
What percentage of federal budget is spent on Medicare?
Dec 15, 2021 · Medicare spending grew 3.5% to $829.5 billion in 2020, or 20 percent of total NHE. Medicaid spending grew 9.2% to $671.2 billion in 2020, or 16 percent of total NHE. Private health insurance spending declined 1.2% to $1,151.4 billion in 2020, or 28 percent of total NHE.
How much money has been spent on Medicare since 1970?
Sep 08, 2021 · Published by Statista Research Department , Sep 8, 2021 In 1970, some 7.5 billion U.S. dollars were spent on the Medicare program in the United States. Fifty years later, this figure stood at 925.8...
How much does the National Health expenditure (NHE) spend per person?
expenditures (accounting for 55 percent of total Medicare expenditures) and a 17.1 percent increase in Medicare private health plan spending. Per enrollee Medicare expenditures increased 1.4 percent in 2020, slowing from 4.2 percent in 2019, as enrollment growth slowed from 2.6 percent in 2019 to 2.1 percent in 2020.
How much did the US spend on health care in 2018?
Total Medicare Spending; Total Medicare Spending. Facebook Twitter LinkedIn ... Filling the need for trusted information on national health issues, the Kaiser Family Foundation is a nonprofit ...

How much did the US spend on Medicare in 2019?
roughly $644 billionThe federal government spent nearly $1.2 trillion on health care in fiscal year 2019 (table 1). Of that, Medicare claimed roughly $644 billion, Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Pro-gram (CHIP) about $427 billion, and veterans' medical care about $80 billion.
How much did the US spend on Medicare in 2020?
$829.5 billionMedicare spending totaled $829.5 billion in 2020, representing 20% of total health care spending. Medicare spending increased in 2020 by 3.5%, compared to 6.9% growth in 2019. Fee-for-service expenditures declined 5.3% in 2020 down from growth of 2.1% in 2019.Dec 15, 2021
How much is spent on Medicare each year?
In fiscal year 2020, the Medicare program cost $776 billion — about 12 percent of total federal government spending. Medicare was the second largest program in the federal budget last year, after Social Security.
What is total health expenditure?
Definition of Total Health Expenditure. This report tracks total health expenditure in the United States. This includes public and private spending on activities that – through the application of medical, paramedical and nursing knowledge and technology – have the goal of promoting health and preventing disease.
What is the total cost of healthcare in the US?
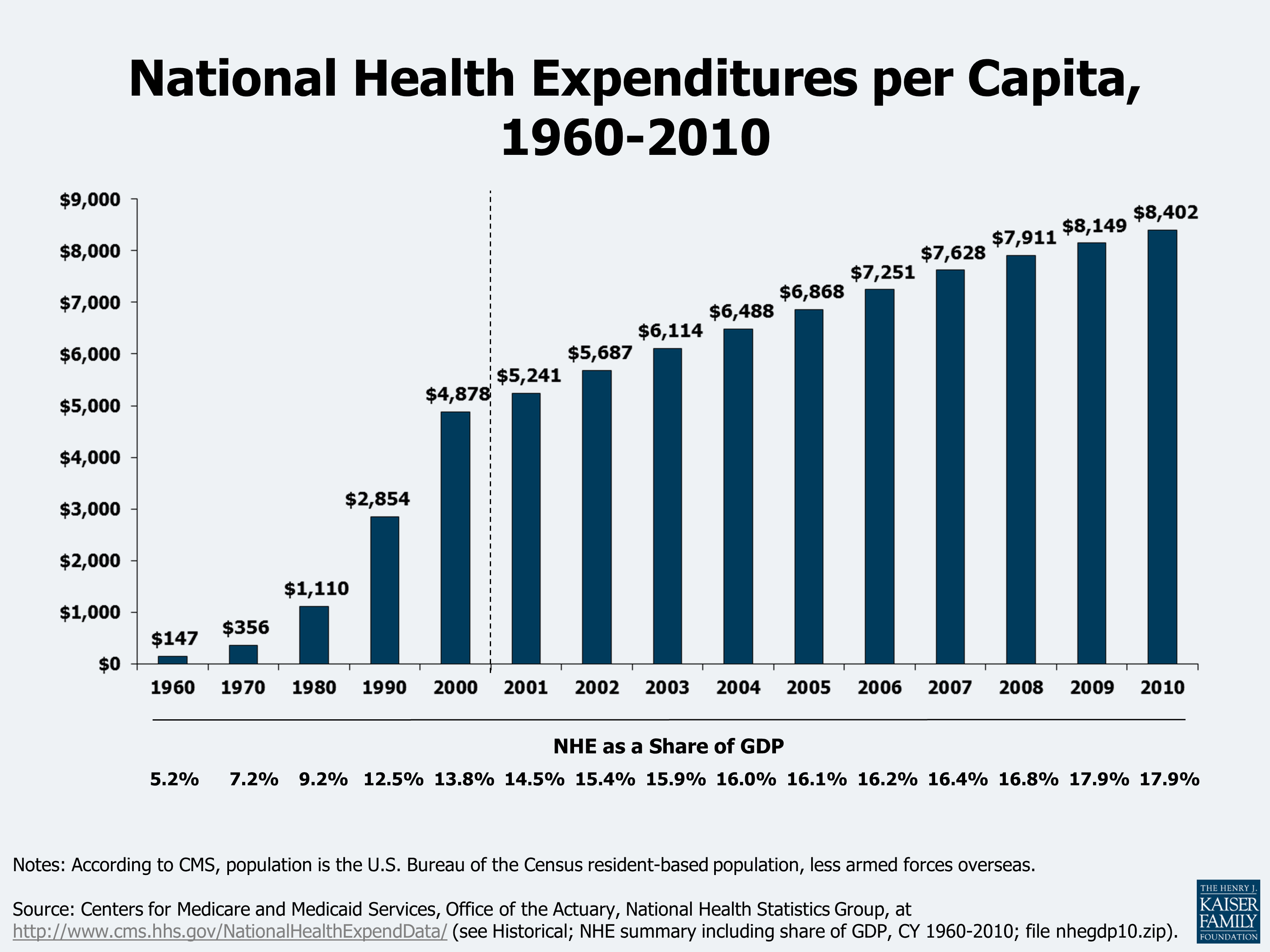
$4.1 trillionU.S. health care spending grew 9.7 percent in 2020, reaching $4.1 trillion or $12,530 per person. As a share of the nation's Gross Domestic Product, health spending accounted for 19.7 percent.Dec 15, 2021
How much did the United States spend on healthcare in 2021?
Dig Deeper. Including this government support, national healthcare spending in 2021 increased by 3.4 percent. This modest growth reflects the fact that federal spending decreased significantly last year, going from $287 billion in 2020 to $170 billion in 2021.Feb 24, 2022
Why has spending on Medicare increased?
Medicare per capita spending is projected to grow at an average annual rate of 5.1 percent over the next 10 years (2018 to 2028), due to growing Medicare enrollment, increased use of services and intensity of care, and rising health care prices.
Does Medicare cover all health care expenses?
For each lifetime reserve day, Medicare pays all covered costs except for a daily coinsurance. : All costs. In Original Medicare, this is the amount a doctor or supplier that accepts assignment can be paid. It may be less than the actual amount a doctor or supplier charges.
What is included in healthcare expenditure?
Total health expenditures represent the amount spent on health care and related activities (such as administration of insurance, health research, and public health), including expenditures from both public and private funds.Feb 25, 2022
What are the types of health expenditure?
The three main categories of public expenditure on health are Medical and Public Health, Family Welfare and Others.
What are the various forms of health expenditure?
Following are the various forms of health expenditures: Preventive medicine, Curative medicine, Social medicine, Provision of clean drinking water, and Good sanitation.Preventive medicine,Curative medicine,Social medicine,Provision of clean drinking water, and.Good sanitation.
How much did Medicare cost in 1970?
In 1970, some 7.5 billion U.S. dollars were spent on the Medicare program in the United States. Almost fifty years later, this figure stood at some 796.2 billion U.S. dollars. This statistic depicts total Medicare spending from 1970 to 2019.
What is Medicare coverage?
Increasing Medicare coverage. Medicare is the federal health insurance program in the U.S. for the elderly and those with disabilities. In the U.S., the share of the population with any type of health insurance has increased to over 90 percent in the past decade.
How much will Alzheimer's cost in 2020?
In 2020, Alzheimer's disease was estimated to cost Medicare and Medicaid around 206 billion U.S. dollars in care costs; by 2050, this number is projected to climb to 777 billion dollars.
How much did private health insurance cost in 2019?
Private Health Insurance (31 percent share): Private health insurance spending increased 3.7 percent to $1.2 trillion in 2019, which was slower than 5.6 percent growth in 2018. This deceleration was driven by a 7.9-percent decline in the net cost of private health insurance, which primarily resulted from the suspension of the health insurance tax in 2019. Spending on private health insurance benefits increased 5.4 percent in 2019, accelerating from growth of 4.4 percent in 2018. On a per enrollee basis, spending for private health insurance was $5,927 in 2019, an increase of 3.2 percent from 2018.
What percentage of government spending is private?
In 2019, the federal government and households accounted for the largest shares of spending (29 percent and 28 percent, respectively) followed by private businesses (19 percent), state and local governments (16 percent), and other private revenues (7 percent).
How much is Medicare spending?
Medicare spending was 15 percent of total federal spending in 2018, and is projected to rise to 18 percent by 2029. Based on the latest projections in the 2019 Medicare Trustees report, the Medicare Hospital Insurance (Part A) trust fund is projected to be depleted in 2026, the same as the 2018 projection. In 2018, Medicare benefit payments totaled ...
How many people are covered by Medicare?
Published: Aug 20, 2019. Medicare, the federal health insurance program for more than 60 million people ages 65 and over and younger people with long-term disabilities, helps to pay for hospital and physician visits, prescription drugs, and other acute and post-acute care services. This issue brief includes the most recent historical ...
Why is Medicare spending so high?
Over the longer term (that is, beyond the next 10 years), both CBO and OACT expect Medicare spending to rise more rapidly than GDP due to a number of factors, including the aging of the population and faster growth in health care costs than growth in the economy on a per capita basis.
When will Medicare be depleted?
In the 2019 Medicare Trustees report, the actuaries projected that the Part A trust fund will be depleted in 2026, the same year as their 2018 projection and three years earlier than their 2017 projection (Figure 8).
Will Medicare spending increase in the future?
While Medicare spending is expected to continue to grow more slowly in the future compared to long-term historical trends, Medicare’s actuaries project that future spending growth will increase at a faster rate than in recent years, in part due to growing enrollment in Medicare related to the aging of the population, increased use of services and intensity of care, and rising health care prices.
Does Medicare Advantage cover Part A?
Medicare Advantage plans, such as HMOs and PPOs, cover Part A, Part B, and (typically) Part D benefits. Beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans pay the Part B premium, and may pay an additional premium if required by their plan; about half of Medicare Advantage enrollees pay no additional premium.
Is Medicare spending comparable to private health insurance?
Prior to 2010, per enrollee spending growth rates were comparable for Medicare and private health insurance. With the recent slowdown in the growth of Medicare spending and the recent expansion of private health insurance through the ACA, however, the difference in growth rates between Medicare and private health insurance spending per enrollee has widened.
What is TME in medical?
All categories of medical expenses paid to providers. All non-claims related payments to providers, such as performance payments. Member cost-sharing payments to providers, such as deductibles, co-payments, and co-insurance. The net cost of private health insurance. Total Medical Expenses (TME) represents the full amount paid to providers ...
What is CHIA in Massachusetts?
CHIA monitors health care spending by public and private payers in Massachusetts using three key metrics: Total Health Care Expenditures (THCE), Total Medical Expenses (TME), and Alternative Payment Methods (APMs). These measures are all reported in CHIA's Annual Report on the Performance of the Massachusetts Health Care System.
How much did Australia spend on health care in 2017?
Australia spent $185 billion on health goods and services in 2017–18, or $7,485 per person. Between 2000–01 and 2017–18, total spending on health increased in real terms (after adjusting for inflation) from $91 billion to $185 billion —an average growth rate of 4.3% per year.
How is Australia's health system funded?
The health system is funded by all levels of governments as well as non-government entities such as individuals, private health insurance providers, and injury compensation insurers.
How many countries are members of the OECD?
The OECD currently has 36 member countries including Australia, which has been a member since 1971.
How much of Medicare is funded by the government?
They financed 15 percent of Medicare’s overall costs in 2019, about the same share as in 1970. The federal government’s general fund has been playing a larger role in Medicare financing. In 2019, 43 percent of Medicare’s income came from the general fund, up from 25 percent in 1970.
What is Medicare budget?
Budget Basics: Medicare. Medicare is an essential health insurance program serving millions of Americans and is a major part of the federal budget. The program was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson in 1965 to provide health insurance to people age 65 and older. Since then, the program has been expanded to serve the blind and disabled.
What are the benefits of Medicare?
Medicare is a federal program that provides health insurance to people who are age 65 and older, blind, or disabled. Medicare consists of four "parts": 1 Part A pays for hospital care; 2 Part B provides medical insurance for doctor’s fees and other medical services; 3 Part C is Medicare Advantage, which allows beneficiaries to enroll in private health plans to receive Part A and Part B Medicare benefits; 4 Part D covers prescription drugs.
How many people are on Medicare in 2019?
The number of people enrolled in Medicare has tripled since 1970, climbing from 20 million in 1970 to 61 million in 2019, and it is projected to reach about 88 million in 30 years.
What is Medicare Advantage?
Medicare is a federal program that provides health insurance to people who are age 65 and older, blind, or disabled. Medicare consists of four "parts": Part A pays for hospital care; Part B provides medical insurance for doctor’s fees and other medical services; Part C is Medicare Advantage, which allows beneficiaries to enroll in private health ...
How much did Medicare cost in 2019?
In 2019, it cost $644 billion — representing 14 percent of total federal spending. 1. Medicare has a large impact on the overall healthcare market: it finances about one-fifth of all health spending and about 40 percent of all home health spending. In 2019, Medicare provided benefits to 19 percent of the population. 2.
What percentage of GDP will Medicare be in 2049?
In fact, Medicare spending is projected to rise from 3.0 percent of GDP in 2019 to 6.1 percent of GDP by 2049. That increase in spending is largely due to the retirement of the baby boomers (those born between 1944 and 1964), longer life expectancies, and healthcare costs that are growing faster than the economy.
Summary
- Was this helpful?Thanks! Give more feedback
Health
| CHARACTERISTIC | TOTAL SPENDING IN BILLION U.S. DOLLARS |
|---|---|
| 2019 | 796.2 |
| 2018 | 740.7 |
| 2017 | 710.2 |
| 2016 | 678.7 |
| 2015 | 560.3 |
| 2014 | 613.3 |
| 2013 | 582.9 |
| 2012 | 574.2 |
Cost
Causes
- In 2017, Medicare spending accounted for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1). Medicare plays a major role in the health care system, accounting for 20 percent of total national health spending in 2016, 29 percent of spending on retail sales of prescription drugs, 25 percent of spending on hospital care, and 23 percent of spending on physici...
Effects
- In 2017, Medicare benefit payments totaled $702 billion, up from $425 billion in 2007 (Figure 2). While benefit payments for each part of Medicare (A, B, and D) increased in dollar terms over these years, the share of total benefit payments represented by each part changed. Spending on Part A benefits (mainly hospital inpatient services) decreased from 47 percent to 42 percent, sp…
Impact
- Slower growth in Medicare spending in recent years can be attributed in part to policy changes adopted as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Budget Control Act of 2011 (BCA). The ACA included reductions in Medicare payments to plans and providers, increased revenues, and introduced delivery system reforms that aimed to improve efficiency and quality of patient care …
Future
- In addition, although Medicare enrollment has been growing around 3 percent annually with the aging of the baby boom generation, the influx of younger, healthier beneficiaries has contributed to lower per capita spending and a slower rate of growth in overall program spending. In general, Part A trust fund solvency is also affected by the level of growth in the economy, which affects …
Funding
- Prior to 2010, per enrollee spending growth rates were comparable for Medicare and private health insurance. With the recent slowdown in the growth of Medicare spending and the recent expansion of private health insurance through the ACA, however, the difference in growth rates between Medicare and private health insurance spending per enrollee has widened.
Assessment
- While Medicare spending is expected to continue to grow more slowly in the future compared to long-term historical trends, Medicares actuaries project that future spending growth will increase at a faster rate than in recent years, in part due to growing enrollment in Medicare related to the aging of the population, increased use of services and intensity of care, and rising health care pri…
Purpose
- Medicare is funded primarily from general revenues (41 percent), payroll taxes (37 percent), and beneficiary premiums (14 percent) (Figure 7). Part B and Part D do not have financing challenges similar to Part A, because both are funded by beneficiary premiums and general revenues that are set annually to match expected outlays. Expected future increases in spending under Part B and …
Benefits
- Medicares financial condition can be assessed in different ways, including comparing various measures of Medicare spendingoverall or per capitato other spending measures, such as Medicare spending as a share of the federal budget or as a share of GDP, as discussed above, and estimating the solvency of the Medicare Hospital Insurance (Part A) trust fund.