
Medicare Act (1965)
- THE CONSTITUTIONAL BASIS FOR MEDICARE. Congress designed Medicare to promote the general welfare of the United States. ...
- CIRCUMSTANCES LEADING TO THE ADOPTION OF MEDICARE. ...
- ADMINISTRATION AND STRUCTURE OF THE MEDICARE PROGRAM. ...
- THE GROWTH AND EXPENSE OF THE MEDICARE PROGRAM. ...
How does the Affordable Care Act impact Medicare?
Jun 02, 2016 · 79 Stat. 286 - Medicare Law - July 30, 1965 On July 30, 1965, President Johnson signed the Medicare Law as part of the Social Security Act Amendments. This established both Medicare, the health insurance program for Americans over 65, and Medicaid, the health insurance program for low-income Americans.
Did the Social Security Act provide Medicare?
Feb 08, 2022 · On July 30, 1965, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed the Medicare and Medicaid Act, also known as the Social Security Amendments of 1965, into law. It established Medicare, a health insurance program for the elderly, and Medicaid, a health insurance program for people with limited income.
Is the Affordable Care Act the same as Medicare?
Mar 17, 2021 · Medicare for All Act of 2021 This bill establishes a national health insurance program that is administered by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
How to find Medicare law?
1965 – The Medicare and Medicaid Act On July 30, 1965, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed into law the Social Security Act Amendments, popularly known as the Medicare bill. It established Medicare, a health insurance program for the elderly, and Medicaid, a …

Teach with this document
This document is available on DocsTeach, the online tool for teaching with documents from the National Archives. Find teaching activities that incorporate this document, or create your own online activity.
Transcript
To provide a hospital insurance program for the aged under the Social Security Act with a supplementary medical benefits program and an extended program of medical assistance, to increase benefits under the Old-Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance System, to improve the Federal-State public assistance programs, and for other purposes.
What are the provisions of the HHS bill?
The bill also establishes a series of implementing provisions relating to (1) health care provider participation; (2) HHS administration; and (3) payments and costs, including the requirement that HHS negotiate prices for prescription drugs.
What is the Medicare for All Act of 2021?
Medicare for All Act of 2021. This bill establish es a national health insurance program that is administered by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Among other requirements, the program must (1) cover all U.S. residents; (2) provide for automatic enrollment of individuals upon birth or residency in the United States;
What is Medicare Part C?
Medicare Part C is an optional Medicare HMO, which enrollees may choose instead of Parts A and B. The HMO sets the additional premiums for Part C, and any deductibles, coinsurance and additional benefits, within the limits set by CMS.
What is the CMS?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), a federal agency within the Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) administers Medicare and Medicaid. DHHS also includes the Food and Drug Administration, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
What are the two major government programs that provide health insurance for working people?
Employers are the major providers of health insurance for working people and their dependents. But two major government programs also exist to ensure that Americans have access to health insurance: Medicaid provides health insurance for the poor, and Medicare provides health insurance for individuals sixty-five and over and the disabled.
How much did Medicare cost in 1970?
Medicare cost $7.7 billion in 1970; thirty years later the cost exceeded $224 billion per year. Medicaid and private health insurance have experienced inflation. Medicare has increasingly adopted price controls and managed care techniques in an attempt to control costs.
What is the constitutional basis for Medicare?
THE CONSTITUTIONAL BASIS FOR MEDICARE. Congress designed Medicare to promote the general welfare of the United States. The program's financing mechanisms proceed under the taxing and spending powers, together with the commerce clause.
How is Medicare funded?
Medicare is a federal program, funded from a mix of payroll taxes, premiums, and general tax revenues. On the benefits side, the government spent roughly $271 billion in 2003, 13 percent of the federal budget. Medicaid, by contrast, is a cooperative program between the states and the federal government.
What is the process of gradually adding benefits to Medicare?
The process of gradually adding benefits to Medicare is called incrementalism. In Medicaid, incrementalism has focused more on expanding eligibility to the near-poor and children. In July, 2003, Congress debated a new prescription drug benefit for Medicare. Expanded coverage predictably results in higher costs.
What is CMS in healthcare?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), administers Medicare, Medicaid, the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), and parts of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) ("Obamacare").
How much does Medicare cost in 2020?
In 2020, US federal government spending on Medicare was $776.2 billion.
What is Medicare and Medicaid?
Medicare is a national health insurance program in the United States, begun in 1965 under the Social Security Administration (SSA) and now administered by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). It primarily provides health insurance for Americans aged 65 and older, ...
How is Medicare funded?
Medicare is funded by a combination of a specific payroll tax, beneficiary premiums, and surtaxes from beneficiaries, co-pays and deductibles, and general U.S. Treasury revenue. Medicare is divided into four Parts: A, B, C and D.
What is a RUC in medical?
The Specialty Society Relative Value Scale Update Committee (or Relative Value Update Committee; RUC), composed of physicians associated with the American Medical Association, advises the government about pay standards for Medicare patient procedures performed by doctors and other professionals under Medicare Part B.
How many people have Medicare?
In 2018, according to the 2019 Medicare Trustees Report, Medicare provided health insurance for over 59.9 million individuals —more than 52 million people aged 65 and older and about 8 million younger people.
When did Medicare Part D start?
Medicare Part D went into effect on January 1, 2006. Anyone with Part A or B is eligible for Part D, which covers mostly self-administered drugs. It was made possible by the passage of the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003. To receive this benefit, a person with Medicare must enroll in a stand-alone Prescription Drug Plan (PDP) or public Part C health plan with integrated prescription drug coverage (MA-PD). These plans are approved and regulated by the Medicare program, but are actually designed and administered by various sponsors including charities, integrated health delivery systems, unions and health insurance companies; almost all these sponsors in turn use pharmacy benefit managers in the same way as they are used by sponsors of health insurance for those not on Medicare. Unlike Original Medicare (Part A and B), Part D coverage is not standardized (though it is highly regulated by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services). Plans choose which drugs they wish to cover (but must cover at least two drugs in 148 different categories and cover all or "substantially all" drugs in the following protected classes of drugs: anti-cancer; anti-psychotic; anti-convulsant, anti-depressants, immuno-suppressant, and HIV and AIDS drugs). The plans can also specify with CMS approval at what level (or tier) they wish to cover it, and are encouraged to use step therapy. Some drugs are excluded from coverage altogether and Part D plans that cover excluded drugs are not allowed to pass those costs on to Medicare, and plans are required to repay CMS if they are found to have billed Medicare in these cases.
What was the Medicare and Medicaid Act of 1965?
1965 – The Medicare and Medicaid Act. On July 30, 1965, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed into law the Social Security Act Amendments, popularly known as the Medicare bill. It established Medicare, a health insurance program for the elderly, and Medicaid, a health insurance program for the poor. “Larry Silver must have given me the assignment ...
When was Medicare enacted?
By: daryln. On July 30, 1965, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed into law the Social Security Act Amendments, popularly known as the Medicare bill. It established Medicare, a health insurance program for the elderly, and Medicaid, a health insurance program for the poor.
How does SSA safeguard the security of information?
We will safeguard the security of the information by requiring the use of access codes to enter the computer systems that will maintain the data and will store computerized records in secured areas that are accessible only to employees who require the information to perform their official duties. Any manually maintained records will be kept in locked cabinets or in otherwise secure areas. Furthermore, SSA employees having access to SSA databases maintaining personal information must sign a sanction document annually, acknowledging their accountability for making unauthorized access to or disclosure of such information.
When was Medicare Part D enacted?
Medicare Part D System. On December 8, 2003, the President signed into law Public Law 108-173, the Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act (MMA) of 2003. This new law amended section 1144 of the Social Security Act to require the Commissioner of Social Security to conduct additional outreach efforts to identify ...
How long has Medicare and Medicaid been around?
Medicare & Medicaid: keeping us healthy for 50 years. On July 30, 1965, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed into law legislation that established the Medicare and Medicaid programs. For 50 years, these programs have been protecting the health and well-being of millions of American families, saving lives, and improving the economic security ...
What is Medicare Part D?
Medicare Part D Prescription Drug benefit. The Medicare Prescription Drug Improvement and Modernization Act of 2003 (MMA) made the biggest changes to the Medicare in the program in 38 years. Under the MMA, private health plans approved by Medicare became known as Medicare Advantage Plans.
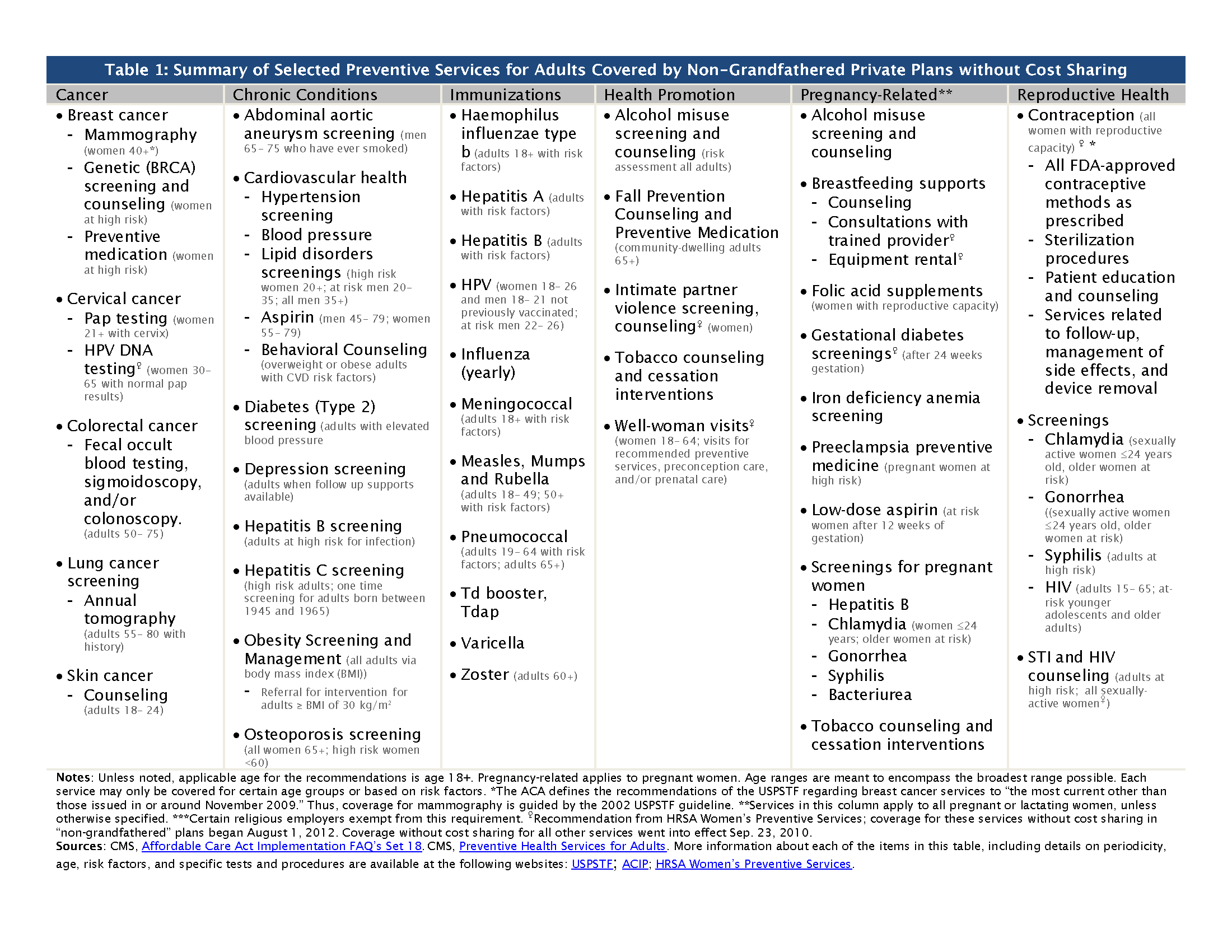
What is the Affordable Care Act?
The 2010 Affordable Care Act (ACA) brought the Health Insurance Marketplace, a single place where consumers can apply for and enroll in private health insurance plans. It also made new ways for us to design and test how to pay for and deliver health care.
When did Medicare expand?
Over the years, Congress has made changes to Medicare: More people have become eligible. For example, in 1972 , Medicare was expanded to cover the disabled, people with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) requiring dialysis or kidney transplant, and people 65 or older that select Medicare coverage.
When was the Children's Health Insurance Program created?
The Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) was created in 1997 to give health insurance and preventive care to nearly 11 million, or 1 in 7, uninsured American children. Many of these children came from uninsured working families that earned too much to be eligible for Medicaid.
Does Medicaid cover cash assistance?
At first, Medicaid gave medical insurance to people getting cash assistance. Today, a much larger group is covered: States can tailor their Medicaid programs to best serve the people in their state, so there’s a wide variation in the services offered.
What is the Medicare at 50 Act?
What the bill does. The Medicare at 50 Act does exactly what its name implies: allow people ages 50 to 64 access to Medicare, down from the current 65 minimum age. The bill would not require that people ages 50 to 64 enroll, but rather allows people to opt in and sign up.
How many Democrats sponsored the Medicare for all bill?
Nearly two-thirds of House Democrats last year sponsored a “Medicare for all” bill, which of course goes much further than a “Medicare for people age 50 and up” bill.
How many Democrats support lowering the age for Medicare?
Yet 77% support lowering the minimum age for Medicare — and that includes 69% of Republicans.
Who introduced the Medicare at 55 Act?
It was introduced in February as bill number S. 470 by Sen. Debbie Stabenow (D-MI). Notably, Sen. Stabenow’s new version offers an eligibility starting five years lower than her previous bill, 2017’s Medicare at 55 Act which never received a Senate vote.
Do Democrats want to expand Medicare?
Context. Almost all Democrats want to expand access to government-run health care, but whether to swing for the fences or not is dividing the party. Medicare is one of the most popular government-run programs, providing health care to those aged 65 and older.
What is 8AD Commonwealth consent?
8AD Commonwealth consent to conferral of functions etc. on Chief Executive Medicare by State and Territory laws. (1) A law of a State or Territory may confer functions, or impose duties, on the Chief Executive Medicare. Note: Section 8AF sets out when such a law imposes a duty on the Chief Executive Medicare.
What is 8AF in Medicare?
8AF When State and Territory laws impose a duty on Chief Executive Medicare. For the purposes of sections 8AD and 8AE, a law of a State or Territory imposes a duty on the Chief Executive Medicare if: (a) the law confers a function on the Chief Executive Medicare; and.
What is evidential material?
evidential material means a thing relevant to a relevant offence or relevant civil contravention, including such a thing in an electronic form. function includes power. medicare benefit means a medicare benefit under Part II of the Health Insurance Act 1973.
What is a pharmaceutical benefit?
pharmaceutical benefit means a pharmaceutical benefit as defined in Part VII of the National Health Act 1953. premises includes a place and a conveyance. relevant civil contravention has the same meaning as in subsection 124B (1) of the Health Insurance Act 1973. relevant offence is defined in section 3A.
What does "Occupier" mean in Medicare?
medicare program has the meaning given by section 41G. occupier, in relation to premises comprising a vessel, vehicle or aircraft, means the person apparently in charge of the vessel, vehicle or aircraft.
What is Section 8AF?
Note: Section 8AF sets out when such a law imposes a duty on the Chief Executive Medicare. (2) The duty is taken not to be imposed by this Act (or any other law of the Commonwealth) to the extent to which: (a) imposing the duty is within the legislative powers of the State or Territory concerned; and.
What is a misdescribed amendment?
If, despite the misdescription, the amendment can be given effect as intended, the amendment is incorporated into the compiled law and the abbreviation “ (md)” added to the details of the amendment included in the amendment history.
The Constitutional Basis For Medicare
- Congress designed Medicare to promote the general welfare of the United States. The program's financing mechanisms proceed under the taxing and spending powers, together with the commerce clause. Although some groups have challenged various features of the law, no litigant has challenged the Constitutional basis of the act as a whole.
Circumstances Leading to The Adoption of Medicare
- Prior to the adoption of Medicare and Medicaid, health insurance in the United States was primarily an employee benefit. In the late 1950s, however, Congress observed that two groups were left out of the employment-focused model: the retired elderly and the unemployed poor. President Lyndon Johnson's landslide election in 1964 paved the way for the adoption of Medica…
Administration and Structure of The Medicare Program
- The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), a federal agency within the Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) administers Medicare and Medicaid. DHHS also includes the Food and Drug Administration, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Institutes of Health(NIH). Medicare does not provide health care directly to seniors. Th…
The Growth and Expense of The Medicare Program
- Many of the services now covered by Medicare were not part of the original benefit package. Over time, Congress has added coverage for home health, hospice, end-stage renal disease, and many other services in response to political demands and medical needs. Congress also added coverage for the disabled in 1972. The legislature is currently debating whether to add an outpat…
Medicare Litigation
- Medicare spawns much litigation nationwide. Some court controversies involve administrative issues, such as whether or not a particular service or product is covered by Medicare. Many providers run afoul of the complex Medicare rules and regulations regarding the provision of care and reimbursement under Medicare. Some of these cases are prosecuted as Medicare "fraud," a…
Bibliography
- Jost, Timothy S. The Threats Facing our Public Health-care Programs and a Rightsbased Response. Oxford, NY: Oxford UniversityPress, 2003. Marmor, Theodore R. The Politics of Medicare. New York: A. de Gruyter, 2000. Vladeck, Bruce C. "Medicare and the Politics of Incrementalism." 26 J Health Politics, Policy and Law153 (Feb. 2001).
Overview
Medicare is a government national health insurance program in the United States, begun in 1965 under the Social Security Administration (SSA) and now administered by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). It primarily provides health insurance for Americans aged 65 and older, but also for some younger people with disabilitystatus as determined by the SSA, includ…
History
Originally, the name "Medicare" in the United States referred to a program providing medical care for families of people serving in the military as part of the Dependents' Medical Care Act, which was passed in 1956. President Dwight D. Eisenhowerheld the first White House Conference on Aging in January 1961, in which creating a health care program for social security beneficiaries was p…
Administration
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), administers Medicare, Medicaid, the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), and parts of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) ("Obamacare"). Along with the Departments of Labor and Treasury, the CMS also implements the insurance reform provisions of the Health Insurance Portability an…
Financing
Medicare has several sources of financing.
Part A's inpatient admitted hospital and skilled nursing coverage is largely funded by revenue from a 2.9% payroll taxlevied on employers and workers (each pay 1.45%). Until December 31, 1993, the law provided a maximum amount of compensation on which the Medicare tax could be imposed annually, in the same way that the Social Security payroll tax operates. Beginning on January 1, …
Eligibility
In general, all persons 65 years of age or older who have been legal residents of the United States for at least five years are eligible for Medicare. People with disabilities under 65 may also be eligible if they receive Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) benefits. Specific medical conditions may also help people become eligible to enroll in Medicare.
People qualify for Medicare coverage, and Medicare Part A premiums are entirely waived, if the f…
Benefits and parts
Medicare has four parts: loosely speaking Part A is Hospital Insurance. Part B is Medical Services Insurance. Medicare Part D covers many prescription drugs, though some are covered by Part B. In general, the distinction is based on whether or not the drugs are self-administered but even this distinction is not total. Public Part C Medicare health plans, the most popular of which are bran…
Out-of-pocket costs
No part of Medicare pays for all of a beneficiary's covered medical costs and many costs and services are not covered at all. The program contains premiums, deductibles and coinsurance, which the covered individual must pay out-of-pocket. A study published by the Kaiser Family Foundation in 2008 found the Fee-for-Service Medicare benefit package was less generous than either the typical large employer preferred provider organization plan or the Federal Employees He…
Payment for services
Medicare contracts with regional insurance companies to process over one billion fee-for-service claims per year. In 2008, Medicare accounted for 13% ($386 billion) of the federal budget. In 2016 it is projected to account for close to 15% ($683 billion) of the total expenditures. For the decade 2010–2019 Medicare is projected to cost 6.4 trillion dollars.
For institutional care, such as hospital and nursing home care, Medicare uses prospective payme…