When did Medicare add managed care to Medicaid?
The Federal Government, however, did not begin regulating Medicaid managed care arrangements until the early 1970s.The introduction of managed care as a formal Medicare option came more than two decades later, with the introduction of the Medicare Advantage program.
When did Medicare become a program?
In 1962, President Kennedy introduced a plan to create a healthcare program for older adults using their Social Security contributions, but it wasn’t approved by Congress. In 1964, former President Lyndon Johnson called on Congress to create the program that is now Medicare. The program was signed into law in 1965.
What is the history of managed care?
Appendix B. A Brief History of Managed Care The origins of managed care can be traced back to at least 1929, when Michael Shadid, a physician in Elk City, Oklahoma, established a health cooperative for farmers in a small community without medical specialists or a nearby general hospital.
What is the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003?
It was made possible by the passage of the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003. To receive this benefit, a person with Medicare must enroll in a stand-alone Prescription Drug Plan (PDP) or public Part C health plan with integrated prescription drug coverage (MA-PD).

What is the Medicare Act of 1965?
On July 30, 1965, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed the Medicare and Medicaid Act, also known as the Social Security Amendments of 1965, into law. It established Medicare, a health insurance program for the elderly, and Medicaid, a health insurance program for people with limited income.
When did managed Medicare Start?
In 1972 Congress first authorized capitation payments for services covered under Parts A and B. But no action was taken until 1976, when Medicare began to field demonstration projects that contracted with HMOs to provide care for Medicare beneficiaries in exchange for prospective payments.
When did Medicare become an act of legislation?
On July 30, 1965, President Lyndon Johnson traveled to the Truman Library in Independence, Missouri, to sign Medicare into law. His gesture drew attention to the 20 years it had taken Congress to enact government health insurance for senior citizens after Harry Truman had proposed it.
When was managed care introduced in the US?
In 1973, Congress passed the Health Maintenance Organization Act, which encouraged rapid growth of Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), the first form of managed care.
Who introduced Medicare?
the Whitlam governmentMedibank. The first iteration of Medicare was called Medibank, and it was introduced by the Whitlam government in 1975, early in its second term. The federal opposition under Malcolm Fraser had rejected Bills relating to its financing, which is why it took the government so long to get it established.
What did the Medicare Modernization Act do?
The 2003 Medicare Modernization Act (MMA) is considered one of the biggest overhauls of the Medicare program. It established prescription drug coverage and the modern Medicare Advantage program, among other provisions. It also created premium adjustments for low-income and wealthy beneficiaries.
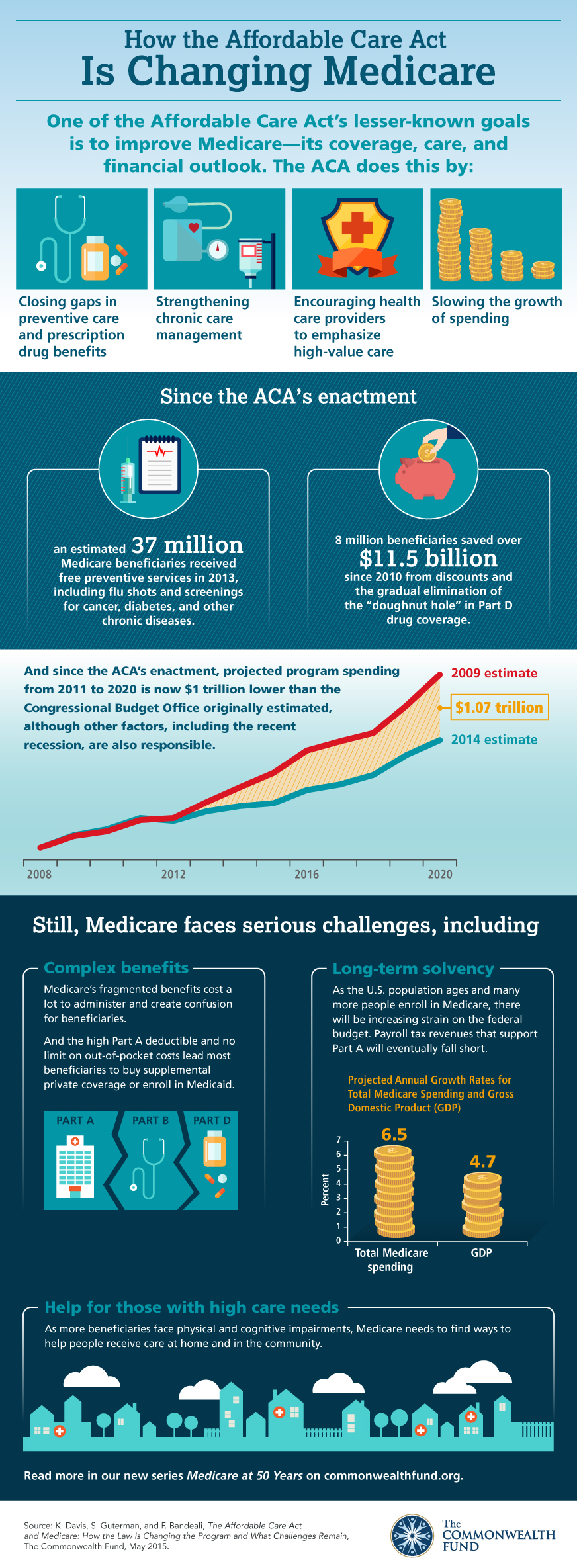
When was the Affordable Care Act passed?
March 23, 2010The Affordable Care Act (ACA), formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, and colloquially known as Obamacare, is a landmark U.S. federal statute enacted by the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by President Barack Obama on March 23, 2010.
Why was Medicare started?
The Medicare program was signed into law in 1965 to provide health coverage and increased financial security for older Americans who were not well served in an insurance market characterized by employment-linked group coverage.
Which was an indirect result of the Taft Hartley Act?
An indirect result of Taft-Hartley was the creation of third-party administrators (TPAs), which administer healthcare plans and process claims, thus serving as a system of checks and balances for labor and management.
What did the HMO Act of 1973 accomplish?
The Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) Act of 1973 provided for a Federal program to develop alternatives to the traditional forms of health care delivery and financing by assisting and encouraging the establishment and expansion of HMOs.
When was managed care founded?
History of managed care The origins of managed care in the United States can be traced to the late 19th century, when a small number of physicians in several U.S. cities began providing prepaid medical care to members of fraternal orders, unions, and other associations of workers.
Which of the following was the objective of the Health Maintenance Organization Act of 1973?
The Health Maintenance Organization Act of 1973 was designed to provide an alternative to the traditional fee-for-service practice of medicine. It was aimed at stimulating the growth of HMOs by providing federal funds to establish new HMOs.
Development of Prepaid Health Plans
Other major prepaid group practice plans were initiated between 1930 and 1960, including the Group Health Association in Washington, DC, in 1937, t...
Public Managed Care Plans
The enactment of the Health Maintenance Organization Act of 1973 (P. L. 93-222) provided a major impetus to the expansion of managed health care. T...
The Influence of Medicare Prospective Payments
Health care costs, however, continued to spiral upward, consuming 10.8 percent of GNP by 1983. In an attempt to slow the growth rate, Congress in 1...
Managed Long-Term Services and Supports
Arizona became the first state to apply managed care principles to the delivery and financing of Medicaid-funded LTSS in 1987, when the federal Hea...
Growth of Commercial Managed Care Plans
During the late 1980s and early 1990s, managed care plans were credited with curtailing the runaway growth in health care costs. They achieved thes...
When did Medicare expand?
Over the years, Congress has made changes to Medicare: More people have become eligible. For example, in 1972 , Medicare was expanded to cover the disabled, people with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) requiring dialysis or kidney transplant, and people 65 or older that select Medicare coverage.
How long has Medicare and Medicaid been around?
Medicare & Medicaid: keeping us healthy for 50 years. On July 30, 1965, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed into law legislation that established the Medicare and Medicaid programs. For 50 years, these programs have been protecting the health and well-being of millions of American families, saving lives, and improving the economic security ...
What is Medicare Part D?
Medicare Part D Prescription Drug benefit. The Medicare Prescription Drug Improvement and Modernization Act of 2003 (MMA) made the biggest changes to the Medicare in the program in 38 years. Under the MMA, private health plans approved by Medicare became known as Medicare Advantage Plans.
What is the Affordable Care Act?
The 2010 Affordable Care Act (ACA) brought the Health Insurance Marketplace, a single place where consumers can apply for and enroll in private health insurance plans. It also made new ways for us to design and test how to pay for and deliver health care.
When was the Children's Health Insurance Program created?
The Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) was created in 1997 to give health insurance and preventive care to nearly 11 million, or 1 in 7, uninsured American children. Many of these children came from uninsured working families that earned too much to be eligible for Medicaid.
Does Medicaid cover cash assistance?
At first, Medicaid gave medical insurance to people getting cash assistance. Today, a much larger group is covered: States can tailor their Medicaid programs to best serve the people in their state, so there’s a wide variation in the services offered.
When did Medicare start?
In 1962, President Kennedy introduced a plan to create a healthcare program for older adults using their Social Security contributions, but it wasn’t approved by Congress. In 1964, former President Lyndon Johnson called on Congress to create the program that is now Medicare. The program was signed into law in 1965.
When did Medicare start paying the same amount?
Before 1988, everyone paid the same amount for Medicare, regardless of income. Today people with higher incomes might pay more, while people with lower incomes might pay less. This change began in 1988 with the creation of programs to help lower-income enrollees pay for their Medicare premiums and other costs.
What is a Medigap plan?
Medigap, also known as Medicare supplement insurance, helps you pay the out-of-pocket costs of original Medicare, like copays and deductibles. These plans are sold by private insurance companies. However. starting in 1980, the federal government began regulating them to ensure they meet certain standards.
How many people will be covered by Medicare in 2021?
That first year, 19 million Americans enrolled in Medicare for their healthcare coverage. As of 2019, more than 61 million Americans were enrolled in the program.
What age does Medicare cover?
When Medicare first began, it included just Medicare Part A and Medicare Part B, and it covered only people ages 65 and over. Over the years, additional parts — including Part C and Part D — have been added. Coverage has also been expanded to include people under age 65 who have certain disabilities and chronic conditions.
What was Medicare Part A and Part B?
Just like today, Medicare Part A was hospital insurance and Medicare Part B was medical insurance. Most people don’t pay a premium for Part A but do need to pay one for Part B. In 1966, the monthly Part B premium was $3. Trusted Source.
When did Medicare expand to include people with disabilities?
The addition of coverage for people with disabilities in 1972. In 1972, former President Richard Nixon expanded Medicare coverage to include people with disabilities who receive Social Security Disability Insurance. He also extended immediate coverage to people diagnosed with end stage renal disease (ESRD).
Where did managed care start?
The origins of managed care can be traced back to at least 1929, when Michael Shadid, a physician in Elk City , Oklahoma, established a health cooperative for farmers in a small community without medical specialists or a nearby general hospital. He sold shares to raise money to establish a local hospital and created an annual fee schedule ...
What was the impact of Medicare on the health care industry in 1982?
Health care costs, however, continued to spiral upward, consuming 10.8 percent of GNP by 1983. In an attempt to slow the growth rate, Congress in 1982 capped hospital reimbursement rates under the Medicare program and directed the secretary of HHS to develop a case mix methodology for reimbursing hospitals based on diagnosis-related groups (DRGs). As an incentive to the hospital industry, the legislation (the Tax Equity and Fiscal Responsibility Act (P. L. 97-248)) included a provision allowing hospitals to avoid a Medicare spending cap by reaching an agreement with HHS on implementing a prospective payment system (PPS) to replace the existing FFS system. Following months of intense negotiations involving federal officials and representatives of the hospital industry, the Reagan Administration unveiled a Medicare PPS. Under the new system, health conditions were divided into 468 DRGs, with a fixed hospital payment rate assigned to each group.
What was the purpose of the Health Maintenance Organization Act of 1973?
93-222) provided a major impetus to the expansion of managed health care. The legislation was proposed by the Nixon Administration in an attempt to restrain the growth of health care costs and also to preempt efforts by congressional Democrats to enact a universal health care plan. P. L. 93-222 authorized $375 million to assist in establishing and expanding HMOs, overrode state laws restricting the establishment of prepaid health plans, and required employers with 25 or more employees to offer an HMO option if they furnished health insurance coverage to their workers. The purpose of the legislation was to stimulate greater competition within health care markets by developing outpatient alternatives to expensive hospital-based treatment. Passage of this legislation also marked an important turning point in the U.S. health care industry because it introduced the concept of for-profit health care corporations to an industry long dominated by a not-for-profit business model. [ii]
What percentage of Americans received managed care in 1993?
By 1993, a majority (51%) of Americans receiving health insurance through their employers were enrolled in managed health care plans. [xi] Eventually, however, benefit denials and disallowances of medically necessary services led to a public outcry and the enactment of laws in many states imposing managed care standards.
When did Arizona start Medicaid?
Arizona became the first state to apply managed care principles to the delivery and financing of Medicaid-funded LTSS in 1987 , when the federal Health Care Financing Administration (later renamed the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services) approved the state’s request to expand its existing Medicaid managed care program.
When did prepaid health insurance start?
Development of Prepaid Health Plans. Other major prepaid group practice plans were initiated between 1930 and 1960, including the Group Health Association in Washington, DC, in 1937, the Kaiser-Permanente Medical Program in 1942, the Health Cooperative of Puget Sound in Seattle in 1947, the Health Insurance Plan of Greater New York in New York City ...
What is the tax equity and fiscal responsibility act?
97-248)) included a provision allowing hospitals to avoid a Medicare spending cap by reaching an agreement with HHS on implementing a prospective payment system (PPS) to replace the existing FFS system.
When did Medicare start regulating managed care?
The Federal Government, however, did not begin regulating Medicaid managed care arrangements until the early 1970s.The introduction of managed care as a formal Medicare option came more than two decades later, with the introduction of the Medicare Advantage program.
When did Obama sign the Affordable Care Act?
In 2010, President Obama signed the Affordable Care Act (ACA), [iii] a measure calling for sweeping changes in the U.S. health care system. Clearly, people with disabilities have a major stake in efforts to restructure the health care and long-term service delivery system in the United States.
What is Medicaid program?
The Medicaid program serves a diverse array of people with disabilities, ranging widely in age and type and severity of disability, and has an extraordinary impact on the health and quality of life of beneficiaries with disabilities.
How can a state implement a voluntary managed care program?
States can implement a voluntary managed care program by obtaining Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) approval of a Medicaid state plan amendment. Once its state plan amendment is approved, a state can operate its managed care program (s) indefinitely without obtaining further CMS approvals.
What is the chapter 1 of Medicaid?
Chapter 1. An Overview of Medicaid Managed Care. Medicaid plays an integral role in financing health care services in the United States, accounting for 16 percent of total health spending and providing coverage for one out of every six Americans. Among the more than 60 million citizens who rely on Medicaid are about 9 million nonelderly people ...
What are the approaches to enrolling Medicaid beneficiaries?
States have used several approaches to enrolling Medicaid beneficiaries in managed care plans. These approaches include voluntary enrollment, mandatory enrollment, and a hybrid model that combines elements of both approaches. [xx]
What is the difference between managed care and conventional health insurance?
The principal difference between managed care and conventional health insurance payment methods is that the responsible entity ( i.e., the managed care organization (MCO)) usually pays for and provides services, either directly or through contracts with third party providers, whereas conventional health insurers underwrite the cost of coverage but are not involved in the delivery of services.
When did Medicare Part D start?
Medicare Part D went into effect on January 1, 2006. Anyone with Part A or B is eligible for Part D, which covers mostly self-administered drugs. It was made possible by the passage of the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003. To receive this benefit, a person with Medicare must enroll in a stand-alone Prescription Drug Plan (PDP) or public Part C health plan with integrated prescription drug coverage (MA-PD). These plans are approved and regulated by the Medicare program, but are actually designed and administered by various sponsors including charities, integrated health delivery systems, unions and health insurance companies; almost all these sponsors in turn use pharmacy benefit managers in the same way as they are used by sponsors of health insurance for those not on Medicare. Unlike Original Medicare (Part A and B), Part D coverage is not standardized (though it is highly regulated by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services). Plans choose which drugs they wish to cover (but must cover at least two drugs in 148 different categories and cover all or "substantially all" drugs in the following protected classes of drugs: anti-cancer; anti-psychotic; anti-convulsant, anti-depressants, immuno-suppressant, and HIV and AIDS drugs). The plans can also specify with CMS approval at what level (or tier) they wish to cover it, and are encouraged to use step therapy. Some drugs are excluded from coverage altogether and Part D plans that cover excluded drugs are not allowed to pass those costs on to Medicare, and plans are required to repay CMS if they are found to have billed Medicare in these cases.
When did Medicare+Choice become Medicare Advantage?
These Part C plans were initially known in 1997 as "Medicare+Choice". As of the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003, most "Medicare+Choice" plans were re-branded as " Medicare Advantage " (MA) plans (though MA is a government term and might not even be "visible" to the Part C health plan beneficiary).
What is CMS in healthcare?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), administers Medicare, Medicaid, the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), and parts of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) ("Obamacare").
How much does Medicare cost in 2020?
In 2020, US federal government spending on Medicare was $776.2 billion.
What is Medicare and Medicaid?
Medicare is a national health insurance program in the United States, begun in 1965 under the Social Security Administration (SSA) and now administered by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). It primarily provides health insurance for Americans aged 65 and older, ...
How is Medicare funded?
Medicare is funded by a combination of a specific payroll tax, beneficiary premiums, and surtaxes from beneficiaries, co-pays and deductibles, and general U.S. Treasury revenue. Medicare is divided into four Parts: A, B, C and D.
What is a RUC in medical?
The Specialty Society Relative Value Scale Update Committee (or Relative Value Update Committee; RUC), composed of physicians associated with the American Medical Association, advises the government about pay standards for Medicare patient procedures performed by doctors and other professionals under Medicare Part B.
What is the history of managed care?
Government intervention to control cost in the healthcare market has a long history. The Health Maintenance Organization Act of 1973 directly promoted the development of HMOs. In the 1980s, the prospective payment system (PPS) for Medicare was introduced in an effort to curtail healthcare costs in hospitals.
What was the purpose of the Health Maintenance Organization Act of 1973?
The Health Maintenance Organization Act of 1973 directly promoted the development of HMOs. In the 1980s, the prospective payment system (PPS) for Medicare was introduced in an effort to curtail healthcare costs in hospitals. Hospitals were reimbursed a predetermined amount for each diagnostic-related group (DRG).
What did private organizations and employers sponsor in the 1990s?
In the 1990s, private organizations and employers sponsored HMOs, PPOs, and physician hospital organization (PHOs) as part of their managed care efforts to reduce costs by eliminating provider incentives for inappropriate care and excess productivity.
What is the purpose of the federal government overseeing managed care?
Following approval of the managed care state plan amendment or waiver, the federal government conducts oversight of states to ensure that they comply with the program accountability requirements and that states hold managed care plans accountable for the services they have agreed to provide to enrollees.
How many managed care plans can a state offer?
The state must offer enrollees a choice of at least two managed care plans except in rural areas, where states can mandate enrollment into a single plan. Allows states to implement managed care and to limit individuals’ choice of providers under Medicaid.
What are the different types of managed care?
State Medicaid programs use three main types of managed care delivery systems: 1 Comprehensive risk-based managed care. In such arrangements, states contract with managed care organizations (MCOs) to cover all or most Medicaid-covered services for their Medicaid enrollees. Plans are paid a capitation rate—that is, a fixed dollar amount per member per month—to cover a defined set of services. 2 Primary care case management (PCCM). In a PCCM program, each enrollee has a designated primary care provider who is paid a monthly case management fee to assume responsibility for managing and coordinating his or her basic medical care. Individual providers are not at financial risk and continue to be paid on a fee-for-service basis for delivering services. 3 Limited-benefit plans. Some states contract with limited-benefit plans to manage specific benefits, such as inpatient mental health or substance abuse benefits, non-emergency transportation, oral health, or disease management.
How many Medicaid beneficiaries are in MCOs?
States increasingly rely on comprehensive risk-based managed care to deliver care to Medicaid enrollees, and today over two-thirds of Medicaid beneficiaries are enrolled in MCOs. Each state contracts separately with MCOs, although many MCOs operate in multiple states.
How does managed care affect outcomes?
Managed care’s effect on outcomes. As enrollment and spending on Medicaid managed care grow, it is important for federal and state governments to know whether they are paying appropriately for adequate quality care and whether enrollees have sufficient access to necessary care .
What percentage of Medicaid beneficiaries are in managed care?
While about 90 percent of Medicaid beneficiaries are enrolled in some form of managed care, the proportion of beneficiaries enrolled in managed care, the rate of enrollment growth, and spending on managed care varies among the major Medicaid eligibility groups (non-disabled children and adults, individuals with disabilities, and individuals age 65 and older).
What is a comprehensive risk based managed care plan?
In such arrangements, states contract with managed care organizations (MCOs) to cover all or most Medicaid-covered services for their Medicaid enrollees. Plans are paid a capitation rate—that is, a fixed dollar amount per member per month—to cover a defined set of services.
Abstract
Context: Twenty-five years ago, private insurance plans were introduced into the Medicare program with the stated dual aims of (1) giving beneficiaries a choice of health insurance plans beyond the fee-for-service Medicare program and (2) transferring to the Medicare program the efficiencies and cost savings achieved by managed care in the private sector..
Trailing the Private Sector, 1985–1997
The reason that Medicare expanded to include risk-based private plans was to share the gains realized from managed care in other settings.
Failed Attempt at Savings: 1997–2003
The BBA's goals with respect to Medicare Advantage can be summarized in the following question: Could Medicare Advantage be reformed so that Medicare could participate in the managed care dividend enjoyed by private employers? In the latter half of the 1990s, Republicans (the new congressional majority), centrist Democrats, and some policymakers began to look to Medicare as a source for reducing the deficit ( Oberlander 2003 ).
Medicare Spends Its Way out of Trouble: 2003–2010
The 2003 Medicare Modernization and Improvement Act (MMA) established a larger role for private health plans in Medicare largely based on a shift away from a focus on cost containment and regulation and toward the “accommodation” of private interests (e.g., the pharmaceutical and insurance industries) and an ideological preference for market-based solutions that stemmed from the Republican control of both the executive and legislative branches of government ( Oberlander 2007 ).
Achieving MA's promise? 2010 and Beyond
The ACA, signed into law by President Obama in March 2010, included another major restructuring of the MA program and significant cuts in MA plan payments. Specifically, for 2011, the payment benchmarks against which plans bid are frozen at 2010 levels.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge funding from the National Institutes on Aging through P01 AG032952, The Role of Private Plans in Medicare. Joseph Newhouse wishes to disclose that he is a director of and holds equity in Aetna, which sells Medicare Advantage plans.
Endnotes
1 Excellent quantitative summaries of the Part C experience are available from the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC), through its annual reports ( http://www.medpac.gov ), and from other researchers (e.g., see Gold 2005, 2007, 2009; Zarabozo and Harrison 2009 ).