Full Answer
How much do Americans spend on Medicare benefits?
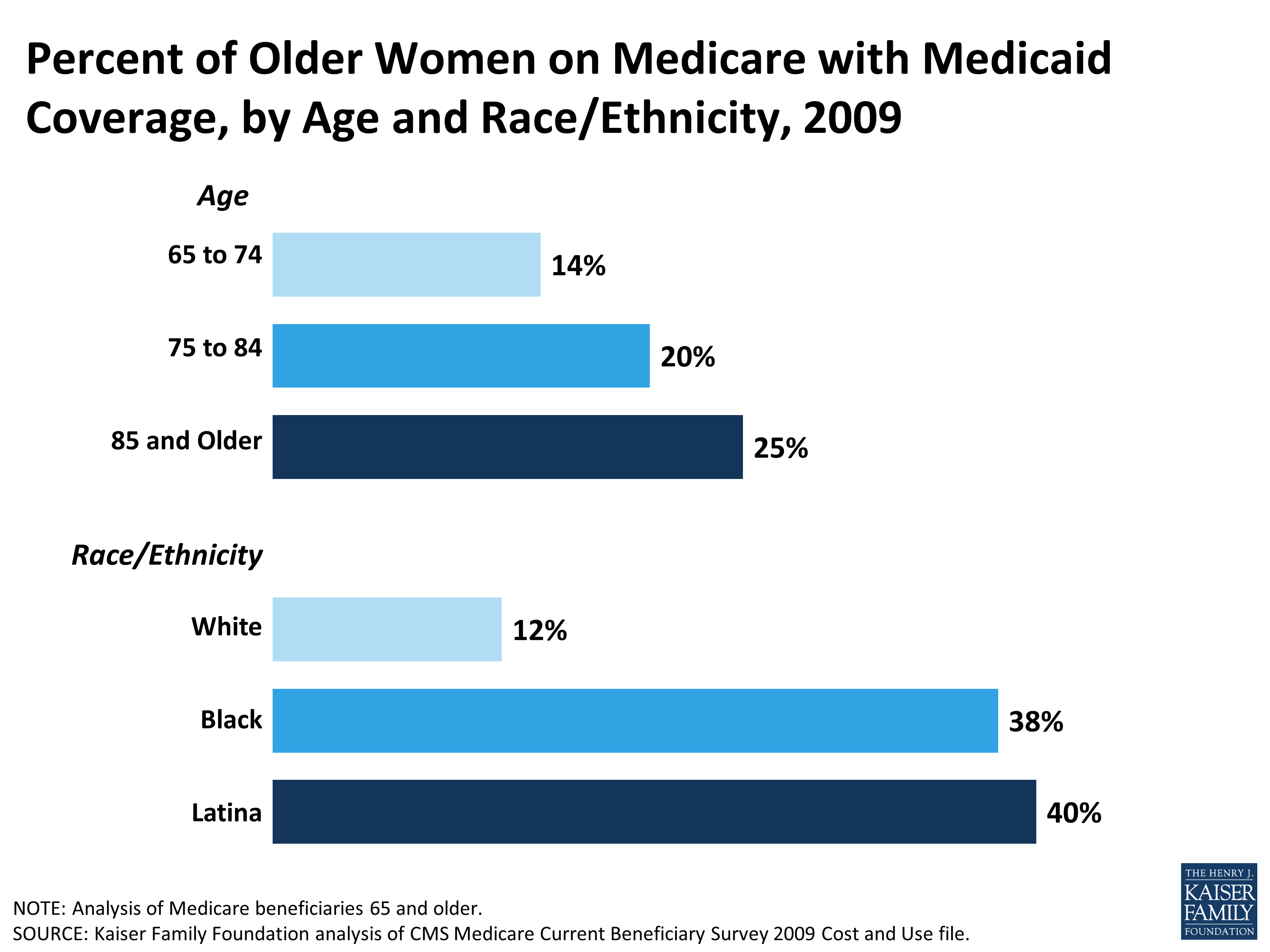
While Medicare has provided nearly five decades of health and economic security to all seniors and people with disabilities, the program has been especially vital to women because: More than half of Medicare’s nearly 61 million beneficiaries are women; for beneficiaries 85 and over, nearly 70 percent are women.
How many people in the United States have Medicare?
Feb 16, 2022 · Percent of Medicare spent on hospital care 2019. 40%. Detailed statistics. Spending distribution of Medicare and Medicaid 2019. Enrollment/Beneficiaries. Enrollment in Medicare program due to age ...
How much does Medicare spend on inpatient hospital services?
women represent over 70 percent of Medicare beneficiaries living in nursing homes and other facilities. Because Medicare’s coverage of long-term care services is very limited, many women have high out-of-pocket costs if they
What is the average growth rate of Medicare spending?
Dec 15, 2021 · Historical NHE, 2020: NHE grew 9.7% to $4.1 trillion in 2020, or $12,530 per person, and accounted for 19.7% of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Medicare spending grew 3.5% to $829.5 billion in 2020, or 20 percent of total NHE. Medicaid spending grew 9.2% to $671.2 billion in 2020, or 16 percent of total NHE.

Do women pay more for Medicare?
What percent of healthcare is female?
What does Medicare spend the most on?
Do women use healthcare more than men?
What percentage of nursing is female?
What percentage of RNs are male?
What percentage of the budget is Medicare?
How much does the average American spend on healthcare 2021?
How much does the average American spend on healthcare 2020?
Why is female life expectancy higher than male?
Why is gender bias in healthcare?
Why do males and females behave differently?
How many people are covered by Medicare?
Published: Aug 20, 2019. Medicare, the federal health insurance program for more than 60 million people ages 65 and over and younger people with long-term disabilities, helps to pay for hospital and physician visits, prescription drugs, and other acute and post-acute care services. This issue brief includes the most recent historical ...
Is Medicare spending going up?
Over the longer term (that is, beyond the next 10 years), both CBO and OACT expect Medicare spending to rise more rapidly than GDP due to a number of factors, including the aging of the population and faster growth in health care costs than growth in the economy on a per capita basis. According to CBO’s most recent long-term projections, net Medicare spending will grow from 3.0 percent of GDP in 2019 to 6.0 percent in 2049.
How much did Medicare pay in 2018?
In 2018, Medicare benefit payments totaled $731 billion, up from $462 billion in 2008 (Figure 2) (these amounts do not net out premiums and other offsetting receipts). While benefit payments for each part of Medicare (A, B, and D) increased in dollar terms over these years, the share of total benefit payments represented by each part changed. Spending on Part A benefits (mainly hospital inpatient services) decreased from 50 percent to 41 percent, spending on Part B benefits (mainly physician services and hospital outpatient services) increased from 39 percent to 46 percent, and spending on Part D prescription drug benefits increased from 11 percent to 13 percent.
Is Medicare spending comparable to private health insurance?
Prior to 2010, per enrollee spending growth rates were comparable for Medicare and private health insurance. With the recent slowdown in the growth of Medicare spending and the recent expansion of private health insurance through the ACA, however, the difference in growth rates between Medicare and private health insurance spending per enrollee has widened.
Does Medicare Advantage cover Part A?
Medicare Advantage plans, such as HMOs and PPOs, cover Part A, Part B, and (typically) Part D benefits. Beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans pay the Part B premium, and may pay an additional premium if required by their plan; about half of Medicare Advantage enrollees pay no additional premium.
How many people are on Medicare in 2019?
In 2019, over 61 million people were enrolled in the Medicare program. Nearly 53 million of them were beneficiaries for reasons of age, while the rest were beneficiaries due to various disabilities.
Which state has the highest Medicare enrollment?
With over 6.1 million, California was the state with the highest number of Medicare beneficiaries .
When was Medicare introduced?
Get in touch with us now. , May 15, 2020. Medicare is a federal social insurance program and was introduced in 1965 . Its aim is to provide health insurance to older and disabled people. In 2018, 17.8 percent of all people in the United States were covered by Medicare.
What is Medicare insurance?
Medicare is a federal social insurance program and was introduced in 1965. Its aim is to provide health insurance to older and disabled people. In 2018, 17.8 percent of all people in the United States were covered by Medicare. Unlike Medicaid, Medicare is not bound to lower incomes or a certain state of poverty.
Which state has the most Medicare beneficiaries?
With over 6.1 million, California was the state with the highest number of Medicare beneficiaries . The United States spent nearly 800 billion U.S. dollars on the Medicare program in 2019. Since Medicare is divided into several parts, Medicare Part A and Part B combined were responsible for the largest share of spending.
What is Medicare 2020?
Research expert covering health, pharma & medtech. Get in touch with us now. , May 15, 2020. Medicare is a federal social insurance program and was introduced in 1965. Its aim is to provide health insurance to older and disabled people. In 2018, 17.8 percent of all people in the United States were covered by Medicare.
How much did Medicaid spend in 2019?
Medicaid spending grew 2.9% to $613.5 billion in 2019, or 16 percent of total NHE. Private health insurance spending grew 3.7% to $1,195.1 billion in 2019, or 31 percent of total NHE. Out of pocket spending grew 4.6% to $406.5 billion in 2019, or 11 percent of total NHE.
How much did private health insurance spend in 2019?
Private health insurance spending grew 3.7% to $1,195.1 billion in 2019, or 31 percent of total NHE. Out of pocket spending grew 4.6% to $406.5 billion in 2019, or 11 percent of total NHE. Hospital expenditures grew 6.2% to $1,192.0 billion in 2019, faster than the 4.2% growth in 2018.
How much did the NHE increase in 2019?
NHE grew 4.6% to $3.8 trillion in 2019, or $11,582 per person, and accounted for 17.7% of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Medicare spending grew 6.7% to $799.4 billion in 2019, or 21 percent of total NHE. Medicaid spending grew 2.9% to $613.5 billion in 2019, or 16 percent of total NHE.
Distribution of Medicare Beneficiaries by Sex
Filling the need for trusted information on national health issues, the Kaiser Family Foundation is a nonprofit organization based in San Francisco, California.
Data are loading
Filling the need for trusted information on national health issues, the Kaiser Family Foundation is a nonprofit organization based in San Francisco, California.
How much did Medicare save in 2014?
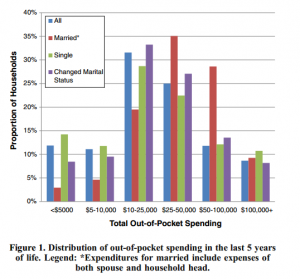
In 2014, half of all Medicare beneficiaries had less than $63,350 in savings, but the amount of median per capita savings was seven times greater for white beneficiaries ($91,950) than black or Hispanic beneficiaries ($12,350 and $9,800, respectively) ( Figure 7 ). 7 Nearly all Medicare beneficiaries had some amount of savings (92%), but savings rates were higher among white beneficiaries (95%) than among black and Hispanic beneficiaries (80% and 76%, respectively). Among those with any savings, the median savings amount was roughly five times higher for white beneficiaries ($102,500) than for black and Hispanic beneficiaries ($22,200 and $23,000, respectively).
What percentage of Medicare beneficiaries are black?
In 7 states (Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, North Carolina, and South Carolina), at least 20 percent of all Medicare beneficiaries are black—at least twice ...
What is Medicare Part D?
The Medicare Part D prescription drug benefit is an important source of drug coverage for Medicare beneficiaries. More than half of all Medicare beneficiaries (57%) were enrolled in a Part D drug plan in 2011, but a larger share of black (66%) and Hispanic (71%) beneficiaries than white beneficiaries (55%) had Part D drug coverage ( Figure 13 ). A smaller share of white beneficiaries may be enrolled in Part D than other beneficiaries because they are more likely to have drug coverage through an employer-sponsored plan (see Figure 10). Medicare beneficiaries with low income and modest assets may qualify for additional financial premium and cost-sharing assistance through the Part D low-income subsidy (LIS) program. Nearly half of all black beneficiaries (46%) and more than one third of all Hispanic beneficiaries (38%) receive LIS under Part D, larger than the share of white beneficiaries with LIS (17%), due to lower levels of income and assets among black and Hispanic beneficiaries.
Which cancer screening is the most expensive?
Of the four major cancer screenings, mammography is the most expensive -- and has generated the most controversy. When a National Institutes of Health panel recommended in 1997 that women in their 40s did not need routine screenings, committee members were accused of condemning American women to death.
Is cervical cancer screening a success?
Cervical cancer screening is considered one of the greatest success stories of preventive medicine. Cervical cancer was one of the leading killers of American women until the 1950s, when women
How old was Terry Waddell's mother?
Terry Waddell knew that her 87-year-old mother did not have long to live. The woman's organs were shutting down because of old age, she said, and her arthritic body had withered to 80 pounds.
Does Medicare cover out of pocket costs?
Even with Medicare’s prescription drug coverage, beneficiaries can face substantial out-of-pocket costs, particularly if they use specialty drugs or multiple high-cost brand-name drugs.
Is Medicare a private insurance?
Medicare is second only to private insurance as a major payer for retail prescription drugs. The program’s share of the nation’s retail prescription drug spending has increased from 18% in 2006 to 30% in 2017.
Does Medicare cover prescription drugs?
Medicare Part B also covers drugs that are administered to patients in physician offices and other outpatient settings. Medicare is second only to private insurance as a major payer for retail prescription drugs. The program’s share of the nation’s retail prescription drug spending has increased from 18% in 2006 to 30% in 2017.
Summary
Health
- In 2017, Medicare spending accounted for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1). Medicare plays a major role in the health care system, accounting for 20 percent of total national health spending in 2016, 29 percent of spending on retail sales of prescription drugs, 25 percent of spending on hospital care, and 23 percent of spending on physici...
Cost
- In 2017, Medicare benefit payments totaled $702 billion, up from $425 billion in 2007 (Figure 2). While benefit payments for each part of Medicare (A, B, and D) increased in dollar terms over these years, the share of total benefit payments represented by each part changed. Spending on Part A benefits (mainly hospital inpatient services) decreased from 47 percent to 42 percent, sp…
Causes
- Slower growth in Medicare spending in recent years can be attributed in part to policy changes adopted as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Budget Control Act of 2011 (BCA). The ACA included reductions in Medicare payments to plans and providers, increased revenues, and introduced delivery system reforms that aimed to improve efficiency and quality of patient care …
Effects
- In addition, although Medicare enrollment has been growing around 3 percent annually with the aging of the baby boom generation, the influx of younger, healthier beneficiaries has contributed to lower per capita spending and a slower rate of growth in overall program spending. In general, Part A trust fund solvency is also affected by the level of growth in the economy, which affects …
Impact
- Prior to 2010, per enrollee spending growth rates were comparable for Medicare and private health insurance. With the recent slowdown in the growth of Medicare spending and the recent expansion of private health insurance through the ACA, however, the difference in growth rates between Medicare and private health insurance spending per enrollee has widened.
Future
- While Medicare spending is expected to continue to grow more slowly in the future compared to long-term historical trends, Medicares actuaries project that future spending growth will increase at a faster rate than in recent years, in part due to growing enrollment in Medicare related to the aging of the population, increased use of services and intensity of care, and rising health care pri…
Funding
- Medicare is funded primarily from general revenues (41 percent), payroll taxes (37 percent), and beneficiary premiums (14 percent) (Figure 7). Part B and Part D do not have financing challenges similar to Part A, because both are funded by beneficiary premiums and general revenues that are set annually to match expected outlays. Expected future increases in spending under Part B and …
Assessment
- Medicares financial condition can be assessed in different ways, including comparing various measures of Medicare spendingoverall or per capitato other spending measures, such as Medicare spending as a share of the federal budget or as a share of GDP, as discussed above, and estimating the solvency of the Medicare Hospital Insurance (Part A) trust fund.
Purpose
- The solvency of the Medicare Hospital Insurance trust fund, out of which Part A benefits are paid, is one way of measuring Medicares financial status, though because it only focuses on the status of Part A, it does not present a complete picture of total program spending. The solvency of Medicare in this context is measured by the level of assets in the Part A trust fund. In years whe…
Benefits
- A number of changes to Medicare have been proposed that could help to address the health care spending challenges posed by the aging of the population, including: restructuring Medicare benefits and cost sharing; further increasing Medicare premiums for beneficiaries with relatively high incomes; raising the Medicare eligibility age; and shifting Medicare from a defined benefit s…