What percentage of federal budget is spent on Medicare?
Medicare is the second largest program in the federal budget. In 2018, it cost $582 billion — representing 14 percent of total federal spending.1. Medicare has a large impact on the overall healthcare market: it finances about one-fifth of all health spending and about 40 percent of all home health spending.
How much does Medicare cost and what does it cover?
How Much Does Medicare Cost and What Does It Cover? Medicare accounts for a significant portion of federal spending. In fiscal year 2019, the Medicare program cost $644 billion — about 14 percent of total federal government spending. After Social Security, Medicare was the second largest program in the federal budget last year. TWEET THIS
Are Social Security and Medicare mandatory spending?
Social Security and Medicare expenditures are funded by permanent appropriations and so are considered mandatory spending according to the 1997 Budget Enforcement Act (BEA).
How much of the federal budget is spent on social security?
Safety net programs: About 8 percent of the federal budget in 2019, or $361 billion, supported programs that provide aid (other than health insurance or Social Security benefits) to individuals and families facing hardship.

How much of the US budget goes to Medicare and Medicaid?
Historical NHE, 2020: NHE grew 9.7% to $4.1 trillion in 2020, or $12,530 per person, and accounted for 19.7% of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Medicare spending grew 3.5% to $829.5 billion in 2020, or 20 percent of total NHE. Medicaid spending grew 9.2% to $671.2 billion in 2020, or 16 percent of total NHE.
What percentage of the federal budget is Social Security?
Employers and employees each pay 6.2 percent of wages, with a cap on the amount of wages subject to the tax ($142,800 for 2021, adjusted annually for growth in economy-wide wages).
What percent of the total federal budget is spent on Medicare?
Overview of Medicare Spending In 2018, Medicare spending (net of income from premiums and other offsetting receipts) totaled $605 billion, accounting for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1).
What are the 5 largest federal expenses?
Military (Discretionary)Social Security, Unemployment, and Labor (Mandatory)Medicare and Health (Mandatory)Government (Discretionary)Education (Discretionary) Whether you owe money to the IRS or you have a State tax debt, our staff of Enrolled Agents and Tax Professionals can help you!
What is the largest portion of the US budget?
Social Security takes up the largest portion of the mandatory spending dollars. In fact, Social Security demands $1.046 trillion of the total $2.739-trillion mandatory spending budget. It also includes programs like unemployment benefits and welfare.
What is the biggest expense of the US government?
As Figure A suggests, Social Security is the single largest mandatory spending item, taking up 38% or nearly $1,050 billion of the $2,736 billion total. The next largest expenditures are Medicare and Income Security, with the remaining amount going to Medicaid, Veterans Benefits, and other programs.
What percent of our taxes go to healthcare?
In other words, the federal government dedicates resources of nearly 8 percent of the economy toward health care. By 2028, we estimate these costs will rise to $2.9 trillion, or 9.7 percent of the economy. Over time, these costs will continue to grow and consume an increasing share of federal resources.
What percentage of healthcare is paid by the government?
The deceleration was largely associated with slower federal Medicaid spending. Despite the slower growth, the federal government's share of health care spending remained at 28 percent.
What are the 3 largest categories of federal government spending?
The U.S. Treasury divides all federal spending into three groups: mandatory spending, discretionary spending and interest on debt. Together, mandatory and discretionary spending account for more than ninety percent of all federal spending, and pay for all of the government services and programs on which we rely.
What are the top 3 items that the federal government spends its money on?
Nearly 60 percent of mandatory spending in 2019 was for Social Security and other income support programs (figure 3). Most of the remainder paid for the two major government health programs, Medicare and Medicaid.
What are the top 3 categories the government spends our tax dollars on?
The three biggest categories of expenditures are: Major health programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid. Social security. Defense and security.
How much did Medicare spend in 2019?
If we look at each program individually, Medicare spending grew 6.7% to $799.4 billion in 2019, which is 21% of total NHE, while Medicaid spending grew 2.9% to $613.5 billion in 2019, which is 16% of total NHE. 3 . The CMS projects that healthcare spending is estimated to grow by 5.4% each year between 2019 and 2028.
How Does Medicaid Expansion Affect State Budgets?
That’s because the federal government pays the vast majority of the cost of expansion coverage , while expansion generates offsetting savings and , in many states, raises more revenue from the taxes that some states impose on health plans and providers. 19
What is CMS and Medicaid?
CMS works alongside the Department of Labor (DOL) and the U.S. Treasury to enact insurance reform. The Social Security Administration (SSA) determines eligibility and coverage levels. Medicaid, on the other hand, is administered at the state level.
What is Medicare contribution tax?
It is known as the unearned income Medicare contribution tax. Taxpayers in this category owe an additional 3.8% Medicare tax on all taxable interest, dividends, capital gains, annuities, royalties, and rental properties that are paid outside of individual retirement accounts or employer-sponsored retirement plans .
What is Medicare 2021?
Updated Jun 29, 2021. Medicare, and its means-tested sibling Medicaid, are the only forms of health coverage available to millions of Americans today. They represent some of the most successful social insurance programs ever, serving tens of millions of people including the elderly, younger beneficiaries with disabilities, ...
How much will healthcare cost in 2028?
The CMS projects that healthcare spending is estimated to grow by 5.4% each year between 2019 and 2028. This means healthcare will cost an estimated $6.2 trillion by 2028. Projections indicate that health spending will grow 1.1% faster than GDP each year from 2019 to 2028.
How much did the Affordable Care Act increase in 2019?
1 2 . According to the most recent data available from the CMS, national healthcare expenditure (NHE) grew 4.6% to $3.8 trillion in 2019.
Why is Medicare underfunded?
Medicare is already underfunded because taxes withheld for the program don't pay for all benefits. Congress must use tax dollars to pay for a portion of it. Medicaid is 100% funded by the general fund, also known as "America's Checkbook.".
What is the main goal in creating the federal budget?
The federal budget sets government spending priorities and identifies the sources of revenue it will use to pay for those priorities. It's a key tool for executing the agenda of a given administration, and the budget process is designed to facilitate cooperation between the White House and Congress in setting these priorities. Often, however, it becomes a source of partisan gridlock.
How does the federal government finance a budget deficit?
The government finances its debt by selling its Treasury notes, bills, and bonds to a variety of creditors, such as state and local governments, corporations, and foreign governments . This increases the national debt that the federal government must pay back over time.
How much is the budget for FY 2021?
In May 2021, President Joe Biden released a $6.011 trillion federal budget proposal for fiscal year (FY) 2022. The U.S. government estimates it will receive $4.174 trillion in revenue, creating a $1.837 trillion deficit for October 1, 2021, through Sept. 30, 2022. 1
What is mandatory spending in 2022?
Mandatory spending is estimated at $4.018 trillion in FY 2022. This category includes entitlement programs such as Social Security, Medicare, and unemployment compensation. It also includes welfare programs such as Medicaid.
How much is discretionary spending?
Discretionary spending, which pays for everything else, will be $1.688 trillion. The U.S. Congress appropriates this amount each year, using the president's budget as a starting point. Interest on the U.S. debt is estimated to be $305 billion.
What happens if the government shuts down?
If the government does shut down, it signals a complete breakdown in the budget creation process.
What percentage of Medicare is from the federal government?
The federal government’s general fund has been playing a larger role in Medicare financing. In 2019, 43 percent of Medicare’s income came from the general fund, up from 25 percent in 1970. Looking forward, such revenues are projected to continue funding a major share of the Medicare program.
What is Medicare budget?
Budget Basics: Medicare. Medicare is an essential health insurance program serving millions of Americans and is a major part of the federal budget. The program was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson in 1965 to provide health insurance to people age 65 and older. Since then, the program has been expanded to serve the blind and disabled.
What Are the Components of Medicare?
Medicare is a federal program that provides health insurance to people who are age 65 and older, blind, or disabled. Medicare consists of four "parts":
How Much Does Medicare Cost and What Does It Cover?
Medicare accounts for a significant portion of federal spending. In fiscal year 2020, the Medicare program cost $776 billion — about 12 percent of total federal government spending. Medicare was the second largest program in the federal budget last year, after Social Security.
How much of Medicare was financed by payroll taxes in 1970?
In 1970, payroll taxes financed 65 percent of Medicare spending.
How is Medicare self-financed?
One of the biggest misconceptions about Medicare is that it is self-financed by current beneficiaries through premiums and by future beneficiaries through payroll taxes. In fact, payroll taxes and premiums together only cover about half of the program’s cost.
How is Medicare funded?
Medicare is financed by two trust funds: the Hospital Insurance (HI) trust fund and the Supplementary Medical Insurance (SMI) trust fund. The HI trust fund finances Medicare Part A and collects its income primarily through a payroll tax on U.S. workers and employers. The SMI trust fund, which supports both Part B and Part D, ...
How much is Social Security spending?
Social Security ($845B or 24% of spending), Healthcare such as Medicare and Medicaid ($831B or 24%), other mandatory programs such as food stamps and unemployment compensation ($420B or 12%) and interest ($229B or 6.5%). As a share of federal budget, mandatory spending has increased over time.
Why did Medicare reduce its %GDP?
The Medicare Trustees have reduced their forecast for Medicare costs as %GDP, mainly due to a lower rate of healthcare cost increases.
What is discretionary spending?
Discretionary spending is typically set by the House and Senate Appropriations Committees and their various subcommittees.
How much will Social Security increase in 2035?
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimates that Social Security spending will rise from 4.8% of GDP in 2009 to 6.2% of GDP by 2035, where it will stabilize. However, the CBO expects Medicare and Medicaid to continue growing, rising from 5.3% GDP in 2009 to 10.0% in 2035 and 19.0% by 2082.
How much did Medicare and Medicaid grow in 2016?
Medicare, Medicaid, and Social Security grew from 4.3% of GDP in 1971 to 10.7% of GDP in 2016. In the long-run, expenditures related to Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid are growing considerably faster than the economy overall as the population matures.
How much of the federal budget is mandatory?
Around two thirds of federal spending is for "mandatory" programs. CBO projects that mandatory program spending and interest costs will rise relative to GDP over the 2016–2026 period, while defense and other discretionary spending will decline relative to GDP.
What is the federal budget?
The United States federal budget consists of mandatory expenditures (which includes Medicare and Social Security), discretionary spending for defense , Cabinet departments (e.g., Justice Department) and agencies (e.g., Securities & Exchange Commission ), and interest payments on debt. This is currently over half of U.S. government spending, the remainder coming from state and local governments.
What percentage of the federal budget is Social Security?
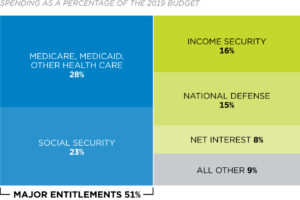
As the chart below shows, three major areas of spending make up the majority of the budget: Social Security: In 2019, 23 percent of the budget, or $1 trillion, paid for Social Security, which provided monthly retirement benefits averaging $1,503 to 45 million retired workers in December 2019. Social Security also provided benefits ...
How much of the federal budget is interest on debt?
In 2019, these interest payments claimed $375 billion, or about 8 percent of the budget.
What is the subcategory of benefits for federal retirees and veterans?
Benefits for federal retirees and veterans: This subcategory combines the veterans’ benefits and services function (700) and the federal employee retirement and disability subfunction (602, which is part of the income security function).
What is Medicare 570?
This category consists of the Medicare function (570), including benefits, administrative costs, and premiums, as well as the “Grants to States for Medicaid” account, the “Children’s health insurance fund” account, the “Refundable Premium Tax Credit and Cost Sharing Reductions,” and two other small accounts supporting the Affordable Care Act’s marketplace subsidies (all in function 550).
How are broad expenditure categories constructed?
The categories are constructed by grouping related programs and activities into broad functions, which are further broken down into subfunctions. The details of how the categories used in this paper were constructed from those functions and subfunctions are described below.
How much did the federal government spend in 2019?
In fiscal year 2019, the federal government spent $4.4 trillion, amounting to 21 percent of the nation’s gross domestic product (GDP). Of that $4.4 trillion, over $3.5 trillion was financed by federal revenues. The remaining amount ($984 billion) was financed by borrowing. As the chart below shows, three major areas of spending make up ...
How many people are out of poverty in 2018?
A CBPP analysis using Census’ Supplemental Poverty Measure shows that government safety net programs kept 37 million people out of poverty in calendar year 2018. Without any government income assistance, either from safety net programs or other income supports like Social Security, the poverty rate would have been 24.0 percent in 2018, nearly double the actual 12.8 percent. And these programs reduced the depth of poverty for millions more, even when not bringing them above the poverty line.
What is the purpose of Social Security?
Social Security was created in order to help those who have retired, become disabled, and who are dependents of a deceased income provider. As money is put into the Social Security fund with every paycheck, the American people are essentially putting money into a fund that they may be able to take advantage of when they have retired, or can no longer work because of a disability. In 2012, 38 percent of the federal budget went to Social Security and Medicare combined. The following is information on Supplemental Security Income and Social Security Disability.
What is SSI support?
Monetary support for people who are in need is provided by the Supplemental Security Income (SSI) program. People who qualify for these benefits are individuals who are older than 65, or blind or disabled adults and children. The eligibility to receive benefits from this program is the same across the nation. Over the last forty years, since payments for this program started, the number of recipients has steadily increased to nearly 8.3 million people as of December 2012. In 2009, Supplemental Security Income accounted for about 1.4 percent of the federal budget. The percentage of the gross domestic product that went to Supplemental Security Income was about 0.33 percent in 2012, and is predicted to remain level through 2014. After that, the federal government expects the percentage to slowly decline.
What percentage of the federal budget is Medicaid?
Medicaid is the third largest mandatory program in the federal budget, accounting for 7 percent of federal spending in 2020, and represents a third of state budgets, on average. As such an important component of government spending and one of the largest payers of healthcare coverage, it has the unique opportunity to be a driver of change and innovation in healthcare.
How Is Medicaid Funded?
Medicaid is financed jointly by the federal government and the states, and on average, the federal government covers nearly two-thirds of the total cost of the program. The program represents 20 percent of state general fund expenditures, on average, and is the second- largest category in their budgets (when federal funds are excluded). Medicaid is administered by the states (but is subject to federal oversight) and as a result, there are actually more than 50 different Medicaid programs (including Washington DC and U.S. territories).
What is the difference between medicaid and medicare?
Persons with disabilities and the elderly make up 23 percent of the program’s enrollees. While Medicare is the primary health insurance program for most people over the age of 65, certain people are eligible for both programs . Those dual- eligible beneficiaries tend to experience high rates of chronic illness. For example, 49 percent of those beneficiaries receive long-term care services, while 60 percent have multiple chronic conditions.
What percentage of Medicaid is children?
Even though children make up about 40 percent of Medicaid beneficiaries, they account for less than 20 percent of the program’s spending. Conversely, the elderly and people with disabilities make up one-quarter of beneficiaries but account for more than half of Medicaid spending.
What is the FMAP formula?
The formula that governs a majority of government funding is called the federal medical assistance percentage (FMAP), and takes into account differences in per capita income among the states. The FMAP ranges from a minimum of 50 percent in wealthier states such as Alaska to 78 percent in Mississippi. INTERACTIVE MAP.
What is Medicaid financed by?
Medicaid is a health insurance program targeted to lower-income recipients that is financed jointly by the federal government and the states . This budget explainer describes what Medicaid is, how it is funded, and who benefits from it.
How much did the US government spend on health insurance in 2020?
Provided health insurance for about 73 million Americans, or about 22 percent of the U.S. population. Cost the federal government $458 billion, though spending in 2020 spiked due to the coronavirus pandemic and legislation to mitigate its impact. Represented about one-fifth of all health spending in the United States.