
You can receive home health care coverage under either Medicare Part A or Part B. Under Part B, you are eligible for home health care if you are homebound and need skilled care. There is no prior hospital stay requirement for Part B coverage of home health care. There is also no deductible or coinsurance for Part B-covered home health care.
Does Medicare Part a cover home health care?
In certain cases, such as after a hospital stay or time spent in a skilled nursing facility, you can receive home health care coverage under Medicare Part A. What exactly is home health care? This type of care is meant to provide health services and equipment to individuals while they are recovering at home.
What is included in home health care?
Home health care includes a wide range of health and social services delivered in the home to treat illness or injury. What home health is covered by Medicare? Services covered by Medicare’s home health benefit include intermittent skilled nursing care, skilled therapy services, and care provided by a home health aide.
What services are covered by Medicare?
Home health services. Medicare Part A (Hospital Insurance) and/or Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) cover eligible home health services like these: Part-time or "intermittent" skilled nursing care. Physical therapy. Occupational therapy. Speech-language pathology services. Medical social services.
What does Medicare pay for home health aide services?
Part-time or intermittent home health aide services (personal hands-on care) Usually, a home health care agency coordinates the services your doctor orders for you. Medicare doesn't pay for: Homemaker services (like shopping, cleaning, and laundry), when this is the only care you need
What are the factors that affect home health management?
Let's look at five key barriers to moving care to the home and explore potential solutions to overcoming these challenges.Patient preference. ... Clinicians' concerns. ... Supporting infrastructure. ... Patient safety. ... Regulatory environment.
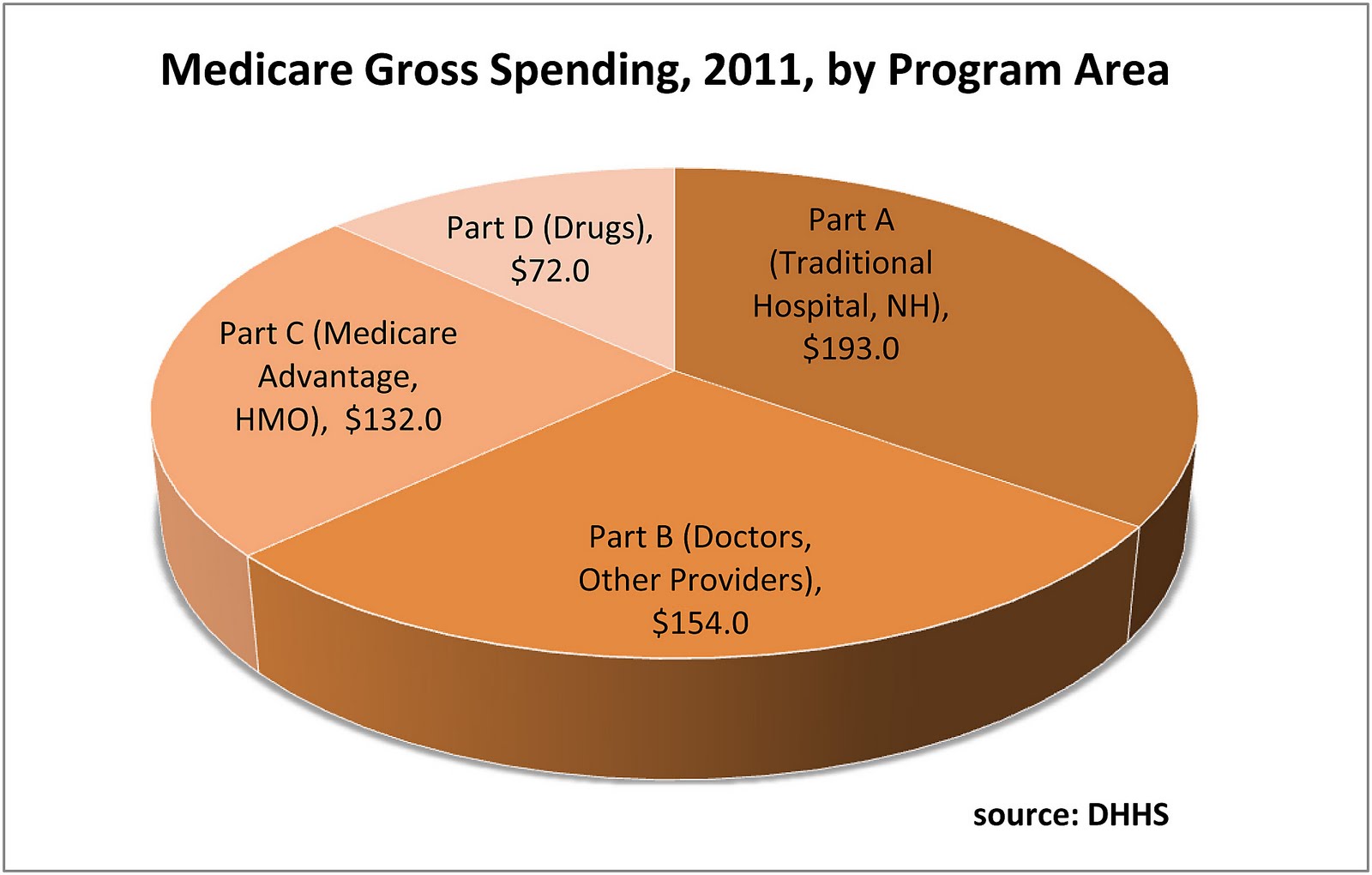
What services are included in Medicare Part A?
Medicare Part A hospital insurance covers inpatient hospital care, skilled nursing facility, hospice, lab tests, surgery, home health care.
Which is generally covered by Medicare for the homebound patient?
Medicare considers you homebound if: You need the help of another person or medical equipment such as crutches, a walker, or a wheelchair to leave your home, or your doctor believes that your health or illness could get worse if you leave your home.
How does Medicare impact patient access to care?
February 03, 2021 - Medicare coverage increases seniors' access to care and reduces affordability barriers, a study published in Health Affairs discovered. “The Medicare program pays for roughly one of every four physician visits in the United States, and in 2019 it covered roughly 60 million people.
What are Medicare Parts A and B?
Part A (Hospital Insurance): Helps cover inpatient care in hospitals, skilled nursing facility care, hospice care, and home health care. Part B (Medical Insurance): Helps cover: Services from doctors and other health care providers. Outpatient care.
What's the difference between Medicare Part A and Part B?
If you're wondering what Medicare Part A covers and what Part B covers: Medicare Part A generally helps pay your costs as a hospital inpatient. Medicare Part B may help pay for doctor visits, preventive services, lab tests, medical equipment and supplies, and more.
Which of the following are homebound criteria?
Medicare uses the following criteria to define homebound: To leave your home, you need help, including the help of another person, crutches, a walker, a wheelchair, or special transportation. Your need for help must stem from an illness or injury. It's difficult for you to leave your home and you typically can't do so.
What is the criteria for being housebound?
A patient is housebound if they are unable to leave their home at all, or if they require significant assistance to leave the house due to illness, frailty, surgery, disability, mental ill-health, or nearing the end of life.
Who qualifies for home health care services?
The patient must be homebound as required by the payer. The patient must require skilled qualifying services. The care needed must be intermittent (part time.) The care must be a medical necessity (must be under the care of a physician.)
What sets the standards for quality of care?
For health care professionals, standards are set through state licensure, board certification, and accrediting and credentialing programs. For drugs and devices, the FDA plays a critical role in standard setting. In general, current standards in health care do not provide adequate focus on patient safety.
How does Medicare measure quality of care?
Data Sources. In fee for service, the strategy uses a combination of claims data and data abstracted from medical records by PROs to identify patients and to assess their needs and what services are provided.
What is a quality of care concern?
Quality of Care Concern: A concern that care provided did not meet a professionally recognized standard of health care. A general quality of care review or a beneficiary complaint review may cover a single or multiple concerns.
How do I contact Medicare for home health?
If you have questions about your Medicare home health care benefits or coverage and you have Original Medicare, visit Medicare.gov, or call 1-800-MEDICARE (1-800-633-4227) . TTY users can call 1-877-486-2048. If you get your Medicare benefits through a Medicare Advantage Plan (Part C) or other
What happens when home health services end?
When all of your covered home health services are ending, you may have the right to a fast appeal if you think these services are ending too soon. During a fast appeal, an independent reviewer called a Beneficiary and Family Centered Care Quality Improvement Organization (BFCC-QIO) looks at your case and decides if you need your home health services to continue.
What is an appeal in Medicare?
Appeal—An appeal is the action you can take if you disagree with a coverage or payment decision made by Medicare, your Medicare health plan, or your Medicare Prescription Drug Plan. You can appeal if Medicare or your plan denies one of these:
Why is home health important?
In general, the goal of home health care is to provide treatment for an illness or injury. Where possible, home health care helps you get better, regain your independence, and become as self-sucient as possible. Home health care may also help you maintain your current condition or level of function, or to slow decline.
Can Medicare take home health?
In general, most Medicare-certified home health agencies will accept all people with Medicare . An agency isn’t required to accept you if it can’t meet your medical needs. An agency shouldn’t refuse to take you because of your condition, unless the agency would also refuse to take other people with the same condition.
What does a home health agency do?
Once your doctor refers you for home health services, the home health agency will schedule an appointment and come to your home to talk to you about your needs and ask you some questions about your health. The home health agency staff will also talk to your doctor about your care and keep your doctor updated about your progress.
What is the goal of home health care?
In general, the goal of home health care is to treat an illness or injury. Home health care helps you: Get better. Regain your independence. Become as self-sufficient as possible. Maintain your current condition or level of function. Slow decline. If you get your Medicare. benefits.
What are some examples of skilled home health services?
Examples of skilled home health services include: Wound care for pressure sores or a surgical wound. Patient and caregiver education. Intravenous or nutrition therapy . Injections. Monitoring serious illness and unstable health status. In general, the goal of home health care is to treat an illness or injury. Home health care helps you:
What to do if you have Medicare Supplement?
If you have a Medicare Supplement Insurance (Medigap) policy or other health insurance coverage, tell your doctor or other health care provider so your bills get paid correctly. If your doctor or referring health care provider decides you need home health care, they should give you a list of agencies that serve your area.
How long does it take for Medicare to pay for home health?
You also must receive home health services within 14 days of your hospital or SNF discharge to be covered under Part A. Any additional days past 100 are covered by Part B. Regardless of whether your care is covered by Part A or Part B, Medicare pays the full cost.
How many days of home health care do you have to be in a hospital?
Specifically, if you spend at least three consecutive days as a hospital inpatient or have a Medicare-covered SNF stay, Part A covers your first 100 days of home health care. You still must meet other home health care eligibility requirements, such as being homebound and needing skilled care. You also must receive home health services within 14 ...
Is home health insurance deductible or coinsurance?
There is no prior hospital stay requirement for Part B coverage of home health care. There is also no deductible or coinsurance for Part B-covered home health care. While home health care is normally covered by Part B, ...
