Hospital revenue composition in the U.S. as of March 2020, by payer
| Characteristic | Average percent of payor mix |
| Medicare | 21.8 % |
| Medicaid | 12.8 % |
| Private/Self/Other | 66.5 % |
What percentage of hospital revenue is paid to Medicaid?
As of this time, Medicaid payments contributed to 21.8 percent of all hospital net revenue, while private/self/other payments accounted for almost 67 percent of hospital revenue. Hospital revenue composition in the U.S. as of March 2020, by payer
How many hospitals will receive higher Medicare payments this year?
More than 1,500 hospitals—roughly 55 percent of program participants—will receive higher Medicare payments as bonuses for delivering excellent care quality across four areas: clinical outcomes, safety, person and community engagement, and efficiency and cost reduction.
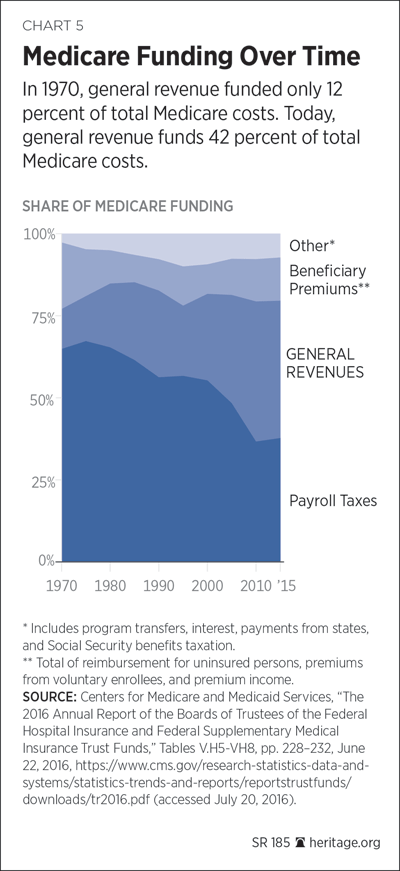
What is the source of revenue for Medicare?
Medicare is funded primarily from general revenues (43 percent), payroll taxes (36 percent), and beneficiary premiums (15 percent) (Figure 7). Figure 7: Sources of Medicare Revenue, 2018
What is the revenue composition of a hospital in the US?
Hospital revenue composition in the U.S. as of March 2020, by payer Characteristic Average percent of payor mix Medicare 21.8 % Medicaid 12.8 % Private/Self/Other 66.5 %
What percentage of hospital revenue is from Medicare and Medicaid?
Hospital revenue composition in the U.S. as of March 2020, by payerCharacteristicAverage percent of payor mixMedicare21.8%Medicaid12.8%Private/Self/Other66.5%
Do hospitals profit from Medicare?
While the average hospital profit margin on Medicare patients has been relatively steady at negative 10%, it is closer to negative 18% for the three-quarters of hospitals that lost money on their Medicare business.
What generates the most revenue for hospitals?
10 physician specialties that generate the most revenue for...Cardiovascular surgery. Average revenue: $3.7 million. ... Cardiology (invasive) Average revenue: $3.48 million. ... Neurosurgery. Average revenue: $3.44 million. ... Orthopedic surgery. ... Gastroenterology. ... Hematology/Oncology. ... General surgery. ... Internal medicine.More items...•
Which is the largest component of hospital costs?
The answer is labor costs, according to the new American Hospital Association (AHA) report, "The Cost of Caring." Labor cost increases are responsible for 35 percent of the overall growth in hospital costs.
How do hospitals generate revenue?
The American health care system for years has provided many hospitals with a clear playbook for turning a profit: Provide surgeries, scans and other well-reimbursed services to privately insured patients, whose plans pay higher prices than public programs like Medicare and Medicaid.
What percentage of hospitals are for profit?
Nearly a quarter — 24 percent — of community hospitals in the U.S. were classified as for-profit in 2019, while more than 57 percent were nonprofit and nearly 19 percent were controlled by a state, county or city government.
What is the most profitable hospital in the US?
The following list ranks the top-performing hospitals across the U.S. by net patient revenue (NPR)....Top 50 hospitals by net patient revenue.Hospital NameStanford HospitalCityStanfordStateCANet Patient Revenue$3,976,584,396# Of Staffed Beds52349 more columns
What are the sources of revenue for a major hospital or medical center?
Hospital operating revenue comes from two payment sources: public payers and private payers. Public payers are health insurance programs funded by the government including Medicare and Medicaid.
What is hospital profitability?
14. The resulting hospital profitability measure is the net income from patient care services scaled by adjusted discharge, case-mix index, and wage index (hereafter, net income from patient care services per adjusted discharge).
What accounts for the majority of healthcare costs?
Medicare and Medicaid together made up 76 percent of home health spending in 2017. reached $96.6 billion in 2017 and increased 4.6 percent, a slower rate of growth compared to the increase of 5.1 percent in 2016.
What are the major expenses in hospitals?
The Costs of Running a Hospital in India Capital expenditure. Employee or staff salaries. Building maintenance and utilities. Worker supplies and patient care supplies. Diagnostic and therapeutic supplies and medications. Share this:
Where does hospital funding come from?
Financing for hospital services comes from a multitude of private insurers as well as the joint federal-state Medicaid program, the federal Medicare program, and out-of-pocket costs paid by insured and uninsured people.
How many people are on Medicare in 2019?
In 2019, over 61 million people were enrolled in the Medicare program. Nearly 53 million of them were beneficiaries for reasons of age, while the rest were beneficiaries due to various disabilities.
Which state has the most Medicare beneficiaries?
With over 6.1 million, California was the state with the highest number of Medicare beneficiaries . The United States spent nearly 800 billion U.S. dollars on the Medicare program in 2019. Since Medicare is divided into several parts, Medicare Part A and Part B combined were responsible for the largest share of spending.
What is Medicare inpatient?
Hospital inpatient services – as included in Part A - are the service type which makes up the largest single part of total Medicare spending. Medicare, however, has also significant income, which amounted also to some 800 billion U.S. dollars in 2019.
What is Medicare 2020?
Research expert covering health, pharma & medtech. Get in touch with us now. , May 15, 2020. Medicare is a federal social insurance program and was introduced in 1965. Its aim is to provide health insurance to older and disabled people. In 2018, 17.8 percent of all people in the United States were covered by Medicare.
How much did hospital revenue increase in 2014?
Hospitals in the western U.S. report average net patient revenue increases much greater than the national numbers —with an increase of $24.6 million from 2014 to 2015, and a change of only $4.7 million between 2017 and 2018.
How much did hospital expenses increase between 2015 and 2018?
Between 2015 and 2018, hospitals with 25 beds or fewer report an average increase of 4.55 percent in operating expense. Hospitals with 251 to 500 beds, in comparison, see an average increase of 4.4 percent in operating expense for the same three-year period.
How many hospitals does definition healthcare have?
Interested in learning more about revenue trends, and how you can leverage financial data to sharpen your sales strategy? Definitive Healthcare provides detailed financial metrics for over 8,800 U.S. hospitals and health systems. Start a free trial today to see how you can:
How much has operating expense increased in the past five years?
On a national scale, year-over-year changes in average operating expense show a $1.4 million increase from 2014 through 2016 before markedly decreasing through 2018. Percentage change in average operating expense has also remained fairly steady in the past five years—ranging from 3.4 percent between 2017 and 2018, and 4.48 percent in the 2014 to 2015 calendar year.
Does operating expense correlate with bed count?
As with trends in net patient revenue, average change in year-over-year operating expense correlates directly with hospital bed count—with smaller hospitals reporting lower increases in dollar amount from year to year. On a percentage change basis, however, smaller hospitals again compete with larger facilities.
Do hospitals see lower net earnings?
While smaller hospitals may see lower increases in net year-over-year earnings by dollar amount, a review of the same revenue trends by percentage change indicates a much more competitive performance at these facilities.
Which region has the most Medicare days?
Comparing the payor patient days by hospital region shows the Midwest has the highest percentage of Medicare days. Hospitals in the West have the least Medicare days and the most Medicaid days. Northeastern hospitals have more payor days from private/self-payors. Year-to-year changes reflect the national results of payor patient days.
Why is Medicare days higher in the Midwest?
The West likely reports higher Medicare days because of its higher volume of impoverished and underinsured patients.
How many beds does Medicare PX have?
Over half of patients' days from Medicare Px are at hospitals with 25 beds or less. The percentage of payor days correlates to hospital bed count. The percentage of Medicare days declines and the percentage of private/self-pay days increases. This is relative to a hospital's number of beds. Facility specialties, insurance coverage, ...
Where do most of the patient days come from Medicaid?
Like in previous data sets, the highest percentage of Medicaid and private/self-pay patient days are at psychiatric hospitals. The coverage of inpatient mental health services is a possible cause for some of these differences. Critical access, long-term acute, and rehabilitation hospitals report over half of their patient days coming from Medicare beneficiaries. This is likely tied to patient demographics.
Why is understanding hospital financial data important?
Understanding hospital financial data can help segment a market and explain its pain points.
Is Medicaid expanding?
The American population is aging and many state Medicaid programs expanded over the last several years. Trends for Medicare and Medicaid continue to show decreases in hospital patient days. The percentage of patient days covered by private/self-payors has increased from 42.1% in 2010 to 50.8% in 2018.
Is Medicaid revenue increasing?
Total revenue for both Medicaid and private/self-pay insurance increased from 2017 data. The percentage of the total payor mix from private /self-pay decreased from 67.9% last year while the Medicare percentage increased from 19.5%. This could be representative of the unemployment increases seen throughout 2020. Businesses need to cope with COVID-19 interruptions .
How many insurances do hospitals have?
Hospitals deal with over 1,000 insurers, 1 which typically have several different plan options. For instance, in the Federally-Facilitated Exchange (FFE) program specifically, there are approximately 120 unique insurers offering over 75,000 discrete health plan options 2 leading to multiple and often unique requirements for hospital bills. Add to that decades of government regulations, which have made a complex billing system even more complex and frustrating for everyone involved.
How many hospitals lost money in 2019?
In 2019, approximately 63 percent of hospitals lost money providing care to Medicare and 58 percent lost money providing care to Medicaid patients and about 30 percent of hospitals were operating on negative operating margins (see chart).
How much will hospitals lose in 2021?
3 As the pandemic has continued to persist well into 2021, a recent report by Kaufman Hall forecasts that hospitals and health systems could face an additional $53 billion to $122 billion in losses in 2021. 4 Today’s fragmented health care system, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, leaves hospitals with a daily balancing act to maintain their mission to the communities they serve while making ends meet. The following is an explanation of key components of hospital billing, including hospital charges, payment and costs.
Why do hospitals need a positive bottom line?
A hospital cannot continue to lose money year after year and remain open. Hospitals need a positive bottom line in order to be able to keep up with new technologies and treatments, replace or improve old buildings, and otherwise invest in maintaining and improving their services to meet the rising demand for care. It also helps ensure they can attract and retain frontline caregivers and other critical staff and purchase personal protective equipment (PPE), drugs and other necessary supplies.
How much uncompensated care does a hospital provide?
Hospitals provided $41.6 billion in uncompensated care, both free care and care for which no payment is made by patients, in 2019. 9. Private insurance and others often make up the difference. Payments relative to costs vary greatly among hospitals depending on the mix of payers.
What is the mission of every hospital in America?
The mission of each and every hospital in America is to serve the health care needs of the people in its community 24 hours a day, seven days a week. But, hospitals’ work is made more difficult by our fragmented health care system — a system that leaves millions of people unable to afford the health care services they need.
Do tax exempt hospitals have to have a financial assistance policy?
Tax-exempt hospitals are prohibited from billing gross charges for those eligible for financial assistance. Under the ACA, tax-exempt hospitals are required to have a written financial assistance policy that is widely distributed in the community.
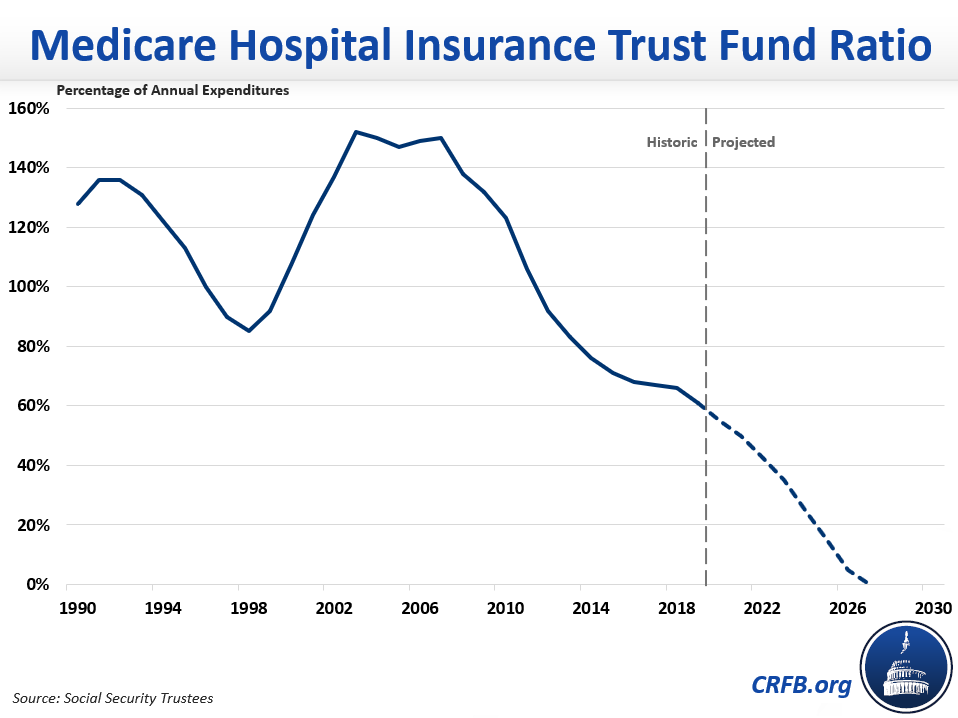
What percentage of Medicare is spending?
Key Facts. Medicare spending was 15 percent of total federal spending in 2018, and is projected to rise to 18 percent by 2029. Based on the latest projections in the 2019 Medicare Trustees report, the Medicare Hospital Insurance (Part A) trust fund is projected to be depleted in 2026, the same as the 2018 projection.
How much does Medicare cost?
In 2018, Medicare spending (net of income from premiums and other offsetting receipts) totaled $605 billion, accounting for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1).
How is Medicare Financed?
Medicare is funded primarily from general revenues (43 percent), payroll taxes (36 percent), and beneficiary premiums (15 percent) (Figure 7) .
Why is Medicare spending so slow?
Slower growth in Medicare spending in recent years can be attributed in part to policy changes adopted as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Budget Control Act of 2011 (BCA). The ACA included reductions in Medicare payments to plans and providers, increased revenues, and introduced delivery system reforms that aimed to improve efficiency and quality of patient care and reduce costs, including accountable care organizations (ACOs), medical homes, bundled payments, and value-based purchasing initiatives. The BCA lowered Medicare spending through sequestration that reduced payments to providers and plans by 2 percent beginning in 2013.
What is the average annual growth rate for Medicare?
Average annual growth in total Medicare spending is projected to be higher between 2018 and 2028 than between 2010 and 2018 (7.9 percent versus 4.4 percent) (Figure 4).
What has changed in Medicare spending in the past 10 years?
Another notable change in Medicare spending in the past 10 years is the increase in payments to Medicare Advantage plans , which are private health plans that cover all Part A and Part B benefits, and typically also Part D benefits.
What is excess health care cost?
Over the next 30 years, CBO projects that “excess” health care cost growth—defined as the extent to which the growth of health care costs per beneficiary, adjusted for demographic changes, exceeds the per person growth of potential GDP (the maximum sustainable output of the economy)—will account for half of the increase in spending on the nation’s major health care programs (Medicare, Medicaid, and subsidies for ACA Marketplace coverage), and the aging of the population will account for the other half.
How much did Medicare pay for inpatient care in 2015?
Medicare's fee-for-service program paid 4,700 hospitals $178 billion in 2015 for inpatient admissions, outpatient services and non-Medicare uncompensated care costs. Here are 34 statistics on Medicare admissions, costs, margins and charges in 2015 from MedPAC's March 2017 report to Congress.
Is Becker's Healthcare hosting a survey?
Your input is needed! Becker's Healthcare is hosting a survey focused Employee Benefits/ Health Plans. Click here to fill out the 5 minute survey to receive a complementary badge to a Becker's conference.
What is hospital expenditure?
Hospital expenditures include money spent toward inpatient care as well as any outpatient service provided by a hospital. Outpatient services might include anything from a routine blood test to an emergency room visit or an outpatient surgery.
Where does Medicare data come from?
The following information is derived mostly from data obtained from three primary sources: The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) including Medicare cost report data, California’s Office of Statewide Health Planning and Development ( OSHPD) and the American Hospital Association (AHA).
How much of the care hospitals provide is uncompensated?
3. Very little of the care hospitals provide is uncompensated; about 2-4% on average. Deductions by Medicare, Medicaid and the insurance companies account for almost all of the differences between billing charges and receipts.
Why are hospitals over billing?
The most obvious reason hospital over-billing has increased so persistently is that hospitals can make more money by doing it. While Medicare and Medicaid control their costs by tying their payments to the actual cost of medical services, private insurance companies appear to be just paying a fixed percentage of what they’re billed. That alone gives hospitals a strong motivation to inflate their billing charges by more each year independent of their costs.
Why do private insurance companies overpay hospitals?
There are two major reasons private insurance companies have been overpaying hospitals. First, it’s not their money most of the time. Most employer sponsored private health insurance policies are covered entirely by employers who self-insure. In such cases, the insurance company only negotiates the payments, but never pays anything toward the medical bills. Since the insurance company isn’t bargaining with their own money in such cases, they have little motivation to drive hard bargains.
Is the proportion of a hospital bill a private insurance company pays substantially higher than the proportion Medicare or Medicaid pays?
6. The proportion of a hospital bill a private insurance company pays is substantially higher, on average, than the proportion Medicare or Medicaid pays, and that difference has grown steadily since 2000.
Do hospitals overbill for uncompensated care?
They don’t over-bill to make up for uncompensated care. Neither charity nor bad debt are significant financial issues for most hospitals in the U.S. Nor has the amount of uncompensated care provided by hospitals increased significantly at any time in the last four decades. In fact, since 2014, uncompensated care provided by California hospitals decreased by around 50%.
