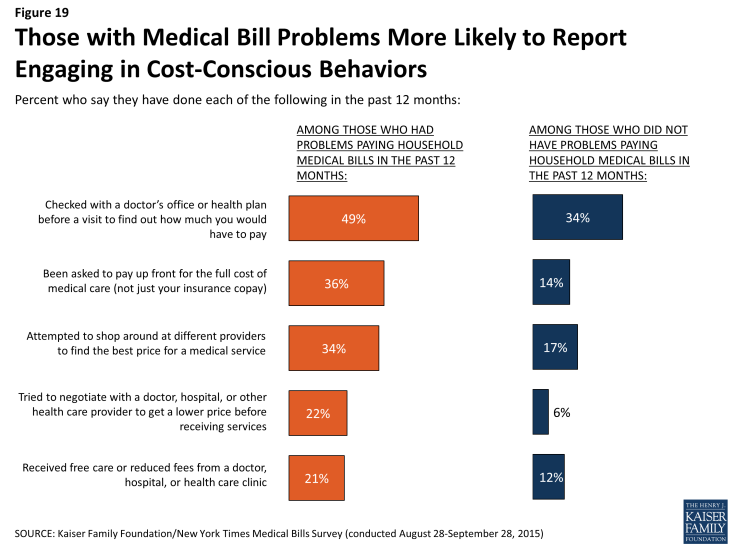
What percentage of Medicare bad debt does a hospital get paid?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) pays hospitals 65% of their gross Medicare bad debt if the documentation is in place to demonstrate appropriate collection efforts and the patient’s inability to pay ( Acute Care hospital inpatient Prospective Payment System, CMS.gov, February 2019).
What are the top drivers of medical debt?
The top drivers of medical debt are often unpredictable, unavoidable procedures. These include emergency room visits (39%), doctor or specialist visits (28%), surgery (26%), childbirth (22%) and dental care (20%). Medical debt is preventing consumers from achieving financial milestones.
How much medical debt do Americans have?
Sixty percent of Americans have been in debt due to medical expenses, our survey found. Medical debt can weigh as heavily on a household’s budget as any other debt, such as credit card debt, auto loans or even student loans. On average, Americans with medical debt owe between $5,000 to $9,999.
How do you tackle Medicare bad debt?
When tackling uncompensated care, specifically as it relates to Medicare bad debt, it is important to address the problem holistically, to ensure all your earned revenue is realized. Healthcare is becoming increasingly unaffordable to many, and patient bad debt is an escalating issue.
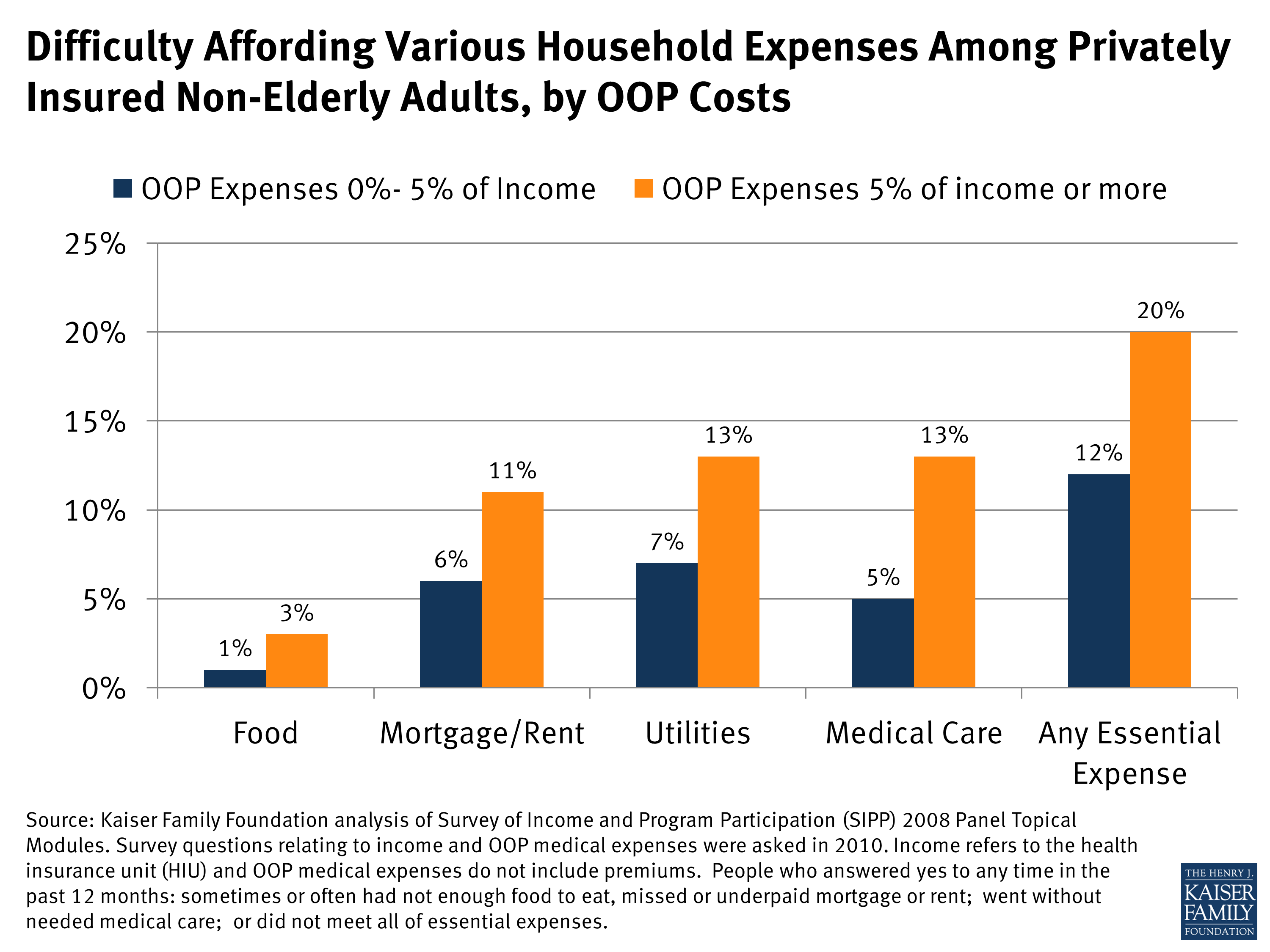
Who has the most medical debt?
Americans Likely Owe Hundreds of Billions of Dollars in Total Medical DebtPeople ages 35-49 (11%) and 50-64 (12%) are more likely than other adults to report medical debt. ... Larger shares of people in poor health (21%) and living with a disability (15%) report medical debt.More items...•
Which income group had the most trouble paying their medical bills?
While these difficulties are rising across income brackets, families with low to moderate income appear to be burdened the most. The report finds that more than half of working-age adults earning less than $40,000 a year reported problems paying medical bills or being in debt from medical expenses.
What of Americans have medical debt?
This analysis of government data estimates that 9% of adults – or roughly 23 million people – owe more than $250 due to health costs. About half of those reporting significant medical debt owe more than $2,000.
What does Medicare spend the most on?
In this report, CBO describes that uninsured population....PROJECTIONS FOR MAJOR HEALTH CARE PROGRAMS FOR FY 2022.MEDICARE (Net of Offsetting Receipts)$768 BillionPREMIUM TAX CREDITS AND RELATED SPENDING$89 BillionCHILDREN'S HEALTH INSURANCE PROGRAM$17 Billion1 more row
What is the leading cause of debt in America?
Main source of debt among consumers in the U.S. 2017-2021 In 2021, 24 percent of U.S. consumers said that their main source of debt was their home mortgage, followed by credit card debt. The share of consumers with no debt increased six percent between 2020 and 2021.
Who has medical debt?
People with lower and modest incomes are more likely to have significant medical debt. We find that 12% of adults with incomes below 400% of the federal poverty level report having significant medical debt.
What is the number one debt in America?
mortgagesConsumers in the United States had 15.24 trillion dollars in debt as of the third quarter of 2021, the majority of which was home mortgages, at 10.44 trillion U.S. dollars. Student loan debt was the second largest component, totaling 1.58 trillion U.S. dollars.
How many Americans are debt free?
And yet, over half of Americans surveyed (53%) say that debt reduction is a top priority—while nearly a quarter (23%) say they have no debt. And that percentage may rise.
What causes medical debt?
Hospitals contribute to medical debt when they overcharge patients who are uninsured or underinsured for care, fail to notify patients about financial assistance or public coverage programs, and use overly aggressive collection tactics or fail to institute financial assistance policies that reflect their communities' ...
How much is Medicare in debt?
Medicare accounts for a significant portion of federal spending. In fiscal year 2020, the Medicare program cost $776 billion — about 12 percent of total federal government spending. Medicare was the second largest program in the federal budget last year, after Social Security.
Does Medicare run a deficit?
Last year, the Medicare Part A fund ran a deficit of $5.8 billion, and that excess of spending over revenue is expected to continue until it finally runs dry.
Which program has the highest expenditure per enrollee in the US?
MedicareYou have no right to use this feature....Health spending per enrollee in the United States in 2018 and 2019, by insurance.Characteristic20182019Medicare12,76713,276Medicaid8,1238,4852 more rows•Sep 8, 2021
What is bad debt in Medicare?
When hospitals and other providers of health care are unable to collect out-of-pocket payments from their patients, those uncollected funds are called bad debt. Historically, Medicare has paid some of the bad debt owed by its beneficiaries on the grounds that doing so prevents those costs from being shifted to others (that is, private insurance plans and people who are not Medicare beneficiaries). The unpaid and uncollectible deductible and coinsurance amounts for covered services furnished to Medicare beneficiaries are referred to as allowable bad debt. In the case of dual-eligible beneficiaries—Medicare beneficiaries who also are enrolled in Medicaid—out-of-pocket obligations that remain unpaid by Medicaid are uncollectible and therefore are included in allowable bad debt. Under current law, Medicare reimburses eligible facilities—hospitals, skilled nursing facilities, various types of health care centers, and facilities treating end-stage renal disease—for 65 percent of allowable bad debt. The Congressional Budget Office estimates that Medicare's spending on allowable bad debt was $3.5 billion in 2017.
How much will Medicare reduce in 2022?
The first alternative—reducing the percentage of allowable bad debt that Medicare reimburses to participating facilities by 20 percentage points (that is, from 65 percent to 45 percent) by 2022—would reduce outlays by $12 billion from 2020 through 2028, CBO estimates. The second alternative, in which the reduction would be doubled from 20 to 40 percentage points (that is, from 65 percent to 25 percent), would reduce outlays over that period by twice as much—$24 billion. The third alternative, eliminating coverage of bad debt, would save $39 billion over that period. The estimated savings associated with other percentage-point reductions would be roughly proportional to the magnitude of the reduction. For each of these alternatives, CBO estimates that the reductions in spending would increase over the period in line with the projected growth in Medicare spending.
What percentage of Medicare is spending?
Key Facts. Medicare spending was 15 percent of total federal spending in 2018, and is projected to rise to 18 percent by 2029. Based on the latest projections in the 2019 Medicare Trustees report, the Medicare Hospital Insurance (Part A) trust fund is projected to be depleted in 2026, the same as the 2018 projection.
How is Medicare Financed?
Medicare is funded primarily from general revenues (43 percent), payroll taxes (36 percent), and beneficiary premiums (15 percent) (Figure 7) .
How much does Medicare cost?
In 2018, Medicare spending (net of income from premiums and other offsetting receipts) totaled $605 billion, accounting for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1).
Why is Medicare spending so slow?
Slower growth in Medicare spending in recent years can be attributed in part to policy changes adopted as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Budget Control Act of 2011 (BCA). The ACA included reductions in Medicare payments to plans and providers, increased revenues, and introduced delivery system reforms that aimed to improve efficiency and quality of patient care and reduce costs, including accountable care organizations (ACOs), medical homes, bundled payments, and value-based purchasing initiatives. The BCA lowered Medicare spending through sequestration that reduced payments to providers and plans by 2 percent beginning in 2013.
What is the average annual growth rate for Medicare?
Average annual growth in total Medicare spending is projected to be higher between 2018 and 2028 than between 2010 and 2018 (7.9 percent versus 4.4 percent) (Figure 4).
What has changed in Medicare spending in the past 10 years?
Another notable change in Medicare spending in the past 10 years is the increase in payments to Medicare Advantage plans , which are private health plans that cover all Part A and Part B benefits, and typically also Part D benefits.
What is excess health care cost?
Over the next 30 years, CBO projects that “excess” health care cost growth—defined as the extent to which the growth of health care costs per beneficiary, adjusted for demographic changes, exceeds the per person growth of potential GDP (the maximum sustainable output of the economy)—will account for half of the increase in spending on the nation’s major health care programs (Medicare, Medicaid, and subsidies for ACA Marketplace coverage), and the aging of the population will account for the other half.
What is medical debt?
Medical debt results from the high or unexpected health care expenses that an individual is unable to pay. It is a significant and growing problem in the United States where public health insurance programs are only available to certain groups of people, mainly the elderly through Medicare and those with low income through Medicaid.
How can we solve the medical debt problem?
One way of solving the medical debt problem could be to enhance health insurance coverage for everyone through a single-payer health care system. Over the last few years, public support and opposition for a Medicare-for-all national health plan has remained fairly consistent. However, changes to the U.S. health system are a highly politicized issue and are difficult to implement. On an individual level, many people are unaware that they can try to lower their medical bills. According to a 2021 survey, the percentage of U.S. adults with medical debts who had successfully negotiated their bill was 60 percent, while 32 percent of respondents were partially successful. Many hospitals are adding to the financial problems of patients by suing them. Data collected on the number of court actions taken by the largest hospitals in the U.S against patients with unpaid bills revealed a striking finding: Between 2018 and 2020, 97 percent of court actions were filed by just 10 of the 100 hospitals analyzed, seeking millions of dollars from patients. Partly due to negative publicity and the COVID-19 pandemic, many hospitals have stopped this practice, but it remains to be seen whether this will last.
What percentage of people with medical debt will be suing hospitals in 2021?
According to a 2021 survey, the percentage of U.S. adults with medical debts who had successfully negotiated their bill was 60 percent , while 32 percent of respondents were partially successful. Many hospitals are adding to the financial problems of patients by suing them.
Is Medicare for all a national plan?
Over the last few years, public support and opposition for a Medicare-for-all national health plan has remained fairly consistent. However, changes to the U.S. health system are a highly politicized issue and are difficult to implement.
Will Americans pay surprise medical bill 2019?
US voters most likely to have difficulty paying surprise medical bill 2019. Americans most likely unable to pay surprise medical bill 2019, by demographic.
Does the US have private health insurance?
The country has both public and private insurers, but data regarding U.S. health insurance by type of coverage shows the majority of people have private health insurance through their employer. Nevertheless, just because an individual has health insurance through their employer does not necessarily make them impervious to medical debt.
What is medical debt?
Medical debt can arise when people must pay out-of-pocket for care not covered by health insurance or to which cost-sharing (such as deductibles) applies. Medical debt might also result from health insurance premiums that individuals find difficult to afford. 2 The consequences of medical debt can be severe.
What is the ACA report on medical debt?
Most of the case studies feature people who struggled with medical debt while covered under health plans that would be considered typical and mainstream today. The report concludes with a discussion of how provisions of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) may influence the factors that contribute to medical debt.
What are the problems with unaffordable medical bills?
People with unaffordable medical bills report higher rates of other problems – including difficulty affording housing and other basic necessities, credit card debt, bankruptcy, and barriers accessing health care. This report examines medical debt through case studies of nearly two dozen people who recently experienced such problems, ...
How many Americans have difficulty paying medical bills?
Endnotes. An estimated 1 in 3 Americans report having difficulty paying their medical bills – that is, they have had problems affording medical bills within the past year, or they are gradually paying past bills over time, or they have bills they can’t afford to pay at all. 1 Medical debt – and a host of related problems – can result ...
What is the ACA case study?
Most of the case studies feature people who struggled with medical debt while covered under health plans that would be considered typical and mainstream today. The report concludes with a discussion of how provisions of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) may influence the factors that contribute to medical debt.
Can medical debt be stopped?
Once it starts, medical debt can be hard to stop. Most of those interviewed struggled for years to climb out of medical debt, and for some, new debts arose even after prior ones had been resolved. This was the case for people with chronic health conditions as well as for people with high medical bills from a single health event. Fifteen of those interviewed used credit cards to pay at least some of their outstanding medical bills, and resulting finance charges increased their debt.
What is Medicare bad debt?
Medicare bad debt is defined as Medicare coinsurance and deductible amounts that are unpaid and uncollectable from the patient. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) pays hospitals 65% of their gross Medicare bad debt if ...
How much bad debt can be recovered from Medicare?
Hundreds of millions of dollars of unrealized Medicare bad debt revenue can be recovered at scale if reporting and analysis are performed efficiently with automation — whether via a fully outsourced consulting service or by using a SaaS solution. Recoveries can be close to a half a million dollars per provider (TransUnion Healthcare proprietary data).
How much of a hospital's annual revenue is patient financial responsibility?
Patient financial responsibility represents more than 30% of a hospital’s annual revenues. When tackling uncompensated care, specifically as it relates to Medicare bad debt, it is important to address the problem holistically, to ensure all your earned revenue is realized. Healthcare is becoming increasingly unaffordable to many, ...
How to find bad debts?
Analyze the data. Examining accounting and transaction codes should provide an in-depth analysis to find bad debts that are payable but may have been missed. Consider having an outside partner analyze the data, which may uncover missed or previously unknown opportunities.
What does every dollar of payment mean for a hospital?
To a hospital, every dollar of payment means a better opportunity to deliver excellent patient care. By finding the right partner and tools, hospitals can accurately and efficiently recover Medicare-bad-debt revenue. The money is waiting — go get it.
Does Medicare give back money?
Secure defendable documentation. Medicare doesn’t like giving money back, so reports need to be defensible on audit. Ensure the process delivers results with the full documentation required for submission to Medicare.
Do people on Medicare have to pay for healthcare?
Although many people struggle to pay for healthcare, the issue is particularly prevalent among Medicare beneficiaries, who are often retired and on a fixed income.
Why is medical debt so different from other types of debt?
Medical debt is unlike other kinds of debts because people often cannot choose whether to incur it. A poorer person may choose to buy a less expensive car than her richer neighbor, but if she has a heart attack and needs surgery, she will get a bill just as big as her neighbor.
How does Medicaid help reduce medical debt?
In states that have expanded, most low-income adults can get coverage without paying premiums, and with minimal cost sharing. Mechanically, Medicaid tends to eliminate the kinds of medical bills that result in outstanding debts.
What is the largest source of debt that Americans owe collections agencies?
The researchers found that, between 2009 and 2020, unpaid medical bills became the largest source of debt that Americans owe collections agencies. Overall debt, both from medical bills and other sources, declined during that period as the economy recovered from the Great Recession.
What is the largest source of debt in collections?
A new study finds that health care has become the country’s largest source of debt in collections. Those debts are largest where Medicaid wasn’t expanded.
Does the $140 billion in debt count as medical bills?
The $140 billion in debt does not count all medical bills owed to health care providers, because it measures only debts that have been sold to collections agencies. The increasing number of lawsuits that hospitals file against patients to collect debt, which can lead to legal fees or wage garnishments, are not included in the figure.
Does Medicaid expand in the South?
The states that have declined to expand Medicaid — particularly in the South — started out having more medical debt before Obamacare passed, and since other states have expanded Medicaid, the chasm has grown wider. In 2020, Americans living in states that did not expand Medicaid owed an average of $375 more than those in states ...
Can medical debt be repaid?
But medical debts are different in another way, too: They are much less likely to be repaid. Prior research suggests that many people with medical debts have other kinds of debt that may be a bigger priority. Failing to pay your utility bills could result in shut-offs, and failing to pay your auto loan could cause your car to be repossessed. Medical debts, in contrast, tend mostly to harm people’s credit reports and peace of mind.
Why do people go into medical debt?
These are just a few of the reasons why people with good health insurance can go into medical debt. Bad luck, denied claims, non- formulary prescriptions, huge cost discrepancies from one facility to another, chronic conditions and the astronomical price of COBRA premiums when you get laid off can also contribute. Even with an awareness of these problems in our current healthcare system, you may not be able to stay out of medical debt. But knowing how so many people find themselves in this situation may give you information that helps you at least reduce the extent of medical debt if it ever happens to you.
Do people with health insurance have medical debt?
But our simple advice ignores a terrible problem: Many people who do have health insurance—good health insurance, at that—still find themselves in medical debt. A 2017 survey showed that 19% of U.S. households could not pay for medical care immediately. 1
How much does a medical debt cost?
On average, Americans with medical debt owe between $5,000 to $9,999. Most (83%) owe more than $1,000, and 13% owe more than $20,000.
How many millennials have medical debt?
Nearly half (48%) of millennials have medical debt, more than any other age group. Two-thirds of millennials have been in debt due to medical bills at some point, as have a similar percentage of Gen Xers (68%). See the generational breakdown below:
How much can you deduct for dental care?
When tax season comes around, you may be able to deduct money used to pay for medical or dental care, up to 7.5% of your adjusted gross income. This is an effective way for families to save money on the cost of health care — however, 44% of those with medical debt didn’t know they could deduct it from their taxes.
How does medical debt affect people?
The cost of medical care may prevent people from seeking the services they need in the present, but it can also prevent them from planning for the future. Seventy-two percent of those who have had medical debt said that it prevented them from achieving key milestones, including:
How do Americans pay off medical bills?
Americans pay off their medical debt with borrowed money. A third of those who paid off medical bills used savings, but nearly a quarter used credit cards and 10% took out a medical loan. Three in four people who have had medical debt tried to negotiate their bill. Nearly all of those who did negotiate ...
How many people negotiate medical bills?
Of those who have negotiated a medical bill, 66% did so themselves, while 26% used a service to help them and 9% had another family member negotiate on their behalf.
What is medical debt?
Medical debt is preventing consumers from achieving financial milestones. A fifth of those with medical debt (19%) said it’s preventing them from buying a home. Additionally, 68% of those in medical debt have lost sleep worrying about it. Americans pay off their medical debt with borrowed money.

Summary
- When hospitals and other providers of health care are unable to collect out-of-pocket payments from their patients, those uncollected funds are called bad debt. Historically, Medicare has paid some of the bad debt owed by its beneficiaries on the grounds that doing so prevents those costs from being shifted to others (that is, private insurance pla...
Health
Cost
Causes
Effects
Impact
Future
Funding
- Slower growth in Medicare spending in recent years can be attributed in part to policy changes adopted as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Budget Control Act of 2011 (BCA). The ACA included reductions in Medicare payments to plans and providers, increased revenues, and introduced delivery system reforms that aimed to improve efficiency and quality of patient care …
Assessment
- In addition, although Medicare enrollment has been growing around 3 percent annually with the aging of the baby boom generation, the influx of younger, healthier beneficiaries has contributed to lower per capita spending and a slower rate of growth in overall program spending. In general, Part A trust fund solvency is also affected by the level of growth in the economy, which affects …
Purpose
- Prior to 2010, per enrollee spending growth rates were comparable for Medicare and private health insurance. With the recent slowdown in the growth of Medicare spending and the recent expansion of private health insurance through the ACA, however, the difference in growth rates between Medicare and private health insurance spending per enrollee has widened.
Benefits
- While Medicare spending is expected to continue to grow more slowly in the future compared to long-term historical trends, Medicares actuaries project that future spending growth will increase at a faster rate than in recent years, in part due to growing enrollment in Medicare related to the aging of the population, increased use of services and intensity of care, and rising health care pri…