What is the current tax rate for Medicare?
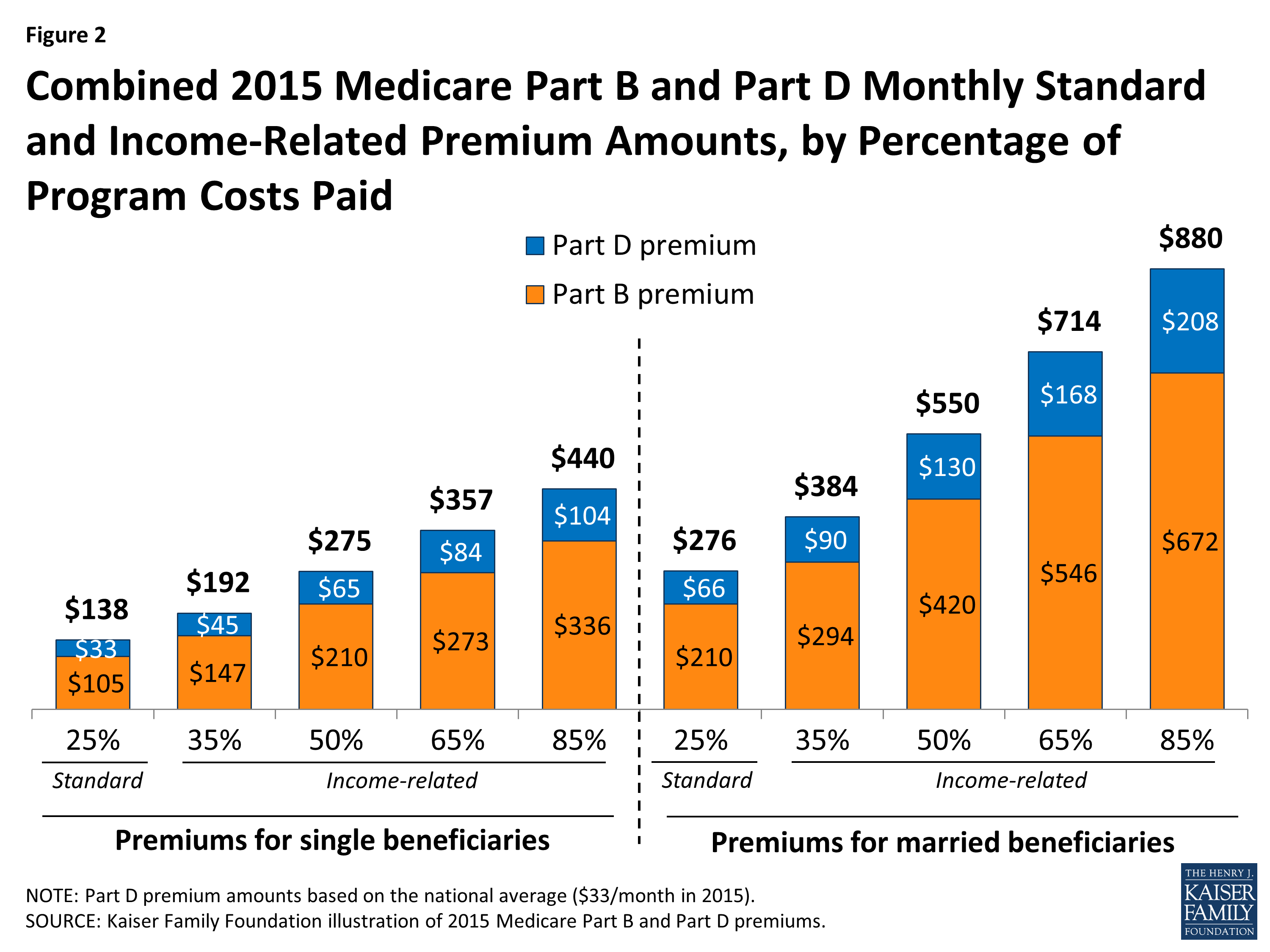
Nov 10, 2016 · For the remaining roughly 30 percent of beneficiaries, the standard monthly premium for Medicare Part B will be $134.00 for 2017, a 10 percent increase from the 2016 premium of $121.80. Because of the “hold harmless” provision covering the other 70 percent of beneficiaries, premiums for the remaining 30 percent must cover most of the increase in …
How to calculate additional Medicare tax properly?
If you’ve accumulated 40 quarter credits (and most people do), then you can enroll in Part A for free. Otherwise, the costs are as follows: For people who earn 30-39 quarter credits, the monthly premium is $227 in 2017. For those who earn fewer than 30 quarter credits, the monthly premium is $413 in 2017.
What is the additional Medicare tax?
2016 2017. o . Tax Rate: Employee 7.65% 7.65% . Self-Employed 15.30% 15.30% . NOTE: The 7.65% tax rate is the combined rate for Social Security and Medicare. The Social Security portion (OASDI) is 6.20% on earnings up to the applicable taxable maximum amount (see below). The Medicare portion (HI) is 1.45% on all earnings. Also, as of January
Why is there a cap on the FICA tax?
3 rows · Oct 18, 2016 · 2017 FICA Rate (Social Security + Medicare withholding) Employee: 7.65% Employer 7.65% ...
What is the Medicare tax rate?
What was the tax rate in 2017?
| Tax rate | Single | Head of household |
|---|---|---|
| 10% | Up to $9,325 | Up to $13,350 |
| 15% | $9,326 to $37,950 | $13,351 to $50,800 |
| 25% | $37,951 to $91,900 | $50,801 to $131,200 |
| 28% | $91,901 to $191,650 | $131,201 to $212,500 |
Who pays the 3.8 Medicare tax?
What is the Medicare tax rate for 2018?
How many tax rates were there for 2018?
What was 2017 standard deduction?
What is the additional 3.8 tax?
What income is subject to the 3.8 Medicare tax?
What is 3.8 Obamacare tax?
How are Medicare wages calculated?
What is the Medicare tax rate for 2021?
What is the Medicare tax rate for 2022?
How much is the average Social Security payment for 2017?
The SSA estimates that the average monthly Social Security benefits payable in January 2017 for all retired workers will be $1,360, up only $5 from the 2016 average payment of $1,355. While the 2017 benefit increase is small, SSI recipients had no cost-of-living adjustment in 2016 due to low inflation.
What is the tax rate for Medicare and Social Security?
Note: The 7.65% tax rate is the combined rate for Social Security and Medicare. The Social Security portion is 6.20% on earnings up to the applicable taxable-maximum amount. The Medicare portion is 1.45% on all earnings.
How much did Social Security increase in 2017?
Monthly Social Security and Supplemental Security Income (SSI) benefits for more than 65 million Americans will increase just 0.3 percent in 2017, the SSA also announced.
What is the maximum Social Security benefit for 2017?
The maximum Social Security benefit for workers retiring at full retirement age in 2017 will be $2,687 per month, up from $2,639 per month in 2016. The SSA estimates that the average monthly Social Security benefits payable in January 2017 for all retired workers will be $1,360, up only $5 from the 2016 average payment of $1,355.
Will Social Security increase Medicare?
For many SSI recipients, their Social Security increase is likely to be offset by higher Medicare premiums, which could be even steeper for those covered by Medicare Part B if they have delayed taking Social Security because they are still working, for instance. Increases in Retirement Earnings Limit.
Tables for Percentage Method of Withholding
The following payroll tax rates tables are from IRS Notice 1036. The tables include federal withholding for year 2017 (income tax), FICA tax, Medicare tax and FUTA taxes.
How to Calculate 2017 Federal Income Tax by Using Federal Withholding Tax Table
1. Find your pay period: weekly, biweekly, semi-monthly, monthly or daily
What is EFTPS in tax?
Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS) Employers must pay their Federal Tax Liabilities through the Electronic Federal Tax Payment System unless they pay less than $2,500 in quarterly payroll tax liabilities and pay their liability when filing their employment tax returns (Forms 941 and 944).
When is the W-2 due for 2016?
The due date for filing 2016 Form W-2 with the Social Security Administration is now January 31st. This also applies to certain Form 1099-MISC reporting for non-employee compensation such as payments to independent contractors.
What is Abacus payroll?
Abacus Payroll, Inc. is a leading provider of payroll solutions for businesses of all sizes. Whether yours is a family-owned small business or a national corporation, we provide payroll, tax and other financial services on time and at an affordable price. Unlike other payroll providers, Abacus Payroll will assign your very own payroll specialist who will understand your payroll needs inside and out. So no more speaking to a different person each time, no more sitting on hold for hours and most importantly no more missed deadlines! Contact us today to see how we can help your business. You can count on us.
Do new employees need to file W-4?
All new employees are required to file Forms W-4 and I-9 which are to be kept on file by the employer. A new Form W-4 should be obtained when an employee’s filing status or exemption changes.
What is the AMT rate for 2017?
In 2017, the 28 percent AMT rate applies to excess AMTI of $187,800 for all taxpayers ($93,900 for unmarried individuals). Under current law, AMT exemptions phase out at 25 cents per dollar earned once taxpayer AMTI hits a certain threshold.
What is the AMT exemption for 2017?
The AMT is levied at two rates: 26 percent and 28 percent. The AMT exemption amount for 2017 is $54,300 for singles and $84,500 for married couples filing jointly (Table 7).
What is PEP tax?
PEP and Pease are two provisions in the tax code that increase taxable income for high-income earners. PEP is the phaseout of the personal exemption and Pease (named after former U.S. House Representative Donald Pease ) phases out the value of most itemized deductions once a taxpayer’s adjusted gross income reaches a certain amount.
Why was the Alternative Minimum Tax created?
The Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) was created in the 1960s to prevent high-income taxpayers from avoiding the individual income tax. This parallel tax income system requires high-income taxpayers to calculate their tax bill twice: once under the ordinary income tax system and again under the AMT.
What is the Medicare tax rate for high income people?
For both of these taxes, employers match their employees' contributions -- for example, the Medicare tax rate is 1.45% each for employers and employees.
How much is FICA tax?
How much are the current FICA tax rates? 1 The Social Security tax rate is 6.2% of earned income up to a certain cap. For 2017, the maximum amount of income that can be subject to Social Security tax is $127,200. No Social Security tax is assessed on income in excess of this amount. 2 The Medicare tax rate is much lower, at 1.45% of earned income. However, there is no wage cap -- every dollar of earned income is subject to Medicare taxes, even if the income is in the millions. High-income individuals pay an additional Medicare tax as part of the Affordable Care Act as well.
What is FICA tax?
FICA, which stands for Federal Insurance Contribution Act, is a tax that is paid by employees as well as their employers, and is often referred to as the payroll tax. The purpose of the FICA tax is to fund the Social Security and Medicare programs, which provide benefits to American retirees.
What is FICA payroll tax?
FICA is the U.S. federal payroll tax, designed to help fund the Social Security and Medicare programs. As of 2017, about 171 million people work and contribute FICA taxes. Image source: Getty Images. The basic idea behind FICA is that the current generation of workers is funding these programs for today's retirees, ...
Will Social Security run out of reserves?
Eventually -- in 2034 for Social Security and 2028 for Medicare -- both will be completely out of reserves and will need to make across-the-board benefit cuts.
Where is Matt from Motley Fool?
Matt is a Certified Financial Planner based in South Carolina who has been writing for The Motley Fool since 2012. Matt specializes in writing about bank stocks, REITs, and personal finance, but he loves any investment at the right price.