it funded? Part B covers certain doctors' services, outpatient care, medical supplies, and preventive services. Optional benefits for prescription drugs available to all people with Medicare for an additional charge.
What is a Medicare Part B buy-in?
Q1. What is “buy-in?” States1 “bought in” (paid) the monthly Medicare Part B premiums for over 10 million individuals and Part A premiums for over 700,000 individuals in 2019. All Medicare beneficiaries enrolled in Part B owe a monthly premium for Part B (a minimum of $148.50 in 2021).
What is Social Security buy-in?
The Social Security Act provides that States may enter into an agreement with SSA which permits State welfare agencies to enroll individuals for part B (SMI) coverage and/or “buy-in” for the payment of medical insurance premiums if the individual is a member of a coverage group (eligible for welfare payments under one ...
How does Medicare make money?
Medicare is funded primarily from general revenues (43 percent), payroll taxes (36 percent), and beneficiary premiums (15 percent) (Figure 7). Part A is financed primarily through a 2.9 percent tax on earnings paid by employers and employees (1.45 percent each) (accounting for 88 percent of Part A revenue).
Is Medicare state or federal?
federalMedicare is the federal health insurance program for: People who are 65 or older. Certain younger people with disabilities. People with End-Stage Renal Disease (permanent kidney failure requiring dialysis or a transplant, sometimes called ESRD)
Who funds Original Medicare?
the U.S. TreasuryMedicare is funded through two trust funds held by the U.S. Treasury. Funding sources include premiums, payroll and self-employment taxes, trust fund interest, and money authorized by the government.
Is Medicare about to collapse?
At its current pace, Medicare will go bankrupt in 2026 (the same as last year's projection) and the Social Security Trust Funds for old-aged benefits and disability benefits will become exhausted by 2034.
What would happen if Medicare ended?
Payroll taxes would fall 10 percent, wages would go up 11 percent and output per capita would jump 14.5 percent. Capital per capita would soar nearly 38 percent as consumers accumulated more assets, an almost ninefold increase compared to eliminating Medicare alone.
What will happen when Social Security runs out of money?
Introduction. As a result of changes to Social Security enacted in 1983, benefits are now expected to be payable in full on a timely basis until 2037, when the trust fund reserves are projected to become exhausted.
What is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid?
The difference between Medicaid and Medicare is that Medicaid is managed by states and is based on income. Medicare is managed by the federal government and is mainly based on age. But there are special circumstances, like certain disabilities, that may allow younger people to get Medicare.
Do Medicare reimbursement rates vary by state?
Over the years, program data have indicated that although Medicare has uniform premiums and deductibles, benefits paid out vary significantly by State of residence of the beneficiary. These variations are due in part to the fact that reimbursements are based on local physicians' prices.
Why do doctors not like Medicare Advantage plans?
If they don't say under budget, they end up losing money. Meaning, you may not receive the full extent of care. Thus, many doctors will likely tell you they do not like Medicare Advantage plans because private insurance companies make it difficult for them to get paid for their services.
Does Medicaid pay Medicare premiums?
Medicaid pays Part A (if any) and Part B premiums. Medicaid is liable for Medicare deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments for Medicare-covered items and services. Even if Medicaid doesn't fully cover these charges, the QMB isn't liable for them.
When was the Medicare buy in manual released?
Manual for State Payment of Medicare Premiums (formerly called “State Buy-in Manual”) On September 8, 2020, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) released an updated version of the Manual for State Payment of Medicare Premiums (formerly called “State Buy-in Manual”). The manual updates information and instructions to states on federal ...
How many people pay Medicare Part B?
States pay Medicare Part B premiums each month for over 10 million individuals and Part A premium for over 700,000 individuals.
What is Medicare buy in?
Medicare buy-in programs were developed to lower out-of-pocket expenses of recipients with modest income and assets. To assess income eligibility, the buy-in model uses the same resource limits but with different thresholds. People who have Medicare benefits plus Medicaid are said to have dual benefits.
What does "buy in" mean in Medicare?
What Does Medicare “Buy-in” Mean? Medicare addresses the issue of medical insurance for the senior population, and some individuals under the age of 65 due to disability. Many Medicare recipients face difficulty paying their healthcare costs and need support.
What is Medicare Premium Payment Program?
The Medicare Savings Program is an overarching name for the following four programs: Medicare operates under the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS).
What is the equivalent of Medicaid in California?
California’s equivalent of Medicaid is Medi-Cal. Only available in certain states is PACE, which stands for Programs of All-Inclusive Care for the Elderly.
What is the Medicaid program?
Assistance with medical coverage. Medicaid is a program jointly held by federal and state governments designed for low-income individuals.
Is Medicare buy in good?
While Medicare buy-in offers a solution to healthcare access, coverage continuity, better health in the community and potentially lower healthcare spending in the long-term, there are challenges, mostly in terms of financing. However, access to affordable and quality medical care is critical for optimum health and cost efficiency.
Who is eligible for medicaid?
Medicaid applicants include families with children as well as individuals who are elderly, disabled or pregnant, and children who are in foster care. Low-income individuals with specific diseases may qualify as well.
What is Medicare for seniors?
Medicare is a federal health insurance program for the aged ( persons age 65 or older), certain younger individuals with disabilities, and individuals with End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD).
When did Medicare Part D change to Medicare?
Medicare Part D State Contribution Payments. Prescription drug coverage costs shifted from Medicaid to Medicare beginning January 2006 as a result of the 2003 Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement and Modernization Act (MMA), creating the Medicare Part D prescription drug program.
What is a buy in transaction code?
The buy-in transaction codes provide a concise, definitive means of communication between the CMS and the State of California. Most transaction codes require no further action on the part of the State; however, there are instances where additional action by the State is appropriate.
Does California have a Medicare buy in agreement?
Medicare Part B Buy-In Agreement. The State of California participates in a buy-in agreement with the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), whereby Medi-Cal automatically pays Medicare Part B premiums for all Medi-Cal members who have Medicare Part B entitlement as reported by Social Security Administration (SSA).
When did Medicare buy in program start?
The Buy-In Program was established in the Social Security Amendments of 1965 and was made effective along with the Medicare program on July 1, 1966. Under the Buy-In Program, States may enroll certain groups of needy people under the Supplementary Medical Insurance Program (also referred to as SMI or Medicare Part B) ...
What is the buy in program?
The legal authority for the Buy-In Program is Section 1843 of the Social Security Act. Generally, States Buy-in for beneficiaries who are cash assistance or are “deemed” cash assistance beneficiaries (see HI 00815.012 for information on deemed cash beneficiaries), are categorically needy under the Medicaid program, ...
What is the purpose of buy in?
The purpose of Buy-in is to permit the State, as part of its total assistance plan, to provide SMI protection to certain groups of needy beneficiaries. It transfers some medical costs for this population from the Title XIX Medicaid program, which is partially State financed, to the Title XVIII Medicare program, ...
What is FFP in Medicaid?
Federal Financial Participation (FFP) is available through the Medicaid program to assist the States with the premium payments for certain groups of beneficiaries (i.e., those needing cash assistance or deemed cash beneficiaries). The legal authority for the Buy-In Program is Section 1843 of the Social Security Act.
Can a beneficiary cancel Medicare?
A beneficiary cannot voluntarily terminate State Buy-in coverage. Prior beneficiary or Buy-in enrollments have no effect on Buy-in eligibility and the State pays the standard premium regardless of the date the beneficiary first became eligible for Medicare Part B.
What happens to Medicare when Part B buy in ends?
When a beneficiary’s Part B buy-in coverage ends because they have lost eligibility for a Medicaid category included in the state’s Part B buy-in coverage group, the beneficiary’s Medicare coverage generally continues without interruption, and the beneficiary becomes responsible for paying their own premiums. Because the state paid the beneficiary’s Part B premiums under a state buy-in agreement, the beneficiary will pay the standard base premium, as if they had enrolled during their Initial Enrollment Period. The beneficiary does not pay a late enrollment penalty, even if they paid a penalty before the state enrolled them in Part B buy-in.
What is 1634 Medicaid?
Some states have “1634” agreements with SSA that enable SSA to make Medicaid eligibility determinations for individuals receiving Supplemental Security Income (SSI) benefits. These states are known as “auto-accrete” states because CMS will automatically enroll (“accrete”), on behalf of the state, SSI beneficiaries in Part B buy-in. Other states are referred to as “alert” states. In alert states, CMS identifies for states SSI recipients who are Medicare-eligible, but the state determines Medicaid eligibility and initiates Part B buy-in enrollment. Please see chapter 1, section 1.6.1.1 and chapter 2, section 2.5.1 of the manual for more information.
Does SSA have to buy in Medicare?
It depends. Before the state can enroll an individual in Part B buy-in, SSA must first determine the individual eligible for Medicare. SSA has already determined an individual eligible for Medicare if they have Medicare Part A or Part B. See chapter 1, section 1.10 of the manual.
When did the Wyoming buy in agreement end?
All State Buy-In Agreements were effective July 1, 1966, except for the following: Wyoming's previous State Buy-In Agreement was effective from July 1, 1966 through July 31, 1967; and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands was effective on July 1, 1989. A number of states, which have bought in for all of their medical assistance ...
What is SSI alert?
States with 1634 agreements are known as Supplemental Security Income (SSI) auto accrete states and those states which make all their own Medicaid eligibility determinations are known as 209 (b), or SSI alert, states. States using SSI standards, but making their own State Buy-in determinations, are shown as alert*.
Does Title XIX cover medically needy?
A number of states, which have bought in for all of their medical assistance recipients under Title XIX, do not provide Title XIX approved medical assistance to the medically needy. In those states, the only noncash recipients who are eligible for State Buy-in (the Medical Assistance Only ...
What is a buy in for Medicaid?
The term "Buy-In" is used because you are buying in (paying a premium) to the Medicaid program. If your net available income is below 150% of the Federal Poverty Level (FPL), you will not have to pay any premium to get Medicaid through the MBI-WPD program. If your net available income is at least 150% but at or below 250% of the FPL, ...
What is Medicaid coverage?
Medicaid coverage is more comprehensive than many other programs including private health insurance. Medicaid covers the medical costs of prescriptions, long-term care, and ongoing medical supplies.
Why is the buy in program for working people with disabilities important?
Why is the Medicaid Buy-In program for Working People with Disabilities important?#N#According to a national survey, the #1 reason that people with disabilities gave for not working was fear of losing their essential medical benefits. This program allows people to keep their benefits, meet their medical needs and to continue working. Medicaid coverage is more comprehensive than many other programs including private health insurance. Medicaid covers the medical costs of prescriptions, long-term care, and ongoing medical supplies. Medicare and some private health insurance companies do not cover all of these costs.
Where can I apply for MBI-WPD?
You can apply for the MBI-WPD at your Local Department of Social Services (LDSS). This toolkit will help you in the process of preparing to apply for the Medicaid Buy-In program for Working People with Disabilities.
Is there a buy in program for disabled people?
No. The Medicaid Buy-In program for Working People with Disabilities (MBI-WPD) is a program that launched July 1, 2003. The MBI-WPD program provides Medicaid health care coverage for working people with disabilities. The Medicare Savings Program (MSP) assists people who are on Medicare through age or disability by paying their monthly Medicare ...
Who approves a pass?
A PASS must be approved by the Commissioner of the Local Department of Social Services, who must review and approve the plan and any subsequent plan changes. The SSA-545-BK form must be used.
Is MBI WPD available in New York?
No. The MBI-WPD program is only for individuals or couples who are disabled and working. There are other programs that cover children and other family members offered online through the New York State of Health, New York´s health insurance marketplace. Go online or call 1 (855) 355-5777 or TTY 1 (800) 662-1220.